What is LED?
LEDs form an integral part in modern electronics, simple indicators for optical communication devices.
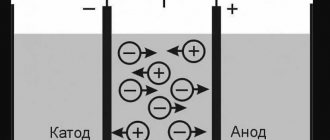
Light-emitting diodes use the properties of a pn junction and emit photons when current flows in the forward direction. LEDs specifically emit light when potentials are applied to the anode and cathode. The history of LEDs dates back to 1907, when Captain Henry Joseph observed the electro-luminescence characteristics of silicon carbide. The first LED was developed in 1962. It was developed by Holonyak, who worked for General Electric (GE). It was a GaAsP device. The first commercial version of LEDs came to market in the 1960s.
The manufacturing of LED technology boomed in the 1970s with the introduction of gallium aluminum arsenide (GaAlAs). These LEDs are high brightness and many times brighter than the old diffuse type. Blue and white LEDs were introduced in 1990, which use indium gallium nitride (InGaN) as a semiconductor. The white LED contains inorganic phosphorus. When the blue light inside the LED hits the phosphor, it emits white light.
What makes an ideal LED?
LEDs are widely used in electronic circuits due to its advantages over lamps. Some important features are:
- The LEDs are encased in plastic so they can withstand mechanical shock.
- Unlike lamps, LEDs do not emit heat and there is virtually no power loss when heated.
- LEDs require very low current and voltages are typically 20 mA at 1.8 volts. So this is ideal in battery circuits.
How many volts are LEDs?
The parameters of LEDs mostly depend on the material from which the pn junction is made, although some of the characteristics still depend on the design. Typical values of operating voltage and glow color for low-power elements at a current of 20 mA are summarized in the table:
| Material | Glow color | Direct voltage range, V |
| GaAs, GaAlAs | Infrared | 1,1 – 1,6 |
| GaAsP, GaP, AlInGaP | Red | 1,5 – 2,6 |
| GaAsP, GaP, AlInGaP | Orange | 1,7 – 2,8 |
| GaAsP, GaP, AlInGaP | Yellow | 1,7 – 2,5 |
| GaP, InGaN | Green | 1,7 – 4 |
| ZnSe, InGaN | Blue | 3,2 – 4,5 |
| Phosphor | White | 2,7 – 4,3 |
Powerful lighting LEDs operate at high currents. Thus, the crystal of the popular LED 5730 is designed for long-term operation at a current of 150 mA. But due to the steep current-voltage characteristic, which stabilizes the voltage drop, its Urab is about 3.2 V, which fits into the value indicated in the table.
LED technology
Brightness is an important aspect of LED. The human eye has a maximum sensitivity to light of about 550 nm in the yellow-green part of the visible spectrum. This is why the green LED emits brighter than the red LED even though both use the same current. Important parameters of LEDs are:
- Luminous Flux Indicates the energy of light coming from the LEDs. It is measured in Lumen (lm) or Milli Lumen (MLM)
- The luminous intensity of a luminous flux covering a large area is luminous intensity. It is defined as Candela (cd) or milli candela (MCD). The brightness of an LED is directly related to its luminous intensity.
- Luminous efficiency This is the relative light energy emitted to the power consumed. It is measured in terms of lumens per watt (lm W).
Forward current, forward voltage, viewing angle and response speed are factors that affect the brightness and efficiency of LEDs. Forward current (I) is the current flowing through an LED when it is forward biased and it should be limited to 10 to 30 milliamps, anything higher will destroy the LEDs.
The viewing angle is from - the axis angle at which the light intensity falls to half the axial value. This is why the indicator shows more brightness in the full state. Tall, bright LEDs have a narrow viewing angle so that the light is focused into a beam. Operating voltage (V) is the voltage drop across the LED. The voltage drop ranges from 1.8 V to 2.6 volts for regular LEDs, but in blue and white it will go up to 5 volts. Response speed represents how quickly the LED turns on and off. This is a very important factor if LEDs are used in communication systems.
Is a ballast resistor required?
LEDs are always connected to a power source via a resistor. This resistor is called a "ballast resistor", which protects the diode from damage caused by excess current. It regulates the forward current to the LED to a safe limit and protects it from burning.
The resistor value determines the forward current and, therefore, the brightness of the LEDs. Vs - Vf equation is used to select a resistor. Vs represents the input voltage of the circuit, Vf is the forward voltage drop of the LED(s) at the permissible current through the LED. The resulting value will be in Ohms. It is better to limit the current to a safe limit of 20 mA.
The table below shows the forward voltage drop across the LED.
| Red | Orange | Yellow | Green | Blue | White |
| 1.8 V | 2 V | 2.1 V | 2.2 V | 3.6 V | 3.6 V |
A typical LED can carry 30 -40 mA of safe current through it . The current rating to give sufficient brightness, a standard red LED is 20 mA. But it could be 40mA for blue and white LED. Current limiting by a ballast resistor protects the diode from excess current flowing through it. The ballast resistor value must be carefully selected to prevent damage to the LEDs and also to obtain sufficient brightness at 20 mA current. The following equation explains how to select a ballast resistor.
R=V/I
Where R is the resistance value in ohms, V is the input voltage to the circuit, and I is the permissible current through the LED in amperes. For a typical red LED, the forward voltage drop is 1.8 volts. So if the supply voltage is 12V (Vs), the voltage drop across the LED is 1.8V (V) and the allowable current is 20mA (IF), then the value of the ballast resistor will be
Vs - Vf / If = 12 - 1.8 / 20 mA = 10.2 / 0.02 = 510 Ohm.
But if a 510 Ohm resistor is not available, then you can choose the closest one, for example a 470 Ohm resistor can be used even if the current through the LED increases slightly. But it is recommended to use a 1K resistor to increase the life of the LEDs, although there will be a slight decrease in brightness.
Below is the arithmetic for choosing a limiting resistor for different versions of LEDs at different voltages.
| Voltage | Red | Orange | Yellow | Green | Blue | White |
| 12 V | 470 Ω | 470 Ω | 470 Ω | 470 Ω | 390 Ω | 390 Ω |
| 9V | 330 Ω | 330 Ω | 330 Ω | 330 Ω | 270 Ω | 270 Ω |
| 6 V | 180 Ω | 180 Ω | 180 Ω | 180 Ω | 120 Ω | 120 Ω |
| 5 V | 180 Ω | 150 Ω | 150 Ω | 150 Ω | 68 Ω | 68 Ω |
| 3V | 56 Ω | 47 Ω | 47 Ω | 33 Ω | — | — |
With the addition of other colors
An LED that can produce different colors is useful in some applications. For example, LEDs can indicate all systems are OK when it turns green, and faulty when it turns red. LEDs that can produce two colors are called Bicolour LEDs.
Bi-color LED covers two LEDs (usually red and green) in an overall package. Two crystals are installed on two terminals. A bi-color LED produces red when current flows in one direction and turns green when the direction of current is reversed.
Tricolor and multicolor LEDs are also available, which have two or more chips housed in a common housing. A tri-color LED has two anodes for a red and green crystal and a common cathode. Thus, it emits red and green colors depending on the anode in which the current is present. If both anodes are connected, the LEDs emit light and the color is yellow. A common anode and separate cathode type LEDs are also available.
The two-color indicator lights up in different colors ranging from green through yellow, orange and red to base on the current flowing through their anodes by selecting a suitable resistor to limit the anode current. Multicolor LEDs contain more than two chips—usually red, green, and blue chips—in a single package. Flashing LEDs in different colors, now available with two outputs. This gives a rainbow of colors that are quite attractive.
How to determine the supply voltage of LEDs
The power supply for LEDs is the main component that converts the mains voltage. As you know, LEDs are powered by current, but the voltage supplied in this case does not matter. It can be either 12 V or 1000 V. The main thing for an LED is current. If there is a shortage of it, the light of the bulbs dims, and if there is an excess, they begin to heat up, and even the heat sink cannot always cope. If a simple incandescent lamp “independently” selects its current, then the LED itself selects the voltage. If an LED requires a voltage of 5 V, and the power supply supplies it with, for example, 5 V, then there is a high probability that the LED will simply burn out. The fact is that a “conflict” arises between the power source and the LED. The first one tries to honestly output 5 V, and the second one tries to take only the 3 V allotted for itself. The LED can “drain” the voltage to the required level if the power supply is weak, but more often than not chaos and destruction still wins in this battle and the LED burns out.
To prevent such problems from arising, it is necessary to stabilize the current. The simplest option is a resistor. It is connected in series with the LEDs. The resistor helps attenuate the power supply and force it to deliver the desired voltage to the LED. If we are talking about powerful LEDs, then a weak resistor cannot cope with them. In this situation, a full-fledged stabilizer will be required.
Calculating a resistor is quite simple. For calculations, you need to know the supply voltage, voltage drop and current. The voltage drop is subtracted from the supply voltage, and the resulting value is divided by the current. Now all that remains is to choose a resistor with the nearest standard resistance. Some people prefer to remove the voltage drop from the formula altogether, since its exact value is not always known, but below are two ways to determine this value.
Infrared diode - source of Invisible light
IR diodes are widely used in remote control (remote control). Infrared diodes actually emit normal light with a specific color that is not sensitive to the human eye because its wavelength is 950 nm, below the visible spectrum. Many sources such as the sun, lamps, even the human body emit infrared rays. It is therefore necessary to modulate the emission from an IR diode to use it in an electronic application to prevent false triggering. Modulation makes the signal from the IR LED significantly higher than the noise. Infrared diodes are found in housings that are opaque to visible light, but transparent to infrared. IR LEDs are widely used in control systems.
Infrared diodes
Installation of lamps in PVC panels
Installation of lamps in PVC panels will take little time if preparation is carried out correctly. Before you begin, you should unpack the equipment, inspect it and understand how the latches work, so as not to spoil anything later. Follow these simple tips:
- After attaching the panel, you need to connect the lamp to the output cable. To do this, the ends of the wires coming from the housing are stripped. This should be done in advance so as not to have to work under the ceiling. It is more convenient to use an electrician's knife or a construction knife with a sharp blade.
- Attach a block to the ends of the cable running along the ceiling. The most commonly used option is to insert the core into the hole and tighten it with a small screw (for this you will need a small Phillips screwdriver). Then connect the lamp in a similar way, it is more convenient if someone holds it while connecting. Connection using terminal blocks.
- Press the fasteners with your fingers so that the lamp body fits into the cut hole. Then push it all the way, the springs will press out the protrusions and tightly fix the element to the ceiling. If the light bulb was not included in the kit, you need to insert it before fixing the lamp.
- After installation is complete, check the operation of the luminaires. If everything is done correctly, no problems will arise.
If the light fixture has a removable ring, insert it into the panel.
Important! If work is carried out in a bathroom, toilet, kitchen or other room with changes in humidity, it is better to choose IP44 class lamps.
Installing lamps in plastic panels is not difficult if you prepare everything you need and understand the installation technology. It is better to use a crown to cut the hole, then it will have an ideal shape. It is advisable to connect the wires with blocks, and not with twists and electrical tape.
Photodiode - It can see light
A photodiode generates current when its pn junction receives photons from visible or infrared light. The primary operation of a photodiode depends on the absorption of photons in the semiconductor material. The photo-generated carriers are separated by an electric field, and the resulting photocurrent is proportional to the incident light. The speed at which carriers move in the depletion region is related to the strength of the electric field throughout the region and the mobility of the carriers.
A photon that is absorbed by a semiconductor in the depletion region will lead to the formation of electron-hole conduction. Holes and electrons will be transported by the electric field to the edges of the depletion region. After the carriers leave the depletion region, they go to the photodiode terminals to generate photo-current in the external circuit. Photodiode response time is typically 250 nanoseconds.
Photodiodes
Color coding of light diodes
On the one hand, color marking allows you to determine the type and characteristics of the LED, on the other hand, there are no uniform designations. Each manufacturer uses its own values. In Russia there is color coding, but it is rarely used - the list of elements consisting of numbers and letters is too large, it is quite difficult to remember, and decoding is inconvenient for the average buyer.
A simpler letter designation is accepted as generally accepted (unofficially). Mainly used for LED strips. In addition to the general characteristics, the degree of protection of the element from the penetration of debris and moisture is indicated - IP and numbers from 0 to 6.
To choose a good option for replacing outdated light bulbs, you need to find out what kind of LEDs there are and set the parameters of the connected electrical network: voltage, current, resistance.
You can’t focus on cost - brands of cheap LEDs often have inflated parameters and use unstable materials.
Laser diodes
A laser diode is similar to a regular clear LED, but produces laserwith high intensity. In a laser beam, a number of atoms vibrate in such a cycle that all emitted radiation of the same wavelength is in phase with each other. Laser light is monochromatic and travels in the form of a narrow beam. The beam of a typical laser diode is 4 mm x 0.6 mm, which only expands to 120 mm at a distance of 15 meters.
The laser diode can be turned on and off at higher frequencies even higher than 1 GHz. So it is quite useful in telecommunication systems. Since laser generates heat to damage body tissues, it is used in surgery to heal lesions in very sensitive parts like retina, brain, etc. Laser diodes are important components in CD players to obtain the data recorded in CDs.
What types of LEDs exist and where are they used?
Optical LEDs are used as display elements and as lighting devices. Each specialization has its own requirements.
Indicator LEDs
The purpose of the indicator LED is to show the status of the device (power supply, alarm, sensor activation, etc.). In this area, LEDs with pn junction glow are widely used. It is not prohibited to use devices with phosphors, but there is no particular point. Here the brightness of the glow is not in the first place. Contrast and wide viewing angles are a priority. Output LEDs (true hole) are used on instrument panels, and output and SMD are used on boards.
Lighting LEDs
For lighting, on the contrary, elements with phosphors are mainly used. This allows you to obtain sufficient luminous flux and colors close to natural. The output LEDs from this area are practically squeezed out by SMD elements. COB LEDs are widely used.
A separate category includes devices designed to transmit signals in the optical or infrared range. For example, for remote controls for household equipment or for security devices. And elements of the UV range can be used for compact ultraviolet sources (detectors of currencies, biological materials, etc.).