In modern life, marking wires by color is not an advertising ploy by the manufacturer to stand out from others. This is a necessity and requirement, without which fast and high-quality installation of electrical wiring is impossible. How does this color help?
- quick identification of wire purpose (phase, neutral or ground)
Manufacturers choose conductor colors not according to their own wishes, but according to the rules. Moreover, not only a color, but also a numerical and alphabetic designation can be applied to the conductor.
The color is applied along the entire length of the core insulation. But in some areas you can also use multi-colored cambrics for heat shrink. They are mainly widely used in cable terminations.
In a three-phase network, wires and buses were previously colored as follows:
To make it easier to remember the order of colors, electricians used the abbreviation ZH-Z-K.
From 01/01/2011, new standards were introduced in accordance with GOST R 50462-2009 (DOWNLOAD):
Now it's time to switch to abbreviations - K-H-S! Subjectively speaking, this marking is inferior in clarity to the previous color scheme Zh-Z-K.
Imagine that there is poor lighting in the control room or room, dust on the wires? Which do you think your eye is better at distinguishing between yellow and green or brown and black? The rules in this case stipulate the need for letter designation and marking of the cores, in addition to color.
What should be the letter designation of wires according to GOST is presented in the following tables:
It is best to apply these letters using special tag rings.
They are a PVC tube, pre-cut, with letters and numbers printed on it.
According to the new rules, marking phase conductors yellow or green is prohibited. Precisely because of their similarity with the yellow-green grounding conductor.
It is also worth noting that the brown color is precisely phase A or L1 (simply L in a single-phase 220V network), and black is phase B or L2. When you conduct wiring for yourself, you may unwittingly miss this moment. But if the electrical work is being done for an industrial facility, then you will be required to strictly adhere to the international standard and correct phasing.
White color is the cheapest option when making core insulation, as it does not require the use of dyes. Therefore, it is most often used by manufacturers of cheap cable brands. There are no special labeling guidelines for this color.
The development of electrical networks and a significant increase in the number of consumers leads to numerous connections. Which is not possible to do with ordinary bare wires due to the danger of jamming and other factors. Therefore, the classic lines made with bare wire were replaced by SIP wire, which managed to occupy a niche for both household and industrial consumers. Such popularity of SIP was made possible due to a number of advantages in comparison with other brands.
Explanation of SIP markings
In comparison with other brands, SIP wire is a current-carrying element for transmitting electricity, which is deciphered by the three letters of the name:
- C – means that the wire is self-supporting;
- And - indicates the presence of insulation around current-carrying conductors;
- P - indicates that this is a wire, despite the presence of an insulating coating and branching along the cores, which is why it can be equated to a cable.
Consider an example of such a designation - SIP-1-3×20+1×25-0.4, here SIP-1 indicates the brand, 3×20 indicates that three insulated cores have a cross-section of 20 mm 2 each, 1×25 means that the neutral core has a cross-section of 25 mm 2, 0.4 is the rated voltage for this model.
Depending on the specific brand, there are five main types of SIP wire, designated by the corresponding numbers after the letter designation. There may be one letter at the end, indicating design differences and operational features. These differences in SIP brands are determined by design parameters, so it would be more appropriate to consider them using specific examples.
What is SIP?
SIP wires are classified as cable products. They are designed to replace bare wires used in the construction of power lines. The lettering printed on the wires states that these are self-supporting insulated wires. According to GOST, several types of products are produced, designated by numbers, depending on the brand of the product. After the numbers there may be a letter designation. Its decoding indicates the material of manufacture of the current-carrying conductors and the presence of insulation of the neutral wire. The use of SIP for highways created a new designation - VLI. This letter decoding indicates isolated overhead lines.
Each brand differs in its design. These are different diameters of the cores, the number of current-carrying wires and the presence of a neutral core, the material of manufacture of the cores and insulation. The only thing that all wires have in common is the presence of insulation. According to GOST, they are designated as wires, but in fact it turns out that they are cables.
Design
Structurally, all types of SIP wires contain cores made in a certain shape with a given number, one of which can serve as a carrier string for the line.
They differ in type as follows:
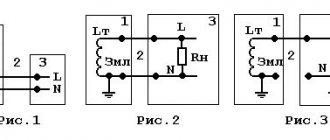
- SIP-1 is a four-core wire in which each of the cores is represented by conductors twisted relative to each other. In this brand of SIP, three of them are designed for three phases and are equipped with thermoplastic insulation, and the fourth is for the neutral terminal, but it is not insulated. In a neutral conductor, the central wire is made of steel and acts as a load-bearing wire. If there is a letter A (SIP-1A) at the end of the marking, the zero terminal will be equipped with insulation.
Rice. 1: SIP-1 wire design - SIP-2 is the same four-wire version as the previous one, with the only difference being that the neutral wire is insulated. In the classic version, the neutral core is insulated with thermoplastic polyethylene, and in the SIP-2A brand, with cross-linked polyethylene, just like the phase ones. The second option is used for areas with significant exposure to atmospheric factors. Like the previous brand, this SIP is used in lines up to 1 kV.
Rice. 2: SIP-2 wire design - SIP-3 - unlike previous brands, is a single-core version of the current-carrying wire. Structurally, in the center of this SIP there is a steel supporting wire, which is surrounded by aluminum current-carrying conductors. It is used in high-voltage lines with a voltage of 6 - 35 kV for laying phases over long distances.
Rice. 3: SIP-3 wire design - SIP-4 is a pair system in which each core has its own pair, but, unlike the previous ones, it does not have a supporting element and a neutral wire. Therefore, this brand cannot be used for installing lines, since there is a possibility of it breaking when exposed to wind loads. Thermoplastic polyethylene is used as insulation here. There is a version of the brand with the letter N (SIP-4N), which indicates that the current-carrying elements are made of aluminum alloy; if the letter H is absent, the specific brand uses pure aluminum wire.
Rice. 4: SIP-4 wire design - SIP-5 - completely identical to the previous brand - also has a paired number of cores and does not contain a neutral wire with a supporting element. The only difference is the type of insulation covering the conductors; in the SIP-5 and SIP-5N brands it is cross-linked polyethylene, which allows you to increase the operating temperature limit by up to 30%.
Rice. 5: SIP-5 wire design
Read also: What is the difference between an alcohol meter and a hydrometer?
SIP cable. Types and device. Labeling and application. Installation
The old uninsulated overhead power lines are gradually becoming a thing of the past. Currently, insulated wires are increasingly used on overhead lines. SIP cable stands for “self-supporting insulated wires”. They are used for the construction of new power lines, as well as for replacing overhead wires that do not have insulation.
Kinds
SIP cable is divided into main types depending on the material and design features. Each individual type of cable differs in diameter and number of cores, the presence of a neutral conductor, and insulation material. A common property of such SIP cables is the presence of insulation. In accordance with GOST, they are considered wires, but in fact they are cables.
Cable SIP-1
This type of cable consists of aluminum cores that are insulated with PET material. To briefly describe this type of insulation, we can say that PET is polyethylene terephthalate, a thermoplastic polyester material in the form of a synthetic fabric or film. This coating does not transmit ultraviolet rays. The neutral core is made in 2 versions: insulated and without insulation. SIP-1A is a cable with an insulated zero. This is indicated by the letter "A".
SIP-2
This type of cable has a similar design. The only difference is the insulation material. All cores are insulated with special polyethylene insulation (PET). This type of cable is used when installing power lines with voltages up to 1000 V. It is used for stringing main lines and auxiliary branches. It is advisable to use such a cable for northern regions and areas with temperate climates. It can also be used for summer cottages, provided the voltage is 380 V.
According to the standard, wires must withstand prolonged heating to a certain temperature. SIP-1A can withstand 70 degrees, and SIP-2A can operate at 90 degrees. When installing the wire, it is necessary to comply with the requirements for the smallest bending radius, which, according to the rules, must be more than 10 times the cable diameter.
Laying conditions
Due to the fact that laying SIP does not require any special skills, it can be done either at home or by the enterprise’s own resources without the involvement of a specialized organization. Laying can be carried out both on supports and on structural elements of buildings and structures. As a rule, fastening to walls is much easier than on a free-standing support.
Therefore, consider the conditions for installing SIP wire on reinforced concrete supports:
- Since the self-supporting insulating wire has an insulated sheath, it is important to provide a suspension that prevents damage to the dielectric layer. To do this, plastic rollers, grips and thimbles are installed, along which the wire can move freely.
- During the installation process, it is forbidden to drag the SIP along the ground or tree branches, as these can damage its insulation.
- To join different sections of SIP, sealed piercing-type clamps are used. Thanks to this design, it is possible to tap a line from an existing one even under voltage.
- Before fixing it on the support, the SIP wire must be pulled out through the moving element (for SIP brands from 1 to 3 using a dynamometer until the normalized load is set). After stretching, it is fixed at the fixation points.
Read also: Charger for ku202 circuit
All fasteners are factory-made, so they can be found complete with self-supporting insulating wire, which will greatly simplify the task.
Rice. 6: Example of fastening a SIP wire to a support
Ground wire color coding
The rules indicate what color the ground wire in electrical installations is. This is a yellow-green wire, the color of which stands out well against the background of the other wires. It is acceptable to use a wire with yellow insulation and a green stripe on it, or it can be green insulation with a yellow stripe. It is not allowed to use any other color of the ground wire, just as it is not allowed to use green-yellow conductors for installing circuits on which voltage is present or may be applied.
The listed labeling rules are observed in the countries of the post-Soviet space and in the countries of the European Union. Other states mark the cores in a different way, which can be seen on imported equipment.
Basic colors for marking abroad:
- neutral – white, gray or black;
- protective grounding – yellow or green.
Standards in a number of countries allow the use of bare metal without insulation as protective grounding.
Grounding wires are switched on prefabricated non-insulated terminals and connect to each other all metal parts of the structure that do not have reliable electrical contact with each other.
Application, advantages and disadvantages
Due to the presence of insulation, SIP has a fairly wide scope of application. It is most often used to introduce electricity into a building, and thanks to the outer layer of insulation, additional measures and devices are not required when passing through walls. Also, a self-supporting insulating wire can be used for local wiring of networks throughout the facility or when connecting subscribers to the lines of an energy supply organization. A separate area of application for SIPs are trunk lines that provide power supply to entire villages or distribution substations.
Compared to other brands of cable and wire products, SIP has a number of advantages, namely:
- SIP wire has significantly lower reactance compared to bare wires;
- Does not require the installation of additional insulators at points of attachment to supports, walls and when entering the building due to the presence of an insulating layer;
- Takes up less space due to the fact that the wires are collected together;
- Not subject to corrosive destruction due to the presence of a protective layer;
- Not afraid of overlap of adjacent phases under strong wind loads;
- Makes it difficult to illegally take power by throwing on wires;
The disadvantages of SIP wire include the greater weight of a linear meter, which is why the spans need to be reduced and supports installed more often. As well as the need to arrange additional insulation for certain categories of premises and consumers.
Scope of application 2x16 and 4x16
In everyday life, the most popular cables are 2x16 and 4x16. Thus, 4x16 wire is used for 0.6/1 kV overhead lines and for overhead branches to the building input. 4x16 cable can be laid along the walls of buildings and other structures.
SIP cable 2x16 is used to reduce the cross-section on branches during the transition from power lines to the internal wiring of the room. As a branch, 2x16 SIP is well suited for a summer house or country house.
Despite all the insulation, SIP is light in weight, which is convenient for installation. You can calculate the weight of a specific brand using tables. For example, the weight of SIP-4 with two cores:
The use of insulated wires instead of bare ones allows you to avoid short circuits and injuries due to current when the line breaks. At home, a cable can be laid by a person even with little qualifications.
Good day. With your permission, I’ll digress a little from the topic.
My brother and neighbor decided to install electricity on our own property. My brother convinced me that according to the new laws I was required to pay 550 rubles. provide 15 kW. All kinds of offices charge 50 thousand rubles to install light on the site. but we decided to save money.
Mosenergo received a piece of paper for 550 rubles. In the store we bought a meter, a box on a pole, machines, SIP4, 15 meters. – budget 6 thousand rubles. Since the main line runs through opposite sections, we had to put up one pole between us to throw the SIP across the road. (+5 thousand rubles for each) if the light was provided by the office, then the cost of the pole would definitely be added.
I assembled the boxes with meters myself and hung them on my pole, but two SIP4 cables across the road were thrown onto our pole by the shabatniks who installed the pole. AND NOW ABOUT THE BLUE PHASE and BLACK ZERO. It's time to get SIP4 into our boxes. I look at the cable: 4 wires with a green stripe, red, blue and one without stripes, i.e. completely black. I decided without any doubt that blue should be ZERO. but my brother led me into doubt (he doesn’t know anything about electrics) they called the shabashniks who erected the pole, they unanimously said ZERO_BLACK. i.e. without markings! As a result, black became zero, now we are waiting for the inspector who must accept the fulfillment of the Technical Conditions. those. check how we mount everything and then connect the second ends of the SIP.
- Is zero really black on SIP? blue phase?
- Is it possible to hang boxes on a pole if the pole is personal?
- What kind of scams can you expect from the inspector? Thanks for any comment.
Depending on the brand, the SIP electrical installation cable is designed to transmit electric current in networks with a voltage of 0.4 - 1, or 10 - 35 kV. The lines laid with this cable compare favorably with their predecessors in cost and do not require highly qualified personnel for installation and operation. What a SIP electric wire is can be understood at first glance - there is insulation on its cores.
Main manufacturers
To avoid troubles when purchasing a wire or cable, you should pay attention not only to the main parameters of the product, but also to its manufacturer. Since low-quality models may have a smaller cross-section, low dielectric resistance to various types of influence, etc. If you have already purchased a self-supporting insulating wire and are not sure of its quality, check whether the cross-section corresponds to that stated in the passport. How to determine the cross section at home is described in the corresponding article - https://www.asutpp.ru/kak-opredelit-sechenie-provoda-ili-zhil-kabelya.html.
If you are just going to buy SIP, pay attention to the following manufacturers:
- Kama cable;
- Rybinskcable;
- GC "Sevkabel"
- Moscabel.
Using wires from the above-mentioned factories, you can be sure that they comply with the declared characteristics.
Self-supporting insulated wire (as the abbreviation SIP stands for) first came to the Russian electrical goods market from Finland (manufacturer Nokia Cables) and France (Alkatel). Classic cable products differ significantly in design and technical parameters from SIP wire.
SIP wires have found application in networks up to 1000 volts and above - up to 35 kV; they are used for main lines and branches. Using a wire of this type, they are inserted into residential buildings and industrial buildings.
Main characteristics of the wire
The technical characteristics of the cable must comply with GOSTR 52373-2005. It indicates that a self-supporting insulated wire is intended for power lines up to 1 kV and higher, but not more than 35 kV. The core cross-section ranges from 16 to 240 square meters. mm. On main sections, the diameter of the cable must exceed the cross-section of the cores of the outgoing lines. Technical characteristics allow SIPs to be used in street lighting networks. For these purposes, there are sufficient cores whose cross-section does not exceed 16 or 25 mm.
GOST displays the characteristics of the main limit values. If some parameters do not correspond, such a cable cannot be used. According to GOST, the SIP characteristic displays the following main parameters;
- maximum permissible load. The larger the cross-section of the core, the higher this indicator;
- maximum operating temperature;
- temperature limit of emergency mode. According to GOST, it reaches 130 o C;
- permissible bending radius. It should not be less than 10 outer diameters of the core;
- 3 year manufacturer's warranty;
- The service life, if all requirements are met, is at least 40 years.
Some characteristics, for example, the weight of an identical cable from different manufacturers, may differ. But they should not go beyond the limits reflected in GOST.
Electrical cable made in Russia
Since the end of the twentieth century, domestic industry (and Sevkabel) has shown the first electrically conductive products. In a short period of time, SIP wire has become popular both in everyday life and in production. This was facilitated by its technical operating parameters.
Experts say that the cost of this wire is generally 25% more than the cost of producing wires without an insulated coating, but the strength of SIP is 70% higher. The Russian government has adopted a program under which enterprises of RAO UES of Russia are transferred to power supply through the operation of self-supporting insulated wires, overhead or otherwise.
This type of cable takes first place when it is necessary to distribute or transform electrical energy. In networks up to 1000 volts (household consumers), SIP grades 1 or 5 are used; for electricity transformation lines up to 20 kV, SIP grade 3 is used. In the territory of the Russian Federation, SIP wire is used for transformation and branches of electrical energy, connecting electricity consumption facilities.
Briefly about the main thing
SIP brand cables are the next generation of wires for overhead power lines, significantly increasing the efficiency of their operation. In domestic use it is mainly used when laying lines from the transformer to the consumer and making branches from them. One of the main advantages when using it is the ease of installation and operation, which allows a person to operate it without much experience in such work. But in any case, we must remember that all manipulations to connect electrical wiring to the network must be carried out by qualified electricians.
Computer technology, radio electronics, electrical engineering
- Home Home
- Electronics Articles on the topic
- Electrical Articles on the topic
- Computer equipment PC, networks, components, reviews
- Device reviews Packages, gadgets, tests, videos
- Register
- Login
Properties characterizing SIP
The rapid spread of SIP brand wires was achieved due to the following characteristics:
- Operating an insulated cable reduced maintenance costs by 80%. A wire of this type is reliable in the uninterrupted transmission of electrical energy to the consumer object. Self-supporting insulated cable eliminates the possibility of short circuits arising from climatic conditions (snow, ice, wire breaks due to wind-fallen trees).
- Reducing costs during the installation of electricity transformation lines, reducing the security zone.
- In megacities, it is allowed to install lines along the facades of buildings and structures. Electrical wiring can be done without expensive installation work. Overhead power transformation lines can combine the transmission of high-voltage and low-voltage voltages, as well as install communication cables on them.
- Overhead (overhead) losses are significantly reduced if standard wires are replaced with a self-supporting cable. Easy installation and the ability to connect new energy consumption facilities without loss of voltage for existing subscribers.
- Increased resistance of SIP electric cables to fire due to its design and the impossibility of a short circuit.
- When using this type of wire for power lines, there are fewer illegal connections and electrical energy losses are reduced. Significantly save money on cable repairs.
Read also: Lifting the barbell to the chin what muscles work
How the SIP cable works
The SIP marking shows its internal structure, the decoding explains the general principle - twisted aluminum strands, covered on top with durable polyethylene, which has a light-stabilizing property that prevents the wire from being exposed to ultraviolet rays.
Structure of the SIP electrical wire:
- (1) - element that conducts current;
- (2) - steel wire core;
- (3) - a shell made of polyethylene, which has increased strength.
SIP cable number 3, phase, is made from aluminum twisted cores, the cable core is steel, having a round shape, the number of cores (aluminum wires) is made according to the specifications for each brand. See photo below:
In the design of the SIP electrical wire, an aluminum supporting conductor can be used; it is not used in SIP-3, SIP-4, SIP-5 structures:
The phase wire is always twisted clockwise around the “neutral” wire.
Technical characteristics of cable lines, SIP and overhead line wires depend on its design:
- brand SIP(N) - the design uses insulating material that is resistant to combustion;
- brand SIP(G) - the electrical cable of this design uses water-repellent insulation;
- SIP(NG) design refers to cross-linked polyethylene in the sheath of an electrical wire, which is resistant to combustion and water penetration.
In modern energy, SIP cables are used according to a radial power distribution scheme. The abbreviation SIP (x) shows that (S) is self-supporting, (I) is insulated, (P) is wire, (x) is the type of design: wire SIP-1, 1A, SIP-2, wire SIP-2a, 3 ,4,5.
Colors for 220V and 380V networks
Installation of single- and three-phase electrical networks is facilitated if the wiring is made with multi-color wire. Previously, a flat two-core white wire was used for single-phase residential wiring. During installation and repair, to eliminate errors, it was necessary to ring each core individually.
Read also: Autumn salad of cabbage and bell pepper
The production of cable products with colored cores in different colors reduces the labor intensity of the work. To indicate phase and zero in single-phase wiring, it is customary to use the following colors:
- red, brown or black – phase wire;
- other colors (preferably blue) – neutral wire.
The phase markings in a three-phase network are slightly different:
- red (brown) – 1 phase;
- black – 2 phase;
- gray (white) – 3 phase;
- blue (cyan) – working zero (neutral)
- yellow-green – grounding.
Domestic cable products comply with the standard for core coloring, so a multiphase cable contains differently colored cores, where the phase is white, red and black , the neutral is blue , and the ground is yellow-green conductors.
When servicing networks installed according to modern standards, it is possible to accurately determine the purpose of the wires in the junction boxes. If there is a bundle of multi-colored wires, the brown one will definitely be phase. The neutral wire in the distribution boxes has no branches or breaks. The exception is branches to multi-pole switching devices with complete circuit breaking.
SIP-1 design
The wire of this design has aluminum conductive elements; the sheath is made of light-resistant polyethylene. The zero structural element is made of aluminum alloy and is not insulated. The design of this type is made in accordance with GOST R52373 2005.
Aluminum conductors that conduct current have a round multi-wire structure; the total number of structural elements can vary from 1 to 4. The round neutral wire is not insulated. The shell is made of cross-linked polyethylene, resistant to light. Insulated conductors are marked with numbers or bright colors.
This type of wire is used for electrical energy transmission lines with a nominal value of up to 0.6 kV and a frequency of 50 Hertz. Installation organizations use this type of wire as branches to connect an object consuming electrical energy. Cable installation is allowed when the ambient temperature is minus 20 degrees. The cable can withstand temperatures up to 90 degrees. The wire manufacturer's warranty is up to 36 months, and the warranty for effective operation is 40 years.
SIP-4 cable marking by color
5.2.7.2 The main conductors of self-supporting insulated wires must have a distinctive designation in the form of longitudinally pressed relief strips on the insulation , as shown in Figure B.1 (Appendix B), or numbers 1, 2, 3, embossed or printed. An insulated zero load-bearing core should not have a distinctive marking. The distinctive designation also be made in the form of colored longitudinal stripes with a width of at least 1 mm. The color of the stripes should be contrasting with black. Auxiliary conductors for lighting circuits must have a distinctive designation: “B1”, “B2” or “B3”, embossed or printed. Marking with numbers and letters, embossed or printed, should be done at intervals of no more than 500 mm. The height of numbers (letters) must be at least 5 mm, width - at least 2 mm (for number 1, the minimum width is 1 mm). Auxiliary conductors for control circuits may not have a distinctive marking. The distinctive sign, whether printed or in the form of colored longitudinal stripes, must be resistant to solar radiation throughout its entire service life.
Figure B.1 1(first core) - one strip; 2 (second core) - two strips; 3 (third core) - three stripes; (zero core) - without designation. Dimensions a,b,h are for reference.
From the above it follows: if, for example, on a Chinese or Russian SIP-4 2x16 mm one of the cores has a colored stripe , this means it is a “phase” . A vein that has no distinctive images, correspondingly “zero” .
Source: radiolubitel.net
SIP-2 design
This version of the self-supporting cable is equipped with an aluminum supporting conductor, has a right-hand twist, and is used for lines up to 1000 volts, for branches in country houses to utility buildings. The cable can withstand temperatures from short circuits in equipment up to 250 degrees. During installation, it is necessary to observe the bend of the wire, this is 10 outer diameters of the wire.
When an overhead line is made using SIP wire, for these purposes they usually use fittings offered on the market by different manufacturers: tension clamps, support clamps, which are used on intermediate supports. Fittings for other purposes - tips, busbar clamps, components for lighting networks, fittings, devices that are used in laying lines along the facade of buildings.
SIP fittings
The SIP cable has its own components designed for quick and safe installation. Linear fittings are presented in a wide range:
- piercing clamps are compatible with any type of cable. The clamps provide a tight connection due to the fact that the insulation from the core is not removed. After installing the clamps over the insulation, tighten the fixing bolts. At this time, the piercing teeth, passing through the insulation, come into contact with the metal of the core;
- Branch fittings are used to provide tension support for the cores. The clamps have a mechanism whose operating principle simplifies the process of installing and dismantling the cable without special equipment. The tensioner can be used to suspend the cable from any surface;
- support and anchor fasteners are designed to secure the clamps. Bandage tape is used along with hooks and clamps. Any fastener is resistant to corrosion and temperature changes.
SIP-3 design
The current-carrying core of the cable in this design has a round shape (multi-wire), the wire is made according to GOST No. R52373 2005 from aluminum alloy. Manufacturers of these products give an effective cable life of up to 40 years.
Cross-linked polyethylene, which has light-repellent properties, is used as a shell. The wire is used in lines up to 20 kV.
Grounding
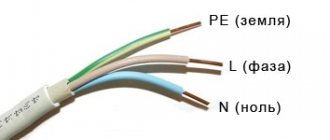
What color is the neutral wire? Electrical standards specify that its insulation may be blue, blue with a white stripe, or light blue. Such markings will be present in a cable with any number of cores. In circuit diagrams, “zero” is marked with the letter N; the circuit is closed to it. Sometimes it is called “minus”, and the phase one is called “plus”.
The main document that you should rely on when producing or purchasing cables is GOST 31947-2012. Before its appearance, there was no uniformity and order in the field of color designation of electrical wiring.
Until now, in old houses you can find wires in the same sheath, the color of which cannot determine what is connected - “phase”, “zero” or “ground”.
For example, when producing 3-core cables, the following combinations are welcome:
If the cable consists of 4 cores, then two standard color options are also recommended:
The diagrams for a 5-core wire look like this:
What kind of lighting do you prefer?
Built-in Chandelier
It is not recommended to use only two colors - red and white.
If you turn to the second important document for electricians - the PUE, then in clause 1.1.29 and clause 1.1.30 you can also find information about the color of the phase-neutral-ground wires. More precisely, the data is not listed there, but there is a reference to GOST R 50462-92, which has long been replaced by a more recent edition of GOST R 50462-2009, which is still in force today.
The material corresponds to the information set out in GOST 31947, but there are some clarifications. For example, wires that perform a dual function should be painted in a special way: if the zero worker is combined with the zero protective wire, then it is painted blue along its entire length and has green-yellow stripes along the edges.
Schematic representation of the color marking of conductors. Along with the color designation, the cores also have a letter: zero - N, protective - PE, combined zero + protective - PEN
Thus, all colors, with the exception of blue (cyan) and green/yellow, can be used to color the insulation of the phase conductor. This group includes white and red colors, which for some reason are not recommended for use by the 2012 edition of GOST.
In this article we will consider the question of how to find phase and zero using a probe and a multimeter.
First, let's define what phase and zero are. Our entire energy system is three-phase, including the low-voltage lines that power residential buildings and apartments. As a rule, the voltage between any two phases is 380 volts - this is line voltage. Everyone knows that the household voltage is 220 volts. How to get this voltage?
For this purpose, a neutral wire is provided in electrical installations with an operating voltage of 380 volts. If you take one of the phases and the neutral wire, then between them there will be a potential difference of 220 volts, that is, this is the phase voltage.
For a person who does not have knowledge of electrical engineering, the above is not very clear. It is important for us to know that each apartment or house receives one phase and one zero. What phase and zero are is discussed in detail here.
Let's consider the first method of determining the phase using a probe (indicating screwdriver). You can read more about the design and operating principle of such screwdrivers here - Indicators and voltage indicators in electrical installations up to 1000 V.
So, you have two wires and you need to determine which one is phase and which is neutral. First, you need to de-energize them by turning off the circuit breaker that powers that line of electrical wiring.
Then you need to strip both wires, that is, remove 1-2 cm of insulation from it. The stripped conductors must be slightly separated so that when voltage is applied, a short circuit does not occur as a result of their contact.
The next step is to identify the phase wire. We turn on the machine, through which voltage is supplied to the conductors. We take the indicator screwdriver by the handle and touch the metal part at the base of the handle with one finger.
Remember that it is strictly forbidden to take the probe below the handle, that is, by the working part. We bring the probe to one of the wires and touch it with the working part. In this case, the finger remains on the metal part of the handle.
If the indicator lamp of the screwdriver lights up, then this wire is a phase wire, that is, a phase. The other wire is correspondingly zero.
If the probe lamp does not light up when you touch the wire, then this is a neutral wire. Accordingly, the other wire is a phase; you can check this by touching an indicator screwdriver.
What to do if the wiring in the apartment is made of three wires? In this case, you not only have phase and neutral, but also a ground wire. Using a probe, you can easily determine where the phase is located among the three wires.
Expert opinion
It-Technology, Electrical power and electronics specialist
Ask questions to the “Specialist for modernization of energy generation systems”
How to determine phase and zero using a probe indicator. Phase wire colors When selecting a resistor, sometimes difficulties arise in determining its value if colored rings are applied to the resistor body instead of a number. Ask, I'm in touch!
SIP wires with insulated neutral
This design is often called “French” - when the supporting neutral wire is made with insulation. This system is characterized by the following diagram: from 1 to 4 current-carrying cores (aluminum), carrying a neutral with insulation.
The current-carrying wires in the structure are twisted around a neutral carrier wire; silanol cross-linked polyethylene is used as insulation, which has the property of repelling light and can withstand temperatures up to 90 degrees. The cable of this design is designed to operate at temperatures ranging from equipment short circuit to 240 degrees.
The products offered on the modern electrical market have many names, which makes it difficult for the average person to choose. Experts always recommend carefully looking at the quality of the cable’s insulating layer, its sheath, and what material they are made of. Each wire can be characterized by operation under different loads. Systematizing information on the design and types of wires, we can conclude that the SIP-2 cable brand is better suited for organizing the transformation of electrical energy along the main line; this wire is used for taps from the “air”. SIP wire grades 4 and 5 are used to connect energy-consuming objects and for façade installation.
The procedure for marking conductors in electrical networks
The most common schemes for organizing existing electrical networks include:
- Three-phase power supply network for a voltage of 380 Volts.
- Single-phase supply for 220 Volts.
- DC power lines.
Each of them uses a given number of conductors, determined by the functional purpose of the system.
The procedure for marking conductors in a three-phase circuit
Three-phase power systems usually use from 3 to 5 wires, providing not only the transfer of useful power, but also protection against electric shock. This function is performed by a special protective conductor (PE), distinguished by a particularly prominent marking (alternating green and yellow stripes). In networks with an isolated neutral, there is no zero (N) at all. Therefore, they involve only three buses, each of which is marked according to the phase characteristic already discussed above.
In a TN-CS type grounding system, which is characterized by the combination of neutral working and protective conductors, the total number of cores is four. When laying these buses separately, five wires will be required (counting ground), each of which will be appropriately marked.
The procedure for marking conductors in a single-phase network
In household single-phase networks, as a rule, only two conductors are involved. The first one represents one of the phases (A, B or C), and the second one is the working zero. Their color is selected according to current standards.
additionally:
The requirements of the PUE for supplying electrical power to residential buildings require the laying of a third (protective) wire.
However, the operating conditions of typical household networks without reliable grounding installed near the house do not always allow this.
The procedure for marking conductors in DC lines
In DC circuits where there are no phase conductors, special markings are used. They are characterized by the presence of only two working tires: positive and negative. The first is usually marked in red, and the second in blue.