Testing internal elements
Always remember that before testing, the relay must be disconnected from the power source! Even capacitors that are disconnected from the network store an accumulated electrical charge.
Take a multimeter and determine the resistance:
if the contact and pole are normally closed, the resistance will be zero;
if the pole and normally open contact - the resistance is greater than 0.
To test the relay acoustically, you need to connect two conductors to contacts 85 and 86. Connect the other ends of the conductors to the battery. You will hear the operating relay immediately - when the conductor and battery come into contact, clicks will appear.
There are clicks, but do the moving and fixed contacts work? Let's find out:
- Take a multimeter and attach its probes to the contacts. If everything is normal, you will hear a whistle.
- If you don't have a multimeter, then you can use a test light. In this case, an additional conductor will be needed. Connect it to the “+” contact and place it on the coil. Connect the second conductor to another contact. We connect the light bulb to “–”. When the relay is turned on, the light should light up.
The cause of non-functioning electrical equipment in the car (for example, fuel pump, heated seats, heated windows, power windows, etc.) may be a faulty relay. Let's look at a simple way to test a car relay for functionality with your own hands.
Connection diagram for 4 and 5 contact relays:
Design and principle of operation of the switching device
An electrical relay is a part that is used as a switch thanks to the control signals that are supplied to it through an electrical circuit. The line connected to the device is called controlled; the line through which a command is already being sent to it - the manager.
It is used in domestic conditions and in all industries to automate various operations. If a household or electrical appliance fails, you must first check the functionality of the switching element. But first it is recommended to familiarize yourself with the types and operating principles of relays.
Principle of operation
The part is an electromagnet, which includes an inductor, an armature and a contact group.
Each component is mounted on a base and enclosed in a protective housing. The armature is located on top of the magnetic system core; in the initial position it is held thanks to a spring, which has the shape of an L-shaped movable plate.
The lower part of the base is equipped with a contact group; on the contrary, the same number of contact bases is mounted. The contacts are ductile because they need to be brought out outside the protective housing to form the device terminal.
The principle of operation of the relay is based on its ability to influence conductive objects with its electromagnetic field. As soon as voltage is applied to the winding terminals, current begins to flow through the relay. When its value reaches a previously programmed value, two forces are formed in the winding, which press the armature to the surface of the coil.
Taking into account the design features, the initial position can be not only closed, but also open. In the second case, when voltage is applied, the line will open. The contacts of the device will return to their original state as soon as the signal of the required magnitude is removed from the relay terminals.
Electronic switch - operating principle
For any practical application, solid state relays should be considered primarily as an electronic switch. Accordingly, like any other switching device, TER is used in circuits where it is necessary to control the switching on and subsequent switching off of power from an electrical load.
Therefore, this type of network electrical switches is often associated with more common mechanical devices:
- push-button switches,
- toggle switches,
- electromechanical relays (EMR), etc.
The noted types of switches are equipped with mechanical contacts that are physically closed/opened - manually or by applying voltage to the electromagnet coil. The performance of such devices can be easily checked on a test bench with a conventional digital (or pointer) multimeter.
Upon testing in the off state, the impedance between the normally open terminals will be high (open communication circuit). On the other hand, in a closed communication circuit state when the device is turned on, the impedance will be low (effectively a short circuit).
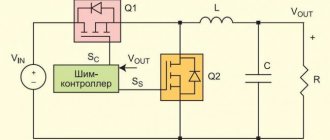
The distinguishing feature of solid state relays from mechanical/electromechanical relays, however, is that the output of the device contains no moving mechanical parts, in principle. The mechanics for switching the load current are replaced by two thyristors connected back in parallel.
Electrical circuit of an electronic action device (EDD), which uses optical-electronic isolation based on the network power potential + control through thyristors
When an input signal is applied to the TER, a relatively small current (about 150 mA) flows through the optical isolator (the trigger circuit in some designs) and then flows to the gate of the forward biased thyristor. The control current turns on the thyristor, opening the channel to the load current for half an AC cycle.
When the polarity of the AC mains is reversed, the first thyristor turns off while the second thyristor conducts the load current for the next half of the AC cycle. This operation is continuously repeated until the input signal is removed from the solid state relay terminals.
Advantages of solid state relays
The absence of moving parts inside the design of a solid-state electronic relay is a clear benefit and advantage compared to electromechanical devices. The absence of moving mechanical parts eliminates the concept of “contact bounce” (contact sparking) every time current is supplied to the load through the relay.
Consequently, the life of a typical SSR is extended by 50 to 500 operations over an EMR equivalent, depending on application conditions and temperature gradients. In addition, the absence of moving parts guarantees the absence of acoustic noise during switching moments.
This feature makes solid-state electronic relays attractive for engineering applications aimed at developing panels or equipment for use in residential or commercial structures. However, the absence of moving parts changes the approach to testing - checking devices. Obviously, you won’t be able to test a solid-state relay with a multimeter in the same way as an electromechanical one.
Types and characteristics
Depending on the element base used, relay regulators are divided into the following types:
- Microcontroller or microprocessor based. Their peculiarity lies in the inclusion of a working algorithm in the built-in chip. Used in expensive cars, such as BMW or Audi.
- Relays are based on switching relay contacts to cut off and stabilize the performance of the electrical network.
- Integrated relays are widely used in the automotive industry. The operating principle is based on solid-state switching parts or integrated semiconductors.
- Hybrid transistor-relay devices and simply transistor ones are based on semiconductor elements. They were actively used in industry until the early 90s.
Short circuit protection
If the insulation in the target is damaged and for other reasons, a short circuit may occur. To avoid damage to the SSR, special fuses are used. They are designed for use in combination with solid-state products.
They are easily recognized by the following specifications:
- gR - fusible inserts operating in a wide range of I. They are used to protect semiconductors. These are some of the fastest-acting devices today.
- gS - like previous fuses, they can operate in all I ranges. They are used in cases of high loads, as well as for protecting semiconductors.
- aR - melt inserts that have no restrictions on I work. They are installed to protect semiconductors from short circuits. The disadvantage of such products is their high price. That's why many people prefer more affordable B-class automatic machines.
Symptoms of a problem
Before checking the relay with a multimeter, you should familiarize yourself with the main signs that the part has failed.
- There are cases when, as a result of the failure of the voltage regulator, the battery boils.
- When the ignition is turned on, the control light on the dashboard does not light up (however, this can be a symptom of other types of malfunctions, for example, a contact has fallen out or burned out).
- The dynamic characteristics of a household appliance or car are reduced, especially when the engine reaches high speeds.
- After starting, the battery indicator does not go out on the dashboard, which indicates a battery problem.
- The indicators on the dashboard simply turn off if the engine speed during operation exceeds 2000 rpm.
- The brightness of the headlights depends on the engine speed. It is quite simple to verify this - you need to stand in front of the wall in the dark and turn on the headlights. The brightness of the glow will change depending on how hard you press the gas.
- The battery is regularly discharged.
These signs may indicate other malfunctions, but first of all it is recommended to check the relay regulator.
How to check wiring
You can diagnose electrical equipment using a voltmeter, ohmmeter or multimeter, or special diagnostic stands. Computer diagnostics are also carried out, during which error codes and main indicators of the machine’s on-board network are read. To independently check circuits and troubleshoot electrical faults, one multimeter or signal lamp is enough.
We use a multimeter
Fuses in the on-board network are considered the “weakest” link in terms of durability. In case of emergency situations (for example, in the event of a short circuit), the safety elements “take the blow”, protecting the rest of the electrics and electrical equipment of the machine. Fuses cannot be restored and must be replaced during repairs.
Checking the voltage
Before checking the wiring in the car, it is necessary to measure the voltage of the electrical circuit between individual components and electrical equipment. You can call like this:
- Set the multimeter to voltmeter mode.
- Connect one probe of the measuring device to the “minus” of the battery or to the ground of the machine.
- Connect the second probe to the supply wire of the circuit.
If a certain value appears on the device display, then there is voltage in this section of the electrical circuit. You can compare the values with those required according to the vehicle's owner's manual.
Looking for a short circuit
After measuring the voltage, search for short circuits. This will require either a multimeter or a pilot light. As for the lamp, if the wiring is in good condition and there is no short circuit, it should not light up.
A short circuit in the wiring, as well as a lack of voltage (zero or infinite resistance in the electrical circuit), indicates a malfunction in one of 2 components:
- Consumer - electrical equipment, devices, fuses, blocks.
- Wiring – broken or shorted wires, poor wiring contacts at the point of connection with the consumer.
Checking for a short circuit can also be done in voltmeter mode. To do this, it is necessary to remove all fuses in the area being tested and connect the probe to the terminals of the fuse element. The value “0” on the screen indicates the presence of a short circuit in the circuit. If, when you try to move the wires, voltage appears in the circuit, then the short circuit is caused by the wiring and the wires will need to be replaced.
Checking the quality of grounding
Cars use a single-wire wiring diagram - this means that the “minus” goes to the ground (body) of the car. However, corrosion of metal parts, their oxidation and destruction, “loosening” lead to grounding failure and, as a consequence, to disruption of on-board circuit contacts.
Checking the grounding, as well as other electrical elements of the car, is carried out using a multimeter. The procedure is as follows:
- Disconnecting the battery.
- Connecting one multimeter probe to the body (metal parts) of the car.
- Connecting the second probe to the grounding element or wiring connection.
Read also: Clamps for wiring in an apartment
The value displayed on the device screen should be compared with the factory data (car operating manual). If the values diverge greatly, then it is necessary to restore the grounding - clean the metal at the connection point, check the reliability of the fastening.
Checking the integrity of the circuit
The connection of wires in the electrical circuit of cars is one of the most vulnerable points in the entire electrical system of the car. In addition to the destruction of insulation, loss of integrity and breaks at the connection points, oxidation of the contacts also often occurs here. Defects can be determined not only using a measuring device, but also visually. If the integrity of the circuit is broken precisely at the connection point, then soldering of wires with connectors will be required. Otherwise, you need to find the damaged area, which will require a signal lamp or multimeter.
Reasons for failure of the relay regulator
In order to minimize the likelihood of repeated breakdowns in the future, you should familiarize yourself with the main reasons for device failure.
- Short circuit in any part of the electrical circuit, including interturn short circuit of the excitation winding.
- The regulator may also fail if the diodes break down or the rectifier bridge breaks down.
- Incorrect connection or reverse direction to the battery terminals.
- Penetration of moisture or large amounts of dust into the generator and/or the regulator itself (such cases are common during heavy rainfall or when washing the car).
- Mechanical damage to the working unit.
- Natural wear and tear, end of service life.
- Initially, the quality of the purchased product is questionable.
Preparing to test the relay for functionality
Checking the relay will not take much time if all the preparatory work is done correctly.
Before you begin diagnosing the device, you need to determine the purpose of the pins of the part being tested. To do this, use the documentation supplied with the device; it contains all the diagrams and operating features, and the characteristics of the device.
There are common cases when the operating diagram is depicted on the relay body itself. Contacts are represented by dots; they are connected by an inductor, the switching elements are straight lines with a dotted line. The power supply pins are shown schematically as a rectangle.
If the relay is built into the circuit, you need to visually inspect the state of the bus and power traces on the board itself. To check the relay with a tester, you can use both digital and analog instruments. No preliminary preparation or setup of testers is required.
In addition to the tester, you need to prepare a regulated power supply. For the results to be reliable, the relay must be removed from the circuit.
The functionality test is carried out in several stages:
- winding;
- normally closed position;
- normally open state.
Then you can proceed directly to diagnosing the relay.
Design features
The solid-state relay is based on an electronic board, which includes three main elements - control and isolation units, as well as a power switch. The following parts are used as power elements:
- For constant I - field-effect transistors, simple transistors, modular elements of the IGBT class, as well as MOSFET transistors.
- For variable I - assemblies based on thyristors, as well as triacs.
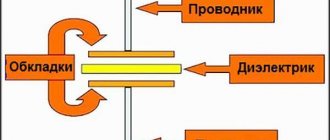
Circuit decoupling is provided by optocouplers - products consisting of a light-emitting and light-receiving device. A dielectric having a transparent structure is installed between them.
The control unit is made in the form of a stabilizing circuit that provides optimal current and voltage levels for the light-emitting element. The voltage at the circuit input should be from 70 to 280 Volts.
As for the load voltage, its value is up to 480 Volts. The location of the electrical appliance (before or after the TTR) does not matter.
As a rule, the device is mounted after the load and then connected to ground. With this version of the circuit, it is possible to protect the internal elements from the flow of short-circuit current (it will flow through the grounding wire).
Diagnostics of windings and contact groups
The winding is an inductance coil on which wire is wound in a spiral.
It is characterized by a certain resistance, which is calculated according to Ohm's law. The resistance value should range from 10 to 100 Ohms. Diagnostics of the winding allows you to find out whether its integrity is compromised. Functionality testing is carried out in several stages:
- The multimeter is turned on in resistance testing mode. On the instrument panel this mode is indicated by the symbol – Ω, the range is set within 2 kOhm.
- One measuring wire is connected to the socket, and the second to the COM.
- The wire probes touch the relay terminals.
The resistance of the inductor can be determined by the deflection of the arrow.
Checking contact groups is carried out in two stages. First, the resistance must be measured offline, and then when voltage is applied to the coil. When checking, you will need a power source, you need to take care of this in advance.
Abnormal voltage readings on the multimeter
If the multimeter shows low voltage in the battery, the battery will simply stop accepting charge. As a result, the car may not start, the indicators on the dashboard may stop working, and troubles may arise while driving.
If the voltage is increased, there is a possibility that the level of electrolyte in the battery bank has decreased, or it has simply boiled away. Another characteristic feature may be the formation of a white coating on the walls of the body. When recharging, the battery may begin to behave unpredictably.