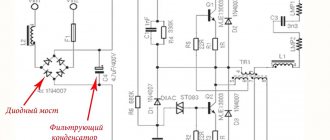
The efficiency of a modern lamp, which uses energy-saving and LED lamps, depends on many factors, and not all of them are determined only by technical characteristics or price. In order to understand the difference in modern light sources, you need to remember the third component of the system - the human eye. The suitability of a lighting device for use in residential premises depends on how well the parameters of the light bulbs are selected.
The most efficient modern light sources
Which ones are more economical?
The name “energy saving” has taken root in our country in relation to compact fluorescent lamps (CFLs). At the time of their widespread use, they were the most economical. Especially if you compare them with conventional incandescent lamps, housekeepers consume 3-4 times less energy. Later they began to “promote” LED light sources. They consume even less electricity, which means they are the most economical.
To decide whether energy-saving or LED lamps are better, you need to compare their parameters
To see the difference, look at the table. It shows the power consumption of LED, fluorescent lamps and those familiar to us with tungsten filament. They all have the same (or almost) lumen output, but as you can see, the power consumption is very different. A 3 W LED lamp is equal in light power to a 7 W energy saving lamp or a 20 W incandescent lamp. A 5 W diode lamp will replace a 12-13 watt “housekeeper” or a 40 watt incandescent. These are averaged data, since the indicators vary somewhat among different manufacturers, but, in general, the proportions remain the same.
| Incandescent lamps | Luminescent and energy saving | LED | Light flow |
| 20 W | 5-7 W | 2-3 W | 250 lm |
| 40 W | 10-13 W | 4-5 W | 400 lm |
| 60 W | 15-16 W | 6-10 W | 700 lm |
| 75 W | 18-20 W | 10-12 W | 900 lm |
| 100 W | 25-30 W | 12-15 W | 1200 lm |
| 150 W | 40-50 W | 18-20 W | 1800 lm |
| 200 W | 60-80 W | 25-30W | 2500 lm |
Just from this table alone it is easy to say that energy-saving or LED lamps are the most economical. But this is not all the advantages of LED technology. Let's talk about them further (as well as about the shortcomings, however).
Criterias of choice
Let's take a closer look at the types of LED lamps depending on their design features. The first thing to consider is the color of the light output. White and bluish shades help improve energy efficiency in the workplace, yellow, on the contrary, allows you to relax and is great for relaxation areas. There is also another division according to purpose:
- for home and office - alternative options to halogen and incandescent lamps;
- for outdoors and industrial enterprises - samples with increased protection from dust and moisture;
- for plants – devices have ultraviolet LEDs;
- spotlights – there is no option for replacing linear lamps;
- automobile lamps - products designed for interior lighting, headlights and signaling devices.
Source ozone.ru
Based on the housing design, the following types of LED lamps are distinguished:
- General purpose . This is a traditional design in the shape of a pear, candle or cylinder. The latter are better known as "corn".
- Directional light . This group of devices is represented by spots and built-in lamps. Such devices are relevant for focusing attention on a specific object, which is found in museums, shopping centers, and places of interest.
- Linear . Tubular-type samples serve as an alternative to luminescent analogues. They are more often in demand in offices and on trading floors.
Various types of LEDs are used to assemble energy-efficient lamps. Prototypes with indicator elements are now practically withdrawn from the market due to low quality and negative effects on the visual organs. Diodes with a power of 1, 3 or 5 W are also in low demand due to the relatively high heating in a compact package.
Today, the best in reliability are considered to be devices with round or rectangular SOV diodes. There is good heat dissipation and uniform luminous flux.
Source vselampi.store
No less common are “corn” type samples, which are distinguished by a large number of open LEDs and low heating of the housing. It is also worth paying attention to the relatively new lamps with filament elements. This development allowed technologists to increase lighting from 120 to 360 degrees. At the same time, the compactness of the device has been preserved and the cost has not increased.
Brief information about the types of LED lamps for the base part is presented in the table.
| Base type | Description |
| For voltage 220-240 Volts | |
| Edison (threaded connection with cartridge) | E14 – diameter 14 mm |
| E27 – 27 mm | |
| E40 – 40 mm | |
| T (tube lamps with double contacts on the end part) | 5 – diameter ⅝ inches or 15.9 mm |
| 8 – 8/8 inches or 25.4 mm | |
| 10 – 10/8 inches or 31.7 mm | |
| 12 – 12/8 inches or 38 mm | |
| For low voltage circuits with 220 V to 12 V converter | |
| G (pin connection, the distance between the pins is indicated in the marking with numbers) | s – 1 contact |
| d – 2 | |
| t – 3 | |
| q – 4 | |
| p – 5 | |
This table provides a comparison of LED lamps and incandescent lamps according to the main technical parameters:
| Criterion | Incandescent | LED |
| Power (Watt) | 15-200 | Limited to a few dozen |
| Voltage (Volts) | 220-240 | 12 or 220-240 |
| Color temperature (Kelvin) | 2700-3200 | 2700-6000 and more |
| Hue | Warm yellow | Warm, cold, neutral |
| Service life (hours) | About 1000 | Up to 100,000 in ideal conditions |
| Light dispersion (degrees) | 360 | From 120 to 360 |
| Light flow | Depends on power | |
From the review of classifications it is clear that virtually all types of lamps can be replaced with LED samples. However, it is worth remembering that in order to remove heat, the housing of powerful devices differs noticeably from the classic one in a larger direction. This is important when the lampshade is small. When replacing halogen light bulbs with diode ones, you will also have to deal with the power supplies, since they must be different. And not all energy-efficient new products can be used in a circuit with a dimmer.
Life time
If we talk about service life, the average for energy-saving ones is 10,000 hours. For LEDs this figure is higher: on average - 30,000 hours, but there are requests from manufacturers for 50-60 thousand hours of operation.
It seems that LED lamps are the leaders here, but there is one nuance. Both technologies have a rather significant drawback: over time, their glow intensity gradually decreases. The so-called “burnout” occurs. In this regard, it is worth focusing not on the stated operating time, but on the warranty period. It more accurately reflects the actual position. After all, if something happens to the lamp at this time, the manufacturer will have to replace the device with a new one. The less often such cases happen, the better. That is why manufacturers tend to underestimate the warranty period, since they bear financial responsibility.
It is better to compare not the working resource, but the warranty period
And if you compare energy-saving and LED lamps in terms of warranty period, there is also a difference. For LEDs the average is 3 years, for housekeepers - 1 year. There are more/less, but these are specific. So here, too, when comparing whether energy-saving or LED lamps are better, the best is LED technology.
Final comparison table
4: comparison of characteristics Below are comparison tables for both types of lamps, from which the advantage of LED lighting devices is clearly visible.
| Comparison parameter | Incandescent lamps | LED bulbs |
| Efficiency | 8 – 10 Lm/W | 90 – 120 Lm/W |
| Heat dissipation | 150 – 250 ºС | No more than 50 ºС |
| Efficiency | 5 – 15% | 90% |
| Lifetime | 1000 hours | 50,000 hours |
| Sensitivity to temperature changes | Available on some models | absent |
| Instant response when switched on | Instantly | Some models have a delay due to the operation of electronics |
| Safety in case of destruction | Scattered fragments | Safe |
| Mechanical strength | Afraid of blows and pressure | Not afraid, can work even without a flask |
Dimensions and appearance
Everyone knows the type and size of energy-saving lamps. This is a tube with a phosphor twisted into a complex spiral. The most compact ones can fit into a medium-sized lampshade, but in most cases they stick out from ordinary lamps, and with built-in ones they don’t look so great at all.
Approximate size difference between an LED and an energy-saving CCL lamp of the same luminous power
LED lamps can have very small sizes. A three-watt crystal can be made in the form of a circle with a diameter of 1.5-2 cm. And this is the equivalent of an energy-saving device of 7 W, which has a minimum size of 32 * 79 mm. Such miniature sizes of LEDs make it possible to make recessed lamps with a very small thickness - 2 cm or less. And this is with a radiator to remove the heat that the LEDs emit during operation. Such small sizes allow them to be built into furniture or to lower suspended and suspended ceilings to a very small height.
This is what recessed luminaires with LEDs look like
If we talk about the more familiar format - with a flask, then the shape and size of the flask can be completely different. This part is optional - the LED does not require a vacuum or a specific gas environment. So this is rather a tribute to tradition. There are bulbless lamps that are called “corn” lamps for their characteristic appearance. Their service life is determined by the quality of the LEDs, and not by the integrity of the shell, which, in fact, does not exist. You can even assemble lighting altogether from individual LEDs on a metal radiator plate or even without it. In general, the size and appearance of LED lamps may vary. And here, when deciding whether energy-saving or LED lamps are better, we certainly come to the conclusion that LED lamps are better - they can be almost invisible, and can have any shape and size.
Types of lamp bases
Today, the following types of bases are widely used:
E14 - or mini base. Lamps are installed in wall lamps, chandeliers, etc. E27 is the most common type of base. Accordingly, they are used in all types of lamps. E40 - Lamps with this base are installed in spotlights, large lighting fixtures, and street lamps. These are DRL lamps, sodium lamps.
G23 - Such sockets are used for table lamps, carriers, etc.
G9 - Same as G23 and in all kinds of backlights.
GU10 - Spotlights - this is the main application of such sockets.
GX53 - Spotlights.
MR16 - Spotlights.
Convenience and safety of use
Everyone knows that in fluorescent lamps the tubes are filled with phosphor, which begins to glow under certain conditions. It takes some time to create these conditions. Sometimes it is almost unnoticeable, and sometimes the delay after turning on can be a second or even a little more. This is not the most pleasant phenomenon to put up with. LED lamps light up immediately after voltage is applied. They are certainly better at this.
Today, more and more people are trying to make lighting with the ability to change the light intensity. This can be achieved either by a complex circuit with a large number of switches, or by installing a dimmer - a small device that allows you to smoothly change the level of glow. But the fact is that not all lamps can work with a dimmer. Energy savers cannot. They need a certain voltage level and its shape, and the dimmer distorts the shape. But some LED lamps can work with this device. Just look for dimmable ones when choosing LED bulbs. This ability is indicated in the technical specifications. The downside is that such light sources with equal characteristics are more expensive.
Table for comparing LED and energy-saving lamps
Another point in favor of LED lamps. Their flask (if there is one) is made of impact-resistant plastic. Energy-saving fluorescent lamps are made of glass. Moreover, damage to the tube is fatal - the light source stops working. In addition, some (cheap) housekeepers contain mercury vapor, so a damaged glass tube with phosphor can cause serious harm to health. This also leads to difficulties with recycling - special enterprises are needed to recycle such lighting devices.
And the last point regarding ease of use - it is impossible to restore either an incandescent lamp or a fluorescent lamp after failure. If damaged, they completely lose their functionality. LED lamps usually consist of a number of crystals located on the body. When one or more crystals fail, the luminous flux decreases, but light is still emitted, albeit in smaller quantities. In addition, if you wish and know how to use a soldering iron, you can replace burnt out elements, restoring their previous brightness.
So, when deciding whether energy-saving or LED lamps are better in terms of ease of use, we see that LED lamps are more practical and safe.
Description of LED and energy-saving lamps
LED lamp (LED) is a light source consisting of LEDs. This is an analogue of a regular light bulb (incandescent, fluorescent, halogen). It is used in everyday life, industry and street lighting.
It has a complex structure, consisting of a group of LEDs installed on cooling radiators, a voltage converter, a control circuit, and optics.
Light. Photo by OZON
An energy-saving (fluorescent) light bulb (ESL) is a hermetically sealed glass bulb containing an inert gas and mercury vapor. Under the influence of electric current, radiation is generated in the bulb. Passing through phosphor-coated walls, this radiation is converted into a luminous flux.
Prices and yet what is better...
Everyone knows that LED lamps are more expensive. This is perhaps the only point where fluorescent lamps are ahead. But today the price difference is not as great as before. They are already almost equal. If we take, for example, light sources from the same manufacturer with the same equivalent (or almost the same) in relation to incandescent lamps, then the prices are almost identical.
Here, even the LED price is lower. True, the color temperature is different...
For example, lamps from Camelion (Chamelion). Energy saving lamp - LH15-FS-T2-M/864/E14 is the equivalent of a 75 W incandescent lamp, costs 160-225 rubles. LED lamp - Camelion LED8-C35/830/E27 (also equivalent to 75 W incandescent) - 170-230 rubles. Both series are basic, without any special bells and whistles, and if you take into account the savings on electricity (8 W versus 15 W) and service life (10,000 hours and 30,000 hours) and all the other “goodies”, then even the question “which is better is energy-saving or LED lamps" does not occur. The solution is probably clear - LED lights are more economical, easy to use and durable. They are best installed instead of incandescent lamps.
But a lot of information has recently appeared in the press and on the Internet that LEDs are harmful - they emit a harmful spectrum and flicker. There is no confirmed data about the spectrum, but luminescent ones flicker, flicker. But they always flicker, and there are LEDs without ripples, they just cost much more. In general, the decision is yours.