The vast majority of people when buying an LED lamp pay attention to two parameters - price and brightness (luminous flux). In fact, there are a dozen more selection criteria that should be paid attention to.
Main selection criteria : manufacturer, luminous flux (brightness), power, supply voltage, color temperature, base type, dispersion angle, dimensions.
Additional criteria : dimming capability, operating temperature range, light flux pulsation.
Let's look at each item of technical specifications in detail.
Light flow
For most LED lamps, the luminous flux is 80-100 lm/W. There are LEDs based on COB technology, whose luminous flux reaches 180 lm/W, but they are not used in household products. In Chinese light bulbs, the normal brightness is 70-80 lm/W.
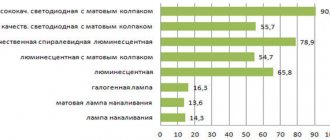
Comparative table of light output of different types of lamps
Detailed analysis: What is the luminous flux of diode lamps.
LED lamps: power characteristics, other indicators
Energy-saving LED has a number of other important advantages, in addition to lower power consumption. To understand them in more detail, let’s take, for example, a 9W LED light bulb (which corresponds to a regular 60W one) and compare their basic parameters. The main ones are:
- Current strength: 0.072 A and 0.27 A, respectively.
- Luminous flux (brightness): 454.2 lm and 612 lm.
- Light output efficiency: 53.4 Lm/W and 10.3 Lm/W.
- Operating temperature: 70 degrees Celsius and 180 degrees Celsius.
- Color temperature: 2700-6000 K and 2800 K, respectively.
- Service life: 30,000 hours and 1,000 hours.
Lighting of this amount of watts is suitable, for example, for a living room. High power devices are not needed here; one LED source is enough instead of several incandescent lamps. Based on the characteristics proposed above, the advantage of a 9W energy-saving lamp over a conventional 60W lamp is obvious. Significant savings in electrical energy, bright white lighting, long service life. Isn't this what you're aiming for when choosing an LED?
Power
The power of an LED lamp is a derivative of the luminous flux, or vice versa. Please note that the LED parameters indicate the total power of the lamp and driver.
| Table of power and luminous flux ratio | |
| LED power, W | Luminous flux, Lm |
| 3-4 | 250-300 |
| 4-6 | 300-450 |
| 6-8 | 450-600 |
| 8-10 | 600-900 |
| 10-12 | 900-1100 |
| 12-14 | 1100-1250 |
| 14-16 | 1250-1400 |
Video
Coffee capsules Nescafe Dolce Gusto Cappuccino, 8 servings (16 capsules)
435 ₽ More details
Coffee capsule Nescafe Dolce Gusto Cafe O Le Coffee with milk, 3 packs of 16 capsules each
1305 ₽ More details
External batteries for smartphones
Colorful temperature
Color temperature is a very important criterion when choosing LEDs.
Warm white light (2700-3200K). Warm light has a spectrum similar to that of an ordinary incandescent light bulb.
Neutral white light (3200-4500K). Bulbs with neutral white light are as close to daylight sunlight as possible. An ideal solution for illuminating the work area.
Cool white light (more than 4500K). These LED lamps have a white-blue glow. The best option for work spaces where increased concentration is required.
Detailed analysis: glow temperature of LED lamps.
How to choose
When choosing a lamp, you should consider the following parameters:
- Required type of base;
- Colorful temperature;
- Light output;
- Lamp power;
Energy-saving devices are a modern and effective solution for any room and purpose.
Comparison of the size of traditional incandescent devices and energy-saving devices
To summarize, it is important to know that when choosing an energy-saving appliance, you need to focus on a reputable manufacturer. Such manufacturers monitor the quality of their products at their factories and the risk of stumbling upon a defective product is minimal.
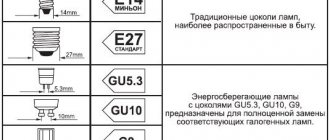
Base type
The most common type of base is E27. On the Internet, most of the technical specifications are for these LED lamps. This is the classic size of the base for ordinary incandescent light bulbs.
| Scheme | Designation | Purpose |
| E14 Minion | Traditional bases, the most popular in everyday life | |
| E27 Standard | ||
| E40 | Designed for high-power light bulbs. Lighting of large rooms or streets | |
| G4 | These sockets are used to completely replace halogen lamps with LEDs | |
| GU5.3 | ||
| GU10 | ||
| GX53 | Used in lamps (built-in or overhead) in furniture or ceilings | |
| G13 | Tubular swivel base used in T8 lamps |
Emitted light
The light that an LED lamp emits also refers to the classification of the product and indicates its technical characteristics.
Light flow
One of the important parameters that determines the technical characteristics of a light source is the luminous flux, that is, its emission power and efficiency. The unit of measurement for light flux is the lumen. The second parameter, efficiency, determines the ratio of the power of the first parameter to the power consumption of the light source Lm/W. In principle, this indicator reflects efficiency.
To compare the luminosity of LEDs with a conventional filament, it is necessary to take into account that a light source with a power of, for example, 40 W creates a luminous flux of about 400 Lm. There are tables for comparing the luminous flux of different light sources. From them you can find out that LED lamps have a luminous flux that is ten times more powerful than that of a conventional light source.
When buying a lamp for your home, you need to study the labeling. Conscientious manufacturers indicate luminous efficiency or luminous flux power. But, most often, the markings contain comparative characteristics of an LED light source in relation to an analogue with a filament. Especially such designations are most present on the packaging of Chinese products. In general, such marking can also be considered correct, although it is more of an advertising nature.
It should be summarized that over time, LEDs exhaust their service life, reducing the power of the luminous flux. This indicates their shortcomings, although nothing is eternal.
Colorful temperature
LED lamps differ from traditional filament light sources in their color rendering. The filament creates one warm color - yellow. LEDs are capable of emitting light over a wide range of colors, which is determined by the color temperature scale.
The color of hot metal is taken as the basis for constructing the scale. The unit of measurement is degrees Kelvin. For example, the yellow color of hot metal has a temperature of 2700°K. The daylight temperature ranges from 4500 to 6000oK. Although the white light at the bottom border has a yellowish tint. All colors with a temperature above 6500oK belong to cold light with a blue tint. When choosing an LED light source for a room, you need to pay special attention to such characteristics. In addition to the fact that when a room is illuminated in different colors, the internal appearance of its decoration is shown, some shades can negatively affect a person’s vision. Eye fatigue highlights the shortcomings of LED lighting, but this can be easily corrected with the correct selection of color rendering.
Light distribution
If conventional light sources create maximum illumination of the space around them, then LEDs have a luminous flux direction in one direction. They emit light in front of them. This light distribution is suitable for a night light or other lighting device that requires a directed beam of light.
In order for the LEDs to produce uniform illumination of the space, they are equipped with a diffuser. Also, uniform distribution of light is achieved by installing LEDs on a plane at different angles. All these methods allow you to create a uniform distribution of light over a certain area. For example, LED lamps can have a luminous flux spread at an angle of 60 or 120°.
Color rendition
There is a color rendering index, denoted Ra. The indicator is responsible for the natural color of an object falling into the illumination field of a certain light source. The index standard is sunlight, which is equal to an index of 100. LED lamps have an index of 80-90 Ra. For comparison, a regular incandescent lamp has a rating of at least 90 Ra. It is generally accepted that an index greater than 80 Ra is high.
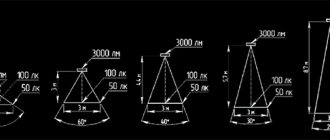
Scattering angle
Manufacturers produce lamps of various shapes and sizes for the E27 base. Depending on the design and design features, the dispersion angle can be from 300 to 3200. Depending on the dispersion angle, the illuminated area also differs. This can be clearly understood from the figure below.
For general lighting, for example, a chandelier in the living room, a model with a maximum scattering angle is required, for a table lamp, on the contrary, with a minimum.
You can understand the approximate angle of dispersion of the light flux by looking at the form factor of the diode light bulb.
Work principles
Several types of lamps are used for lighting. The most common are:
- With filaments;
- Luminescent;
- LED.
Candles and kerosene lamps have long gone out of use, but some people still refer to the wattage of incandescent lamps as candle power. This definition is not true.
The first electric lighting devices were incandescent lamps. The product uses a thread made of refractory metal. When current is passed through it, the thread begins to glow. However, the energy required to heat this body is much greater than the energy spent on luminosity. This lamp consists of several main elements:
- Flask;
- Filament or spiral;
- Base.
Air is pumped out of the bulb to extend the life of the filament.
The base is usually made of a standard shape marked E14 or E27, for the interchangeability of products. Halogen light bulbs have a similar design. Vapors of noble gases are added to their flask to increase the quality of color rendering. Such products are used in advertising, daylight and street lighting.
Later, fluorescent lighting appeared. Their operating principle differs in that the light creates a gas discharge that occurs in the bulb under the influence of an electric current. The inside of the flask is coated with a luminescent substance, that is, a substance that glows under certain conditions. Its reliability and service life have already proven to be several times higher than conventional incandescent lamps.
In the 60s of the twentieth century, a new principle of light generation appeared. It turned out to be a diode semiconductor junction emitting electromagnetic radiation in the visible range under the influence of electric current. Such products were called LEDs. They have the best performance in terms of power consumption versus useful illumination. Lamps using these elements are more reliable, more durable and safer than incandescent, halogen, and fluorescent light bulbs.
Operating temperature range
By default, the normal operating temperature of LEDs is from -30C0 to +60C0. In some regions, outdoor temperatures during winter may fall below these limits.
It is also not recommended to install such lamps in rooms with high temperatures, for example, a sauna steam room, or near powerful heat sources.
Working in extreme temperatures
For LEDs, the upper limit of ambient temperature corresponds to a 30% drop in luminous flux.
The operation of LED lamps at low temperatures significantly reduces the heating of the semiconductor crystal, which increases its uninterrupted operation time.
Advantages and disadvantages
Advantages:
- Saving electricity: such devices have a high efficiency and low power with high light output. Compared to a traditional incandescent lamp, the electricity savings are significant (4-5 times).
- Long service life: conventional incandescent devices have a tungsten filament, which is sensitive to voltage changes and wears out quickly, so such devices do not last long. Energy-saving ones have a fundamentally different design and are able to work without replacement for a very long time (5-10 times longer than conventional devices).
- Low heat dissipation: in energy-saving devices, all electrical energy is spent on maximum light emission and minimal thermal energy emission, therefore, in comparison with conventional incandescent devices, they heat up significantly less and can be used in plastic or paper lamps and other materials that do not tolerate heat well.
- Possibility of choosing color temperature: as mentioned above, energy-saving devices have different color temperatures due to LEDs of different colors or shades of phosphor covering the body of the device.
You may be interested in this Features of filament lamps
Flaws:
- High price: energy-saving lamps are significantly more expensive than traditional incandescent lamps due to the complexity of their production. For example, if an incandescent one costs 15 rubles, then an energy-saving one with similar lighting characteristics will cost from 100 to 150 rubles.
- Danger of fluorescent devices: such devices contain mercury and argon vapors, which are dangerous to the human body and can lead to poisoning if the lamp is damaged.
- The need for special disposal: due to the high hazard class, fluorescent lamps are toxic waste and require special disposal at the end of their service life.
- Difficult to adjust brightness: To adjust the brightness, special dimmers are required that can operate energy-saving lamps.
Actual parameters of LED lamps
The table below shows the results of testing twenty-six LED light bulbs from various manufacturers. For famous brands Osram and Philips, passport data always corresponds to real parameters. For others, the luminous flux of the product may be a quarter lower than the declared parameters.
Table of correspondence between denominations of different manufacturers
Pay attention to the bottom position. Bellight LEDs produced in Poland have significant discrepancies in their design parameters. Such diodes are definitely not worth buying. Not only will you pay twice as much for “virtual” lumens, but with such a pulsation coefficient, installing them in residential areas is hazardous to health.
For clarity, we present data from testing Chinese light bulbs.
Emission and efficiency of an incandescent light bulb
Before dealing with the question of the applicability of the formula for calculating “low voltage” modes, attention should be paid to one point.
The light bulb is an almost perfect converter of electrical power into radiant energy.
The fact that light bulb developers strive hard to increase the efficiency of the light bulb does not in any way affect this statement. An incandescent lamp is an ideal converter of electrical power into radiation.
The fact is that developers strive to increase the output of LIGHT energy, and it is in this sense that efficiency is calculated. The developer strives to increase the conversion factor of electrical power into LIGHT radiation, into radiation in the visible range.
This efficiency of the light bulb is really SMALL. However, the light bulb emits perfectly IN THE ENTIRE spectrum and very much in the infrared range, where our eyes cannot see.
To calculate purely electrical parameters, it is not at all important to us IN WHICH range the light bulb emits. It is only important for us to remember that the light bulb ALWAYS EMMITS if only some (even the smallest) voltage is applied to it. And it is important to remember that the supplied power is dissipated in the form of radiation.
How much electrical power is supplied to the lamp, it is SUCH power that will be dissipated in the form of radiation .
No one has canceled the law of conservation of energy, and no one has canceled the second law of thermodynamics either. This means that as much as has arrived, so much must leave. And it will disappear precisely in the form of radiation, because there is simply NO WHERE more energy can go – only into radiation. This is a very important circumstance.
Structurally, the filament is a thin tungsten wire with a diameter of about 50 microns and a length of about half a meter, rolled into a spiral of an intricate configuration.
The vacuum in the flask eliminates the possibility of convection heat transfer - ONLY THROUGH RADIATION.
Of course, some of the heat escapes through the antennae of the lamp on which the spiral is attached, but this is minuscule.
To visualize this smallness, we can draw an analogy.
Let me repeat, the tungsten thread itself is exactly the size of a hair from a first-grader’s braid, 50 cm long and 50 microns in diameter.
If you visually enlarge this hair... it’s as if we have wires with a diameter of 1 mm and a length of 10 meters! Common sense dictates that this wiring should NOT be cooled by heat exchange at the edges. Yes, something will be lost at the contact points, but the main power will be dissipated along the entire length of the wiring.
For the case of a spiral located in a vacuum, all the power will go into RADIATION and it doesn’t matter in what range of the spectrum...
conclusions
For all its attractiveness, buying an LED lamp has many pitfalls.
Purchasing products from world-famous brands eliminates the occurrence of “surprises” during operation. Only such a lamp will cost 2-3 times more expensive. The most famous LED manufacturers are Philips, Osram, Bosh, Ikea.
The middle price range, when price reductions do not affect quality, includes the following manufacturers: Jazzway, Feron, Navigator, Unitel, Lexman, Wolta. Among their assortment, there are not entirely successful models, but mostly they encounter small discrepancies between the real and the rated light flux.
Super budget LED . From time to time, very inexpensive LED lamps mainly of Chinese origin appear on the market. These products are guaranteed to have an increased luminous flux and contain the simplest current stabilizers. The lifespan of such paws is not much longer than energy-saving ones.
Please rate the article. We tried our best:)
Did you like the article? Tell us about her! You will help us a lot :)
Design
In general, a compact luminescent device consists of a bulb, an electronic board and a base.
Fluorescent lighting device
Sealed glass tube
The flask is a hollow type (or a sealed curved glass tube), which is connected with its terminals to an electronic board.
Types of flasks
Inert gas inside it and mercury vapor
Such a tube is filled at the factory with special gases (mercury vapor, argon and other gases). Such gases are very dangerous for humans if the device is damaged, and it is important to be careful when using fluorescent energy-saving devices.
Phosphor layer
The body of the gas-discharge device is coated with a special composition - phosphor (a mixture of calcium halophosphate and other elements).
An electric discharge creates ultraviolet radiation in a flask with mercury vapor, which is changed into a visible light flux using a phosphor.
Electronic board
The electronic board in gas-discharge devices is an important component, and the service life and quality of its glow depend on the quality of its assembly. Structurally, such a board consists of:
- The thermistor is an element that ensures a smooth start of the device and helps to warm up the lamp coils without blinking.
- The starting capacitor is the element that directly starts the device.
- Filters - protect the electronic board from interference;
- Capacitive filter - reduces pulsations and eliminates flickering of the device;
- Current-limiting choke - stabilizes the device and limits the current;
- Fuse - protects the device and turns off the lamp when overloaded;
You may be interested in How to arrange lighting in the garage
Principle of operation
A voltage is applied to the dinistor, which forms a pulse. This pulse arrives at the transistor and causes it to open. As soon as the start is made, the circuit is closed by the diode bridge, the capacitor is charged and re-opening does not occur.
The transistor operates on a transformer with several windings and a ferrite core. Voltage is applied to the transformer filaments and a glow appears in the bulb. In this case, the voltage reaches a high value (up to 600 V).
When the inert gas in the flask is completely ionized, the voltage is reduced to sufficient to maintain the lamp glow, which ensures the energy-saving properties of the lighting device.
Selecting a lighting fixture
Energy saving lamp device
For many years, fluorescent light sources were used along with incandescent lamps. But they had a drawback - large sizes. The development of technology made it possible to make the flask thinner, bend it in the shape of a “U” or a spiral, and make the electromagnetic choke, which consumed reactive power in addition to active power, electronic and place it in a regular base.
energy saving lamp and incandescent lamp
Thus, the size of fluorescent devices became comparable to incandescent lamps, and they took their place in lighting equipment.
Application in everyday life
Light sources of this type are widely used in everyday life. The table of luminous flux of fluorescent lamps and LEDs illustrates this. Application possibilities range from home lighting to illumination of nightclubs and discos. This includes room lighting, lighting for specialized workplaces, ultraviolet disinfection, decoration, and automotive lighting. Energy-saving lamps are an alternative light source that is recommended to be used, despite the high cost. In any case, it pays off and benefits the person.