Simple power regulator circuit
The very first devices whose task was to control and regulate power were based on Ohm's law. These are the simplest circuits that made it possible to regulate only one voltage source per device.
Ohm's law states that the power of electricity is directly equal to the square of the current. The device used was called a rheostat.
The rheostat can be connected either in series or obliquely, i.e. in the opposite direction. By changing the resistance, you can adjust the voltage power, everything is quite simple.
How does a thyristor work?
A thyristor is a controlled semiconductor device capable of conducting current in one direction. The word “controlled” was used for a reason, because with its help, unlike a diode, which also conducts current only to one pole, you can select the moment when the thyristor begins to conduct current. The thyristor has three outputs:
- Anode.
- Cathode.
- Control electrode.
In order for current to begin flowing through the thyristor, the following conditions must be met: the part must be in a circuit that is energized, and a short-term pulse must be applied to the control electrode. Unlike a transistor, controlling a thyristor does not require holding the control signal. The nuances do not end there: the thyristor can be closed only by interrupting the current in the circuit, or by generating an anode-cathode reverse voltage. This means that the use of a thyristor in DC circuits is very specific and often unwise, but in AC circuits, for example in a device such as a thyristor power regulator, the circuit is constructed in such a way that a condition for closing is ensured. Each half-wave will close the corresponding thyristor.
Most likely, you don’t understand everything? Do not despair - below we will describe in detail the process of operation of the finished device.
Features of the rheostat
When current enters the rheostat, it begins to divide between the device and the load itself. If a sequential switching circuit is selected, then the voltage and current are monitored. When using a parallel connection circuit, the potential difference is controlled.
The rheostat itself can be completely different.
- Coal
- Liquid
- Metal
- Ceramic
When using a rheostat, you must remember the laws of physics. So the electricity that will be taken cannot simply evaporate. The rheostat will convert it into heat.
This must be taken into account in case you plan to supply large values to the device. In the case of a large load and heat generation, the need to remove excess heat must also be taken into account.
As a cooling system for the rheostat, you can use a blower or a container with oil in which the rheostat is placed. Both options have both advantages and disadvantages.
The rheostat is quite an interesting device; you can assemble a power regulator circuit with your own hands. However, it has one rather significant drawback: it is not possible to use a small device to pass large amounts of electricity through it.
How it works?
The information described below is valid for most schemes. Letter designations will be taken in accordance with the first circuit of the thyristor regulator
A thyristor power regulator, the operating principle of which is based on phase control of the voltage value, also changes the power. This principle lies in the fact that under normal conditions the load is affected by the alternating voltage of the household network, changing according to a sinusoidal law. Above, when describing the operating principle of a thyristor, it was said that each thyristor operates in one direction, that is, it controls its own half-wave from a sine wave. What does it mean?
If you periodically connect a load using a thyristor at a strictly defined moment, the value of the effective voltage will be lower, since part of the voltage (the effective value that “falls” on the load) will be less than the mains voltage. This phenomenon is illustrated in the graph.
The shaded area is the area of stress that is under load. The letter “a” on the horizontal axis indicates the opening moment of the thyristor. When the positive half-wave ends and the period with the negative half-wave begins, one of the thyristors closes, and at the same moment the second thyristor opens.
Modern devices
With the development of semiconductor technology, it was possible to make a significant step from the rheostat to more technologically advanced equipment, which is devoid of the disadvantages of its predecessor. Today, it is possible to use radioelements with an efficiency of 80%, which is very high in comparison with the same rheostat.
The use of such elements makes it quite easy and simple to use modern devices on networks with a voltage of 220 V, which is very convenient. At the same time, modern devices do not require large and complex cooling systems, as was the case in the past.
With the invention of integrated circuits, it was actually possible to make the power control device as miniature as possible, and at the same time increase the value of the maximum voltage that it can pass through itself.
Instructions on how to make a power regulator
To make a power regulator you will need:
- radio components in accordance with the applied circuit;
- printed circuit board;
- housing for a future device;
- soldering iron;
- tweezers;
- side cutters;
- mounting plate holder;
- needle;
- brush;
- ferric chloride for etching printed circuit boards;
- solder;
- rosin or flux.
The housing, depending on the designer’s imagination, can be glued together from plastic according to the dimensions of the product, you can select ready-made housings from sockets, tees, or build the device into the tool for which the regulator is being made.
Varieties
Instructions on how to make a power regulator will depend on the specific type of this device chosen. Let's look at what types of devices there are today.
- Phase. One of the most common, used in lamps. Its task is to control the brightness of incandescent or halogen lamps.
- A triac power regulator is a device that regulates power by changing the number of voltage half-cycles, which are the ones that affect the load.
- Tristor. They are not very popular, but in some cases they can become an indispensable thing. The operating principle is based on a certain delay in turning on the tristor switch in the system during the half-cycle of the current.
Travel regulator. One of the most high-tech. Allows you to smoothly change voltage levels, reducing or increasing the electrical power that is supplied to the electric motor or elsewhere.
POWER ADJUSTMENT
Most often, device power regulators are made using thyristors, using it as a powerful output switch. But a thyristor in an alternating current circuit is inconvenient because it requires power through a rectifier bridge, which, with a high load power, must be installed on a radiator. In this regard, a triac is more convenient for a key element. The main difference between a triac is the ability to switch not only direct, but also alternating current, which can flow in any direction - both from the anode to the cathode, and in the opposite direction.
For reference: triacs with a positive voltage at the anode can be turned on by pulses of any polarity supplied to the control electrode relative to the cathode, and with a negative voltage at the anode - by pulses only of negative polarity. Controlling a triac with direct current requires a lot of power, and with pulse control, a driver is needed that provides short pulses when the mains voltage passes through zero, which reduces the level of interference compared to regulators that use the phase-pulse control method.
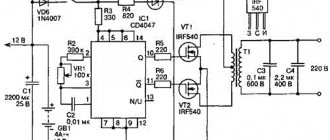
The power control device contains a triac, a time (phase) delay unit, a compensating circuit and a power source. The compensating circuit R8 C2 adds a voltage proportional to the supply voltage to the voltage of the zener diode VD3. This sum is the base-to-base voltage of the KT117 unijunction transistor. Reducing the supply voltage reduces the supply voltage of the transistor and causes a decrease in the time delay. This differs from the well-known triac power regulator circuit on the BT136-600 and the DB-3 dinistor in the stabilization of control pulses and, accordingly, greater accuracy and consistency of the output voltage.
When setting up a power control device, you need to connect it to the network with a load through an autotransformer, and install a voltmeter in parallel with the load. By changing the voltage with variable resistor R8 at the regulator input, we achieve the minimum voltage at the load. The transformer is made on a Sh5x6 core, the primary winding is 40 turns, the secondary winding is 50 turns PEL-0.2 - 0.3. In my version of the power control device, I installed a transformer on a ferrite ring K20x10x6 with two identical windings of 40 turns each - everything worked perfectly. To visually monitor the voltage (power) on the load, I installed a small AC voltmeter assembled from a recording level indicator of a reel-to-reel Soviet tape recorder. We connect it naturally parallel to the load. Red LEDs indicate that the power control device is connected to the network and illuminate the scale.
This regulator can be connected to an active load with a power of up to two kilowatts - electric stoves, electric kettles, electric fireplaces, irons, etc., and when replacing the triac with a more powerful one, for example TC132-50, up to 10 kW. A real example of use: a neighbor’s 16 A automatic machines constantly knock out the plugs when using a Tefal 2 kW electric kettle. Replacing them is impossible, since he does not live in his own apartment. The problem was solved by this adjustment device, set to 80% power.
Useful modifications: when working with an inductive load, in parallel with the power regulator triac it is necessary to turn on an RC circuit to limit the rate of rise of the anode voltage. Any triac regulator is a source of radio interference, so it is advisable to equip the power regulator with a radio interference filter. The LC radio noise filter is a conventional G-filter with a coil and a capacitor. A coil of 100 turns of wire wound on a ferrite rod with a diameter of 8 mm and a length of 50 mm is used as a choke L. A wire diameter of 1 mm corresponds to a maximum load power of approximately 700 W. A fuse for the rated load current protects the triac from a short circuit in the load. When setting up, observe safety measures, since all elements of the device for power regulation are galvanically connected to a 220 V network.
Questions and comments regarding the scheme – go to the FORUM
- TRANSFORMERLESS PSU FOR 5, 9, 12, 24 V
- SELECTING A PULSE PSU WHEN PURCHASING
- OVER VOLTAGE PROTECTION
- 3-30V 5A POWER SUPPLY
Adjustment
It is worth understanding that the adjustment of the device does not depend on the shape of the input signal. Based on the type of placement, devices are divided into stationary and mobile.
- The differences are obvious, the first type is securely attached to a specific place.
- The second option, on the contrary, has the ability to be in any place where it is convenient for the master.
The voltage regulation device is currently an electrical circuit, thanks to which it becomes possible to regulate the voltage in a particular building if everything is connected correctly.
Rating of the best power regulators from Aliexpress
| Photo | Name | Rating | Price | |||
| Complete regulators | ||||||
| #1 | Wenfu GT10000W-SL | ⭐ 5 / 5 | Find out the price | |||
| #2 | YXD Wish 10000W | ⭐ 4.9 / 5 | Find out the price | |||
| #3 | Wenfu ST-BTA41 | ⭐ 4.8 / 5 1 - voice | Find out the price | |||
| #4 | Wenfu GT10000W | ⭐ 4.7 / 5 3 - votes | Find out the price | |||
| #5 | SNDY SNT4000W | ⭐ 4.6 / 5 1 - voice | Find out the price | |||
| #6 | CHMAWAY 4000W | ⭐ 4.5 / 5 | Find out the price | |||
| Built-in models | ||||||
| #1 | YXD Wish X4CN | ⭐ 5 / 5 2 - votes | Find out the price | |||
| #2 | RQG 4000W | ⭐ 4.9 / 5 2 - votes | Find out the price | |||
| #3 | YXD Wish ACMC100-1 | ⭐ 4.8 / 5 | Find out the price | |||
| #4 | SHENGKU VR-AC220V | ⭐ 4.7 / 5 1 - voice | Find out the price | |||
| #5 | Akin W205 | ⭐ 4.6 / 5 | Find out the price | |||
| Dimmers | ||||||
| #1 | Goodland DC12-24V | ⭐ 5 / 5 | Find out the price | |||
| #2 | Foocle FLS820 | ⭐ 4.9 / 5 1 - voice | Find out the price | |||
| #3 | Vyeofar VF30A-RF | ⭐ 4.8 / 5 | Find out the price | |||
| #4 | HWAYEH DC10-60V | ⭐ 4.7 / 5 1 - voice | Find out the price | |||
| #5 | Luyu LV-2.4G-4054 | ⭐ 4.6 / 5 2 - votes | Find out the price | |||
| #6 | DIY More CZB6721960 | ⭐ 4.5 / 5 | Find out the price | |||
Which power regulator would you choose or recommend?
Take the survey
Recommendations
If you do not have experience and knowledge of how to handle electrical appliances, then it is best not to touch them. If the wiring is incorrect, the network can receive a short circuit, as a result of which this device, as well as several others that were connected to the network, burned out.
Using the services of professionals significantly saves time and money, which you would still have to spend on a specialist if you did everything yourself. During the work, you can ask a professional about the manipulations being carried out.
He will tell you in detail what and how to connect and connect. Will share tips and tricks, conduct a practical lesson with devices.
Thyristor voltage
First, let's figure out how a thyristor differs from a triac. A thyristor contains 3 pn junctions, and a triac contains 5 pn junctions. Without going into details, in simple terms, a triac conducts in both directions, while a thyristor conducts only in one. Graphic designations of the elements are shown in the figure. This is clearly visible from the graphics .
The operating principle is absolutely the same. This is what power regulation is based on in any circuit. Let's look at several thyristor-based regulator circuits. The first is the simplest circuit, which basically repeats the triac circuit described above. The second and third are using logic, circuits that better dampen the interference created in the network by switching thyristors.
Simple scheme
A simple phase control circuit on a thyristor is presented below.
Its only difference from the triac circuit is that only the positive half-wave of the mains voltage is adjusted. The timing RC circuit, by adjusting the resistance value of the potentiometer, regulates the trigger value, thereby setting the output power supplied to the load. On the oscillogram it looks like this.
From the oscillogram it can be seen that power regulation occurs by limiting the voltage supplied to the load. Figuratively speaking, the regulation consists of limiting the flow of mains voltage to the output. By adjusting the charging time of the capacitor by changing the variable resistance (potentiometer). The higher the resistance, the longer it takes to charge the capacitor and the less power will be transferred to the load. The physics of the process is described in detail in the previous diagram. In this case, it is no different.
With logic based generator
The second option is more complicated. Due to the fact that switching processes on thyristors cause great noise in the network, this has a bad effect on elements installed on the load. Especially if the load is a complex device with fine settings and a large number of microcircuits.
Read also: 24 volt soldering iron regulator with thermocouple
This DIY implementation of a thyristor power regulator is suitable for active loads, for example, a soldering iron or any heating devices. There is a rectifier bridge at the input, so both waves of the mains voltage will be positive. Please note that with such a circuit, an additional +9 V DC voltage source will be needed to power the microcircuits. Due to the presence of a rectifier bridge, the oscillogram will look like this.
Both half-waves will now be positive due to the influence of the rectifier bridge. If for reactive loads (motors and other inductive loads) the presence of oppositely polar signals is preferable, then for active ones a positive power value is extremely important. The thyristor also turns off when the half-wave approaches zero, the holding current is supplied to a certain value and the thyristor is turned off.
Based on transistor KT117
The presence of an additional constant voltage source can cause difficulties; if it is not there, you will have to install an additional circuit. If you do not have an additional source, then you can use the following circuit, in which the signal generator to the control output of the thyristor is assembled using a conventional transistor. There are circuits based on generators built on complementary pairs, but they are more complex, and we will not consider them here.
In this circuit, the generator is built on a dual-base transistor KT117, which, when used in this way, will generate control pulses with a frequency set by trimming resistor R6. The diagram also includes an indication system based on the HL1 LED.
- VD1-VD4 is a diode bridge that rectifies both half-waves and allows for smoother power adjustment.
- EL1 - incandescent lamp - is represented as a load, but it can be any other device.
- FU1 is a fuse, in this case it is 10 A.
- R3, R4 - current-limiting resistors - are needed so as not to burn the control circuit.
- VD5, VD6 – zener diodes – perform the role of stabilizing the voltage at a certain level at the emitter of the transistor.
- VT1 - transistor KT117 - must be installed with exactly this location of base No. 1 and base No. 2, otherwise the circuit will not work.
- R6 is a tuning resistor that determines the moment when a pulse arrives at the control output of the thyristor.
- VS1 – thyristor – element that provides switching.
- C2 is a timing capacitor that determines the period of appearance of the control signal.
The remaining elements play a minor role and mainly serve to limit current and smooth out pulses. HL1 provides an indication and signals only that the device is connected to the network and is energized.
Power regulators are widely used in everyday life. Their use is very diverse: from regulating the brightness of lighting to controlling the speed of various engines, they can be used to set the required temperature of various heating devices. Thus, power can be adjusted for any type of load, both reactive and active.
A power regulator is a specific electronic circuit with which you can control the amount of energy supplied to the load.