The device of light bulbs
Externally, the design of both lamps is almost the same. At the bottom they have a threaded base, which has the same markings. Therefore, if you decide to switch from conventional light bulbs to LEDs, you will not have to change the chandelier or insert another socket. The upper part of the devices is also inherently similar in appearance. However, there are design differences inside, which we will discuss in the comparison below.
What is the difference between an LED lamp and an incandescent lamp?
Let's compare the device and the operating principle of both devices. An ordinary light bulb includes the following elements in its design:
- base (screwed into the cartridge);
- glass flask filled with inert gas (protects the tungsten filament from the influence of the external environment);
- electrodes with hooks (conductive elements and devices for fixing tungsten filament);
- filament (radiation source);
- rod (device in which electrodes are fixed);
- insulating materials.
When voltage is applied, the tungsten filament heats up to 3000 °C. At this temperature it begins to glow. The design and operating principle of modern retro incandescent lamps are similar. But compared to regular light bulbs, they have a stylish design. They are distinguished by an unusual (antique) shape of the flask, which can be made of transparent or golden glass.
LED analog device:
- base;
- aluminium case;
- plastic protective cap;
- ballast transformer;
- board with LEDs;
- control and power board.
Compared to an incandescent lamp, the LED analogue has a different operating principle. Light is emitted as a result of the contact of two dissimilar materials under voltage. The main condition for the formation of a luminous flux is that one material must be negatively charged, the other positively charged.
How color, light and temperature are related
The human eye perceives light of different wavelengths as different colors. The combination of light of all colors in certain proportions is perceived by us as white light, and we say “ warm white.”
"when there are more red tones, like the Sun in the morning and evening;
“ day white light
” - like sunlight during the day.
We know that when strongly heated, a substance begins to glow. Our natural source of light is the Sun. It shines like a hot body with a temperature of approximately 5500K.
It is important for us that a heated body emits light over the entire range of light wavelengths, a continuous spectrum
.
And it is precisely this natural distribution of wavelengths
, the combination of all colors at high temperatures of the emitting substance, close to solar (4000-6000 K) that gives us the feeling
of white in
different shades - warm, daytime, cold. This light, natural white, is most favorable for our eyes.
The light bulb says 5000 K. But light bulbs do not and cannot have such a high temperature; the maximum for ordinary incandescent lamps is 2500 K, for halogen lamps it is about 3000 K (that’s why their light is “whiter”). How do you get cool white light?
In fact, our eyes are easily deceived. The combination of red, green and blue colors (as in picture tubes of old TVs or monitors) in different proportions is perceived by the eye as colored or white light of different shades. To produce this artificial white light, a combination of two or more phosphors, substances that glow at a certain wavelength of visible light in ultraviolet light,
, emitted by a diode or gas discharge.
Light bulbs, the light of which is perceived by a person as similar to natural white, are designated - 3500 K (warm white), 4500 K (white or daylight white, neutral white), 5000 K or even 6000K - cool white light. As we have already said, the most comfortable light for a person is daytime white; warm white is good for recreational areas, and cold white is good for certain work processes.
It has been proven that the color temperature of artificial lighting affects human performance: for example, colder light increases performance, but causes rapid fatigue.
Conclusion
:
There are different light bulbs, and different places where people stay need different lighting (in terms of illumination and color temperature) so that they feel comfortable and can stay there for a long time.
Color rendition
There is another parameter that shows quality
artificial white light.
This is the color rendering index Ra
(another name is CRI, Color Rendering System), which shows the ability of a light source to correctly convey the colors of illuminated objects.
In other words, how natural everything looks in his light. Ra=100 for a natural source, sunlight, which has all wavelengths of visible light, all colors (continuous spectrum). The index is zero
if the source is monochrome light of only one wavelength. After all, we will not see that the grass is green if we illuminate it with pure blue light.
The higher this index, the better a person distinguishes colors and shades. But it turned out that everything was much more serious. The quality of artificial lighting and its color rendering index directly affect people’s well-being, their ability to concentrate, perform complex work, and fatigue. Two different white light sources can have the same color temperature but a different color rendering index. The same colored object - say, a basket of fruit - can look completely different in their light, natural and unnatural. And in one case people will work well, but in another they will get tired quickly, their eyes will hurt, etc.
Conclusion
:
For people, the quality of artificial light, expressed in the color rendering index, is important.
Ripple factor
The last parameter we will touch on is the quality of light from our light bulb. The sunlight doesn't pulsate, it's 0%. The lower the pulsation of light intensity, the better for the eyes. The pulsation frequency is important here. We sometimes notice low-frequency pulsation with the naked eye. The eye cannot recognize a high frequency, but a negative effect may be present.
Correspondence between the power of incandescent and LED lamps - table
LED lamps and incandescent lamps have different coefficients of performance (efficiency). This indicator tells you what percentage of electrical energy is converted into light and what percentage into heat. The higher the efficiency, the less the bulb heats up, and the brighter the radiation.
Efficiency of compared light sources:
- incandescent - 4–5% of the energy consumed is required to produce light;
- LED lamps - on average, 75% of consumed electricity is converted into light waves (sometimes the efficiency reaches 95%).
Due to the large difference in efficiency, at the same power, a conventional light bulb produces dimmer light. Therefore, LEDs are used to create complete indoor lighting. Let us show the correspondence of an incandescent lamp and an LED lamp in terms of power with equal luminous flux in the table.
Table of correspondence between the power of incandescent and LED lamps
| Luminous Flux (Lm) | Power ratings (W) | |
| Incandescent | LED | |
| 220-250 | 25 | 2 |
| 400-420 | 40 | 5 |
| 560-620 | 60 | 6,5 |
| 800-880 | 75 | 10 |
| 1000-1040 | 100 | 12 |
Color spectrum
Both lamps can operate in a different color spectrum - from warm yellow to cool blue. The color of the glow can be determined by the color temperature. This characteristic is measured in Kelvin. The value is indicated on the packaging (for example - 4300K). The more Kelvins, the cooler the light.
Light temperature determines the color of the lamp's glow
However, it is necessary to take into account that the color spectrum may differ from different manufacturers. For cheap Chinese companies, the luminous flux characteristics indicated on the packaging do not always correspond to reality. Therefore, it is better to choose quality products from trusted suppliers. When checking, be sure to pay attention to the color of the glow. Be sure to check all lamps you buy.
It is very important that lamps with the same glow color are installed in the same room. Otherwise, vision problems may occur. Vision is also affected by the presence of flicker. It is better to choose devices with minimal flicker.
High-quality LED lamps with high-quality driver components (current source) do not flicker. For residential buildings, doctors recommend using “warm”, natural light.
Lamp life
The service life of lighting sources depends on their type. The leadership in this indicator belongs to LED lamps, which provide uninterrupted lighting for up to 50,000 hours. If you turn on the LED lamp for 10 hours every day, it will last up to 14 years.
Classic incandescent lamps are significantly inferior to LED bulbs. They can last up to 1000 hours. Therefore, when turned on daily for 10 hours, Ilyich’s light bulbs will work for just over 3 months. Retro incandescent lamps of modern production do not have this drawback. They belong to durable retro electrics - their service life reaches 2500 hours.
Which lamp is better in terms of fire safety?
The tungsten filament converts only 5% of the electricity consumed into light. The other 95% of the energy is released as heat. Therefore, the glass flask becomes very hot. The temperature of the glass part of the switched on device depends on the power. At 25 W the flask heats up to 100 °C, 40 W - 113 °C, 75 W - 268 °C. In contact with it, plastic products melt and the following materials easily catch fire:
- wool;
- paper;
- cotton.
The temperature of the LED analogue reaches 60–65 o C. Therefore, from the point of view of fire safety, it is safer to use LEDs for lighting houses and apartments.
Attention! The top part of the flask heats up the most. As you move to the base (base), the temperature decreases: to 80 °C for an incandescent lamp and to 36–37 °C for an LED analogue.
Are filament lamps different from regular LED lamps in any way, other than their appearance?
The technology of the filament itself is somewhat different, but it is also an LED lamp, only in a glass bulb (as a rule). A typical filament is a rod of artificial sapphire or glass with a diameter of 1.5 mm and a length of 30 mm. Such rods are also called filament threads. Using COG (Chip-on-Glass) technology, 28 blue LEDs are placed on the filament, which are connected in series.
In some models, the filament may contain several red LEDs to achieve a warmer shade of glow, while the total number of LEDs in the filament is also 28. The structure is coated on top with a layer of silicone-based phosphor.
The power consumption of one filament is in the range of 0.8 - 1.3 W. By collecting the required number of filaments in a flask, you can get an LED lamp of the required power. There are known models of filament LED lamps containing up to 16 filament threads.
The key advantage of filament lamps is their attractive appearance; they are as close in appearance as incandescent lamps, so they can be used everywhere. Their typical use now is designer lighting in lofts, cafes, restaurants, and home use in chandeliers and floor lamps.
How to recycle lamps?
Many electrical appliances require special disposal. For example, fluorescent, sodium, halogen and metal halide devices contain mercury, which is harmful to nature and human health. Therefore, they cannot be disposed of as household waste by simply throwing them in the trash. They should be taken to special recycling centers.
LED lamps, classic and retro incandescent lamps do not contain mercury and other harmful substances. Therefore, they can be thrown into solid waste bins.
Advice! Although LEDs and incandescent bulbs are safe, you can recycle them in a way that is good for nature. To do this, hand over broken lamps to a recycling and recycling facility.
Modern electric light sources
Progress since the advent of incandescent lamps has not stood still, and new sources of electric artificial light have appeared, greatly displacing traditional light bulbs.
Incandescent lamps.
Although they have very
low efficiency
and corresponding light output (5-8 lm/W) compared to modern sources and most of the energy is spent on heat, these bulbs still shine in millions of fixtures.
The reasons are tradition
(people know from their own experience what to expect from these “Ilyich bulbs”, which sometimes burn for decades, unlike newfangled “economical”, but by no means cheap lamps that go out after a couple of months) and the
price
, which compares favorably with the above.
The structure of such a lamp is familiar to everyone - in a glass flask from which the air has been pumped out, on the “legs” there is a spiral made of tungsten, the most refractory metal. It is heated by an electric current passing through it.
Light
incandescent lamps are real light of heated metal with a continuous spectrum, yellow-white, approximately 2700 K. Therefore, there are no problems with color rendering, and there is practically no pulsation either. Their light is familiar and pleasing to the eye.
Incandescent lamps most often have a classic threaded base.
The age of these light bulbs has passed, but they remain
. Since they consume approximately 10 times more electricity than modern LEDs, all over the world they are trying to limit their production and use, and various bans are being introduced.
Halogen lamps
the same incandescent lamps, but in the flask (no longer glass, but quartz) there is not a vacuum, but neutral gases under pressure, with the addition of a mixture of different halogens - fluorine, chlorine, bromine vapor, iodine. Such lamps last 2-4 times longer, and the spiral in them can heat up to high temperatures, which doubles the light output, up to 13-25 lm/W. They are powerful and bright and are often placed in spotlights, including car headlights.
The inventors of halogen lamps are almost magicians. They ensured that tungsten evaporating from the filament (the main cause of burnout of incandescent lamps), which usually settles on the colder walls of the bulb, is picked up by halogens and transferred back to the spiral, extending its service life.
The bulb of halogen lamps is small, heating up to high temperatures (therefore, protection is often installed, for example, an additional external bulb). When installing a halogen lamp in your car's headlight or lamp, do not touch its bulb with your bare hands - grease and sweat will get onto the surface, which will then burn out, leave stains and can reduce the life of the lamp.
The light of a halogen lamp is whiter than that of a conventional incandescent lamp (color temperature 3200 K), even contains a little ultraviolet, is comfortable, close to sunlight, with excellent color rendering.
Halogen lamps are a step forward compared to conventional incandescent lamps.
They are relatively inexpensive and widely used in a variety of fields. No one is going to stop producing them.
Fluorescent lamps
– a common name for long glass lamps under the ceiling of offices and workshops.
This also includes the housekeeper lamp.
(compact fluorescent lamp) with a regular screw base, where a tube twisted into a spiral glows.
They belong to gas-discharge light sources
.
The discharge (arc) burns in mercury vapor present in a flask filled with a neutral gas. This discharge produces invisible ultraviolet radiation. It is converted into visible light in a phosphor
- a substance that absorbs ultraviolet radiation, emitting light in the visible range (luminescence, hence the name of lamps).
The phosphor can vary, emitting light of different colors, or white light of different shades - warm, daylight, cold
.
The quality of light from fluorescent lamps can vary, from low with mediocre color rendering from cheap products to high, with a continuous spectrum and color rendering of more than 90%.
The light output of fluorescent lamps is approximately 5 times higher than that of incandescent lamps (25-50 lm/W). The service life is also many times longer, reaching 90,000 hours.
The light of fluorescent lamps is diffused, which is good for general lighting and does not cause glare.
There are also disadvantages
- The main one is the mercury content. Used lamps require special disposal, which, alas, is unattainable in our realities.
- Degradation of the phosphor over time - the lamps lose their luminosity.
- Not very pleasant light from budget models, low light transmission.
- Flickering, pulsating light in the budget segment;
- The need for starting devices is either heavy, noisy chokes with starters, or quite expensive electronic ballasts;
- Limitations on the number of “starts” - the starting spirals burn out.
Now fluorescent lamps are rapidly losing ground to LED lamps. There are even diode tube lamps that can be installed in old fluorescent lamps after a simple change in their circuit. Well, household fluorescent “housekeepers,” although they still serve faithfully in many lamps, are no longer bought, since LED lamps have become cheaper.
In addition to these light sources, there are others that are not very common in everyday life, but are widely used in industry and other areas. These types of arc lamps are high-pressure mercury lamps, sodium lamps and metal halide lamps.
And now we finally come to the most important and most controversial. Meet -
LED light sources.
A rarity just 20 years ago, now they are everywhere. They improved and became cheaper. Several years ago there was a turning point in the market situation - LED light bulbs became cheaper than compact fluorescent lamps, “housekeepers”.
Light is released when electric current flows through specially designed semiconductor elements, LEDs. Semiconductors typically emit monochrome light. Light that will be perceived as white can be obtained by combining red, green and blue. A phosphor is also used to coat the LEDs. It is important for us that the spectrum of LEDs is not continuous, like incandescent lamps, but consists of separate stripes
. Therefore, LEDs, especially budget ones, may have a low color rendering index and uncomfortable light. For the best (and more expensive) models it is quite acceptable and can be more than 90.
LED lamps need a driver
, a power supply that will maintain a certain amount of current flowing through the LEDs.
Nowadays a huge variety of shapes and types of LED lamps are produced. Among them are filament lamps
, in which the LEDs are made in the form of threads. Their appearance and yellowish light are similar to incandescent lamps, allowing you to create a vintage atmosphere.
LED lamps with imitation of live fire are very beautiful. This high-tech replacement for an open fire is easy on the eyes and relaxing.
By connecting three LEDs with basic colors and controlling their brightness, you can get all shades of color and white light of any temperature ( RGB lamps
). Such lamps can be controlled remotely, from a control panel or even from a mobile phone via WiFi, playing out entire light shows.
Controlling the brightness of a lamp (from the lamp control panel, or the “wheel” on the switch) is called dimming
. Not all LED bulbs support it. In addition, LEDs require special dimming devices; those used for incandescent lamps are not suitable (except for light bulb models specially designed for them).
What are the benefits of LED lamps:
- Long service life, up to 100 thousand hours according to manufacturers' requests.
- High light output, 80-150 lm/W.
- There are any colors and color temperatures. RGB lamps can change color.
- They do not have a glass bulb that can break and no mercury inside.
- Operate stably over a wide range of network voltages.
- Many models support dimming.
The disadvantages include the relatively high price and problems of low-quality lamps
– low color rendering, short service life.
The problem is the poor quality of some LED lamps.
In the era of incandescent lamps, the problem of light quality simply did not arise; all light bulbs shone the same. However, with LEDs it has come to the fore. Some manufacturers save on everything and bring to the market inexpensive models with a very low color rendering index that produce uncomfortable light. Usually they do not reach the declared power.
If sufficient heat dissipation is not provided, as happens in cheap lamps, the diodes work with overload and quickly burn out. Low-quality drivers also quickly fail (the light also pulsates with them). As a result, the light bulb stops working and falls short of its stated lifespan.
Conclusion
:
Don't expect the stated wattage, color rendering or lifespan from the cheapest LED models.
Pay your attention to more expensive, but much higher quality models from well-known brands in lighting technology, which, although made in China, like everything else, try to maintain the level. There are also domestic products on the market in the mid-price range, whose manufacturers directly purchase high-quality components (diodes, radio components for drivers) from the world's leading manufacturers, and assemble lamps and luminaires of very good quality themselves.
Advantages and disadvantages of lamps
LED and classic lamps differ not only in design, but also in operational characteristics, aesthetic and other qualities. Therefore, their pros and cons are also different. The main advantage of Ilyich light bulbs is their low cost - depending on the power, they can be bought for 10–50 rubles. Stylish retro lamps are more expensive. However, it pays off in high aesthetics and increased service life.
The advantages of LED lamps include:
- Long service life - LEDs last on average 10–50 times longer.
- Insensitive to voltage surges - the lamp does not burn out during power surges.
- High efficiency - 75–95% of electricity is converted into light.
- Low energy consumption - due to low power, with the same luminous flux, LEDs consume approximately 10 times less energy.
- Small heat emissions - the lamps do not heat up very much, and therefore there is no risk of fire of flammable materials.
Attention! Incandescent light bulbs only emit yellow light. LEDs can shine with both white (daylight) and yellow light.
From the comparison it is clear that classical lighting sources are inferior in basic indicators to LED lamps. But with the popularization of retro style in the interior, the production of improved retro incandescent lamps was scaled up. They last longer, shine brighter and have an unusual design that takes you back to the historical past. For a complete immersion in history, the light bulbs can be complemented with stylish retro wiring and retro-style switches.
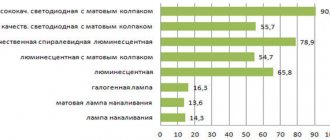
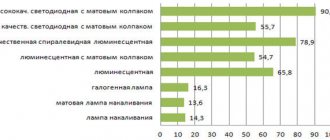
The most important properties of lamps
In order to clearly demonstrate the main advantages and disadvantages of a particular type of lighting, it is best to compare two light bulbs according to the most important characteristics.
It is necessary to compare the following indicators:
- Power;
- Light output;
- Heat dissipation;
- efficiency;
- Price;
- Environmentally friendly.
Another important parameter is the brightness of the light. LEDs win in this regard, since they have the most favorable ratio of power and brightness, which cannot be said about incandescent lamps.