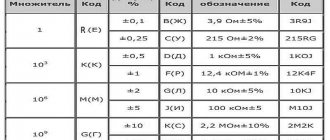
The main purpose resistors – converting current into voltage or performing the reverse process, limiting the current indicator, absorbing electrical energy. Used in almost all complex electrical circuits, so pay attention to the color coding.
Due to their small size, resistors are rarely marked with a numerical or letter value. Most often, colors are applied, which determine all the basic qualities. In order to choose the right resistor, you should know the features of applying colored dots or lines.
Resistor markings
As you already understood, resistors, being elementary components of electronics, provide current limitation and voltage reduction. This allows, for example, to work on LEDs with a supply voltage.
But ohmic resistances are inevitable not only in power supplies, but also in audio and video signal processing, as well as in digital technologies. In short, electrical resistance can be found in almost every electronic device. Therefore, it is not surprising that the devices themselves come in a variety of designs, and, regardless of the design, they must be appropriately labeled.
And so that the marking does not look like something complicated and incomprehensible to someone, they came up with a calculator to determine the resistance.
Non-standard marking of imported resistors
Despite the accepted rules for color marking, some companies use their own standards. These include:
- Philips is a manufacturer of consumer and industrial electronics that has introduced some of its standards in the field of resistor marking. Thus, it can be noted that the company uses colors not only to indicate the main characteristics, but also to display production technology and the properties of components. To do this, the body itself is painted a certain color, and the rings are arranged in a certain order relative to each other.
- CGW and Panasonic also introduced their own labeling rules. This is how these manufacturers apply information about the special properties of the resistor.
Almost all manufacturers in the world have adopted established rules, which simplifies the procedure for identifying denominations.
In conclusion, we note that in addition to color markings, alphanumeric designations may be present. They are applied to the surface of fairly large resistor designs and can also be used to reveal performance characteristics.
Resistor color coding calculator
Of course, a unique device that is easily used and operated for determining and coding electrical resistance (what is it? (symbol R) in electrical engineering is a measure of an electrical quantity (U) that is necessary for a certain electric current (I) to flow through an electrical conductor; electrical resistance, for example, of a heating coil that heats up and evaporates the liquid, expressed in Ohms).
The calculator is designed so “easy” that it will allow you to find the resistance component in the shortest possible time.
How to determine the resistance of a resistor by color?
Basically, today, it is almost impossible to find resistors older than 15-20 years, although some old rare “Records” and “Electrons” are still pleasing to the eye in some apartments.
Filled with Soviet electronics, old televisions and radios usually included standard resistors in brown or green colors with letter markings.
It is not difficult to understand the nominal value of an element by its alphanumeric encoding if you have a rare waste paper reference book at hand, especially since most of them were metal-film, varnished devices with the property of heat resistance - MLT.
In the Soviet Union, consumer electronics were a byproduct of defense industries, but were assembled from the same parts as military equipment. Such resistors differed from each other in size - the larger the element, the greater the resistance.
Today's component labeling is largely different in that there are several varieties - simple, standard color-coded cylindrical resistors and SMD elements.
Why does the resistor calculator require a color code?
Although high power and bulk resistors can be labeled without any problems, the same cannot be said for small wire resistors.
Due to lack of “space” the numbers must be very small. In addition, when assembling printed circuit boards, you should always ensure that the resistor markings are legible. After all, you see, it will be very strange if you first need to remove a component in order to then be able to read its electrical value.
Largely because of this, color coding was introduced.
Resistor values.
Resistor values are not arbitrary numbers. There are special series of values , which represent values from 0 to 10. So, resistor values (resistance values) can have values that are defined as the value from the corresponding series multiplied by 10 to the integer power. Let's look at the main rows - E3, E6, E12 and E24:
The number in the name of the series means the number of numbers in the series of denominations in the range from 0 to 10. In series E3 there are three numbers - 1.0, 2.2, 4.7, similarly in other series. Thus, if the resistor is from the E3 series, then its nominal value (resistance) can be 1 Ohm, 2.2 Ohm, 4.7 Ohm, 10 Ohm, 22 Ohm, 47 Ohm... 1 KOhm... 22 KOhm, etc. There are also nominal series E48, E96, E192 - their difference from the series we considered is only that there are even more permissible values.
This concludes our article. Today we looked at the main points that will be important when working with resistors, and in one of the following articles we will continue this topic, and next in line will be variable resistors. stay tuned