general information
The white LEDs that are used today first appeared in 1996. However, only in 2005 they began to be used specifically as a lighting source. This type of light bulb is energy saving.
The luminous power of LED lamps is their main characteristic . It shows the energy efficiency of this type of lighting. The power of LED lamps is measured in watts. Manufacturers are gradually trying to increase the quality of the glow without changing their power. That is why the consumer receives a high-quality lighting source, but at the same time saves energy. For comparison, you can use an incandescent light bulb with a rating of 100 W. A LED with the same level of illumination will have only 12 W.
Correspondence between the power of LED lamps and incandescent lamps
If you want to obtain a luminous flux (brightness) of a certain value and compare LED lamps and incandescent lamps, then the former have lower power. Accordingly, when using LED lighting, the amount of electricity consumed increases.
| LED lamp, power in W | 2-3 | 4-5 | 8-10 | 10-12 | 12-15 | 18-20 | 25-30 |
| Incandescent lamp, power in W | 20 | 40 | 60 | 75 | 100 | 150 | 200 |
| Luminous flux, Lm | 250 | 400 | 700 | 900 | 1200 | 1800 | 2500 |
This table will help you choose LED lamps to effectively replace old lighting.
In terms of luminous flux, a 60W incandescent lamp corresponds to a 9W LED lamp. In addition to lower power consumption with the same light output, the LED lamp has other advantages. The energy efficiency of LED lamps is 7.5 times greater. This is when illuminated by an LED light source and incandescent lamps of the same power.
The effectiveness of replacing incandescent lamps with LED lamps is obvious. You get bright white light and save on electricity by matching the wattage and purchasing new bulbs.
Comparison table of 40W incandescent lamp, 15W fluorescent lamp and 5W LED lamp
| Characteristics | LED lamp | Fluorescent Lamp | Incandescent lamp |
| Power consumption | 5 W | 15W | 40 W |
| Light output efficiency | 90 Lm/W |
| 10.5 Lm/W |
| Light flow | 450 Lm | 450 | 420 Lm |
| Working temperature | 70°C | 60°C | 180°C |
| Life time | Up to 50,000 hours | Up to 25,000 hours | Up to 1,000 hours |
| Environmental friendliness | Yes | Contains mercury | Yes |
| The need for recycling | Does not require special disposal measures | Requires special disposal measures | Does not require special disposal measures |
| Use in damp and dusty areas | Maybe | undesirable, service life is reduced | Maybe |
| On delay | No | Yes | No |
| Frequent power on and off | does not affect service life | shortens service life | shortens service life |
| Flicker | No | Maybe | No |
| Heating of the lamp surface | 30 degrees | 60 degrees | 120 degrees |
| Vibration resistance | Yes | No | No |
| Maintenance | rarely | moderately | Often |
Comparison table of 60W incandescent lamps, 20W fluorescent lamps and 9W LED lamps
| Characteristics | LED lamp | Fluorescent Lamp | Incandescent lamp |
| Power consumption | 9W | 20W | 60 W |
| Light output efficiency | 78 Lm/W |
| 12 Lm/W |
| Light flow | 700 Lm |
| 720 Lm |
| Working temperature | 70°C | 60°C | 180°C |
| Life time | Up to 50,000 hours | Up to 25,000 hours | Up to 1,000 hours |
| Environmental friendliness | Yes | Contains mercury | Yes |
| The need for recycling | Does not require special disposal measures | Requires special disposal measures | Does not require special disposal measures |
| Use in damp and dusty areas | Maybe | undesirable, service life is reduced | Maybe |
| On delay | No | Yes | No |
| Frequent power on and off | does not affect service life | shortens service life | shortens service life |
| Flicker | No | Maybe | No |
| Heating of the lamp surface | 30 degrees | 60 degrees | 120 degrees |
| Vibration resistance | Yes | No | No |
| Maintenance | rarely | moderately | Often |
Comparative table of 100W incandescent lamp, 25W fluorescent lamp and 12W LED lamp.
| Characteristics | LED lamp | Fluorescent Lamp | Incandescent lamp |
| Power consumption | 12 W | 25W | 100 W |
| Light output efficiency | 75 Lm/W |
| 13.6 Lm/W |
| Light flow | 900 Lm |
| |
| Working temperature | 70°C | 60°C | 180°C |
| Life time | Up to 50,000 hours | Up to 25,000 hours | Up to 1,000 hours |
| Environmental friendliness | Yes | Contains mercury | Yes |
| The need for recycling | Does not require special disposal measures | Requires special disposal measures | Does not require special disposal measures |
| Use in damp and dusty areas | Maybe | undesirable, service life is reduced | Maybe |
| On delay | No | Yes | No |
| Frequent power on and off | does not affect service life | shortens service life | shortens service life |
| Flicker | No | Maybe | No |
| Heating of the lamp surface | 30 degrees | 60 degrees | 120 degrees |
| Vibration resistance | Yes | No | No |
| Maintenance | rarely | moderately | Often |
Types of diode light bulbs
The first criterion for dividing is the material of the case:
- Glass (frosted or transparent);
- Aluminum;
- Plastic;
- Ceramics.
By type of base:
- Screw (letter designation – E);
- Pin (letter designation - G).
On the base, in addition to the letter indicating its type, numbers are indicated that indicate for the first type the diameter, measured in millimeters, and for the second type this is the length between the pins.
Thus, the following types of LEDs can be distinguished:
- E14 (bulbs with a smaller diameter base, suitable for some lamps);
- E27 (regular, which are suitable for installation, for example, in chandeliers, where the socket is designed for incandescent light bulbs);
- G4 (can be used, for example, to illuminate pictures).
- GU5.3, G9 (replacement for halogen bulbs);
- GU10 (used for built-in lamps that serve as lighting, as well as in hoods);
This list shows only the main types.
Power table for LED lamps
Depending on the type of paw on the base, the indicators may be as follows:
It is clear from the table that higher power LED bulbs produce greater luminous flux. Depending on the power of LED lamps, their purpose changes. An E27 or E14 light bulb with a power of 5 W will be sufficient for the home. But for a large workshop you will need a stronger light source.
At the beginning, the power of LED lamps for the home is indicated in the table. However, this is not the minimum value for this type of lighting. There are diode lamps with a rating of 2 W. And the maximum power of LED lamps can reach up to 180 W.
Benefits from using LED lamps. Calculation
The review would be incomplete without a practical comparison of the two lamps over the long term. Take, for example, a 40 W incandescent light bulb. Let's further assume that a person uses it on average 6 hours a day, that is, in total over 365 days this will be about 87,600 Wh per year.
An equivalent LED lamp, depending on the manufacturer, consumes 4.5 W or 9855 W/hour per year. To sum it up simply, the conclusion suggests itself: an incandescent lamp consumes 8.88 times more energy.
How to choose an LED lamp?
More details!
Disadvantages of LED lamps
There are, of course, disadvantages to LED lighting that are worth mentioning. First of all, this is its price. At the moment, their cost is higher among analogues. But the low power requirement of LED lamps described above and the longer operating life more than compensate for the high prices.
The heating level of LED sources is much lower than that of incandescent lamps, but is still present and can have a negative impact on the lighting system. For this purpose, special heat-removing radiators are installed in the models, but the installation of models with high power requires additional cooling measures.
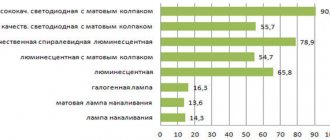
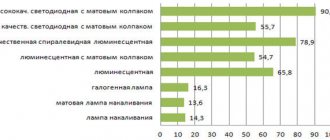
Correspondence of the power of LED lamps to other types of lighting
From the table we can conclude that diode lamps are less energy-consuming compared to others. With different powers, the luminous flux of LED lamps and the other two types remains the same.
Thus, the rated power of LED lamps that need to be installed in the house can be calculated based on the table above. Also on the packaging of some light bulbs there is information about equivalent indicators. For example, a 5 W LED light bulb corresponds to a 40 W incandescent light bulb. Moreover, in both cases they will have the same glow.
Table of correspondence between power and luminous flux
Unlike light bulbs with a spiral, the main selection criterion for which is power (W), you need to buy LED lamps based on luminous flux (lm). It is this physical quantity that indicates how much light power a particular light source emits. By the way, the packaging of all currently produced incandescent lamps also indicates the value of the luminous flux. The buyer just needs to learn how to correctly compare watts and lumens. And to make this task easier, below is a table of power and luminous flux for the three main types of lamps.
| Incandescent lamp | CFL | LED lamp | Light flow |
| 20 W | 5–7 W | 2–3 W | ~200 lm |
| 40 W | 10–13 W | 4–5 W | ~400 lm |
| 60 W | 15–16 W | 8–10 W | ~700 lm |
| 75 W | 18–20 W | 10–12 W | ~900 lm |
| 100 W | 20–25 W | 12–15 W | ~1200 lm |
| 150 W | 40–50 W | 18–20 W | ~1800 lm |
| 200 W | 60–80 W | 25–30 W | ~2500 lm |
From the comparison table it follows that a 100 W incandescent light bulb should be replaced with a 12-15 W LED light bulb. Why? Because their luminous fluxes are approximately equal and amount to 1200–1400 lm. At the same time, on the front side of the packaging of many LED lamps you can see 10 W = 100 W. But if you look at the table with the technical parameters of the LED light bulb, you can immediately see the discrepancy in the luminous flux.
In addition, the buyer must take into account 2 more important nuances:
- the light output of warm LED lamps (2700°K) is approximately 20% lower than that of similar neutral lamps (4000°K);
- the plastic diffuser bulb “eats” up to 10% of the emitted light. The exception is filament LED lamps with a transparent glass bulb, which have no scattering losses.
If you wish, you can independently calculate the approximate luminous flux of an LED lamp. To do this, you should use an empirical relationship: for every 1 watt of power consumed, the lamp emits about 100 lm. It is also necessary to subtract the energy losses on the driver (approximately 1 watt) and on the diffuser (approximately 100 lumens). As a result, it turns out that a 10 W light bulb creates a luminous flux of about 800 lm.
It is worth noting that the efficiency of LEDs is growing every year. Therefore, new models of LED lamps will have greater luminous power.
Colorful temperature
Possible indicators:
- From 2700 to 3000K;
- 4000K;
- 6500K.
This concept is also one of the characteristics of diode lamps. It is measured in Kelvin (K). The color of the glow depends on this indicator. For example, a color temperature value between 2700K and 3000K indicates that the light will be yellowish.
Lamps with a color temperature of 4000K have a white glow. This type of light is usually used in shopping centers. And if the indicator is 6500K, then the light will be cold white. Such lamps are used only in industrial premises.
For the home, lamps with a color temperature level of 2700K – 3000K are best suited.
How does suction power affect cleaning?
One of the main characteristics of both a robotic and a conventional vacuum cleaner is the power with which it is able to suck up debris.
This parameter affects the quality of the gadget’s operation as follows:
- With a higher power, the device does a better job of cleaning, since it can suck up not only dust, but also larger debris. With low power, you can only rely on dust collection.
- Robotic vacuum cleaners do not clean carpets very well, and with low power, they generally will not clean the carpet of debris.
Life time
Despite the low power consumption of LED lamps, their service life is an important point. After all, if they break down quickly, then there is no point in purchasing them, since there will be no energy savings.
When purchasing diode light bulbs, the buyer is given a guarantee for the product. Typically the warranty period is from 3 to 5 years. This is already a good indicator. However, based on statistics, the service life is approximately 50 thousand hours, which corresponds to 6 years. However, many users note that the quality of the glow deteriorates over time.
Pros and cons of purchasing this type of light bulbs
Positive and negative aspects can be assessed using the following indicators:
- Price;
- Dimensions;
- Directional light;
- Ripple.
As for the first characteristic, we can say that the cost can be twice as much as for a regular light bulb. This is the main disadvantage of the product. However, it is worth considering that due to energy savings, the cost of the product will pay for itself.
When replacing a light bulb, you need to consider its size. LED dimensions may be larger compared to conventional ones. This may affect the appearance; the light bulb may stick out strongly from the lamp or may not fit there at all.
LED bulbs have a slightly different direction of light, which may be unusual at first. Their side lighting is poor.
The positive thing is that there is no light pulsation. However, not all light bulbs have this phenomenon. You need to purchase a quality product to avoid pulsation that is unpleasant to the eye.
Some conclusions
An important characteristic of all types of light sources is power. The power of LED lamps is measured in watts (W). An important indicator is also the luminous flux. It directly depends on the power of the product. For home, 5-10 W is best. If you wish to replace, the equivalent power of LED lamps can be found in the table above.
Despite their considerable cost, light bulbs of this type will last a long time and save energy. Therefore, such an acquisition will soon pay for itself. When choosing, it is important to pay attention to the color temperature of the product. The color of the glow depends on this indicator.