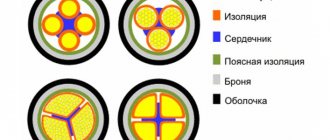
Marking and decoding of abbreviations
All cable manufacturers mark their products; an inscription is applied to the outer insulating PVC sheath of the AVBbShv cable using the hot stamping method or a special printer. The sequence of letters means:
- A – conductor material aluminum;
- B – insulation of current-carrying conductors is made of polyvinyl chloride;
- BB – double armored shell made of non-galvanized steel strip;
- Shv – PVC hose as an outer insulating sheath.
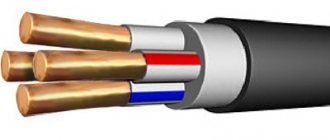
The numbers following this letter designation indicate the number of aluminum cores and their cross-section. AVBbShv 3x25 in this case 3 cores with a cross section of 25 mm2. There may be a designation AVBBShv 3x25 + 1x16, this indicates that three cores are 25 mm each, the fourth is an additional 16 mm2. The main conductors are used to connect the phases and the neutral wire; an additional wire of a smaller cross-section is connected to the common ground loop.
For ease of connection during installation work, in accordance with the requirements of the PUE (rules for the operation of electrical installations), the wires in the cable are marked with the color of the insulation according to their functional purpose. In single-phase networks:
- Blue, the wire is used as the neutral wire in the network;
- A core with red, white, brown or black insulation is connected to the phase;
- Yellow-green conductor to the ground loop.
In three-phase networks, cables with four or five cores are used, sometimes the neutral wire is combined with grounding. In these cases, the blue or yellow-green wire is connected to a grounded neutral. In circuits with five wires, blue is connected to neutral, yellow-green to ground, the rest to phases (A; B; C).
Explanation of cable markings AVBbShv
There is a special marking on the outer surface of the insulating sheath of any cable. Characters are applied in different ways, from printing to hot stamping.
Let's spell out the abbreviation AVBBShV:
- “A” - indicates that all cores are made strictly from aluminum (if the marking of any cable does not have the letter “A” at the very beginning, then the product is copper);
- “B” – insulation is made of high-quality polyvinyl chloride;
- “B” – the product is armored with durable steel tape;
- “b” – there is no protective cushion between the conductors and the armored layer;
- “Shv” – the shell is made from PVC hose.
The alphabetic abbreviation must be followed by numerical designations. With their help, it is customary to indicate the exact number of cores and the cross-sectional area of each. For example, if after AVBbShv there is the inscription 4x40, then we are talking about a four-core cable with a cross-section of each conductor of 40 square meters. mm. In addition to the main cores, a zero circuit can be added, which has a completely different cross-section. This happens in the AVBbShv 4x40 + 1x25 cable. In addition to four lived 40 sq.m. mm, there is a zero contour with a cross-section of 25 sq. mm.
Power cable design
The section shows its internal structure, in this case, a four-core cable.
The AVBbShv power cable is an armored electrical product with aluminum cores hidden in a reliable PVC casing. The marking of a product indicates its specific structure and materials used in production:
- A - the conductor is made of aluminum;
- B - the core is covered with PVC insulation;
- BB - protection made of plate steel (galvanized or not galvanized);
- Shv - the presence of a protective layer of pressed PVC with an additive to improve the performance characteristics of bitumen and viscous adhesive composition.
The core of soft aluminum wire is located in the very center of the product. Cables designed for use in electrical installations with a voltage of 6 kV are produced only in a three-core version. Products with a cross-section over 25 mm2 are made only in sector and multi-wire segment forms to increase the reliability of the electric main.
Cable AVBBShV in sector form, manufactured with a diameter of at least 25 mm2
The cable cores are covered with an insulating sheath made of non-flammable PVC plastic, characterized by the required strength and performance properties. Shielding strips that can withstand up to 6 kV are made of a special conductive material that matches the base of the insulating layer - 0.3 mm thick rubberized fabric or cable paper.
To make metallized screens, copper foil with a thickness of 0.06 mm or more is used, or two thin strips of copper are laid on top of each other with a small gap. The cable armor is made from zinc-coated steel strips twisted in a spiral. Provides reliable protection against all kinds of mechanical deformations.
Design
The AVBBShv power cable consists of an aluminum electrical conductor. An analogue of the cable marked VBBShV contains copper conductors. The power element of the cable with a core cross-section of 16 mm2 has a multi-wire design, in the form of two, three or four aluminum cores of round or sector shape twisted together. Three- and four-core cables are made from conductors of the same cross-section or containing one neutral conductor of a smaller cross-section. To insulate the conductors, the conductors are covered with a polyvinyl chloride sheath. The structure of fused conductors is placed in insulation made of heat-resistant PVC plastic. The conductors in multicore cables are painted in different colors to distinguish them from each other. The grounding conductor of the cable is two-colored, yellow-green, and the neutral conductor is blue. The cable is wrapped in a layer of belt insulation consisting of pressed polyvinyl chloride.
The protective layer of armor of the AVBBShV armored cable is created by two galvanized steel tapes. The entire cable structure is externally covered with a PVC plastic hose.
Purpose and scope of application
The cable is widely used in the construction of conductive mains in industrial and civil construction with voltage from 1 to 10 kV with a frequency of 50 Hz for supplying and directing current to stationary installations.
AVBbShv is a universal cable suitable for installation in various conditions:
- underground;
- in areas with periodic flooding;
- in conditions of high humidity of underground tunnels;
- at altitudes up to 4000 m;
- inside structures and buildings;
- in explosion and fire hazardous areas;
- overhead power line supports.
The cable has a wide range of uses due to the presence of double armor and multi-layer PVC insulation of various densities, which make it possible to easily withstand high tensile and other deformation loads, snow and wind influences. For power transmission lines, a cable of significant capacity is usually used, additionally coated with a bitumen-polymer layer.
Tip #1. If we consider AVBBShV from the point of view of application for domestic and economic needs, then the power cable has shown itself to be excellent for underground supply of communications to the house.
Electrical Requirements
The cables must withstand an alternating voltage test with a frequency of 50 Hz for 10 minutes. The test voltage values are given in the table.
| Rated cable voltage, kV | Test voltage value |
| 0,66 | 3 |
| 1 | 3,5 |
| 3 | 9,5 |
| 6 | 15 |
Electrical insulation resistance of cables, MOhm
| Core cross-section, mm2 | Electrical resistance, MOhm |
| With PVC insulation for voltage 0.66 and 1 kV | |
| 1 and 1.5 | 12 |
| 2,5-4 | 10 |
| 6 | 9 |
| 10-240 | 7 |
| With PVC insulation for voltage 3 kV | |
| 1 — 240 | 12 |
| With PVC insulation for voltage 6 kV | |
| 1 — 240 | 50 |
| With polyethylene insulation | |
| 1 — 240 | 150 |
Cable Specifications
Based on the results of various tests, the following maximum permissible values have been established for all modifications of the AVBBShV cable:
- Maximum operating temperature in the environment in the range -50 ̊С…+50 ̊С;
- The maximum temperature of the current-carrying conductors is no more than 70 °C; above this is considered an emergency operating mode. Operation in this mode is allowed only for 8 hours during the day, and during the entire operation of the cable no more than 1000 hours;
- The composition of the cable insulation prevents the spread of flame (non-flammable);
- A short circuit occurs within 5 seconds at a temperature of 160 °C;
- Manufacturers make two types of cables with rated voltages of 1000V and 600V;
- Electricity is transmitted at voltages of 220V and 380V with a frequency of 50Hz;
- Installation work without heating may be carried out at a temperature of no more than -15 ̊C;
If all operating rules are observed, manufacturers provide a warranty of 5 lei and a cable operating life of up to 30 years.
Table of produced cross-sections of AVBBShV cable with sector (triangular) conductors:
| Number of cores and S-Sections, mm² | Permissible U, kV | Outer Ø of cable, mm | Weight kg/1km |
| Cables with sector conductors | |||
| 3 :70 | 1 | 34,70 | 1738 |
| 3 :95 | 1 | 39,25 | 2130 |
| 3 :120 | 1 | 41,90 | 2435 |
| 3 :150 | 1 | 44,85 | 2866 |
| 3 :185 | 1 | 52,20 | 3491 |
| 4 :70 | 1 | 39.00 | 2139 |
| 4 :95 | 1 | 41,5 | 2559 |
| 4 :120 | 1 | 45,5 | 3012 |
| 4 :150 | 1 | 50,00 | 3568 |
| 3 :95+1 :50 | 1 | 40,30 | 2350 |
| 3 :120+1 :70 | 1 | 42,60 | 2712 |
| 3 :150+1 :70 | 1 | 48,60 | 3240 |
The characteristics of cables with other wire designs, round and stranded with the same cross-sections, may differ; this must be taken into account when choosing a cable and calculating the necessary parameters.
| Weight AVBBShv with round stranded conductors | |||
| Number of cores and cross-section mm2 | kg/1 km cable, 660 V | Kg1 km cable, 1000 V | |
| 2 :10 | 425 | 439 | |
| 2 :16 | 510 | 525 | |
| 2 :25 | 661 | 675 | |
| 2 :35 | 985 | 1011 | |
| 2 :50 | 1255 | 1285 | |
| 2 :70 | 1572 | ||
| 2 :95 | 2024 | ||
| 2 :120 | 2367 | ||
| 2 :150 | 3025 | ||
| 3 :10 | 485 | 505 | |
| 3 :16 | 595 | 616 | |
| 3 :25 | 785 | 807 | |
| 3 :35 | 1106 | 1135 | |
| 3 :50 | 1426 | 1460 | |
| 3 :70 | 1575 | ||
| 3 :95 | 1970 | ||
| 3 :120 | 2278 | ||
| 3 :150 | 2641 | ||
| 3 :185 | 3135 | ||
| 3 :240 | 3892 | ||
| 3 :16+1 :10 | 680 | 700 | |
| 3 :25+1 :16 | 905 | 930 | |
| 3 :35+1 :16 | 1205 | 1234 | |
| 3 :50+1 :25 | 1556 | 1594 | |
| 3 :70+1 :35 | 1780 | ||
| 3 :95+1 :50 | 2210 | ||
| 3 :120+1 :70 | 2592 | ||
| 3 :150+1 :70 | 2997 | ||
| 3 :185+1 :95 | 3551 | ||
| 3 :240+1 :120 | 4390 | ||
| 4 :10 | 561 | 584 | |
| 4 :16 | 700 | 720 | |
| 4 :25 | 960 | 985 | |
| 4 :35 | 1290 | 1325 | |
| 4 :50 | 1671 | 1711 | |
| 4 :70 | 1937 | ||
| 4 :95 | 2400 | ||
| 4 :120 | 2805 | ||
| 4 :150 | 3310 | ||
| 4 :185 | 3890 | ||
| 4 :240 | 4916 | ||
Cable installation: features
Installation of the product must be carried out in the temperature range allowed for it and in compliance with the bending radius in difficult areas (mines, tunnels, trenches). Severe deformation is contraindicated for the cable.
Depending on the functional purpose of the object, three-phase or single-phase network, the appropriate cable is selected according to the number of wires and their cross-sectional area. This depends on the power consumption of electrical installations; the greater the power and current loads, the larger the cross-section of the conductors. In order not to go into calculation formulas, use pre-calculated tables that indicate the values of power, currents, voltages, and what cross-section is required for certain parameters.
When laying underground power lines, the cable should be laid in accordance with SNiP and PUE standards - it must be reliably protected from mechanical deformation. If the soil is too aggressive and there is a risk of flooding with groundwater, AVBbShv is additionally placed in a PVC pipe. It is allowed to bury the cable in the ground no more than 0.7 m. If it is necessary to place it at a depth exceeding 0.5 m, AVBbShv is additionally placed in a pipe. The maximum length of the underground line should not exceed 5 m.
Power cable AVBBShv for underground installation in plastic pipes
For underground installation, the following requirements must be met:
- the soil layer separating two cables running crosswise must be at least 0.5 m;
- the power cable is laid at a distance of 1 m from water pipes and 2 m from gas pipes;
- bushes should be located at a distance of at least 1 m from the cable, trees - 1-2 m;
- it is allowed to place two power cables in a single trench with a distance between them of at least 10 cm;
- laying the power cable under the foundation is not allowed;
- laying the cable parallel to buildings should be carried out at a distance from them of no less than 0.7 m.
It is not permitted to lay AVBbShv in the ground under children's playgrounds, parking lots, and temporary structures. In exceptional cases, the depth of the cable increases to 1.3 m. To protect the AVBBShV cable and energy consumers, as well as electrical equipment connected to the cable line from short circuits and external influences, grounding is necessary. Another, no less important goal is to protect people from electric shock.
Grounding can be done in one of two ways:
- one-sided;
- two-way.
In the second case, the cable screen made of peroxide cross-linked film is connected to the ground loop. The disadvantage of this method is that it reduces the service life of the cable. The one-way method involves connecting only one edge of the screen to the ground electrode. When performing work, special electrical equipment and additional safety measures will be required.
Table for selecting cross-section by power and current for armored cables with PVC insulation:
| Table 1.3.7. PUE Permissible continuous load currents in armored cables with solid aluminum cores with polyvinyl chloride insulation | |||||
| S-Section, mm2 | Currents in cable wires (Amps) | ||||
| 1 core | 2 cores | 3 cores | |||
| laying method | |||||
| by air | by air | underground | By air | Underground | |
| 2,5 | 22 | 22 | 33 | 20 | 30 |
| 4 | 30 | 30 | 41 | 25 | 37 |
| 6 | 37 | 37 | 54 | 31 | 45 |
| 10 | 61 | 56 | 81 | 41 | 71 |
| 16 | 74 | 71 | 104 | 61 | 91 |
| 25 | 104 | 91 | 134 | 74 | 114 |
| 35 | 131 | 104 | 161 | 91 | 141 |
| 50 | 164 | 134 | 204 | 111 | 174 |
| 70 | 211 | 164 | 244 | 141 | 211 |
| 95 | 251 | 201 | 294 | 171 | 254 |
| 120 | 294 | 231 | 341 | 201 | 294 |
| 150 | 341 | 271 | 391 | 234 | 334 |
| 185 | 391 | 311 | 441 | 271 | 384 |
| 240 | 464 | — | — | — | — |
To select the wire cross-section, you must first calculate the maximum power consumption and currents, taking into account the required cable length, use the calculator indicated above or another.
AVBBShv cable design
The main element of any conductor is the current-carrying core, which is made from a certain metal. The AVBBShv wire is no exception. Above we gave a decoding of this abbreviation, and now you know that the cable core is made of aluminum. This allows you to reduce the weight and cost of the product; however, copper wires are considered to be of higher quality and more reliable in all respects.
Another point is that the design of one core (and there are several of them in the cable) can be single-wire or multi-wire, and when considering the cross-section, sector and round shapes are found.
Cables with one, two or three cores use current-carrying conductors of the same cross-section. In a wire with four cores, one of them is made of a smaller cross-section and used as a neutral wire.
To ensure reliable protection of each core and prevent short circuits, a high-quality polyvinyl chloride sheath is used with a resistance of 7-10 MΩ per kilometer. A more specific value depends on the cable cross-section.
Manufacturers strive to follow the general rules for coloring the insulating sheath of cores depending on their purpose. The ground conductor is usually made yellow-green, the neutral conductor is blue, the phase conductor is red, brown or black. Much less often, there are numerical codings on the shell of individual cores.
AVBbShv is compact, which is associated with the most dense arrangement of current-carrying conductors. Any free space must be filled with polyvinyl chloride plastic. However, for small gauge wire, padding is not required.
Polyethylene terephthalate tape is used for additional protection of the cores and interweaves them together. A steel strip is added on top of it, acting as armor and protecting the products from external mechanical loads. On the other hand, it does not help with stretching. A bitumen layer can be used as armor instead of steel.
Finally, the outer sheath is made of polyvinyl chloride plastic, which prevents the cable from catching fire when laid alone.
Features of laying, cutting and connecting cables
The trench for the cable must be at least 0.7 m deep and at least 0.5 m wide.
The structure of the cable with an armored sheath presupposes its laying in conditions where powerful mechanical impacts on it are possible, which it successfully withstands. Therefore, it is not recommended to lay an expensive cable with armor where it can be done with another less expensive one. AVBbShv is often laid underground, from power transmission towers or transformer substations to the switchgear of objects to which power is supplied.
Taking into account the weight and rigidity of the cable, laying is carried out from a drum, which is installed above the trench on special trestles. The cable is sequentially unwound and placed on the bottom of the trench, sprinkled and compacted with a 7-10 cm layer of sand.
Afterwards, everything is covered with sand to a depth of 5-7 cm, laid with a layer of brick, and warning tape is placed on top. The brick and tape provide a protective layer in case of excavation work to prevent damage to the cable.
At the ends of the cable at the connection points, the cable is cut, the layer of insulation and armored tape is removed. To prevent moisture from entering by sucking condensate under the insulating layer or by direct flow of water, in networks up to 10 kV, the ends are sealed in different ways:
- Steel funnel;
- Rubber glove;
- PVC funnel with epoxy resins;
- Polyvinyl chloride tapes and heat-shrinkable tubes;
Removal of the insulating and armored layer is carried out at a certain distance from the ends, depending on the device used to seal the ends of the cable.
- G – bare ends of cores;
- F – insulating layer of the current-carrying core;
- P – layer of belt insulation;
- O – intermediate insulation shell;
- 4 – armored cable tapes;
- A – cutting distance from the ends of the cable to the armored tape
Dimensions for cutting with epoxy funnels KVEp and KVEZ
| Types of epoxy resin funnels | Cutting dimensions, cm | ||||
| A | ABOUT | P | G | B | |
| KVEp-1, KVEp-2 | 17 | 3,5 | 2 | 4,0 | — |
| KVEp-3, KVEp-4 | 21 | 5,0 | 2 | 4,5 | — |
| KVEp-5, KVEp-6 | 24 | 5,0 | 2 | 5,0 | — |
| KVEp-7 | 24,5 | 5,0 | 2 | 3,5 | — |
| KVEZ-1 | W+5.5 | 3,5 | 2 | — | 9,0 |
| KVEZ-2, KVEZ-3 | W+5.5 | 3,5 | 2 | 2,5 | 9,5 |
| KVEZ-4, KVEZ-5 | W+5.5 | 3,5 | 2 | 2,5 | 12 |
The sizes of the funnels are selected according to the size of the cable; for rubber gloves and PVC tapes, the cutting of insulation has different dimensions
An example of installing a cable with a rubber glove at the end in a switchgear or control panel
Dimensions for cutting cables for KVV PVC tape:
| Sealing type | Cable cross-section in mm2, voltage, kV | Cutting length in cm | ||||
| 1 | 6 | 10 | A | ABOUT | P | |
| KVV-1 | Up to 24 | — | — | W+6.5 | 3,0 | 1,5 |
| KVV-2 | 36…50 | 10…24 | — | W+7.0 | 5,0 | 2,0 |
| KVV-3 | 70…94 | 35…51 | 16…24 | F+10.5 | 8,0 | 2,5 |
| KVV-4 | 120… 151 | 70…94 | 35… 71 | F+10.5 | 8,0 | 2,5 |
| KVV-5 | 184 | 120…151 | 95…121 | F+12.5 | 10,0 | 2,5 |
| KVV-6 | 241 | 184 | 151 | F+12.5 | 10,0 | 2,5 |
| KVV-7 | — | 241 | 184 | F+12.5 | 10,0 | 2,5 |
| KVV-8 | — | — | 241 | F+12.5 | 10,0 | 2,5 |
Aluminum lugs along the cross-section of the conductor are attached to the ends of the current-carrying conductors using a crimping method, then they are screwed to the busbars on switchgears. A wire with a tip must be soldered to the armored tape, which is attached to the ground loop on both sides of the cable.
AVBbShv
View prices →
Description
AVBbShv cable is an armored power cable with aluminum conductors, in PVC insulation and in a PVC hose. The AVBbShv cable is used for the transmission and distribution of electricity in stationary installations at a rated alternating voltage of 660 V and 1000 V at a frequency of 50 Hz; single-core cables are used in direct voltage networks.
AVBBShv cable design:
- The conductor is aluminum, single-wire or multi-wire, round or sector-shaped.
- Insulation is made of polyvinyl chloride plastic.
- Marked with numbers, starting from zero (zero core).
- Marked by color: neutral conductor - blue (light blue), grounding - green-yellow.
- A tape of polyethylene terephthalate film or polyvinyl chloride plastic compound is applied over the twisted insulated cores with overlap. It is permissible to manufacture without tape while maintaining the mobility of the insulated cores and the possibility of separating the sheath from the insulation without damage.
- The cable sheath is made of polyvinyl chloride plastic.
- Protective cover type “BbShv” in accordance with GOST 7006, consisting of armor made of two galvanized steel strips and an external protective hose made of PVC plastic.
Explanation of the AVBBShv cable:
A - Aluminum conductor B - Insulation of conductors made of polyvinyl chloride plastic B - Armor made of two steel tapes b - Without a cushion, which is the inner part of the protective cover, applied under the armor in order to protect the element underneath from corrosion and mechanical damage by armor tapes or wires Shv - Protective cover in the form of an extruded hose made of polyvinyl chloride plastic.
Characteristics
Conditions for laying and operating the AVBbShv cable:
- 1. AVBbShv cables are operated at ambient temperatures from minus 50 °C to plus 50 °C.
- At relative humidity up to 98% and temperature up to 35 °C
- 2. AVBbShv cables are laid in the ground (trenches) without preheating at a temperature not lower than minus 15 °C. The minimum bending radius is not less than 7.5 Dn for multi-core cables and not less than 10 Dn for single-core cables (Dn is the outer diameter of the cable, mm.)
- 3. The long-term permissible heating temperature of the cores during operation is not higher than 70 °C.
- 4. The maximum permissible core temperature during a short circuit is not higher than 160 °C. The duration of the short circuit is no longer than 4 seconds.
- 5. Permissible heating of cable cores in emergency mode is not higher than 80°C. The duration of cable operation in emergency mode is no longer than 8 hours per day and 1000 hours over the entire service life of the cable.
- 6. AVBbShv cables are allowed to be used in DC networks at voltage values 2.4 times higher than the voltage between the core and the screen or metal sheath.
- 7. Electrical insulation resistance per 1 km of length, measured at the long-term permissible heating temperature of the cable cores during operation, must be at least 0.005 MOhm.
Group characteristics
Power cables with plastic insulation for low voltage
This group includes cables with aluminum or copper conductors with plastic insulation in a plastic sheath, with or without protective covers, intended for the transmission and distribution of electricity in stationary installations at a rated alternating voltage of 0.66 - 6 kV with a frequency of 50 Hz at ambient temperature from -50°С to +50°С.
Brands, design elements and applications
| Cable brand | Core material A - aluminum M - copper | Insulation P - polyethylene B -PVC plastic | Shell P - polyethylene B -PVC plastic compound Vng - PVC plastic compound of reduced flammability | Protective cover (section 4.1) |
| APVG | A | P | IN | absent |
| AVVG | A | IN | IN | absent |
| VVG | M | IN | IN | absent |
| AVVGng | A | IN | Vng | absent |
| VVGng | M | IN | Vng | absent |
| AVVGz | A | B (with filling) | IN | absent |
| VVGz | M | B (with filling) | V | absent |
| AVBbShv | A | IN | absent | BbShv |
| VBBShv | M | IN | absent | BbShv |
| AVBbShng | A | IN | absent | BbShng |
| VBBShng | M | V | absent | BbShng |
| AVVB | A | V | IN | B |
| VVB | M | V | IN | B |
| AVVBG | A | V | IN | BG |
| VVBG | M | V | V | BG |
The basic brands in this group of cables are APVG, AVVG, VVG, AVVGz, VVGz, AVBbShv, VBBShv. Cables are produced in accordance with GOST 16442-80.
APVG, AVVG, VVG cables are intended for installation in dry and wet industrial premises, on special cable racks, and in blocks. At the same time, cables of the AVVGz and VVGz brands are used for power supply to electrical installations that require cable sealing during entry, and they are recommended for laying in the ground with low corrosive activity and the absence of the possibility of mechanical damage and tensile forces.
Cables of the AVBbShv and VBBShV brands are intended for all of the above applications (except for laying in blocks), but if there is a risk of mechanical damage during operation.
To the designation of cable brands AVVG, VVG, AVBbShv VBBShV in tropical design, add the letter “T” through a hyphen, for cables with single-wire conductors - the letter “ozh” in brackets, for cables in flat design - through a hyphen, the letter “P”
Cables of the AVVGng, VVGng, AVBbShng and VBBShng brands differ from the basic brands in that the sheath or hose is made of low-flammability PVC plastic and are used to ensure the fire safety of cable chains when laid in bundles.
Cables of brands AVVB, VVB, AVVBG, VVBG differ from cables of brands AVVG and VVG in the presence of protective covers of type B and BG and are intended mainly for the same areas of application as cables of brands AVBbShv and VBbShv.
Design parameters
The number of cores in the cables, the range of nominal cross-sections of the cores and rated voltages are indicated in the table.
| Cable brand | Number of cores | Nominal core cross-section, mm2 | |||
| Rated cable voltage, kV | |||||
| 0,66 | 1 | 3 | 6 | ||
| VVG | 1,2,3 and 4 | 1,5-50 | 1,5-240 | — | — |
| VVGz | 2,3 and 4 | 1,5-50 | 1,5-50 | — | — |
| AVVG, APVG | 1,2,3 and 4 | 2,5-50 | 2,5-240 | — | — |
| AVVGz | 2,3 and 4 | 2,5-50 | 2,5-50 | — | — |
| AVBbShv, VBBbShv | 2,3 and 4 | 4-50 | 6-240 | 6-240 | — |
| AVVG, VVG, AVBbShv, VBBShv | 3 | — | — | — | 35-240 |
| AVVG, APVG | 5&6 | 2,5-50 | 2,5-35 | — | — |
| VVG | 5&6 | 1,5-25 | 1,5-25 | — | — |
For four-core cables, the largest nominal cross-section of the cores is 185 mm2.
Cables for voltages of 3 and 6 kV are made only with three cores. Two-core cables must have cores of the same cross-section. Three-, four- and five-core cables must have all conductors of the same cross-section or one conductor of a smaller cross-section (grounding or neutral conductor). Six-core cables must have four cores of equal cross-section and two wires of smaller cross-section.
The nominal cross-sections of neutral conductors (smaller cross-section) and grounding conductors must correspond to those indicated in the table.
Nominal sections of cores, mm2
| Basic | 1,5 | 2,5 | 4 | 6 | 10 | 16 | 25 | 35 | 50 | 70 | 95 | 120 | 150 | 185 | 240 |
| Zero | 1,5 | 1,5 | 2,5 | 4 | 6 | 10 | 16 | 16 | 25 | 35 | 50 | 70 | 70 | 95 | 120 |
| Grounding | 1,0 | 1,5 | 2,5 | 2,5 | 4 | 6 | 10 | 16 | 16 | 25 | 35 | 35 | 50 | 50 | 70 |
Current-carrying conductors can be single-wire or multi-wire in accordance with the table and must comply with classes 1 and 2.
| Core name | Nominal core cross-section, mm2 | |||
| round | shaped | |||
| copper | aluminum | copper | aluminum | |
| Solid wires | 1,0-50 | 2,5-240 | 25-50 | 25-240 |
| Stranded cores | 16-240 | 25-240 | 25-240 | 25-240 |
The current-carrying conductors of single-core cables of all cross-sections and multi-core cables with a cross-section of up to 16 mm2 must be round in shape. Conducting conductors of belt-insulated cables with a cross-section of 25 mm2 or more must be sector or segment shaped.
The radius of curvature of single-wire sector cores must be at least 0.5 mm.
It is allowed to manufacture cables with round conductors with a cross-section of up to 50 mm2.
The conductors are insulated, depending on the brand, with PVC plastic or polyethylene. The current standard provides for insulation made of cross-linked polyethylene (designation Pv).
The insulated cores of multi-core cables must have a distinctive color. The insulation of the neutral conductors should be blue (light blue).
The insulation of the grounding conductors must be two-color (green-yellow), with one color covering at least 30 and no more than 70% of the insulation surface, and the other the rest.
The color marking must be continuous or in the form of a longitudinal stripe with a width of at least 1 mm.
It is allowed to mark cores insulated with polyvinyl chloride plastic with numbers, starting from zero. Marking with numbers is done by embossing or printing. The height of the numbers is at least 4.0 mm. The distance between numbers should not be more than 35 mm.
The insulation of single-core cables can be of any color.
Cable insulation thickness, mm
| Rated voltage, kV | Nominal core cross-section, mm2 | Insulation made of polyethylene or polyvinyl chloride plastic | XLPE insulation |
| 0,66 | 1-2,5 | 0,6 | 0,7 |
| 4 and 6 | 0,7 | 0,7 | |
| 10 and 16 | 0,9 | 0,7 | |
| 25n35 | 1,1 | 0,9 | |
| 50 | 1,3 | 1,0 | |
| 1 | 1-2,5 | 0,8 | 0,7 |
| 4-16 | 1,0 | 0,7 | |
| 25 and 35 | 1,2 | 0,9 | |
| 50 | 1,4 | 1,0 | |
| 70 | 1,4 | 1,1 | |
| 95 | 1,5 | 1,1 | |
| 120 | 1,5 | 1,2 | |
| 150 | 1,6 | 1,4 | |
| 185 | 1,7 | 1,6 | |
| 240 | 1,9 | 1,7 | |
| 3 | 6-240 | 2,2 | 2,0 |
| 6 | 10-240 | 3.0 - for polyethylene | 3,0 |
| 3.4 - for polyvinyl chloride plastic compound |
Twisted insulated conductors must have gaps between them filled.
In cables of the AVVGz and VVGz brands, the PVC filling is applied simultaneously with the sheath and must be separated from the insulation and sheath without damage.
Cables with sector conductors, cables of the AVVG, APVG, VVG brands for voltages up to 1 kV inclusive, as well as cables of the AVBbShv and VBbShv brands with conductors with a cross-section of up to 25 mm2 inclusive can be without filling.
In cables of the AVVG, VVG, APVG brands for voltages up to 1 kV inclusive, a tape made of polyethylene terephthalate film or polyvinyl chloride plastic compound or other equivalent material and a sheath made of pressed-out polyvinyl chloride plastic compound must be overlapped over the twisted insulated conductors.
It is allowed to manufacture cables without tapes over twisted insulated cores, provided that the mobility of the insulated cores is maintained and the sheath can be separated from the insulation without damaging it.
In cables of all brands, except those indicated and brands AVVGz, VVGz, belt insulation must be applied over the twisted insulated cores.
The belt insulation must be pressed out of the insulation material or from polyvinyl chloride plastic compound or applied by winding or longitudinally with strips of polyethylene terephthalate film, polyvinyl chloride plastic compound or other equivalent material.
For cables with voltages up to 3 kV inclusive, belt insulation consisting of two strips of polyethylene terephthalate film and two strips of crepe paper is allowed.
The nominal thicknesses of PVC shells must correspond to category Obp-2
Reference values of outer diameters and weights of cables of individual standard sizes are indicated in the tables
Taking into account significant tolerances, actual values may differ by 5-10% down or up.
On the plastic sheath or protective hose, no more than every 300 mm, the distinctive index of the manufacturer and the year of manufacture of the cable must be applied.
Electrical Requirements
The cables must withstand an alternating voltage test with a frequency of 50 Hz for 10 minutes. The test voltage values are given in the table.
| Rated cable voltage, kV | Test voltage value |
| 0,66 | 3 |
| 1 | 3,5 |
| 3 | 9,5 |
| 6 | 15 |
Electrical insulation resistance of cables, MOhm
| Core cross-section, mm2 | Electrical resistance, MOhm |
| With PVC insulation for voltage 0.66 and 1 kV | |
| 1 and 1.5 | 12 |
| 2,5-4 | 10 |
| 6 | 9 |
| 10-240 | 7 |
| With PVC insulation for voltage 3 kV | |
| 1 — 240 | 12 |
| With PVC insulation for voltage 6 kV | |
| 1 — 240 | 50 |
| With polyethylene insulation | |
| 1 — 240 | 150 |
Outer diameters of cables for voltage 0.66 kV, mm
| Nominal core cross-section, mm2, nx S | AVVG, VVG | AVBbShv, VBBbShv |
| 1x1.5 | 5,0 | — |
| 1x2.5 | 5,5 | — |
| 1x4 | 6,1 | — |
| 1x6 | 6,6 | — |
| 1x10 | 7,8 | — |
| 1x16 | 9,3 | — |
| 1x25 | 11 | — |
| 1x35 | 12 | — |
| 1x50 | 14 | — |
| 2x1.5 | 7,6 | — |
| 2x2.5 | 9,1 | — |
| 2x4 | 10,5 | 15 |
| 2x6 | 11,5 | 16 |
| 2x10 | 14 | 19 |
| 2x16 | 16 | 20 |
| 2x25 | 19 | 24 |
| 2x35 | 21 | 26 |
| 2x50 | 25 | 29 |
| 3x1.5 | 8,0 | — |
| 3x2.5 | 9,5 | — |
| 3x4 | 11 | — |
| 3x6 | 12 | 16 |
| 3x10 | 14,5 | 17 |
| 3x16 | 17 | 19 |
| 3x25 | 20,5 | 21 |
| 3x35 | 23 | 25 |
| 3x50 | 27 | 31 |
Weights of cables for voltage 0.66 kV, kg/km
| Nominal cross-section of cores, mm2 | AVVG | VVG | AVBbShv | VBBShv |
| 1x1.5 | — | 37 | — | — |
| 1x2.5 | 35 | 51 | — | — |
| 1x4 | 45 | 70 | — | — |
| 1x6 | 55 | 91 | — | — |
| 1x10 | 80 | 140 | — | — |
| 1x16 | 115 | 215 | — | — |
| 1x25 | 160 | 320 | — | — |
| 1x35 | 200 | 420 | — | — |
| 1x50 | 260 | 570 | — | — |
| 2x1.5 | — | 67 | — | — |
| 2x2.5 | 75 | 105 | — | — |
| 2x4 | 97 | 140 | 320 | 370 |
| 2x6 | 120 | 190 | 360 | 440 |
| 2x10 | 170 | 290 | 460 | 590 |
| 2x16 | 220 | 410 | 550 | 750 |
| 2x25 | 330 | 630 | 700 | 1050 |
| 2x35 | 400 | 820 | 810 | 1300 |
| 2x50 | 560 | 1200 | 1050 | 1700 |
| 3x1.5 | — | 90 | — | — |
| 3x2.5 | 90 | 140 | — | — |
| 3x4 | 120 | 200 | 360 | 440 |
| 3x6 | 150 | 260 | 400 | 520 |
| 3x10 | 220 | 410 | 520 | 710 |
| 3x16 | 290 | 600 | 630 | 940 |
| 3x25 | 440 | 810 | 830 | 1300 |
| 3x35 | 550 | 1300 | 1000 | 1700 |
| 3x50 | 760 | 1700 | 1300 | 2200 |
Outer diameters of cables for voltage 1 kV, mm
| Nominal cross-section of cores, mm2 | AVVG, VVG | AVBbShv, VBBbShv |
| 1x1.5 | 5,4 | — |
| 1x2.5 | 5,8 | — |
| 1x4 | 6,7 | — |
| 1x6 | 7,2 | — |
| 1x10 | 8 | — |
| 1x16 | 9,5 | — |
| 1x25 | 11 | — |
| 1x35 | 12 | — |
| 1x50 | 14 | — |
| 1x70 | 17 | — |
| 1x95 | 19 | — |
| 1x120 | 21 | — |
| 1x150 | 23 | — |
| 1x185 | 25 | — |
| 1x240 | 28 | — |
| 2x1.5 | 8,4 | — |
| 2x2.5 | 10 | — |
| 2x4 | 11,5 | — |
| 2x6 | 12,5 | 17 |
| 2x10 | 14 | 19 |
| 2x16 | 16 | 21 |
| 2x25 | 20 | 24 |
| 2x35 | 22 | 26 |
| 2x50 | 25 | 30 |
| 3x1.5 | 9,4 | — |
| 3x2.5 | 10,5 | — |
| 3x4 | 12 | — |
| 3x6 | 13 | 18 |
| 3x10 | 15 | 20 |
| 3x16 | 17 | 22 |
| 3x25 | 21 | 25 |
| 3x35 | 23 | 28 |
| 3x50 | 27 | 31 |
| 3x70 | 29 | 33 |
| 3x95 | 32 | 37 |
| 3x120 | 36 | 40 |
| 3x150 | 39 | 44 |
| 3x185 | 43 | 47 |
| 3x240 | 49 | 53 |
Weights of cables for voltage 1 kV, kg/km
| Nominal cross-section of cores, mm2 | AVVG | VVG | AVBbShv | VBBShv |
| 1x1.5 | — | 42 | — | — |
| 1x2.5 | 39 | 55 | — | — |
| 1x4 | 55 | 80 | — | — |
| 1x6 | 60 | 100 | — | — |
| 1x10 | 80 | 145 | — | — |
| 1x16 | 120 | 220 | — | — |
| 1x25 | 165 | 320 | — | — |
| 1x35 | 200 | 420 | — | — |
| 1x50 | 270 | 580 | — | — |
| 1x70 | 340 | — | — | — |
| 1x95 | 430 | — | — | — |
| 1x120 | 530 | — | — | — |
| 1x150 | 630 | — | — | — |
| 1x185 | 760 | — | — | — |
| 1x240 | 970 | — | — | — |
| 2x1.5 | — | 80 | — | — |
| 2x2.5 | 85 | 120 | — | — |
| 2x4 | 115 | 170 | — | — |
| 2x6 | 135 | 210 | 400 | 480 |
| 2x10 | 175 | 300 | 470 | 590 |
| 2x16 | 230 | 430 | 560 | 770 |
| 2x25 | 340 | 660 | 720 | 1050 |
| 2x35 | 420 | 860 | 850 | 1300 |
| 2x50 | 580 | 1200 | 1050 | 1700 |
| 3x1.5 | — | 115 | — | — |
| 3x2.5 | 105 | 155 | — | — |
| 3x4 | 145 | 220 | — | — |
| 3x6 | 170 | 290 | 460 | 570 |
| 3x10 | 230 | 420 | 540 | 730 |
| 3x16 | 300 | 610 | 650 | 960 |
| 3x25 | 450 | 930 | 850 | 1300 |
| 3x35 | 560 | — | 1000 | 1700 |
| 3x50 | 780 | 1200 | 1300 | 2200 |
| 3x70 | 1050 | 1700 | 1600 | 2900 |
| 3x95 | 1350 | 2400 | 2000 | 3800 |
| 3x120 | 1650 | 3100 | 2300 | 4600 |
| 3x150 | 2000 | 3900 | 2700 | 5600 |
| 3x185 | 2400 | 4800 | 3200 | 6700 |
| 3x240 | 3100 | 5900 | 3900 | 8500 |
terms of Use
Permissible operating temperatures, °C
| Type of cable insulation | Long-term permissible core heating temperature | Maximum permissible temperature at short circuit currents |
| Polyvinyl chloride plastic compound | 70 | 160 |
| Polyethylene | 70 | 130 |
| Cross-linked polyethylene | 90 | 250 |
The shelf life of cables in open areas is no more than 2 years, under a canopy - no more than 5 years, in enclosed spaces - no more than 10 years.
← Back
Advantages and disadvantages of AVBbShv
The main advantages of the cable include:
- Strength, resistance to mechanical stress;
- Versatility in laying methods;
- Wide range of cross-sections;
- Long-term service life.
The disadvantage can be considered the large weight, in the presence of an armored layer, which creates some inconvenience when laying, especially by air, and the high price compared to other brands without armor.
Approximate prices for 1m of cable in Russia:
| AVBbShv 5x2.5 | from 38.37 rub. |
| 5x4 | from 50.59 rub. |
| 5x6 | from 56.51 rub. |
| 5x10 | from 79.88 rub. |
| 5x16 | from 106.10 rub. |
| 5x25 | from 151.27 rub. |
| 5x35 | from 195.47 rub. |
| 5x50 | from 248.65 rub. |
| 5x70 | from 372.53 rub. |
| 5x95 | from 483.13 rub. |
| 5x120 | from 573.88 rub. |
| 5x150 | from 700.09 rub. |
| 5x185 | from 830.01 rub. |
| 5x240 | from 1058.46 rub. |
Weight of cables and wires - table
Wire weight A
| Name | kg/m |
| A-120 | 0.32100 |
| A-150 | 0.40600 |
| A-16 | 0.04300 |
| A-185 | 0.50200 |
| A-240 | 0.65500 |
| A-25 | 0.06800 |
| A-300 | 0.79400 |
| A-35 | 0.09400 |
| A-50 | 0.13500 |
| A-70 | 0.18900 |
| A-95 | 0.25200 |
Cable weight AVBBShv
| Name | kg/m |
| AVBbShv 1Х120 | 0.92200 |
| AVBbShv 1Х150 | 1.13500 |
| AVBbShv 1Х185 | 1.33000 |
| AVBbShv 1Х240 | 1.61300 |
| AVBbShv 1Х25 | 0.34700 |
| AVBbShv 1Х35 | 0.46400 |
| AVBbShv 1Х50 | 0.55600 |
| AVBbShv 1Х500 | 2.86200 |
| AVBbShv 1Х70 | 0.66000 |
| AVBbShv 1Х95 | 0.80400 |
| AVBbShv 2Х10 | 0.38000 |
| AVBbShv 2Х120 | 1.66700 |
| AVBbShv 2Х150 | 2.07500 |
| AVBbShv 2Х16 | 0.48900 |
| AVBbShv 2Х185 | 2.55300 |
| AVBbShv 2Х240 | 3.10500 |
| AVBbShv 2Х25 | 0.65500 |
| AVBbShv 2Х35 | 0.77900 |
| AVBbShv 2Х4 | 0.25600 |
| AVBbShv 2Х50 | 0.99100 |
| AVBbShv 2Х6 | 0.29200 |
| AVBbShv 2Х70 | 1.18800 |
| AVBbShv 2Х95 | 1.50200 |
| AVBbShv 3Х10 | 0.46300 |
| AVBbShv 3Х10+1Х6 | 0.50700 |
| AVBbShv 3Х120 | 2.11100 |
| AVBbShv 3Х120+1Х50 | 2.27000 |
| AVBbShv 3Х120+1Х70 | 2.50000 |
| AVBbShv 3Х150 | 2.69500 |
| AVBbShv 3Х150+1Х50 | 2.91800 |
| AVBbShv 3Х150+1Х70 | 3.04300 |
| AVBbShv 3Х150+1Х95 | 3.17900 |
| AVBbShv 3Х16 | 0.59200 |
| AVBbShv 3Х16+1Х10 | 0.67300 |
| AVBbShv 3Х185 | 3.27200 |
| AVBbShv 3Х185+1Х50 | 3.50200 |
| AVBbShv 3Х185+1Х70 | 3.56300 |
| AVBbShv 3Х185+1Х95 | 3.74900 |
| AVBbShv 3Х240 | 4.11600 |
| AVBbShv 3Х240+1Х120 | 4.61200 |
| AVBbShv 3Х240+1Х70 | 4.41600 |
| AVBbShv 3Х240+1Х95 | 4.50100 |
| AVBbShv 3Х25 | 0.78100 |
| AVBbShv 3Х25+1Х16 | 0.90400 |
| AVBbShv 3Х35 | 0.94000 |
| AVBbShv 3Х35+1Х16 | 1.03600 |
| AVBbShv 3Х35+1Х25 | 1.10800 |
| AVBbShv 3Х4 | 0.28600 |
| AVBbShv 3Х4+1Х2.5 | 0.31900 |
| AVBbShv 3Х50 | 1.21500 |
| AVBbShv 3Х50+1Х25 | 1.36900 |
| AVBbShv 3Х50+1Х35 | 1.42900 |
| AVBbShv 3Х6 | 0.33000 |
| AVBbShv 3Х6+1Х4 | 0.37200 |
| AVBbShv 3Х70 | 1.50900 |
| AVBBShv 3Х70+1Х25 | 1.63100 |
| AVBbShv 3Х70+1Х35 | 1.66200 |
| AVBbShv 3Х70+1Х50 | 1.79300 |
| AVBbShv 3Х95 | 1.88600 |
| AVBbShv 3Х95+1Х35 | 2.04300 |
| AVBbShv 3Х95+1Х50 | 2.12800 |
| AVBbShv 3Х95+1Х70 | 2.26600 |
| AVBbShv 4Х10 | 0.53700 |
| AVBbShv 4Х120 | 2.64000 |
| AVBbShv 4Х150 | 3.35300 |
| AVBbShv 4Х16 | 0.65300 |
| AVBbShv 4Х185 | 4.11200 |
| AVBbShv 4Х2.5 | 0.27600 |
| AVBbShv 4Х240 | 5.12300 |
| AVBbShv 4Х25 | 0.94000 |
| AVBbShv 4Х35 | 1.13900 |
| AVBbShv 4Х4 | 0.32400 |
| AVBbShv 4Х50 | 1.48300 |
| AVBbShv 4Х6 | 0.37800 |
| AVBbShv 4Х70 | 1.85400 |
| AVBbShv 4Х95 | 2.35000 |
| AVBbShv 5Х10 | 0.60800 |
| AVBbShv 5Х120 | 3.16700 |
| AVBbShv 5Х150 | 4.05800 |
| AVBbShv 5Х16 | 0.78800 |
| AVBbShv 5Х185 | 4.95000 |
| AVBbShv 5Х2.5 | 0.30800 |
| AVBbShv 5Х240 | 6.32800 |
| AVBbShv 5Х25 | 1.08200 |
| AVBbShv 5Х35 | 1.30400 |
| AVBbShv 5Х4 | 0.36500 |
| AVBbShv 5Х50 | 1.72700 |
| AVBbShv 5Х6 | 0.44800 |
| AVBbShv 5Х70 | 2.19100 |
| AVBbShv 5Х95 | 2.81200 |
AVVG cable weight
| Name | kg/m |
| AVVG 1Х10 | 0.07200 |
| AVVG 1Х120 | 0.49100 |
| AVVG 1Х150 | 0.62900 |
| AVVG 1Х16 | 0.10600 |
| AVVG 1Х185 | 0.79600 |
| AVVG 1X2.5 | 0.03300 |
| AVVG 1Х240 | 1.00800 |
| AVVG 1Х25 | 0.15000 |
| AVVG 1Х300 | 1.32000 |
| AVVG 1Х35 | 0.18600 |
| AVVG 1X4 | 0.03900 |
| AVVG 1Х400 | 1.60000 |
| AVVG 1Х50 | 0.25000 |
| AVVG 1X6 | 0.04900 |
| AVVG 1Х70 | 0.32100 |
| AVVG 1Х95 | 0.41500 |
| AVVG 2x10 | 0.12900 |
| AVVG 2Х120 | 1.05300 |
| AVVG 2Х150 | 1.34800 |
| AVVG 2x16 | 0.22000 |
| AVVG 2Х185 | 1.68600 |
| AVVG 2x2.5 | 0.05300 |
| AVVG 2Х240 | 2.14100 |
| AVVG 2Х25 | 0.31300 |
| AVVG 2Х35 | 0.38900 |
| AVVG 2x4 | 0.07100 |
| AVVG 2Х50 | 0.54100 |
| AVVG 2x6 | 0.08700 |
| AVVG 2Х70 | 0.69700 |
| AVVG 2Х95 | 0.89600 |
| AVVG 3x10 | 0.21500 |
| AVVG 3Х10+1Х6 | 0.23000 |
| AVVG 3Х120 | 1.45700 |
| AVVG 3Х120+1Х70 | 1.73500 |
| AVVG 3Х150 | 1.87500 |
| AVVG 3Х150+1Х95 | 2.27100 |
| AVVG 3x16 | 0.28900 |
| AVVG 3Х16+1Х10 | 0.32400 |
| AVVG 3Х185 | 2.35900 |
| AVVG 3Х185+1Х95 | 2.70400 |
| AVVG 3x2.5 | 0.08800 |
| AVVG 3Х240 | 3.00100 |
| AVVG 3Х240+1Х120 | 3.43000 |
| AVVG 3Х25 | 0.41900 |
| AVVG 3Х25+1Х16 | 0.49200 |
| AVVG 3Х35 | 0.52700 |
| AVVG 3Х35+1Х16 | 0.70000 |
| AVVG 3x4 | 0.11600 |
| AVVG 3Х4+1Х2.5 | 0.12600 |
| AVVG 3Х50 | 0.73700 |
| AVVG 3Х50+1Х25 | 0.84800 |
| AVVG 3x6 | 0.14100 |
| AVVG 3Х6+1Х4 | 0.15900 |
| AVVG 3Х70 | 0.95500 |
| AVVG 3Х70+1Х35 | 1.09800 |
| AVVG 3Х95 | 1.27100 |
| AVVG 3Х95+1Х35 | 1.40900 |
| AVVG 3Х95+1Х50 | 1.47400 |
| AVVG 4x10 | 0.26700 |
| AVVG 4x120 | 2.11600 |
| AVVG 4x150 | 2.52600 |
| AVVG 4x16 | 0.37900 |
| AVVG 4x185 | 3.08500 |
| AVVG 4x2.5 | 0.10900 |
| AVVG 4x240 | 3.96500 |
| AVVG 4x25 | 3.55300 |
| AVVG 4x35 | 0.71600 |
| AVVG 4x4 | 0.14800 |
| AVVG 4x50 | 0.97100 |
| AVVG 4x6 | 0.18100 |
| AVVG 4x70 | 1.33100 |
| AVVG 4x95 | 1.76300 |
| AVVG 5x10 | 0.62000 |
| AVVG 5Х120 | 2.33800 |
| AVVG 5Х150 | 3.01700 |
| AVVG 5x16 | 0.79000 |
| AVVG 5Х185 | 3.76200 |
| AVVG 5x2.5 | 0.31000 |
| AVVG 5Х240 | 4.81000 |
| AVVG 5x25 | 1.20000 |
| AVVG 5x35 | 1.51000 |
| AVVG 5x4 | 0.42000 |
| AVVG 5x50 | 1.67000 |
| AVVG 5x6 | 0.49000 |
| AVVG 5Х70 | 1.53800 |
| AVVG 5Х95 | 2.03400 |
AKVVG cable weight
| Name | kg/m |
| AKVVG 10x2.5 | 0.20800 |
| AKVVG 10x4 | 0.27400 |
| AKVVG 10x6 | 0.37100 |
| AKVVG 14x2.5 | 0.26700 |
| AKVVG 19x2.5 | 0.34100 |
| AKVVG 27x2.5 | 0.47300 |
| AKVVG 37x2.5 | 0.61700 |
| AKVVG 4x10 | 0.25100 |
| AKVVG 4x2.5 | 0.10300 |
| AKVVG 4x4 | 0.13200 |
| AKVVG 4x6 | 0.16600 |
| AKVVG 5x2.5 | 0.12100 |
| AKVVG 5x4 | 0.16000 |
| AKVVG 7x10 | 0.41200 |
| AKVVG 7x2.5 | 0.15200 |
| AKVVG 7x4 | 0.19900 |
| AKVVG 7x6 | 0.25600 |
Automatic reclosure wire weight
| Name | kg/m |
| Automatic reclosure 1X10 | 0.04300 |
| APV 1Х120 | 0.41200 |
| Automatic reclosure 1Х150 | 0.51100 |
| APV 1Х16 | 0.06600 |
| APV 1X185 | 0.61900 |
| Automatic reclosure 1X2.5 | 0.01400 |
| Automatic reclosure 1Х240 | 0.80800 |
| APV 1Х25 | 0.09700 |
| APV 1Х300 | 1.05000 |
| APV 1Х35 | 0.12800 |
| Automatic reclosure 1X4 | 0.01900 |
| APV 1Х50 | 0.18000 |
| Automatic reclosure 1X6 | 0.02600 |
| APV 1Х70 | 0.25200 |
| APV 1Х95 | 0.33100 |
APPV wire weight
| Name | kg/m |
| APPV 2Х2.5 | 0.02800 |
| APPV 2X4 | 0.03900 |
| APPV 2X6 | 0.05200 |
| APPV 3X2.5 | 0.04200 |
| APPV 3X4 | 0.05800 |
| APPV 3X6 | 0.07800 |
AC wire weight
| Name | kg/m |
| AS-120/19 | 0.46560 |
| AS-120/27 | 0.52220 |
| AS-150/19 | 0.54830 |
| AS-150/24 | 0.59290 |
| AS-16/2.7 | 0.06350 |
| AS-185/24 | 0.69510 |
| AS-185/29 | 0.72130 |
| AS-185/43 | 0.83880 |
| AS-240/32 | 0.90240 |
| AS-25/4.2 | 0.09910 |
| AS-300/39 | 1.11550 |
| AS-35/6.2 | 0.14660 |
| AS-50/8.0 | 0.19100 |
| AS-70/11 | 0.27210 |
| AS-95/16 | 0.37920 |
Cable weight VBBSh(v)ng
| Name | kg/m |
| VBBSH(v)ng 2x25 | 0.90400 |
| VBBSH(v)ng 2x6 | 0.39300 |
| VBBSH(v)ng 3x1.5 | 0.25100 |
| VBBSH(v)ng 3x10 | 0.61600 |
| VBBSH(v)ng 3x16 | 0.81800 |
| VBBSH(v)ng 3x2.5 | 0.29600 |
| VBBSH(v)ng 3x25 | 1.14900 |
| VBBSH(v)ng 3x4 | 0.39000 |
| VBBSH(v)ng 3x6 | 0.47200 |
| VBBSH(v)ng 4x10 | 0.73900 |
| VBBSH(v)ng 4x120 | 5.35300 |
| VBBSH(v)ng 4x150 | 6.52600 |
| VBBSH(v)ng 4x16 | 1.01000 |
| VBBSH(v)ng 4x185 | 7.92800 |
| VBBSH(v)ng 4x2.5 | 0.34300 |
| VBBSH(v)ng 4x240 | 10.09200 |
| VBBSH(v)ng 4x25 | 1.46300 |
| VBBSH(v)ng 4x35 | 1.85200 |
| VBBSH(v)ng 4x4 | 0.46100 |
| VBBSH(v)ng 4x50 | 2.54700 |
| VBBSH(v)ng 4x6 | 0.56400 |
| VBBSH(v)ng 4x70 | 3.34000 |
| VBBSH(v)ng 4x95 | 4.40000 |
| VBBSH(v)ng 5x 2.5 | 0.40400 |
| VBBSH(v)ng 5x10 | 0.89800 |
| VBBSH(v)ng 5x120 | 7.01300 |
| VBBSH(v)ng 5x150 | 8.36900 |
| VBBSH(v)ng 5x16 | 1.23300 |
| VBBSH(v)ng 5x25 | 1.80000 |
| VBBSH(v)ng 5x35 | 2.31900 |
| VBBSH(v)ng 5x4 | 0.54800 |
| VBBSH(v)ng 5x50 | 3.38400 |
| VBBSH(v)ng 5x6 | 0.66900 |
| VBBSH(v)ng 5x70 | 4.39900 |
| VBBSH(v)ng 5x95 | 5.74100 |
| VBBSH(v)ng-LS 3x 4 | 0.50433 |
| VBBSH(v)ng-LS 3x1.5 | 0.32256 |
| VBBSH(v)ng-LS 3x10 | 0.76244 |
| VBBSH(v)ng-LS 3x16 | 1.06735 |
| VBBSH(v)ng-LS 3x2.5 | 0.38076 |
| VBBSH(v)ng-LS 3x6 | 0.60113 |
| VBBSH(v)ng-LS 4x1.5 | 0.36667 |
| VBBSH(v)ng-LS 4x10 | 0.91380 |
| VBBSH(v)ng-LS 4x120 | 5.87739 |
| VBBSH(v)ng-LS 4x16 | 1.28896 |
| VBBSH(v)ng-LS 4x2.5 | 0.43828 |
| VBBSH(v)ng-LS 4x240 | 10.87495 |
| VBBSH(v)ng-LS 4x25 | 1.86395 |
| VBBSH(v)ng-LS 4x35 | 2.33582 |
| VBBSH(v)ng-LS 4x4 | 0.58894 |
| VBBSH(v)ng-LS 4x50 | 2.82644 |
| VBBSH(v)ng-LS 4x6 | 0.70978 |
| VBBSH(v)ng-LS 4x70 | 3.79585 |
| VBBSH(v)ng-LS 4x95 | 4.88399 |
| VBBSH(v)ng-LS 5x1.5 | 0.41252 |
| VBBSH(v)ng-LS 5x10 | 1.08493 |
| VBBSH(v)ng-LS 5x120 | 7.81216 |
| VBBSH(v)ng-LS 5x16 | 1.47601 |
| VBBSH(v)ng-LS 5x2.5 | 0.49627 |
| VBBSH(v)ng-LS 5x25 | 2.37379 |
| VBBSH(v)ng-LS 5x35 | 2.71927 |
| VBBSH(v)ng-LS 5x4 | 0.67567 |
| VBBSH(v)ng-LS 5x50 | 3.73796 |
| VBBSH(v)ng-LS 5x6 | 0.81858 |
| VBBSH(v)ng-LS 5x70 | 4.89813 |
| VBBSH(v)ng-LS 5x95 | 6.36168 |
VBBShV cable weight
| Name | kg/m |
| VBBShv 2x10 | 0.62561 |
| VBBSHV 2x120 | 3.20600 |
| VBBSHV 2x150 | 3.85000 |
| VBBShv 2x16 | 0.84625 |
| VBBSHV 2x185 | 4.71200 |
| VBBShv 2x2.5 | 0.25817 |
| VBBSHV 2x240 | 5.88800 |
| VBBShv 2x25 | 0.91287 |
| VBBShv 2x35 | 1.15689 |
| VBBShv 2x4 | 0.33346 |
| VBBSHV 2x50 | 1.63300 |
| VBBShv 2x6 | 0.51978 |
| VBBSHV 2x70 | 2.07300 |
| VBBSHV 2x95 | 2.71400 |
| VBBShv 3x1.5 | 0.25156 |
| VBBShv 3x10 | 0.76055 |
| VBBSHV 3x10+1x6 | 0.70500 |
| VBBSHV 3x120 | 4.38000 |
| VBBSHV 3x120+1x50 | 5.87400 |
| VBBSHV 3x120+1x70 | 6.11300 |
| VBBSHV 3x150 | 5.34900 |
| VBBSHV 3x150+1x50 | 5.87400 |
| VBBSHV 3x150+1x70 | 6.11300 |
| VBBSHV 3x150+1x95 | 6.40700 |
| VBBShv 3x16 | 1.05603 |
| VBBSHV 3x16+1x10 | 1.01400 |
| VBBSHV 3x185 | 6.51900 |
| VBBSHV 3x185+1x50 | 7.05000 |
| VBBSHV 3x185+1x70 | 7.22300 |
| VBBSHV 3x185+1x95 | 7.56400 |
| VBBShv 3x2.5 | 0.29788 |
| VBBSHV 3x240 | 8.30200 |
| VBBSHV 3x240+1x120 | 9.51900 |
| VBBSHV 3x240+1x70 | 9.01500 |
| VBBSHV 3x240+1x95 | 9.25600 |
| VBBSHV 3x25 | 1.22200 |
| VBBSHV 3x25+1x16 | 1.44100 |
| VBBSHV 3x35 | 1.56100 |
| VBBSHV 3x35+1x16 | 1.75300 |
| VBBShv 3x4 | 0.39374 |
| VBBSHV 3x4+1x2.5 | 0.40100 |
| VBBSHV 3x50 | 2.16100 |
| VBBSHV 3x50+1x25 | 2.46700 |
| VBBSHV 3x50+1x35 | 2.58700 |
| VBBShv 3x6 | 0.60593 |
| VBBSHV 3x6+1x4 | 0.49600 |
| VBBSHV 3x70 | 2.81600 |
| VBBSHV 3x70+1x25 | 3.08400 |
| VBBSHV 3x70+1x35 | 3.14800 |
| VBBSHV 3x70+1x50 | 3.41000 |
| VBBSHV 3x95 | 3.67500 |
| VBBSHV 3x95+1x35 | 4.03800 |
| VBBSHV 3x95+1x50 | 4.22400 |
| VBBSHV 3x95+1x70 | 4.48100 |
| VBBShv 4x1.5 | 0.19703 |
| VBBShv 4x10 | 0.91204 |
| VBBShv 4x120 | 5.39875 |
| VBBShv 4x150 | 6.61792 |
| VBBShv 4x16 | 1.16987 |
| VBBShv 4x185 | 7.97710 |
| VBBShv 4x2.5 | 0.34688 |
| VBBShv 4x240 | 10.19731 |
| VBBShv 4x25 | 1.64133 |
| VBBShv 4x35 | 2.11729 |
| VBBShv 4x4 | 0.46610 |
| VBBShv 4x50 | 2.58566 |
| VBBShv 4x6 | 0.71510 |
| VBBShv 4x70 | 3.38260 |
| VBBShv 4x95 | 4.44308 |
| VBBShv 5x1.5 | 0.36470 |
| VBBShv 5x10 | 0.94280 |
| VBBShv 5x120 | 6.92515 |
| VBBShv 5x150 | 8.46949 |
| VBBShv 5x16 | 1.31486 |
| VBBSHV 5x185 | 10.37000 |
| VBBShv 5x2.5 | 0.44006 |
| VBBSHV 5x240 | 13.31400 |
| VBBShv 5x25 | 2.02080 |
| VBBShv 5x35 | 2.47057 |
| VBBShv 5x4 | 0.58449 |
| VBBShv 5x50 | 3.33294 |
| VBBShv 5x6 | 0.71493 |
| VBBShv 5x70 | 4.35263 |
| VBBShv 5x95 | 5.69177 |
Runway wire weight
| Name | kg/m |
| Runway 1x1.5 | 0.03100 |
| Runway 1x10 | 0.12500 |
| Runway 1x16 | 0.19500 |
| Runway 1x2.5 | 0.04300 |
| Runway 1x25 | 0.28800 |
| Runway 1x35 | 0.38500 |
| Runway 1x4 | 0.06200 |
| Runway 1x50 | 0.53900 |
| Runway 1x6 | 0.08200 |
Cable weight KVBBShv
| Name | kg/m |
| KVBBShv 10x1 | 0.42100 |
| KVBBShv 10x1.5 | 0.49200 |
| KVBBShv 10x2.5 | 0.62800 |
| KVBBShv 10x4 | 0.81300 |
| KVBBShv 10x6 | 1.03900 |
| KVBBShv 14x1 | 0.49500 |
| KVBBShv 14x1.5 | 0.58700 |
| KVBBShv 14x2.5 | 0.76600 |
| KVBBShv 19x1 | 0.59100 |
| KVBbShv 19x1.5 | 0.71000 |
| KVBBShv 19x2.5 | 0.96200 |
| KVBBShv 27x1 | 0.75600 |
| KVBBShv 27x1.5 | 0.92000 |
| KVBBShv 27x2.5 | 1.26400 |
| KVBBShv 37x1 | 0.93000 |
| KVBBShv 37x1.5 | 1.14700 |
| KVBBShv 37x2.5 | 1.59900 |
| KVBBShv 4x1 | 0.25700 |
| KVBbShv 4x1.5 | 0.29000 |
| KVBbShv 4x2.5 | 0.35300 |
| KVBBShv 4x4 | 0.43600 |
| KVBBShv 4x6 | 0.53500 |
| KVBBShv 5x1 | 0.28600 |
| KVBbShv 5x1.5 | 0.32500 |
| KVBBShv 5x2.5 | 0.40000 |
| KVBBShv 5x4 | 0.60800 |
| KVBBShv 7x1 | 0.32800 |
| KVBbShv 7x1.5 | 0.37900 |
| KVBbShv 7x2.5 | 0.47600 |
| KVBBShv 7x4 | 0.67300 |
| KVBBShv 7x6 | 0.76800 |
VVGng cable weight
| Name | kg/m |
| VVGng 1x1.5 | 0.04535 |
| VVGng 1x10 | 0.14618 |
| VVGng 1x120 | 1.24898 |
| VVGng 1x150 | 1.28341 |
| VVGng 1x16 | 0.21833 |
| VVGng 1x185 | 1.86587 |
| VVGng 1x2.5 | 0.05807 |
| VVGng 1x240 | 2.42145 |
| VVGng 1x25 | 0.32083 |
| VVGng 1x300 | 3.01960 |
| VVGng 1x35 | 0.41736 |
| VVGng 1x4 | 0.08109 |
| VVGng 1x50 | 0.57123 |
| VVGng 1x6 | 0.10281 |
| VVGng 1x70 | 0.76061 |
| VVGng 1x95 | 0.99990 |
| VVGng 3x1.5 | 0.12200 |
| VVGng 3x10 | 0.38657 |
| VVGng 3x120 | 3.72183 |
| VVGng 3x150 | 4.58950 |
| VVGng 3x16 | 0.59049 |
| VVGng 3x185 | 5.58089 |
| VVGng 3x2.5 | 0.15778 |
| VVGng 3x240 | 7.20467 |
| VVGng 3x25 | 0.86301 |
| VVGng 3x35 | 1.23422 |
| VVGng 3x4 | 0.22527 |
| VVGng 3x50 | 1.69279 |
| VVGng 3x6 | 0.26841 |
| VVGng 3x70 | 2.27206 |
| VVGng 3x95 | 2.99867 |
| VVGng 4x1.5 | 0.12957 |
| VVGng 4x10 | 0.49707 |
| VVGng 4x120 | 4.89016 |
| VVGng 4x150 | 6.02776 |
| VVGng 4x16 | 0.77994 |
| VVGng 4x185 | 7.38462 |
| VVGng 4x2.5 | 0.17306 |
| VVGng 4x240 | 9.48129 |
| VVGng 4x25 | 1.21034 |
| VVGng 4x35 | 1.60576 |
| VVGng 4x4 | 0.28172 |
| VVGng 4x50 | 2.21757 |
| VVGng 4x6 | 0.36554 |
| VVGng 4x70 | 2.97299 |
| VVGng 4x95 | 3.97283 |
| VVGng 5x1.5 | 0.17942 |
| VVGng 5x10 | 0.68921 |
| VVGng 5x120 | 6.11735 |
| VVGng 5x150 | 7.53085 |
| VVGng 5x16 | 0.98100 |
| VVGng 5x185 | 9.23425 |
| VVGng 5x2.5 | 0.24143 |
| VVGng 5x240 | 11.96456 |
| VVGng 5x25 | 1.52441 |
| VVGng 5x35 | 2.01088 |
| VVGng 5x4 | 0.35160 |
| VVGng 5x50 | 2.79182 |
| VVGng 5x6 | 0.45834 |
| VVGng 5x70 | 3.72202 |
| VVGng 5x95 | 4.92343 |
| VVGng-FRLS 1x120 | 1.47347 |
| VVGng-FRLS 1x150 | 1.80574 |
| VVGng-FRLS 1x16 | 0.26234 |
| VVGng-FRLS 1x185 | 2.16345 |
| VVGng-FRLS 1x240 | 2.73595 |
| VVGng-FRLS 1x25 | 0.36969 |
| VVGng-FRLS 1x35 | 0.54333 |
| VVGng-FRLS 1x50 | 0.73581 |
| VVGng-FRLS 1x70 | 0.96283 |
| VVGng-FRLS 1x95 | 1.22481 |
| VVGng-FRLS 2x1.5 | 0.15904 |
| VVGng-FRLS 2x2.5 | 0.19533 |
| VVGng-FRLS 2x4 | 0.27321 |
| VVGng-FRLS 2x6 | 0.38117 |
| VVGng-FRLS 3x1.5 | 0.26526 |
| VVGng-FRLS 3x10 | 1.02208 |
| VVGng-FRLS 3x16 | 1.35468 |
| VVGng-FRLS 3x2.5 | 0.33276 |
| VVGng-FRLS 3x4 | 0.44963 |
| VVGng-FRLS 3x6 | 0.59620 |
| VVGng-FRLS 4x1.5 | 0.39649 |
| VVGng-FRLS 4x10 | 1.29791 |
| VVGng-FRLS 4x120 | 5.57221 |
| VVGng-FRLS 4x150 | 6.88389 |
| VVGng-FRLS 4x16 | 1.78408 |
| VVGng-FRLS 4x185 | 8.27394 |
| VVGng-FRLS 4x2.5 | 0.67047 |
| VVGng-FRLS 4x25 | 2.65826 |
| VVGng-FRLS 4x35 | 3.35278 |
| VVGng-FRLS 4x4 | 0.75430 |
| VVGng-FRLS 4x50 | 2.61684 |
| VVGng-FRLS 4x6 | 0.94172 |
| VVGng-FRLS 4x70 | 3.55136 |
| VVGng-FRLS 4x95 | 4.60112 |
| VVGng-FRLS 5x1.5 | 0.37576 |
| VVGng-FRLS 5x10 | 1.04761 |
| VVGng-FRLS 5x120 | 7.42489 |
| VVGng-FRLS 5x150 | 9.12044 |
| VVGng-FRLS 5x16 | 1.51740 |
| VVGng-FRLS 5x185 | 11.17287 |
| VVGng-FRLS 5x2.5 | 0.45700 |
| VVGng-FRLS 5x25 | 2.18777 |
| VVGng-FRLS 5x35 | 2.76435 |
| VVGng-FRLS 5x4 | 0.63036 |
| VVGng-FRLS 5x50 | 3.47523 |
| VVGng-FRLS 5x6 | 0.79293 |
| VVGng-FRLS 5x70 | 4.59643 |
| VVGng-FRLS 5x95 | 6.06415 |
| VVGng-LS 1x1.5 | 0.04956 |
| VVGng-LS 1x10 | 0.15576 |
| VVGng-LS 1x120 | 1.38116 |
| VVGng-LS 1x150 | 1.68481 |
| VVGng-LS 1x16 | 0.23084 |
| VVGng-LS 1x185 | 2.03769 |
| VVGng-LS 1x2.5 | 0.06297 |
| VVGng-LS 1x240 | 2.63110 |
| VVGng-LS 1x25 | 0.37229 |
| VVGng-LS 1x35 | 0.54589 |
| VVGng-LS 1x4 | 0.08801 |
| VVGng-LS 1x50 | 0.66346 |
| VVGng-LS 1x6 | 0.11071 |
| VVGng-LS 1x70 | 0.86325 |
| VVGng-LS 1x95 | 1.11986 |
| VVGng-LS 2x1.5 | 0.15283 |
| VVGng-LS 2x10 | 0.49131 |
| VVGng-LS 2x120 | 2.78798 |
| VVGng-LS 2x150 | 3.45205 |
| VVGng-LS 2x16 | 0.66764 |
| VVGng-LS 2x185 | 4.05432 |
| VVGng-LS 2x2.5 | 0.19462 |
| VVGng-LS 2x240 | 5.16336 |
| VVGng-LS 2x25 | 0.96818 |
| VVGng-LS 2x35 | 1.21197 |
| VVGng-LS 2x4 | 0.28584 |
| VVGng-LS 2x50 | 1.27084 |
| VVGng-LS 2x6 | 0.35581 |
| VVGng-LS 2x70 | 1.72830 |
| VVGng-LS 2x95 | 2.28020 |
| VVGng-LS 3x1.5 | 0.18448 |
| VVGng-LS 3x10 | 0.63546 |
| VVGng-LS 3x120 | 3.79479 |
| VVGng-LS 3x150 | 4.66707 |
| VVGng-LS 3x16 | 0.86480 |
| VVGng-LS 3x185 | 5.67253 |
| VVGng-LS 3x2.5 | 0.25388 |
| VVGng-LS 3x240 | 7.31250 |
| VVGng-LS 3x25 | 0.99962 |
| VVGng-LS 3x35 | 1.48437 |
| VVGng-LS 3x4 | 0.36943 |
| VVGng-LS 3x50 | 1.73856 |
| VVGng-LS 3x6 | 0.45980 |
| VVGng-LS 3x95 | 2.31973 |
| VVGng-LS 4x1.5 | 0.24322 |
| VVGng-LS 4x10 | 0.79975 |
| VVGng-LS 4x120 | 4.98411 |
| VVGng-LS 4x150 | 6.12906 |
| VVGng-LS 4x16 | 1.11709 |
| VVGng-LS 4x185 | 7.50718 |
| VVGng-LS 4x2.5 | 0.31168 |
| VVGng-LS 4x240 | 9.62382 |
| VVGng-LS 4x25 | 1.49335 |
| VVGng-LS 4x35 | 1.89543 |
| VVGng-LS 4x4 | 0.45845 |
| VVGng-LS 4x50 | 2.27668 |
| VVGng-LS 4x6 | 0.57419 |
| VVGng-LS 4x70 | 3.03532 |
| VVGng-LS 4x95 | 4.05333 |
| VVGng-LS 5x1.5 | 0.26445 |
| VVGng-LS 5x10 | 0.81703 |
| VVGng-LS 5x120 | 6.15494 |
| VVGng-LS 5x150 | 7.57253 |
| VVGng-LS 5x16 | 1.10676 |
| VVGng-LS 5x185 | 9.28441 |
| VVGng-LS 5x2.5 | 0.33943 |
| VVGng-LS 5x25 | 1.63181 |
| VVGng-LS 5x35 | 2.12485 |
| VVGng-LS 5x4 | 0.49063 |
| VVGng-LS 5x50 | 3.42808 |
| VVGng-LS 5x6 | 0.62385 |
| VVGng-LS 5x70 | 3.74901 |
| VVGng-LS 5x95 | 4.95434 |
VVG cable weight
| Name | kg/m |
| VVG 1x1.5 | 0.03500 |
| VVG 1x10 | 0.12600 |
| VVG 1x120 | 1.20600 |
| VVG 1x150 | 1.48400 |
| VVG 1x16 | 0.19600 |
| VVG 1x185 | 1.85100 |
| VVG 1x2.5 | 0.04700 |
| VVG 1x240 | 2.36800 |
| VVG 1x25 | 0.29100 |
| VVG 1x35 | 0.38500 |
| VVG 1x4 | 0.06300 |
| VVG 1x50 | 0.54100 |
| VVG 1x6 | 0.08300 |
| VVG 1x70 | 0.73000 |
| VVG 1x95 | 0.97800 |
| VVG 2x1.5 | 0.06600 |
| VVG 2x10 | 0.26300 |
| VVG 2x120 | 2.53100 |
| VVG 2x150 | 3.10900 |
| VVG 2x16 | 0.39300 |
| VVG 2x185 | 3.86800 |
| VVG 2x2.5 | 0.09000 |
| VVG 2x240 | 4.94300 |
| VVG 2x25 | 0.60500 |
| VVG 2x35 | 0.80100 |
| VVG 2x4 | 0.13100 |
| VVG 2x50 | 1.14900 |
| VVG 2x6 | 0.17300 |
| VVG 2x70 | 1.54300 |
| VVG 2x95 | 2.05900 |
| VVG 3x1.5 | 0.13360 |
| VVG 3x10 | 0.44278 |
| VVG 3x10+1x6 | 0.42900 |
| VVG 3x120 | 3.68489 |
| VVG 3x120+1x70 | 4.35800 |
| VVG 3x150 | 4.54097 |
| VVG 3x150+1x95 | 5.50000 |
| VVG 3x16 | 0.68706 |
| VVG 3x16+1x10 | 0.66300 |
| VVG 3x185 | 5.52948 |
| VVG 3x185+1x95 | 6.55200 |
| VVG 3x2.5 | 0.16983 |
| VVG 3x2.5+1x1.5 | 0.14900 |
| VVG 3x240 | 7.13336 |
| VVG 3x240+1x120 | 8.37800 |
| VVG 3x25 | 0.91990 |
| VVG 3x25+1x16 | 1.02800 |
| VVG 3x35 | 1.22111 |
| VVG 3x35+1x16 | 1.39700 |
| VVG 3x4 | 0.17500 |
| VVG 3x4+1x2.5 | 0.20800 |
| VVG 3x50 | 1.67002 |
| VVG 3x50+1x25 | 1.89800 |
| VVG 3x6 | 0.31834 |
| VVG 3x6+1x4 | 0.28300 |
| VVG 3x70 | 2.24013 |
| VVG 3x70+1x35 | 2.55300 |
| VVG 3x95 | 2.96352 |
| VVG 3x95+1x35 | 3.34700 |
| VVG 3x95+1x50 | 3.51600 |
| VVG 4x1.5 | 0.16527 |
| VVG 4x10 | 0.56942 |
| VVG 4x120 | 4.84943 |
| VVG 4x150 | 5.97558 |
| VVG 4x16 | 0.84384 |
| VVG 4x185 | 7.32500 |
| VVG 4x2.5 | 0.21257 |
| VVG 4x240 | 9.40477 |
| VVG 4x25 | 1.19748 |
| VVG 4x35 | 1.59144 |
| VVG 4x4 | 0.31197 |
| VVG 4x50 | 2.19183 |
| VVG 4x6 | 0.40569 |
| VVG 4x70 | 2.93828 |
| VVG 4x95 | 3.93076 |
| VVG 5x1.5 | 0.17212 |
| VVG 5x10 | 0.64901 |
| VVG 5x120 | 6.00100 |
| VVG 5x150 | 7.41300 |
| VVG 5x16 | 0.90700 |
| VVG 5x185 | 9.20000 |
| VVG 5x2.5 | 0.23310 |
| VVG 5x240 | 11.82600 |
| VVG 5x25 | 1.47662 |
| VVG 5x35 | 1.87300 |
| VVG 5x4 | 0.35712 |
| VVG 5x50 | 2.68400 |
| VVG 5x6 | 0.47768 |
| VVG 5x70 | 3.62700 |
| VVG 5x95 | 4.92400 |
How to choose the right cable?
Before purchasing a cable for use at home, it is necessary to determine the required cross-section of the cores in accordance with the current power. In this case, you should also take into account the number and power of household electrical appliances and the total load on the network.
When choosing, you should take into account the fact that many manufacturers, to save money, reduce the cross-sectional area of the cores by 10% (which is allowed according to the specifications). Reducing the area reduces the technical characteristics of the wire, which can lead to an emergency situation, so products from trusted manufacturers should be preferred. You can check the cross-section using a special tool or by visual inspection of the casing.
Understanding the rules for deciphering the name abbreviation will also greatly help when selecting a cable. By marking you can determine the internal structure and types of materials used in manufacturing.
Tip #2: When purchasing, you should be extremely careful, as a large number of fakes have appeared recently.
AVBbShv 4x16 - reliable, high-quality and time-tested power cable
Design and performance characteristics
The cable is designed to transmit three-phase voltage and has 2, 3, 4 or 5 cores. Their cross-section can be different - classic round, triangular or another segmental shape.
Design differences:
- conductors with a cross section of up to 16 mm - single-core, more than 16 mm - twisted stranded;
- the shape of the core is sectoral, in the form of a triangle, less often round;
- All conductors, in addition to individual insulation, have a common insulation, on top of which there is armor protection;
- one neutral conductor may have a smaller cross-section and/or a different shape than the others, if there are 4 or more conductors (allowed by the standard);
- if the cross-section of each conductor is more than 6 mm, an “airbag” based on bitumen and a special insulating coating is used between the armor and the top PVC coating;
- The ground insulation color is yellow-green, the zero color is blue or cyan, the phase color is white.
For additional convenience when connecting, phase conductors, if there is more than one, are marked with a digital or alphanumeric code - either 1, 2, 3, or L1-L3.
The cable design also contains additional under-armor insulation made of PVC or PET tapes.
Standard cable AVBBShv - main technical characteristics:
- Operating voltage - depending on the cross-section of the cores, it can be 660, 1000, 6000 and 10000 V AC. At the same time, for a voltage of 660 V, cables of this type are produced only with round cores.
- The permissible ambient temperature during operation is from –50 to +50 degrees Celsius.
- The minimum temperature during installation is up to –15 degrees (at this temperature the product does not need to be heated during installation).
- The maximum working temperature tolerance is up to +70 degrees.
- The maximum permissible emergency tolerance is up to +80.
- The highest withstand temperature of the cores during a short circuit is up to 160 degrees Celsius for 4 seconds.
- The maximum permissible air humidity in the room where the cable passes is 98%, while the air temperature can reach 35 degrees. Note: this indicator is improved for tropical cables.
- The maximum bending radius for single-core types of cable is 10 times its own diameter, for multi-core cables it is 7.5.
- The construction length of a cable with a core cross section of 6–16 mm is 450 m, from 25 to 70 mm - 300 m, from 95 mm and more - 200 m.
The standard climatic version is UHL, for dry and temperate climates. There is, as mentioned above, a “tropical” version of the product. It is marked with the letter T, which means that different layers of additional anti-mold composition are applied to the insulation.
Please note: this type of cable product is sensitive to bending and deformation. This is the weak point of the aluminum from which the cores are made.
Overview of the main manufacturers
| Cable brand | Manufacturer | Characteristics | Estimated cost, rub./m |
| AVBBShv 4x150-1 | Kolchuginsky, RF | Number of cores: 4 Section: 150 mm2 | 410 |
| AVBbShv 2x 16 | Beltelekabel, RB | Number of cores: 2 Section: 16 mm2 | 310 |
| AVBBShv 4x240-1 | Pskovkabel | Number of cores: 4 Section: 240 mm2 | 630 |
| AVBbShv 4x50-0.66 | Sevkabel, RF | Number of cores: 4 Section: 50 mm2 | 200 |
Before purchasing a cable, you must carefully determine the load from all powerful electrical appliances in the house.
FAQ
Question No. 1. Is it possible to lay an underground line using an AVBbShv power cable on a peat bog?
It is possible, only the cable needs to be laid in a plastic pipe to prevent contact with an aggressive environment.
Question No. 2. When laying an inclined route, is it allowed to use AVBbShv cable?
Power cable brand AVBBShV can be laid in cable trunks running both horizontally and at an incline.
Question No. 3. Is there any protection for the cable from mold, since its scope of application extends to places with high humidity?
There is no protection as such. For such operating conditions, it is necessary to use a cable marked with the letter “T”.
Question No. 4. Is it possible to use AVBBShv for laying home electrical wiring?
Despite the fact that the use of aluminum wire is not welcomed by electricians for wiring a home network, due to its low cost, the cable is often used in home electrical wiring.
Question No. 5. Is laying cables in overhead lines allowed?
Yes. If there is a risk of cable damage under underground installation conditions, an overhead line may be installed.
Application area
Well, one of the questions that most interests you is: where is this type of electrical cable used?
According to the standards, the scope of application of AVBbShv is as follows:
- climate: tropical, dry, temperate;
- explosion and fire hazardous premises;
- zones of high humidity - collector, tunnel, mine, etc., and the route can be either horizontal or inclined;
- in the air, if there is a danger of mechanical damage to the power line;
- in the ground, only if the cable is not subject to tensile forces during operation.
As you can see, the scope of application of AVBbShV is quite extensive and does not have significant restrictions.
We draw your attention to a very important nuance: if the marking contains the letter “T” (tropical), then the product has increased resistance to mold damage
As for domestic use, the AVBbShv power cable has proven itself very well for underground laying of lines to the house (as shown in the photo). Despite the fact that the cores of the product are aluminum (they try not to use them because of their fragility), the conductor is popular when installing electrical wiring in the house and country house. High demand is associated with the low cost of the product. Unlike its more reliable copper analogue - VBBShV, aluminum is 3-4 times cheaper, which allows you to save a decent amount of money.
If you decide to use this cable option in your own electrical wiring, be sure to calculate the cable cross-section for power and current so that the cores can withstand current loads from electrical appliances.
Typical installation errors
Acceptable errors when using cable AVBbShv
- Before you buy an expensive armored cable, study the conditions of the facility that needs to be provided with power, all possible methods, the required power, cross-section and other parameters. If there is no way to install the cable by air in cable ducts, where the possibility of gross unauthorized mechanical impact is excluded, then only lay AVBbShv underground.
- Be sure to connect the armored sheath to the ground loop on both sides of the cable;
- It is recommended to seal the cable ends at the connection points hermetically, using epoxy funnels or rubber gloves with heat-shrinkable tapes. This must be done even in heated rooms; cables tend to draw condensation from the air under the insulating layer. Accumulation of moisture can cause arcing of the insulation and short circuit.
- Do not connect the ends of the cores to the RU busbars without crimped factory lugs. Clamping the end of the wire tucked around the bolt between the busbar and the washer does not provide the quality of contact as the factory tip. Poor contact burns out at high currents.
- Technical characteristics of the ASB cable
- Technical characteristics of PV-1 wires
- Overview of NYM cable technical characteristics, applications and manufacturers
- Wire PV-3: technical characteristics, scope, manufacturers
- Application, technical characteristics and installation of RKGM wire