In this article we will tell you what electrical power is and how it can be calculated.
Definition.
Electric current power (denoted by the letter P) is a physical quantity defined as the amount of work done by a source of electrical voltage to transfer electric charge (q) along a conductor per unit time t.
Generally speaking, the power of an electric current shows how much electrical energy is converted in a certain time. It also describes the consumer’s energy consumption.
Formulas
Many household electrical appliances have labels indicating their wattage. Power (P) refers to the work (A) performed by an electrical appliance per unit of time (t). Therefore, in order to find the average power of the electric current, it is necessary to divide its work by time, that is, P = A / t.
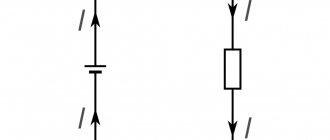
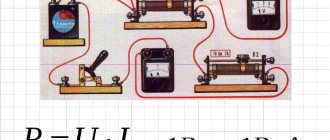
Let's look at what electric power is. To do this, consider an electrical circuit (see Figure 1), consisting of a current source, wires and some kind of electrical receiver, which can be a resistor, battery, electric motor, etc.
Rice. 1. An electrical circuit in which the voltage and current are constant
The recommended electrical voltage is also indicated on the electrical equipment. How are these two quantities related to each other? From a school physics course, we know that the voltage (U) between the ends of a given electrical receiver is determined as follows: U = A / q, where: A is the work done by the source of electrical voltage to transfer electric charge (q) along the conductor.
The amount of electric charge is calculated by the formula: q = I * t
We have A = P * t; A = U*q, and q = I * t. After transforming the formulas we get: A = P*t = U*q = U*I*t
It follows (by dividing both sides of the equation by t) that P = U*I. That is, we can say that the amount of energy transferred from the current source to the resistor is determined by the formula: P = U * I
From this formula we can find that U = P / I, I = P / U.
According to Ohm's law for a circuit section I = U/R, where R is the electrical resistance of the circuit section. Therefore, from the formula P = U*I, two other formulas for the power of electric current follow, that is, P = U2/R, P = I2R.
The formula P = I2R is convenient to use for electrical circuits with a series connection of conductors, because the strength of the electric current in such a connection in the conductors is the same.
For parallel-connected conductors, it is more convenient to express work and power through the same electrical voltage for them, excluding the strength of the electric current, i.e. it is better to use the formula P = U2/R.
If electrical appliances are connected in series or in parallel, their electrical power is summed up. In this case, to calculate the total power, the following formula is used:
Ptotal = P1 + P2 + … + Pn, where P1, P2, … is the power of individual electrical receivers.
Using the Joule-Lenz law to transmit electricity over a distance
Joule-Lenz law
When electricity is transmitted over a distance, the problem of loss on transmission lines arises. The law shows the amount of heat that is released by a conductor when current passes.
Power lines are used by businesses and cities, which means more power and more current are needed.
The amount of heat is related to the resistance of the current and the conductor; in order to avoid heating, it is necessary to reduce the amount of heat.
It is not always possible to use the wire cross-section; this is expensive due to the price of copper and the weight of the cables; therefore, the cost of the supporting structure increases.
The figure shows high voltage power lines. These are huge structures made of metal, created to raise the cable to a height that is safe for people on the ground to avoid electric shock.
To do this, it is necessary to reduce the current, therefore, the voltage increases.
Power lines between cities use voltages of 220 and 110 kV, and those who consume them are reduced to the required value using transformer substations. Or with many transformer substations slowly reducing it to a safe value, for example, 6 kV.
That is, the current will decrease thousands of times, but at the same power consumption. According to the Joule-Lenz law, heat in this case is determined by the power that is lost on the cable.
Units of measurement and designation
The unit of power in the International System of Units (SI) is the watt. In this case, the Russian designation: W , international: W ). 1 W = 1 J/s. From the formula P = U*I it follows that: 1 watt = 1 volt * 1 ampere, or 1 W = 1 VA.
There are also power units that are multiples of watts: hectawatt (gW), kilowatt (kW), megawatt (MW). In other words, 1 GW = 100 W, 1 kW = 1000 W, 1 MW = 1,000,000 W.
The units of power used in electrical engineering are multiples of the watt: microwatt (µW), milliwatt (mW), hectowatt (gW), kilowatt (kW) and megawatt (MW). In other words, 1 µW = 1*10-6 W, 1 mW = 1*10-3 W, 1 gW = 1*102 W, 1 kW = 1*103 W, 1 MW = 1*106 W.
Each electrical appliance has a certain power (indicated on the device). Here are typical wattage ratings for some electrical appliances.
| Device | Power, W |
| TV in standby mode | 0,5 |
| Flashlight lamp | About 1 |
| Incandescent lamps | 25-150 |
| Fridge | 160 |
| Electric heater | 500-2000 |
| Vacuum cleaner | Up to 1300-1800 |
| Electric kettle | Around 2000 |
| Iron | 1200-2200 |
| Washing machine | Up to 2300 |
Previously, the unit of measurement used to denote power was horsepower (hp), which is still known today. Convert from horsepower to watts using the expression: 1 hp. = 735.5 W.
An example of calculating the power of electric current
In the end, you will be able to test your knowledge with 2 common examples.
Imagine that in the first problem you have a resistor R = 50 Ohm through which an electric current I = 0.3A flows. What electrical power is converted in this resistor?
You can find the solution by finding the appropriate formula and plugging in the given values into it. That is, we get: P = I2R = 0.32 * 50 = 4.5 W
In the second problem, a resistor R is given, the electrical resistance of which is 700 Ohms. The technical description states that the maximum power of this resistor is 10 W. How high can the voltage applied to this resistor be?
To solve this problem, we select the appropriate formula: P = U2/R, from where we find Umax = Pmax * R = 700 * 10 = 83.67 V.
This means that the maximum voltage can be 83.67 V. To be on the safe side, you should choose an electrical voltage well below this limit.
I wrote in more detail about how to find the power of an electric current in the article:
Electric current power measurement
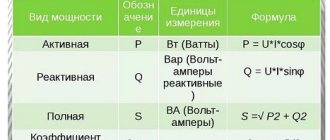
You can measure the strength of electric current using a voltmeter and an ammeter. To calculate the required power, multiply the electrical voltage by the current. Electric current and voltage can be found from instrument readings.
Rice. 2. Electric current power measurement
Remember that you should always detect electrical voltage in parallel with the load and electrical current in series.
There are special devices - wattmeters - that determine the power of the electric current in a circuit, which, in fact, replace two devices - an ammeter and a voltmeter.
Features of parallel connection of current sources
The electrical circuits of radio-electronic devices contain the most conductors and capacitors. Among all the properties, one parameter is of decisive importance:
With different methods of inclusion in the circuit, the total, resulting value is important; the difference in ratings is not critical.
Parallel connection of power sources with different emfs to the load has a serious drawback: even in the absence of an external load, a source with a higher electromotive force is discharged through a source with a lower emf. The process continues until the EMF values become the same, part of the total capacitance is lost.
In electrical engineering, parallel connection of power sources with different characteristics is used to operate on a common load, but not directly.
To be included in the circuit, complex alignment, synchronization, blocking, and protection circuits are used.
In everyday life, parallel installation of several identical galvanic elements is used: in flashlights, control panels for equipment, in radio-controlled toys.
They connect poles of the same name: plus with plus, minus with minus.
Such inclusion does not require any additional switches or security elements. The EMF between the poles of all sources is equal:
The total current increases, it is equal to the sum of the currents from each source:
How to find voltage formula: what is voltage, how to find load resistance
Devices are divided into general and special purpose elements. Special parts have increased characteristics of resistance, frequency, operating voltage or special requirements for accuracy.
Expert opinion
It-Technology, Electrical power and electronics specialist
Ask questions to the “Specialist for modernization of energy generation systems”
Voltage divider on resistors: calculation, theory and operating principle For a material with homogeneous properties and a known resistance value and conductor length, the specific parameter is calculated using the formula below. Ask, I'm in touch!
Units of electrical current used in practice
The passports of electricity consumers - light bulbs, stoves, electric motors - usually indicate the strength of the electric current in them. Based on power, it is quite simple to find the work done by electric current over a given period of time; you just need to use the formula A = P*t.
Expressing power in watts and time in seconds, we get work in joules: 1 W = 1 J/s, where 1 J = 1 W*s.
But this unit of work is inconvenient to use in practice, since electrical receivers consume it over long periods of time, as, for example, in household appliances - for several hours, in electric trains - for several hours or even a day, and the calculation of consumed energy is based on In most cases, the electric meter is checked once a month.
Therefore, when calculating the work of a current or the energy consumed and generated, in all these cases it is necessary to convert these time periods into seconds, which complicates the calculations.
Peryshkin A.V. Physics 8. – M.: Bustard, 2010. [2]
Therefore, in practice, when calculating the work of electric current, it is more convenient to express time in hours, and the work of electric current not in joules, but in other units: for example, watt-hour (Wh), hectowatt-hour (gWh), kilowatt-hour (kW*h).
Peryshkin A.V. Physics 8. – M.: Bustard, 2010. [2]
The following relationships will be true:
- 1 Wh = 3600 J;
- 1 gWh = 100 Wh = 360,000 J;
- 1 kWh = 1000 Wh = 3,600,000 J.
Task. There is an electric lamp designed for a current of 100 watts. The lamp works for 6 hours every day. We need to find the work of electric current for one month (30 days) and the cost of consumed electricity, assuming that the tariff is 500 kopecks per kW/h.
Let's write down the condition of the problem and solve it.
Input data : P = 100 W, t = 6 h * 30 = 180 h, tariff = 500 kW/kWh.
The solution of the problem. We know that A = P*t, so we get: A = 100 W*180 h = 18,000 W*h = 18 kW*h.
We calculate the cost as follows: Cost = 500 kW*h * 18 kW*h = 9000 kopecks = 90 rubles.
Answer: A = 18 kWh, cost of consumed electricity = 90 rubles.
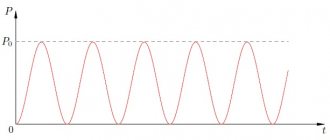
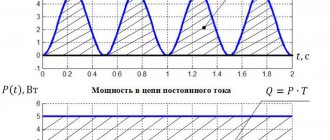
Direct and alternating current.
Let me briefly remind you that direct current (DC) is a current that does not change its magnitude and direction over a certain period of time. Alternating current (AC) is a current that periodically changes both in magnitude and direction over a certain period of time.
In the figure above, the graphs show diagrams of direct (a) and alternating (b) current. The period of time during which a complete cycle of current change occurs is called a period. The period is designated by the letter T and is measured in seconds. The period of time during which half of the complete cycle of current change occurs is called a half-cycle. Consequently, the period of change of current (EMF or voltage) consists of two half-cycles. It is quite obvious that all periods of the same alternating current are equal to each other. During one period of its change, the current reaches its maximum value twice. The maximum value of an alternating current (emf or voltage) is called its amplitude or amplitude current value.