Radiation Angle
The emission angle refers to the angle at which the light intensity is halved.
The luminous flux of the lamp is emitted within this angle. The beam angle affects the illumination area and the luminous intensity of the lamp. With the same lamps, a lamp with a smaller radiation angle will have a greater luminous intensity, and therefore create greater illumination. The diameter of a spot of half illumination refers to the diameter of a light spot, at the edge of which the illumination is half that in the center.
Secondary optics is an optical system in the form of a lens or reflector designed to concentrate the light flux. Such a system is usually used so that the height of the lamp suspension can be selected to ensure the necessary illumination and its unevenness. The higher you need to hang the lamp, the smaller the angle of radiation you need to choose.
It must be borne in mind that this only applies to LED lamps in which the LEDs are located in the same horizontal plane and shine downwards.
Without the use of secondary optics, the radiation angle is assumed to be 120 degrees.
An example of hanging a lamp with a luminous flux of 3000 lm, suspended at different heights, having secondary optics with different angles and providing 100 lux of illumination on the axis. with a spot diameter of half illumination of 3 m:
More accurate results will be obtained if you contact specialists who use special computer programs for calculations, for example “DIALUX”.
Source
Main settings
Any LED lamp has many technical parameters, but if you consider the choice for a house or apartment, then it is enough to familiarize yourself only with the basic characteristics.
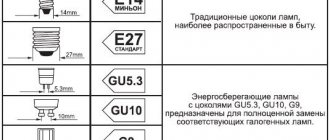
Base
And the first thing you should pay attention to in an LED lamp is the type of base. There are many types of them, but in residential buildings and apartments only some of the ones listed below are most often used.
E27. This base is the standard in the post-Soviet space. Therefore, in Russia and the CIS countries, the majority of LED lamps for the home with an operating voltage of 220 V. E14 are produced specifically for it. It is similar to E27, but has a smaller diameter. Used to work with “candle” or “minion” type bulbs, which have a small bulb diameter and low power. Used in small lighting or decorative structures. G4. Designed specifically for small lamps in MR11 housing, which are used in decorative lighting. GU 5.3. It has two pin contacts spaced 5.3 mm apart. Most often found in halogen and LED lamps MR16. GU 10. Also a two-pin connection with a distance between contacts of 10 mm. As a rule, such a base is used to power kitchen hoods or built-in lamps. G13. Used in T8 tubular fluorescent and LED lamps. It has two pins, with a distance of 13 mm between them. GX53. Most often installed in lamps for suspended or suspended ceilings.
Power
The second parameter that you definitely need to pay attention to when choosing an LED lamp is its power. The amount of electrical energy used directly depends on this parameter. Many consumers, when choosing a replacement for old artificial lighting sources, are guided by this indicator.
There are many graphs and tables of correspondence between the power and luminous flux of different types of light bulbs. LED lamps have a power several times less than filament, gas-discharge or fluorescent light sources. Below, for clarity, is a graph with comparative characteristics, thanks to which it is easier to understand the relationship between power and luminous flux of the most common types of lamps used in homes.
As you can see from the graph, for example, a 100 W incandescent light bulb corresponds to a 12 Watt LED light bulb and a 25 Watt compact fluorescent lamp (CFL). It is worth noting that any graph only gives an approximate picture of the relationship between different types of light bulbs. An accurate table cannot be constructed for many reasons, but the two main ones are:
- as a rule, each manufacturer uses its own production technology;
- Over time, components for LED lamps and production technologies are improved, which affects all technical characteristics of the final product.
When selecting an LED light bulb by power, it is worth remembering that the difference between LEDs and an incandescent filament, with the same luminous flux, can vary from 7 to 10 times.
Light flow
A more important parameter to pay attention to when choosing any lamp for your home is luminous flux. Roughly speaking, the physical meaning of this characteristic is to indicate the amount of light emitted. Luminous flux is measured in lumens. Unfortunately, not everyone, even famous manufacturers, indicate this parameter on the packaging. If this parameter is not indicated anywhere, then, when choosing products from a well-known manufacturer, the luminous flux can be calculated taking into account 90–100 lumens per watt of power.
Large manufacturers do not install more efficient LEDs in LED lamps for the home, since this is not rational due to the strong increase in the cost of the final product.
For example, the luminous flux of a 12 W LED lamp will be equal to 1080–1200 lumens, which approximately corresponds to a 100 W incandescent lamp.
In LED lamps with a frosted bulb, the luminous flux is approximately 20% less than the calculated value.
Colorful temperature
The color temperature of a lamp is expressed in Kelvin and indicates the shade of white light. Manufacturers produce LED light bulbs with color temperatures ranging from 1800 to 6600 Kelvin. The lower the Kelvin value, the warmer the light, like a candle flame. A higher Kelvin value indicates that the light is more natural or cool white, similar to daytime sunlight.
When choosing an LED lamp to illuminate your home, you should definitely pay attention to the shade of its glow. If you need a bright daylight bulb, it is recommended to choose a product with a neutral white color temperature of about 4 thousand Kelvin. If you need to replace an old incandescent lamp in your home, but at the same time maintain a cozy, warm atmosphere in the evening, then you should choose an LED lamp with warm white light.
Color rendering index
Under one LED lamp, objects in the apartment can look natural, but under another they can have completely unnatural colors. This is due precisely to the color rendering indicator, which shows how natural the surrounding objects look. Color rendering index is a relative value, ranging from 0 to 100. It is designated as CRI (from the English color rendering index) or Ra. The higher this indicator, the better the human eye distinguishes colors and shades. A CRI of 100 means this is what the object looks like in good daylight sunlight. It is believed that good LED lamps for an apartment have a color rendering index above 75 CRI.
Scattering angle
The choice of LED lamps must take into account the scattering angle. This parameter shows at what angle the emitted light is scattered. If the lamp has a small angle, say 30°, then it is like a small flashlight, in which a powerful light beam shines over a long distance almost in a straight line, without illuminating nearby objects. A light bulb with a small beam angle is not always suitable for the home.
Dimmable
Today, many houses and apartments are equipped with simple devices for adjusting the brightness of lighting fixtures - dimmers. The design of a conventional LED lamp is such that it cannot work with a dimmer. The reason for this lies in the built-in driver, which converts the AC voltage into the operating current of the LEDs. If the voltage supplied to the lamp is too low, then the driver simply does not supply power to the LEDs or supplies it intermittently, which causes chaotic flickering. The solution to the problem is to use dimmable LED lamps with a modified driver. The packaging of such light bulbs indicates the possibility of using them with a dimmer.
If you plan to use an LED lamp paired with a dimmer in your home, then you must definitely choose a light bulb with the ability to adjust the brightness.
The nature of LED glow
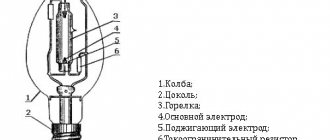
It took some time for people to figure out how to use this heat for heating rooms and for lighting. In the latter case, it is necessary to heat the wire so much that it begins to glow. And not the red color of steel heated in a furnace, but brightly to the point of dazzling. It turns out that light in this case is only the second product after heat. The current produces heat, and the heat heats the metal, causing it to glow.
Incandescent lamp
This two-step scheme for using electricity is a common occurrence. Both when using electricity and when generating it. Because the mechanical energy of water, for example, does not immediately produce current, but first rotates a turbine attached to the generator rotor; the rotor and stator together produce an alternating magnetic field, and the field forms an electric current in the conductors. The same is true with thermal generation.
Semiconductors have made it possible to immediately, without intermediaries, convert one type of energy into another. Accordingly, the efficiency immediately increased, which contributed to efficiency and economy. In solar panels, solar energy is directly converted into electrical energy. And electric energy is simply emitted in the form of light. At the same time, the mechanics of the process are simple - a simple semiconductor plate with certain properties. This is the very revolution of the 21st century, which has long been predicted, and the possibilities of which have not yet been fully studied.
We are interested in a semiconductor - a light emitter made in the form of a diode, an LED.
Its properties are interesting. It has many advantages. But there have already been some disadvantages. Or maybe its disadvantages are simply not entirely understood and unrealized advantages?
A semiconductor emits light inertia-free. You can apply a constant voltage, or you can apply an alternating voltage. Moreover, over a wide range of voltages. And it will begin to glow, and in the same way as voltage was applied to it. Constant - the light will be constant, variable - it will start blinking. This is considered a disadvantage of LED lamps. But this is not their drawback, but the lack of voltage that is applied to it. Provide smoothed, stabilized, or even constant, and they will shine continuously and softly.
Light scattering angle
Absolutely the same picture with the angle of light scattering. The LED is produced in the form of small rectangular plates, and one of its faces shines. Well, the light from it will be, accordingly, like from a flat luminous plate, or a luminous window. That is, its scattering is normal for incoherent light.
Most of the light travels perpendicularly, and around the directional axis (perpendicular to the surface) its flux decreases in inverse proportion to the tangent of the deflection angle. In general, the radiation pattern of an elementary LED is approximately the same as the pattern of a flat lamp made from the same LEDs. It turns out that it shines forward as a cone with a blurred boundary. The approximate angle of the cone of light is about 120°.
Now they produce LED lamps shaped exactly like incandescent lamps: with an Edison thread, a glass container, and even an imitation of a spiral inside the container. Moreover, the spiral is made of a wire coated with a semiconductor, and this wire emits light.
Radiation patterns of various lamps
Here are the radiation patterns of different LED lamps currently produced:
- matte hemisphere with E27 base. Lights the same as a flat lamp;
- E27, but the diagram is much wider. Approximately like ordinary incandescent light bulbs of the same shape;
- the same, but E14 is a “fat” candle;
- E14 – frosted candle;
- “corn” E27 and E14;
- GU10;
- MR16;
- E14 – candle with three petals;
- E14 and E27 with cone lens.
From the radiation patterns you can see how the lamp will behave in different types of connections. Where there is a blockage at the top of the diagram, it is clear that if the lamp is placed in the chandelier with the balloon facing up, the ceiling will remain unlit. Some of these lamps are good in chandeliers, some are good in table lamps.
Human imagination is inexhaustible. There are still many experiments ahead with diode cords, tapes, matrices, backlights of varying degrees of source secrecy. Until some element is finally unified as a common, easily plug-in module for all systems. Then it will be possible to “build light” the way you want.
Source
Power
The power consumption of the lighting element is one of the main factors influencing the energy consumption of the device within 1 hour. Optimal indicators of 6-13 W correspond to a power of 50-100 W for incandescent lamps. The total energy consumption also takes into account the power of the drivers, which work together with the LEDs. They consume about 10-15% of the energy of the total power of the device.
Energy consumption of different types of light bulbs.
What is an LED module
An LED module (block, cluster) is a device or part of it, consisting of one or more LEDs and emitting light. In addition to the different number of diodes, the modules differ in size, voltage, current, brightness, color, and control method. The classic cluster contains mechanical, optical and heat-dissipating elements, but there is no control device.
The LED module may contain:
- only series-connected diodes;
- LEDs and current limiting elements;
- diodes, current limiters and a controller that controls the color and brightness of the light;
- LEDs, current limiters, controller and control unit that allows you to connect the cluster to the network.
Some modules are equipped with reflectors, lenses, and elements that protect from the sun. The sizes of such blocks are larger.
LED clusters are:
- independent (can be selected for installation outside the luminaire or housing);
- built-in (can be selected for installation in a housing or lighting fixture, replaced if it fails);
- one-piece (can be selected for installation in a housing or lighting fixture, cannot be replaced).
Regardless of the type, the module can be with or without a control device.
LED modules are also classified according to the place of use:
In the first, the diodes are soldered on the board, the brightness indicators are low, but the contrast level is high. DIPs are large, open, with two legs, bright, not contrasting, equipped with visors that protect from sunlight. Internal clusters are used to illuminate premises for various purposes, including residential ones. Clusters with DIP are used in landscape design and in the manufacture of advertising structures.
Reference! LED modules with a built-in control unit with a socket are LED lamps.
Let's sum it up
An LED light bulb for home needs should be selected depending on its purpose, selecting the degree of light output, color temperature, lighting angle:
- for a table lamp on a desktop, a bedside shelf, a bathroom, a small room, you won’t need a powerful model, more powerful than 500 lumens, 650 lumens may be too much, 400 may be too little;
- for the dining room and recreation area, you should choose models with a warm color;
- to work you will need a model with cool light;
- the larger the viewing angle, the larger the area of the room will be flooded with light (weak, diffused);
- It is important to check the efficiency of the light - how much light can be obtained at a certain power consumption, 50-70 lm/W are outdated low-level LED models.
You should avoid poorly described models without a name - the less information, the more the manufacturer tries to hide shortcomings.
Using LEDs allows you to pay low electricity bills and save nature. By choosing a high-quality model, we get a powerful, long-lasting device. Feedback on the selection of the model and features of use can be left in the form of comments.
What to look for when choosing
The first thing you need to do before purchasing is to determine where the light source will be used - indoors or outdoors. The next parameter is the manufacturer. You should not immediately buy a module from an unknown manufacturer that is installed in a lighting fixture for a fluorescent or incandescent lamp. The best option is to choose a lighting fixture that is designed for LEDs and provides good heat dissipation.
It is important to choose the right power supply. This power factor should be 0.9, it is desirable to have a device that protects against voltage surges, interference and overheating. The seller must know the country of origin and provide a quality certificate.
Temperature of the light produced
Its “shade” depends on the temperature of the light:
- warm white (2700-3200K);
- day white (3500-4500K);
- white (5000-6000K)
- cold white (6000-8000K).
Important! An incandescent light bulb has a light temperature of 2700 K, a halogen bulb has a light temperature of 3000 K, and an LED bulb has a light temperature of 2200K - 10,000 K. When purchasing, the choice is made according to the kelvins indicated on the package, since the definitions of “daytime”, “cold”, “warm” vary from person to person. manufacturers differ.
The deviations regulated by standard C78.377A and the effect of each shade on humans should be taken into account. Warm white light relaxes, daylight improves performance, cold white light creates contrasts necessary when performing work that requires high precision.
SNiP 23-05-95 for residential premises recommends light with a temperature of 3000-4000K. If the interior color is blue or green, the temperature should be more than 4000 K. In a room with a lot of yellow and red color, the temperature should not exceed 3500 K.
Radiation angle indicator
The emission angle is the angle at which the light intensity decreases by 2 times. The light flux is emitted within these limits. The illumination area depends on the angle of radiation - the smaller the angle, the higher the illumination. In production and offices, the main part of the light beam should fall only on the work surface, without violating the requirements for uniformity of lighting.
Light sources equipped with lenses and reflectors that concentrate the light beam help to meet all the requirements. It is necessary to take into account that the angle is selected depending on the height at which the lamp will be hung. The greater the height, the smaller the radiation angle should be.
Important! All of the above applies to modules in which the diodes are located on the same plane and point straight down.
Without optics, LEDs have an emission angle of 20-120 degrees (except for filaments with an angle of up to 300 degrees). The beam is brighter in the center, the illumination decreases at the edges of the corner. A large assortment of modules allows you to choose products with almost any radiation unit.
additional characteristics
These parameters affect the durability of the device and the comfort of its use.
Radiator
The design of high-quality ice lamps implies the presence of a radiator - it is responsible for cooling the LED block. If the selected product does not have a ribbed surface with longitudinal holes (they are responsible for free air circulation) between the base and the bulb, then it is not recommended to buy it.
It is advisable that the radiator is made not of plastic, which is often found in cheap lamps, but of aluminum - they are more reliable and safer.
Important! It is undesirable to purchase frosted lamps not only because of the reduced luminous flux, but also because it is almost impossible to discern the presence and quality of the radiator on such a product.
Scattering angle
Unlike incandescent lamps, the angle of light dispersion with LED lamps can vary significantly. This depends on exactly how the LEDs are positioned, whether the device has a special diffuser lens, and whether it is coated with a phosphor.
The minimum scattering angle of an LED lamp is 30°; narrowly directed light is emitted by lamps in which the LEDs are located on the same plane.
Devices in which LEDs are placed at several levels provide diffused light (angle 60° or 90°).
Package
When choosing a lamp, you need to pay attention to its appearance. A quality product must have packaging that displays all the information important to the consumer:
- power;
- base type;
- Colorful temperature;
- luminous flux (in lm);
- warranty period;
- color rendering coefficient (in K);
- scattering angle;
- manufacturer information.
The lamp itself should not have burrs or unpainted areas, the structure should be completely closed, without protruding wires.
If 2 or more items from this list are missing, purchasing the product is not recommended.
Size guide markings
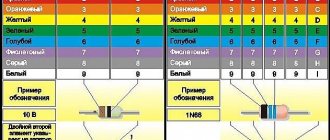
The dimensions of SMD LED housings can be determined by markings. For example, the length and width of SMD 5050 are 5 cm, the dimensions of SMD 3528 are 3.5x2.8 cm.
By marking DIP diodes, you can determine not only the dimensions. For example, for a round product, the marking 5RHWWC3000mcd6500K34V70 means that it is round (RH) with a diameter of 5 mm, the color is cold white (W), the body is transparent (WC), voltage 3.4 V, dispersion angle 70 degrees. The marking of the square DIP 8x8red50mcd2.1V indicates that the length and width are 8 mm, the color is red, the light intensity is 50 mcd, the voltage is 2.1 V.
On LED lamps with screw bases E 14 E 27, the numbers indicate the diameter of the bases. GU 5.3, GU 10 and G 13 are swivel sockets with a two-pin connector. The numbers indicate the distance between them.
Attention! When choosing light bulbs for luminaires with a pin base, sockets with appropriately sized spaces between the pins are required.
There are filament LED lamps with E 27 or E 14 sockets in which the driver is installed. Their sizes and shapes are different, most are similar to ordinary incandescent lamps, the numbers are the diameter of the base.
Glow degradation time
Manufacturers of LED modules and lamps indicate a long service life - from 20 thousand hours (for old models), up to 30-50 thousand hours for new SMDs, up to 100 thousand hours - for the most modern products. For the average consumer, it is important to know whether these numbers can be trusted.
Typically, service life is the period of time during which products stop working, not completely, but until the luminous flux parameters drop to a certain level. Some manufacturers take 30% as a threshold, others – 50%, but neither the technical documentation nor advertising materials indicate this, which prevents you from choosing a model.
Most often, the service life is 50 thousand hours (5 years and 8 months). It is impossible to verify this through testing. Models change very quickly, within 5 years others appear, and the old ones are no longer made. Tests are carried out quickly under extreme conditions.
The degradation time depends on:
- decreased diode performance;
- phosphor aging period;
- mechanical deformations;
- reduction in the characteristics of the primary optics.
The luminous flux is reduced mainly due to crystal degradation as a result of current leakage from the light-emitting areas. Degradation manifests itself as a decrease in voltage. In order for the service life to correspond to the declared one, the lighting device must operate in conditions in which the temperature does not increase. The current must correspond to the value specified by the manufacturer; it is advisable to install a device in the circuit that protects against static electricity. The crystal degrades very quickly if the solder joints are destroyed (there was a defect in production).
When a phosphor ages, it is not the brightness that changes, but the hue of the glow (a blue color appears). The primary optics are made from silicone and plastic. When exposed to ultraviolet light emitted by the LED, these materials become cloudy. The same thing happens when the temperature is too high. The service life is also reduced by a low-quality driver (if its power does not match the power of the diodes) and a decrease in the characteristics of the secondary optics (if any).
Attention! In the documents, manufacturers indicate the period that the LED is capable of operating under optimal conditions at the current and voltage specified in the technical documentation. Therefore, it is not necessary to increase the current to increase brightness.
Power and luminous flux
One of the first parameters of any LED lamp is power. It is for this characteristic that most consumers choose a light bulb, and then look at all the others. When considering this parameter, you need to take into account that its value in the description is indicated as a total value for the lamp and driver.
At the same time, energy consumption and luminous flux are directly dependent on each other. This is especially clearly shown in the table below.
| Power, W | Luminous flux, lm |
| 3,5 | 275 |
| 5 | 400 |
| 7 | 500 |
| 9 | 750 |
| 11 | 1000 |
| 15 | 1300 |
Attention! A regular 150W incandescent lamp has the same luminous flux parameters as an LED lamp of only 20-25W. With similar characteristics, the latter provides brightness no worse than the first, while its service life is much longer, and energy consumption costs are 7 times less!
How to choose the right LED lamp
To choose the right LED lamps, you should consider that even products from the most popular manufacturers have disadvantages.
An important element is the radiator installed between the case and the base. If it is made of plastic, it is not able to provide proper heat dissipation. LED bulbs with an aluminum radiator last longer. The spirals in it are located so as to ensure the best air circulation.
Important! It is impossible to determine the radiator material in the store. The only way is to knock on the place where it is located with a metal object and determine the material by sound.
Features of choice for ceiling lamps
Choosing the right LED lamp model for a ceiling light is quite difficult.
Attention! If there is a chandelier or other lighting fixture at home and there are no plans to change it, the LED lamp is selected according to the base (it must match the socket) and the angle of dispersion of the light flux.
If the ceiling lamp is a chandelier, then after choosing the base, the required dispersion angle is determined. You can use the table for this:
There are the following types of LED lamps, differing in shape:
- pears (the most common, for large lampshades with base E 27);
- spherical (for small round lampshades);
- candles and candles in the wind (with a minion base for flat and narrow lighting fixtures);
- reflectors (with base GU 10 and GU 5.3 for recessed spotlights);
- linear (with G 13 base for devices intended for lighting large areas);
- corn.
You can choose lamps for industry, street (with a high level of protection), cars, plants.
Before choosing a lamp, the installation location is determined. For a chandelier, choose a pear with a VWFL dispersion angle; for illuminating individual interior elements, candles or candles in the wind with an NFL angle are suitable; for suspended ceilings, reflectors with a GU 10 and GU 5.3 base and an FL or WFL angle are suitable.
Rules for replacing incandescent and halogen light bulbs:
- if the incandescent lamp in the lamp is changed, it is necessary to accurately determine the dimensions of the shades, since some products based on LEDs are very large;
- The power supply for halogen lamps is not suitable for LEDs;
- dimmers do not support all diodes;
- The design of filament lamps is unfinished, so they have many disadvantages.
Reference! Most sources of filament are very expensive, all are unsuitable for repair, are poorly cooled (especially cheap ones), and have a fragile flask. There are no statistics on reliability yet; the stated service life is 2-2.5 years.
Review of LED lamps: popular manufacturers and cost of lamps
It will be easier to choose high-quality LED lamps if you study the list of the most frequently purchased products, assessing the advantages and disadvantages of each.
LED lamps, according to manufacturers, can serve regularly for up to 25 years. Long service life, product quality stated on the packaging, luminous flux and color rendering index are provided by well-established manufacturers on the market:
- General Electric (USA);
- Osram (Germany);
- Philips (Holland);
- CREE (USA);
- BLV (Germany);
- SUPRA (Japan);
- NICHIA (Japan).
The minimum cost of lamps from these manufacturers is 300 rubles.
Trustworthy domestic companies:
- Start;
- Optogan;
- Gauss;
- Kreonix.
The price of products starts from 150 rubles.
On the market you can find other LED lamps for the home from unknown brands and Chinese companies at a price significantly lower than the average. However, it is unwise to purchase such products - such savings will not justify themselves: there are no guarantees that the lamp will last a long time. In addition, due to low-quality materials and non-compliance with production standards, such products may be environmentally unsafe.
Choosing LED lamps is an activity that requires care and a thorough approach. However, the long service life and proper operation of the purchased devices will allow you to forget about the problem of lighting an apartment or house for at least 5 years - this is exactly the warranty period that manufacturers give for their products.
Common types of LED lamps
New lighting fixtures are purchased after the construction of a house is completed, when moving to a new apartment, or during renovations. Which one to choose depends primarily on the installation location and light level requirements.
Ceiling lamps are:
- for residential premises and offices;
- industrial, warehouse;
- street (landscape and for facades);
- for housing and communal services;
- for baths, saunas and swimming pools.
Indoor devices can be built-in or suspended, installed on walls, ceilings or interior items.
In any lighting device, not only the characteristics of the light sources are important, but also the design, type of installation, and purpose. Built-in models have high light output and can be chosen for various rooms.
Important! Dome luminaires are not suitable for residential premises, despite their good light transmission and high level of protection.
A ceiling lamp can be surface-mounted, recessed (in a pendant structure) or pendant (chandelier). Built-in models are produced with a housing equipped with a protective screen that prevents glare. LEDs are rarely chosen for chandeliers unless they have a lampshade or shade. The reason is the unattractive appearance due to the base in which the radiator is hidden.
Important! For a chandelier with a dense lampshade or frosted shades, you need to choose lamps with transparent bulbs, for crystal ones - with frosted bulbs. If you want to save money, you can buy light bulbs that support dimming.
LED lamps are often used in portable lamps and night lights. The former are suitable for focusing attention on individual areas or interior items, the latter - in places where it is necessary to turn the device in different directions.
About the manufacturers
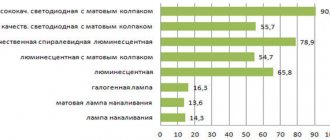
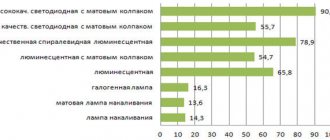
The most difficult and controversial point of all is the recommendations and choice of manufacturer. Firstly, assessments are subjective, secondly, they can be “seasoned” with advertising, and thirdly, they can be mistaken for advertising. To avoid the influence of advertising and sellers, we found the results of a vote on one of the forums (about the reliability of LED lamps from different manufacturers). They are posted in the form of photos.
Well-known brands still win
There are two opposing approaches - it is better to buy the same light bulb from a trusted manufacturer, even if it is more expensive. They will not risk their reputation, so they control production. This makes sense, since losing a conquered market is really more expensive than maintaining quality. And with well-known manufacturers there are usually fewer problems with warranty cases. Again, reputation. In addition, they collect damaged products for a reason - they study the causes of the breakdown, find weak components, and thereby improve quality.
The second approach is the opposite - why pay more just for the name. If you're lucky, you can find an inexpensive, but good and reliable light bulb from an unknown or little-known manufacturer. But how much money will be spent on those that will quickly burn out... In general, everyone chooses what they consider more correct.