Enter the resistor marking directly into the image of its body below and you will see the value of this SMD resistor below it. I also have a resistor color coding calculator on my website. The SMD resistor marking calculator accepts the following values:
- Three digits (123)
- Two digits separated by the letter R (4R7)
- Of four digits (1234)
- Three digits separated by the letter R (4R37)
- Designation from the EIA-96 table of two numbers and one Latin letter from the series “ZYRXSABHCDEF” (02A)
Resistor value:
Examples of resistor decodings
Resistors with two numbers and a separator (4R7 1R0 2R2)
In this case, "R" acts as a decimal point. Thus:
- 2R2 - 2.2 Ohm
- 1R0 - 1 Ohm
- 4R7 - 4.7 Ohm
Three-digit resistors (103 102 100)
For such resistors, the first two digits are the value, and the third digit indicates the number of zeros after the value.
- 100 — 10 Ohm
- 102 — 1,000 Ohm or 1 KOhm
- 103 — 10,000 Ohm or 10 KOhm
Four-digit resistors (0805 1206 2512)
As in previous examples, the first digits are directly the value, and the last digit indicates the number of zeros after the value:
- 0805 — 8,000,000 Ohm or 8 MOhm
- 1206 — 120,000,000 Ohm or 120 MOhm
- 2512 — 25 100 Ohm or 25.1 KOhm
Resistor 000
There are SMD resistors with zero resistance. They are designated by zeros (0, 00 or 000), or may have a longitudinal line on the body. Such resistors are often used as fuses. Since, despite almost zero resistance, they still have a certain power, which depends on the size of the resistor. I will write about this below.
Marking table for SMD constant resistance resistors
| Code | Meaning | Code | Meaning | Code | Meaning | Code | Meaning |
| R10 | 0.1 Ohm | 1R0 | 1 ohm | 100 | 10 ohm | 101 | 100 Ohm |
| R11 | 0.11 Ohm | 1R1 | 1.1 Ohm | 110 | 11 ohm | 111 | 110 Ohm |
| R12 | 0.12 Ohm | 1R2 | 1.2 Ohm | 120 | 12 ohm | 121 | 120 Ohm |
| R13 | 0.13 Ohm | 1R3 | 1.3 Ohm | 130 | 13 ohm | 131 | 130 Ohm |
| R15 | 0.15 Ohm | 1R5 | 1.5 Ohm | 150 | 15 ohm | 151 | 150 Ohm |
| R16 | 0.16 Ohm | 1R6 | 1.6 Ohm | 160 | 16 ohm | 161 | 160 Ohm |
| R18 | 0.18 Ohm | 1R8 | 1.8 Ohm | 180 | 18 ohm | 181 | 180 Ohm |
| R20 | 0.2 Ohm | 2R0 | 2 ohm | 200 | 20 ohm | 201 | 200 Ohm |
| R22 | 0.22 Ohm | 2R2 | 2.2 Ohm | 220 | 22 Ohm | 221 | 220 Ohm |
| R24 | 0.24 Ohm | 2R4 | 2.4 Ohm | 240 | 24 ohm | 241 | 240 Ohm |
| R27 | 0.27 Ohm | 2R7 | 2.7 Ohm | 270 | 27 Ohm | 271 | 270 Ohm |
| R30 | 0.3 ohm | 3R0 | 3 ohm | 300 | 30 ohm | 301 | 300 Ohm |
| R33 | 0.33 Ohm | 3R3 | 3.3 Ohm | 330 | 33 Ohm | 331 | 330 Ohm |
| R36 | 0.36 Ohm | 3R6 | 3.6 Ohm | 360 | 36 Ohm | 361 | 360 Ohm |
| R39 | 0.39 Ohm | 3R9 | 3.9 Ohm | 390 | 39 Ohm | 391 | 390 Ohm |
| R43 | 0.43 Ohm | 4R3 | 4.3 Ohm | 430 | 43 Ohm | 431 | 430 Ohm |
| R47 | 0.47 Ohm | 4R7 | 4.7 Ohm | 470 | 47 Ohm | 471 | 470 Ohm |
| R51 | 0.51 Ohm | 5R1 | 5.1 Ohm | 510 | 51 Ohm | 511 | 510 Ohm |
| R56 | 0.56 Ohm | 5R6 | 5.6 Ohm | 560 | 56 Ohm | 561 | 560 Ohm |
| R62 | 0.62 Ohm | 6R2 | 6.2 Ohm | 620 | 62 Ohm | 621 | 620 Ohm |
| R68 | 0.68 Ohm | 6R8 | 6.8 Ohm | 680 | 68 Ohm | 681 | 680 Ohm |
| R75 | 0.75 Ohm | 7R5 | 7.5 Ohm | 750 | 75 Ohm | 751 | 750 Ohm |
| R82 | 0.82 Ohm | 8R2 | 8.2 Ohm | 820 | 82 Ohm | 821 | 820 Ohm |
| R91 | 0.91 Ohm | 9R1 | 9.1 Ohm | 910 | 91 Ohm | 911 | 910 Ohm |
| 102 | 1 kOhm | 103 | 10 kOhm | 104 | 100 kOhm | 105 | 1 mOhm |
| 112 | 1.1 kOhm | 113 | 11 kOhm | 114 | 110 kOhm | 115 | 1.1 mOhm |
| 122 | 1.2 kOhm | 123 | 12 kOhm | 124 | 120 kOhm | 125 | 1.2 mOhm |
| 132 | 1.3 kOhm | 133 | 13 kOhm | 134 | 130 kOhm | 135 | 1.3 mOhm |
| 152 | 1.5 kOhm | 153 | 15 kOhm | 154 | 150 kOhm | 155 | 1.5 mOhm |
| 162 | 1.6 kOhm | 163 | 16 kOhm | 164 | 160 kOhm | 165 | 1.6 mOhm |
| 182 | 1.8 kOhm | 183 | 18 kOhm | 184 | 180 kOhm | 185 | 1.8 mOhm |
| 202 | 2 kOhm | 203 | 20 kOhm | 204 | 200 kOhm | 205 | 2 mOhm |
| 222 | 2.2 kOhm | 223 | 22 kOhm | 224 | 220 kOhm | 225 | 2.2 mOhm |
| 242 | 2.4 kOhm | 243 | 24 kOhm | 244 | 240 kOhm | 245 | 2.4 mOhm |
| 272 | 2.7 kOhm | 273 | 27 kOhm | 274 | 270 kOhm | 275 | 2.7 mOhm |
| 302 | 3 kOhm | 303 | 30 kOhm | 304 | 300 kOhm | 305 | 3 mOhm |
| 332 | 3.3 kOhm | 333 | 33 kOhm | 334 | 330 kOhm | 335 | 3.3 mOhm |
| 362 | 3.6 kOhm | 363 | 36 kOhm | 364 | 360 kOhm | 365 | 3.6 mOhm |
| 392 | 3.9 kOhm | 393 | 39 kOhm | 394 | 390 kOhm | 395 | 3.9 mOhm |
| 432 | 4.3 kOhm | 433 | 43 kOhm | 434 | 430 kOhm | 435 | 4.3 mOhm |
| 472 | 4.7 kOhm | 473 | 47 kOhm | 474 | 470 kOhm | 475 | 4.7 mOhm |
| 512 | 5.1 kOhm | 513 | 51 kOhm | 514 | 510 kOhm | 515 | 5.1 mOhm |
| 562 | 5.6 kOhm | 563 | 56 kOhm | 564 | 560 kOhm | 565 | 5.6 mOhm |
| 622 | 6.2 kOhm | 623 | 62 kOhm | 624 | 620 kOhm | 625 | 6.2 mOhm |
| 682 | 6.8 kOhm | 683 | 68 kOhm | 684 | 680 kOhm | 685 | 6.8 mOhm |
| 752 | 7.5 kOhm | 753 | 75 kOhm | 754 | 750 kOhm | 755 | 7.5 mOhm |
| 822 | 8.2 kOhm | 823 | 82 kOhm | 824 | 820 kOhm | 815 | 8.2 mOhm |
| 912 | 9.1 kOhm | 913 | 91 kOhm | 914 | 910 kOhm | 915 | 9.1 mOhm |
You can always buy SMD resistors inexpensively and without unnecessary hassles on Aliexpress, but you need to pay attention to reviews, since there is always a risk of ending up with an unscrupulous seller.
What is an SMD resistor - internal structure
This device consists of a ceramic substrate coated with a resistive layer of a certain material and contact pads, as well as a protective coating (polymer, resin, glass). The layer resistance depends on the type of material and its thickness. Various constituent elements can be made of chromium, nickel, tin, ruthenium, silver or palladium oxides, as well as various alloys.
The design of the SMD resistor includes:
- A substrate made of a dielectric with good thermal conductivity – aluminum oxide.
- The resistive layer is a thin metal (chromium) or oxide film (ruthenium oxide) up to 10 microns thick. The material of the resistive layer has a low TCR, which ensures stability of parameters when temperature changes and the ability to produce precision resistors. To produce parts with a nominal resistance of less than 100 ohms, constantan is used for the resistive layer. The resistive element determines most of the electrical properties of an SMD resistor.
- Contact areas. They are formed from several layers. The inner layer is made of precious metals - palladium or silver. The intermediate layer is nickel, the outer layer is lead-tin. The use of these materials ensures ideal connectivity of the layers, which determines the reliability of contacts and the noise level.
The composition of the resistive layer, the nature of its processing, and the technology of application to the substrate are most often the know-how of the manufacturer and are kept in the strictest confidence.
Color coding of resistors
On the one hand, the multi-colored stripes (or rings) present on the parts made the process of factory marking easier. On the other hand, this often confuses novice radio amateurs.
However, you can figure it out if you want. It is enough to understand the principle of color marking once and no further problems will arise.
Before you begin to “decipher” the resistor, you need to position it in front of your eyes so that the colored rings are located on the left side.
Please note: gold or silver stripes are usually not taken into account when decoding. We simply skip them.
Next it reads the number by stripes:
- 0 - black;
- 1- brown;
- 2 - Red;
- 3 - Orange;
- 4 - Yellow;
- 5 - Green;
- 6 - Blue;
- 7 - Purple;
- 8 - Gray;
- 9 - White.
The third colored stripe on the resistor is responsible for the number of zeros that need to be added to the resulting value. To do this, you will need a plate that contains the values for each specific color.
The names and types of SMD resistor housings may vary. For example, the symbol in square brackets is used in accordance with the accepted standards of the JEDEC Engineering Standards Committee (USA), and the curly braces refer to JEITA (Japan).
Also, sometimes there may be designations enclosed in parentheses - this is how resistor cases are usually designated, which are accepted as a standard in a particular company.
| 2 outputs | 3 pins | 4 pins | 5 pins | 6 pins | >8 pins | ||||||
| smcj [do214ab] 7.0x6.0x2.6mm | d2pak [to263] 9.8x8.8x4.0mm | mbs [to269aa] 4.8x3.9x2.5mm | d2pak5 [to263-5] 9.8x8.8x4.0mm | mlp2x3 [mo229] (dfn2030-6) (lfcsp6) 3.0x2.0x0.75mm | tssop8 [mo153] 4.4x3.0x1.0mm | ||||||
| smbj [do214aa] 4.6x3.6x2.3mm | dpak [to252aa] 6.6x6.1x2.3mm | sop4 4.4x4.1x2.0mm | dpak5 [to252-5] 6.6x6.1x2.3mm | ssot6 [mo193] 3.0x1.7x1.1mm | chipfet 3.05x1.65x1.05mm | ||||||
| (gf1) [do214ba] 4.5x1.4x2.5mm | (smpc) [to277a] 6.5x4.6x1.1mm | ssop4 4.4x2.6x2.0mm | sot223-5 6.5x3.5x1.8mm | dfn2020-6 [sot1118] (wson6 | llp6) 2.0x2.0x0.75mm | tdfn8 (wson8) (lfcsp8) 3.0x3.0x0.9mm | ||||||
| smaj [do214ac] 4.5x2.6x2.0mm | sot223 [to261aa] {sc73} 6.5x3.5x1.8mm | sot223-4 6.5x3.5x1.8mm | mo240 (pqfn8l) 3.3x3.3x1.0mm | sot23-6 [mo178ab] {sc74} 2.9x1.6x1.1mm | (mlf8) 2.0x2.0x0.85mm | ||||||
| sod123 [do219ab] 2.6x1.6x1.1mm | sot89 [to243aa] {sc62} 4.7x2.5x1.7mm | sot143 2.9x1.3x1.0mm | sot89-5 4.5x2.5x1.5mm | tsot6 [mo193] 2.9x1.6x0.9mm | msop8 [mo187aa] 3.0x3.0x1.1mm | ||||||
| sod123f 2.6x1.6x1.1mm | sot23f 2.9x1.8x0.8mm | sot343 2.0x1.3x0.9mm | sot23-5 [mo193ab|mo178aa] {sc74a} (tsop5/sot753) 2.9x1.6x1.1mm | sot363 [mo203ab|ttsop6] {sc88|sc70-6} (us6) 2.0x1.25x1.1mm | vssop8 3.0x3.0x0.75mm | ||||||
| sod110 2.0x1.3x1.6mm | sot346 [to236aa] {sc59a} (smini) 2.9x1.5x1.1mm | sot543 1.6x1.2x0.5mm | sct595 2.9x1.6x1.0mm | sot563f {sc89-6|sc170c} [sot666] 1.6x1.2x0.6mm | sot23-8 2.9x1.6x1.1mm | ||||||
| sod323 {sc76} 1.7x1.25x0.9mm | sot23 [to236ab] 2.9x1.3x1.0mm | (tsfp4-1) 1.4x0.8x0.55mm | sot353 [mo203aa] {sc88a|sc70-5} (tssop5) 2.0x1.25x0.95mm | sot886 [mo252] (xson6/mp6c) 1.45x1.0x0.55mm | sot765 [mo187ca] (us8) 2.0x2.3x0.7mm | ||||||
| sod323f {sc90a} 1.7x1.25x0.9mm | dfn2020 (sot1061) 2.0x2.0x0.65mm | (tslp4) 1.2x0.8x0.4mm | sot553 (sot665|esv) {sc107} 1.6x1.2x0.6mm | wlcsp6 1.2x0.8x0.4mm | usoic10 (rm10|micro10) 3.0x3.0x1.1mm | ||||||
Characteristics
These miniature resistors are perfect for surface mounting. Marking allows you to find out the size, power and resistance of the product.
The shape of SMD resistors is rectangular, square, round, oval, the profile is low. Low-profile elements are placed on the board very compactly and significantly save usable space.
SMD resistors are classified according to a number of parameters, such as:
- Nominal resistance
. This value is measured under certain environmental parameters, the most important of which is temperature. Usually the nominal resistance is considered to be measured at a temperature of +20 °C and normal atmospheric pressure. - Tolerance on nominal resistance
. Possible tolerances are from 0.05 to +5%. The most popular and affordable parts with tolerances of +/-1% and +/-5%. More accurate models must be pre-ordered, and they are much more expensive than less accurate analogues. - Temperature coefficient of resistance change (TCC)
. This parameter characterizes the reversible relative change in the resistance of the part when the temperature fluctuates by 1 °C. Temperature changes in the part are possible due to changes in ambient temperature or self-heating of the resistor. The unit of measurement for this value is ppm. Modern SMD resistors are produced with TCR, the value of which is in the range of +/-5...+/-200 ppm. If parts from the same manufacturer are used to create a circuit, then the values of their nominal resistances and TCR are closer to each other than is reflected in the passport for each part. Therefore, using parts from the same manufacturer allows you to improve the accuracy of the circuit both at a constant temperature and when it changes. - Power dissipation
. This parameter depends on the size and is determined from the table.
Dimensions of SMD parts housings
SMD resistors
| TYPE: | Type Explanation: | |||||
| S.R. | Resistor Chip Resistor chip | |||||
| Size (inches) | Size(mm) | Component Thickness | Tape width | Component pitch in the ribbon | Quantity in standard packaging (180 mm/7 inches) paper tape | Qty per standard package (180 mm/7 inches) plastic tape |
| 01005 | 0402 | 0.12 mm ± 0.02 | 8 mm | 2 mm | 20000 | – |
| 0201 | 0603 | 0.23 mm ± 0.03 | 8 mm | 2 mm | 15000 | – |
| 0402 | 1005 | 0.35 mm ± 0.05 | 8 mm | 2 mm | 10000 | – |
| 0603 | 1608 | 0.45 mm ± 0.1 | 8 mm | 4 mm | 5000 | – |
| 0805 | 2012 | 0.55 mm ± 0.1 | 8 mm | 4 mm | 5000 | – |
| 1206 | 3216 | 0.55 mm ± 0.15 | 8 mm | 4 mm | 5000 | – |
| 1210 | 3225 | 0.55 mm ± 0.15 | 8 mm | 4 mm | 5000 | 4000 |
| 2010 | 5025 | 0.55 mm ± 0.15 | 8/12 mm | 4/8 mm | – | 4000 |
| 2512 | 6332 | 0.55 mm ± 0.15 | 12 mm | 4/8 mm | – | 4000/2000 |
| TYPE: | Type Explanation: | ||||
| SRM | Melf Resistor Melf resistor (round) | ||||
| Size (inches) | Name | Component size | Tape width | Component pitch in the ribbon | Qty per standard package (180 mm/7 inches) plastic tape |
| 0604 | – | 1.6 mm X 1.0 mm | 8 mm | 4 mm | 3000 |
| 0805 | Micro | 2.2 mm X 1.1 mm | 8 mm | 4 mm | 3000 |
| 1206 | Mini | 3.2 mm X 1.6 mm | 8 mm | 4 mm | 3000 |
| 1406 | Mini | 3.5 mm X 1.4 mm | 8 mm | 4 mm | 3000 |
| 2308 | Melf | 5.9 mm X 2.2 mm | 12 mm | 4 mm | 1500 |
SMD capacitors
| TYPE: | Type Explanation: | |||||
| S.C. | Ceramic Chip Capacitor Ceramic chip capacitor | |||||
| Size (inches) | Size(mm) | Component Thickness | Tape width | Component pitch in the ribbon | Quantity in standard packaging (180 mm/7 inches) paper tape | Qty per standard package (180 mm/7 inches) plastic tape |
| 01005 | 0402 | 0.2 mm ± 0.03 | 8 mm | 2 mm | 20000 | – |
| 0201 | 0603 | 0.3 mm ± 0.03 | 8 mm | 2 mm | 15000 | – |
| 0402 | 1005 | 0.5 mm ± 0.1 | 8 mm | 2 mm | 10000 | – |
| 0603 | 1608 | 0.8 mm ± 0.1 | 8 mm | 4 mm | 4000 | – |
| 0805 | 2012 | 0.6 – 1.25 mm | 8 mm | 4 mm | 4000 | 3000 |
| 1206 | 3216 | 0.6 – 1.25 mm | 8 mm | 4 mm | 4000 | 3000 |
| 1210 | 3225 | 1.25 mm – 1.5 mm | 8 mm | 4 mm | – | 3000 |
| 1812 | 4532 | 2 mm (Max.) | 12 mm | 8 mm | – | 1000 |
| 2225 | 5664 | 2 mm (Max.) | 12 mm | 8 mm | – | 1000 |
Tantalum capacitors SMD
| TYPE: | Type Explanation: | |||||
| SD | Molded Tantalum Tantalum capacitor (polar component) | |||||
| Size (inches) | Code | Component Thickness | Component size | Tape width | Component pitch in the ribbon | Qty per standard package (180 mm/7 inches) plastic tape |
| 3216 | A | 1.6 mm | 3.2 mm X 1.6 mm | 8 mm | 4 mm | 2000 |
| 3528 | B | 1.9 mm | 3.5 mm X 2.8 mm | 8 mm | 4 mm | 2000 |
| 6032 | C | 2.5 mm | 6.0 mm X 3.2 mm | 12 mm | 8 mm | 500 |
| 7343 | D | 2.8 mm | 7.3 mm X 4.3 mm | 12 mm | 8 mm | 500 |
| 1608 | J | 0.8 mm | 1.6 mm X 0.8 mm | 8 mm | 4 mm | 4000 |
| 2012 | P/R | 1.2 mm | 2.0 mm X 1.2 mm | 8 mm | 4 mm | 2500/3000 |
Electrolytic capacitors SMD
| TYPE: | Type Explanation: | ||||
| S.E. | Aluminum Capacitor Aluminum capacitor (polar component) | ||||
| Case diameter | Case height | Tape width | Component pitch in the ribbon | Qty per standard package (180 mm/7 inches) plastic tape | Qty per standard pack (330 mm/13 inches) plastic tape |
| 3 mm | 5.5 mm | 12 mm | 8 mm | 100 | 2000 |
| 4 mm | 5.5 mm | 12 mm | 8 mm | 100 | 2000 |
| 5 mm | 5.5 mm | 12 mm | 12 mm | 100 | 1000 |
| 6.3 mm | 5.5 mm | 16 mm | 12 mm | 100 | 1000 |
| 8 mm | 6 mm | 16 mm | 12 mm | 100 | 1000 |
| 8 mm | 10 mm | 24 mm | 16 mm | 100 | 500 |
| 10 mm | 10 mm | 24 mm | 16 mm | 100 | 300 – 500 |
| 10 mm | 14 – 22 mm | 32 mm | 20 mm | – | 250 – 300 |
| 12.5 mm | 14 mm | 32 mm | 24 mm | – | 200 – 250 |
| 12.5 mm | 17 mm | 32 mm | 24 mm | – | 150 – 200 |
| 12.5 mm | 22 mm | 32 mm | 24 mm | – | 125 – 150 |
| 16 mm | 17 mm | 44 mm | 28 mm | – | 125 – 150 |
| 16 mm | 22 mm | 44 mm | 28 mm | – | 75 – 100 |
| 18 mm | 17 mm | 44 mm | 32 mm | – | 125 – 150 |
| 18 mm | 22 mm | 44 mm | 32 mm | – | 75 – 100 |
| 20 mm | 17 mm | 44 mm | 36 mm | – | 50 |
SMD transistors
| TYPE: | Type Explanation: | |||||||
| SOT | SOT Transistor SOT transistor | |||||||
| Type of shell | Number of pins | Tape width | Component pitch in the ribbon | Case size A (mm) | Case size B (mm) | Case size S (mm) | Case height H (mm) | Qty per standard package (180 mm/7 inches) plastic tape |
| SOT723 | 3 | 8 mm | 4 mm | 1.2 | 0.8 | 1.2 | 0.5 | 8000 |
| SOT346 | 3 | 8 mm | 4 mm | 2.9 | 1.6 | 2.8 | 1.1 | 3000 |
| SOT323 | 3 | 8 mm | 4 mm | 2.0 | 1.25 | 2.1 | 0.9 | 3000 |
| SOT416 | 3 | 8 mm | 4 mm | 1.6 | 0.8 | 1.6 | 0.7 | 3000 |
| SOT523F | 3 | 8 mm | 4 mm | 1.6 | 0.8 | 1.6 | 0.7 | 3000 |
| SOT23 | 3 | 8 mm | 4 mm | 2.9 | 1.3 | 2.4 | 0.95 | 3000 |
| SOT23-5 | 5 | 8 mm | 4 mm | 2.9 | 1.6 | 2.8 | 1.1 | 3000 |
| SOT23-6 | 6 | 8 mm | 4 mm | 2.9 | 1.6 | 2.8 | 1.1 | 3000 |
| SOT89 | 3 | 12 mm | 8 mm | 4.5 | 2.5 | 4.0 | 1.5 | 1000 |
| SOT143 | 4 | 8 mm | 4 mm | 2.9 | 1.6 | 2.8 | 0.95 | 3000 |
| SOT223 | 3 | 16 mm | 8 mm | 6.5 | 3.6 | 7.0 | 1.6 | 2500 |
| SOT323 | 3 | 8 mm | 4 mm | 2.0 | 1.25 | 2.1 | 0.9 | 3000 |
| SOT343 | 4 | 8 mm | 4 mm | 2.0 | 1.25 | 2.1 | 0.9 | 3000 |
| SOT353 | 5 | 8 mm | 4 mm | 2.0 | 1.25 | 2.1 | 0.9 | 3000 |
| SOT363 | 6 | 8 mm | 4 mm | 2.0 | 1.25 | 2.1 | 0.9 | 3000 |
| SOT23-8 | 8 | 8 mm | 4 mm | 2.9 | 1.6 | 2.9 | 1.2 | 3000 |
Power transistors SMD
| TYPE: | Type Explanation: | |||||||
| DPAK | DPAK Transistor DPAK Transistor | |||||||
| Type of shell | Number of pins | Tape width | Component pitch in the ribbon | Case size L (mm) | Case size W (mm) | Case height H (mm) | Case size S (mm) | Qty per standard pack (330 mm/13 inches) plastic tape |
| DPAK | 3 | 16 mm | 8 mm | 6 | 6.5 | 2.3 | 10 | 2500 |
| D2PAK | 3 | 24 mm | 16 mm | 9.2 | 10 | 4.4 | 15 | 500 – 800 |
| D2PAK-5 | 5 | 24 mm | 16 mm | 9.2 | 10 | 4.4 | 15 | 500 – 800 |
| D2PAK-7 | 7 | 24 mm | 16 mm | 9.2 | 10 | 4.4 | 15 | 500 – 800 |
| D3PAK | 3 | 24 mm | 24 mm | 14 | 16 | 4.7 | 18.8 | 500 |
MELF SMD diodes
| TYPE: | Type Explanation: | |||
| SOD | SOD, SM, Melf Diode/Rectifier SOD, SM, Melf diodes (round) | |||
| Component type | Component size (diameter X length) | Tape width | Component pitch in the ribbon | Qty per standard package (180 mm/7 inches) plastic tape |
| MiniMELF/SOD-80 (LL34) | 1.6 mm X 3.5 mm | 8 mm | 4 mm | 2500 |
| MELF (LL35/LL41) | 2.5 mm X 5.0 mm | 12 mm | 4 mm | 1500 |
| MELF (SM1) | 2.5 mm X 5.0 mm | 12 mm | 4 mm | 1750 |
SOD SMD diodes
| TYPE: | Type Explanation: | |||||||
| S.M. | Rectangular Diode Gull Wing Lead | |||||||
| Type of shell | Tape width | Component pitch in the ribbon | Case size L (mm) | Case size W (mm) | Case height H (mm) | Case size S (mm) | Case size B (mm) | Qty per standard package (170 mm/7 inches) plastic tape |
| SOD923 | 8 mm | 2 mm | 0.8 | 0.6 | 0.4 | 1.0 | 0.2 | 8000 |
| SOD723 | 8 mm | 2 mm | 1.0 | 0.6 | 0.5 | 1.4 | 0.3 | 8000 |
| SOD523 | 8 mm | 4 mm | 1.2 | 0.8 | 0.6 | 1.6 | 0.3 | 3000 |
| SOD323 | 8 mm | 4 mm | 1.7 | 1.25 | 0.7 | 2.5 | 0.3 | 3000 |
| SOD123 | 8 mm | 4 mm | 2.7 | 1.5 | 1.3 | 3.6 | 0.7 | 3000 |
| DO215AC | 12 mm | 4 mm | 4.3 | 2.6 | 2.2 | 6.1 | 1.4 | 1800 |
| DO215AA | 12 mm | 8 mm | 4.3 | 3.6 | 2.3 | 6.2 | 2.0 | 1000 |
| DO215AB | 16 mm | 8 mm | 7.0 | 6.0 | 2.3 | 1 0 | 3.0 | 900 |
SM SMD Diodes
| TYPE: | Type Explanation: | |||||||
| S.M. | Rectangular Diode C-Bend Lead (Modified J-Lead) | |||||||
| Type of shell | Tape width | Component pitch in the ribbon | Case size L (mm) | Case size W (mm) | Case height H (mm) | Case size S (mm) | Case size B (mm) | Qty per standard package (170 mm/7 inches) plastic tape |
| S.M.A.J. | 12 mm | 4 mm | 4.3 | 2.6 | 2.2 | 5.0 | 1.5 | 1800 |
| SMBJ | 12 mm | 8 mm | 4.3 | 3.6 | 2.3 | 5.4 | 2.0 | 750 |
| SMCJ | 16 mm | 8 mm | 7.0 | 6.0 | 2.3 | 8.0 | 3.0 | 850 |
Surface Mount Technology of SMD Resistors
Installation of surface resistors in amateur workshops is carried out using a hair dryer, and in production conditions it occurs in special ovens.
Stages of mounting parts on a board in serial and mass production:
- Small spacers made of silver or gold, lead-tin plates are placed on the board, on which SMD components will be fixed.
- Using the machine, solder paste and a mixture consisting of flux and solder are applied to the prepared mounting pads.
- After preparing the printed circuit board, components are fed into the device (Pick machine) in trays, on rolls of tape or in tubes. The machines then place them on the board. Equipment productivity can reach 60,000 elements per hour.
- The assembled board enters the oven at a temperature sufficient to melt the solder.
- After removal from the oven, the boards are cooled and cleared of loose solder particles.
Quality is checked by visual inspection, during which missing parts and the degree of cleaning are determined.
The development and implementation of surface mount technology (SMT) has made it possible to automate the board assembly process and make it faster, simpler, cheaper and more efficient. In practice, a hybrid of surface-mount and through-hole mounting technologies may be encountered.
The use of surface-mount resistors has a positive effect on the weight and size of radio-electronic devices and their frequency parameters.
Coding table for planar SMD parts
The first 2 characters of the chip element are indicated. By clicking on them you will be taken to a page with another table, which shows various options for the remaining symbols with a brief description of the functions and parameters for each.
| 00 | 01 | 02 | 03 | 04 | 05 | 06 | 07 | 08 | 09 | 0A | 0B | 0C | 0D | 0E | 0F | 0G | 0H | 0I | 0J | 0K | 0L | 0M | 0N | 0P | 0Q | 0R | 0S | 0T | 0U | 0V | 0W | 0X | 0Y | 0Z |
| 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 1A | 1B | 1C | 1D | 1E | 1F | 1G | 1H | 1I | 1J | 1K | 1L | 1M | 1N | 1P | 1Q | 1R | 1S | 1T | 1U | 1V | 1W | 1X | 1Y | 1Z |
| 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 2A | 2B | 2C | 2D | 2E | 2F | 2G | 2H | 2I | 2J | 2K | 2L | 2M | 2N | 2P | 2Q | 2R | 2S | 2T | 2U | 2V | 2W | 2X | 2Y | 2Z |
| 30 | 31 | 32 | 33 | 34 | 35 | 36 | 37 | 38 | 39 | 3A | 3B | 3C | 3D | 3E | 3F | 3G | 3H | 3I | 3J | 3K | 3L | 3M | 3N | 3P | 3Q | 3R | 3S | 3T | 3U | 3V | 3W | 3X | 3Y | 3Z |
| 40 | 41 | 42 | 43 | 44 | 45 | 46 | 47 | 48 | 49 | 4A | 4B | 4C | 4D | 4E | 4F | 4G | 4H | 4I | 4J | 4K | 4L | 4M | 4N | 4P | 4Q | 4R | 4S | 4T | 4U | 4V | 4W | 4X | 4Y | 4Z |
| 50 | 51 | 52 | 53 | 54 | 55 | 56 | 57 | 58 | 59 | 5A | 5B | 5C | 5D | 5E | 5F | 5G | 5H | 5I | 5J | 5K | 5L | 5M | 5N | 5P | 5Q | 5R | 5S | 5T | 5U | 5V | 5W | 5X | 5Y | 5Z |
| 60 | 61 | 62 | 63 | 64 | 65 | 66 | 67 | 68 | 69 | 6A | 6B | 6C | 6D | 6E | 6F | 6G | 6H | 6I | 6J | 6K | 6L | 6M | 6N | 6P | 6Q | 6R | 6S | 6T | 6U | 6V | 6W | 6X | 6Y | 6Z |
| 70 | 71 | 72 | 73 | 74 | 75 | 76 | 77 | 78 | 79 | 7A | 7B | 7C | 7D | 7E | 7F | 7G | 7H | 7I | 7J | 7K | 7L | 7M | 7N | 7P | 7Q | 7R | 7S | 7T | 7U | 7V | 7W | 7X | 7Y | 7Z |
| 80 | 81 | 82 | 83 | 84 | 85 | 86 | 87 | 88 | 89 | 8A | 8B | 8C | 8D | 8E | 8F | 8G | 8H | 8I | 8J | 8K | 8L | 8M | 8N | 8P | 8Q | 8R | 8S | 8T | 8U | 8V | 8W | 8X | 8Y | 8Z |
| 90 | 91 | 92 | 93 | 94 | 95 | 96 | 97 | 98 | 99 | 9A | 9B | 9C | 9D | 9E | 9F | 9G | 9H | 9I | 9J | 9K | 9L | 9M | 9N | 9P | 9Q | 9R | 9S | 9T | 9U | 9V | 9W | 9X | 9Y | 9Z |
| A0 | A1 | A2 | A3 | A4 | A5 | A6 | A7 | A8 | A9 | A.A. | AB | A.C. | AD | A.E. | A.F. | A.G. | A.H. | A.I. | A.J. | A.K. | AL | A.M. | AN | AP | AQ | AR | AS | AT | AU | AV | A.W. | AX | AY | AZ |
| B0 | B1 | B2 | B3 | B4 | B5 | B6 | B7 | B8 | B9 | B.A. | BB | B.C. | BD | BE | B.F. | B.G. | B.H. | B.I. | B.J. | B.K. | B.L. | B.M. | BN | B.P. | BQ | BR | B.S. | BT | B.U. | B.V. | B.W. | BX | BY | BZ |
| C0 | C1 | C2 | C3 | C4 | C5 | C6 | C7 | C8 | C9 | C.A. | C.B. | CC | CD | C.E. | CF | C.G. | CH | C.I. | C.J. | CK | C.L. | C.M. | CN | C.P. | C.Q. | CR | C.S. | C.T. | C.U. | CV | CW | CX | C.Y. | CZ |
| D0 | D1 | D2 | D3 | D4 | D5 | D6 | D7 | D8 | D9 | D.A. | D.B. | DC | DD | DE | DF | DG | D.H. | D.I. | DJ | DK | D.L. | DM | DN | D.P. | DQ | D.R. | D.S. | D.T. | D.U. | D.V. | DW | DX | DY | DZ |
| E0 | E1 | E2 | E3 | E4 | E5 | E6 | E7 | E8 | E9 | E.A. | E.B. | E.C. | ED | E.E. | E.F. | E.G. | E.H. | EI | EJ | E.K. | EL | E.M. | EN | E.P. | EQ | ER | ES | ET | EU | EV | E.W. | EX | EY | EZ |
| F0 | F1 | F2 | F3 | F4 | F5 | F6 | F7 | F8 | F9 | F.A. | FB | F.C. | FD | F.E. | FF | FG | FH | FI | F.J. | FK | FL | FM | FN | FP | FQ | FR | FS | F.T. | F.U. | F.V. | FW | FX | FY | FZ |
| G0 | G1 | G2 | G3 | G4 | G5 | G6 | G7 | G8 | G9 | GA | G.B. | G.C. | G.D. | G.E. | GF | GG | G.H. | G.I. | G.J. | GK | G.L. | G.M. | GN | G.P. | GQ | GR | G.S. | GT | G.U. | G.V. | G.W. | GX | G.Y. | GZ |
| H0 | H1 | H2 | H3 | H4 | H5 | H6 | H7 | H8 | H9 | H.A. | HB | HC | HD | HE | HF | HG | HH | HI | H.J. | H.K. | H.L. | H.M. | HN | HP | HQ | HR | H.S. | HT | HU | H.V. | HW | HX | HY | HZ |
| I0 | I1 | I2 | I3 | I4 | I5 | I6 | I7 | I8 | I9 | I.A. | I.B. | IC | ID | I.E. | IF | I.G. | IH | II | IJ | IK | IL | I.M. | IN | IP | IQ | IR | IS | IT | IU | IV | IW | IX | IY | IZ |
| J0 | J1 | J2 | J3 | J4 | J5 | J6 | J7 | J8 | J9 | JA | JB | JC | JD | JE | JF | JG | JH | JI | JJ | JK | JL | J.M. | JN | J.P. | J.Q. | JR | JS | JT | J.U. | JV | JW | JX | JY | JZ |
| K0 | K1 | K2 | K3 | K4 | K5 | K6 | K7 | K8 | K9 | K.A. | K.B. | KC | KD | KE | KF | KG | KH | KI | KJ | KK | KL | K.M. | KN | KP | KQ | KR | KS | KT | KU | KV | KW | KX | KY | KZ |
| L0 | L1 | L2 | L3 | L4 | L5 | L6 | L7 | L8 | L9 | L.A. | LB | L.C. | LD | L.E. | LF | LG | L.H. | LI | L.J. | L.K. | LL | L.M. | LN | LP | L.Q. | LR | L.S. | LT | L.U. | LV | LW | LX | LY | LZ |
| M0 | M1 | M2 | M3 | M4 | M5 | M6 | M7 | M8 | M9 | M.A. | M.B. | M.C. | M.D. | M.E. | M.F. | MG | M.H. | MI | MJ | MK | M.L. | MM | MN | MP | MQ | M.R. | MS | M.T. | M.U. | MV | M.W. | MX | M.Y. | MZ |
| N0 | N1 | N2 | N3 | N4 | N5 | N6 | N7 | N8 | N9 | N.A. | N.B. | NC | ND | NE | NF | NG | N.H. | NI | NJ | N.K. | NL | N.M. | NN | NP | N.Q. | NR | N.S. | NT | NU | N.V. | NW | NX | NY | NZ |
| P0 | P1 | P2 | P3 | P4 | P5 | P6 | P7 | P8 | P9 | PA | P.B. | PC | P.D. | P.E. | PF | PG | PH | P.I. | P.J. | PK | P.L. | P.M. | PN | PP | PQ | PR | PS | P.T. | P.U. | PV | PW | PX | PY | PZ |
| Q0 | Q1 | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 | Q5 | Q6 | Q7 | Q8 | Q9 | QA | QB | QC | QD | QE | QF | QG | QH | QI | Q.J. | QK | QL | QM | QN | QP | QR | QS | QT | QU | QV | QW | QX | QY | QZ | |
| R0 | R1 | R2 | R3 | R4 | R5 | R6 | R7 | R8 | R9 | R.A. | R.B. | R.C. | R.D. | RE | RF | RG | RH | R.I. | R.J. | RK | R.L. | R.M. | RN | R.P. | RQ | R.R. | R.S. | RT | RU | RV | RW | RX | R.Y. | RZ |
| S0 | S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 | S5 | S6 | S7 | S8 | S9 | S.A. | S.B. | S.C. | SD | S.E. | SF | S.G. | SH | S.I. | S.J. | S.K. | SL | S.M. | SN | SP | S.Q. | S.R. | SS | ST | S.U. | SV | S.W. | SX | S.Y. | SZ |
| T0 | T1 | T2 | T3 | T4 | T5 | T6 | T7 | T8 | T9 | T.A. | TB | TC | T.D. | T.E. | TF | TG | T.H. | T.I. | T.J. | TK | TL | TM | TN | TP | T.Q. | TR | T.S. | TT | T.U. | TV | TW | TX | T.Y. | TZ |
| U0 | U1 | U2 | U3 | U4 | U5 | U6 | U7 | U8 | U9 | U.A. | UB | U.C. | UD | UE | U.F. | U.G. | UH | UI | U.J. | UK | UL | U.M. | UN | U.P. | UQ | UR | US | UT | UU | UV | U.W. | UX | UY | UZ |
| V0 | V1 | V2 | V3 | V4 | V5 | V6 | V7 | V8 | V9 | V.A. | VB | V.C. | V.D. | V.E. | VF | VG | VH | VI | V.J. | VK | VL | V.M. | VN | V.P. | VQ | VR | VS | VT | VU | V.V. | VW | VX | VY | VZ |
| W0 | W1 | W2 | W3 | W4 | W5 | W6 | W7 | W8 | W9 | W.A. | W.B. | W.C. | W.D. | WE | W.F. | W.G. | W.H. | WI | W.J. | W.K. | W.L. | W.M. | WN | W.P. | W.Q. | WR | W.S. | W.T. | W.U. | W.V. | WW | W.X. | W.Y. | WZ |
| X0 | X1 | X2 | X3 | X4 | X5 | X6 | X7 | X8 | X9 | XA | XB | XC | XD | XE | XF | XG | XH | XI | XJ | XK | XL | XM | XN | XP | XQ | XR | XS | XT | XU | XV | XW | XX | XY | XZ |
| Y0 | Y1 | Y2 | Y3 | Y4 | Y5 | Y6 | Y7 | Y8 | Y9 | YA | YB | YC | YD | YE | YF | YG | YH | YI | YJ | YK | YL | YM | YN | YP | YQ | YR | YS | YT | YU | YV | YW | YX | YY | YZ |
| Z0 | Z1 | Z2 | Z3 | Z4 | Z5 | Z6 | Z7 | Z8 | Z9 | ZA | ZB | ZC | ZD | ZE | ZF | ZG | ZH | ZI | ZJ | ZK | ZL | ZM | ZN | ZP | ZQ | ZR | ZS | ZT | ZU | ZV | ZW | ZX | ZY | ZZ |
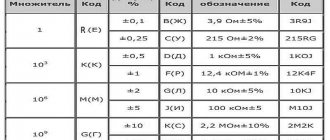
Three-digit resistor numbering with 1% tolerance
Resistors with a tolerance of 1% of size 0603 are marked using three-digit numbering. The first two characters are numbers indicating the resistance value in Ohms, taken from the table below. The last character is a letter indicating the value of the multiplier: S=0.1; R=1; B=10; C=100; D=1000; E=10000; F=100000. For example, the marking 28C means that the resistor has a value of 191 × 100 ohms = 19.1 kOhms.
| = 19.1 KOhm |
| Code | Meaning | Code | Meaning | Code | Meaning | Code | Meaning |
| 01 | 100 | 25 | 178 | 49 | 316 | 73 | 562 |
| 02 | 102 | 26 | 182 | 50 | 326 | 74 | 576 |
| 03 | 105 | 27 | 187 | 51 | 332 | 75 | 590 |
| 04 | 107 | 28 | 191 | 52 | 340 | 76 | 604 |
| 05 | 110 | 29 | 196 | 53 | 348 | 77 | 619 |
| 06 | 113 | 30 | 200 | 54 | 357 | 78 | 634 |
| 07 | 115 | 31 | 205 | 55 | 365 | 79 | 649 |
| 08 | 118 | 32 | 210 | 56 | 374 | 80 | 665 |
| 09 | 121 | 33 | 215 | 57 | 383 | 81 | 681 |
| 10 | 124 | 34 | 221 | 58 | 392 | 82 | 698 |
| 11 | 127 | 35 | 226 | 59 | 402 | 83 | 715 |
| 12 | 130 | 36 | 232 | 60 | 412 | 84 | 732 |
| 13 | 133 | 37 | 237 | 61 | 422 | 85 | 750 |
| 14 | 137 | 38 | 243 | 62 | 432 | 86 | 768 |
| 15 | 140 | 39 | 249 | 63 | 442 | 87 | 787 |
| 16 | 143 | 40 | 255 | 64 | 453 | 88 | 806 |
| 17 | 147 | 41 | 261 | 65 | 464 | 89 | 825 |
| 18 | 150 | 42 | 267 | 66 | 475 | 90 | 845 |
| 19 | 154 | 43 | 274 | 67 | 487 | 91 | 866 |
| 20 | 158 | 44 | 280 | 68 | 499 | 92 | 887 |
| 21 | 162 | 45 | 287 | 69 | 511 | 93 | 909 |
| 22 | 165 | 46 | 294 | 70 | 523 | 94 | 931 |
| 23 | 169 | 47 | 301 | 71 | 536 | 95 | 953 |
| 24 | 174 | 48 | 309 | 72 | 549 | 96 | 976 |
Online calculator for color resistor markings
Due to the miniature size of low-power resistors and to facilitate readability, color markings of resistors were introduced, applied to them in the form of 3, 4 or 5 stripes (rings). To use the calculator, the resistor must be placed in such a way that the strip closest to the resistor terminal is on the left or the widest strip, which is always the first when determining the value, is placed on the left.
The resistance value is always determined by the first three bands. The first two stripes of marking are numbers, and the third is the multiplier. The fourth ring shows the permissible error in resistance accuracy from the nominal value of the resistor.
Resistors with an accuracy of up to 20% are marked with three rings, with an accuracy of 10% and 5% - with four, for all other more accurate ones, markings with five or six rings are used.
To determine the resistor value using our online calculator, you need to select the colors of all rings - the program will automatically determine and display the value.
Your browser does not support canvas elements.
| Ring 1 | Ring 1 | Ring 2 | Factor | Tolerance in % |
2W resistors with a resistance of less than 0.01 Ohm
| 0.001Ω ± 1% | ±50 ppm/°C | 2 W | LR2512-22 R001 F2 | |
| 2512 | 0.005Ω ± 1% | ±25 ppm/°C | 2 W | LR2512-22 R005 F4 |
| 2512 | 0.01Ω ± 1% | ±15 ppm/°C | 2 W | LR2512-22 R010 F2 |
| 2512 | 0.025Ω ± 2% | ±15 ppm/°C | 2 W | LR2512-FMF25GPJR025 |
| 2512 | 0.05Ω ± 1% | ±15 ppm/°C | 2 W | LR2512-22 R050 F4 |
Packaging: In blister tape on a reel with a diameter of 180 mm, 2000 pieces LR2512