A large range of electrical protection modules with different response characteristics makes it difficult to select the required model. Each parameter specified by the manufacturer must be taken into account correctly. Only in this case will your safety be ensured.
The article on the site provides a detailed overview of the operating characteristics of a differential machine with an explanation of the operating principle of each of them for a novice user. All you have to do is read them and put them into practice.
Safety is important
When designing and installing a low-voltage electrical network, one of the main tasks for specialists is protection against short circuits and ensuring the maximum level of safety.
To solve this problem, special devices are used, one of which is a differential automatic machine (difavtomat).
Below we will consider the following questions:
- What is this product?
- What are they used for, and what types of automatic machines are there?
- What elements does it consist of, and how does it work?
- How to decipher the symbols and connect the difavtomat?
- What are the reasons for the triggering?
Scope of application
The difavtomat is used to solve the following problems:
- Protection of a certain section of the network from the flow of increased currents that occur in the event of a short circuit or overload.
- Preventing fire or people being exposed to voltage due to leakage caused by poor-quality wire insulation or failure of household appliances.
In the first case, the differential circuit breaker operates as a circuit breaker, and in the second - as an RCD (residual current device).
What types are there?
A differential machine is a universal device that can be easily used in single- and three-phase networks.
In the first case, products with two poles are used, and in the second - with four.
Design features, principle of operation and circuit diagram of the difavtomat
Considering the designation of a device according to GOST, it is easy to identify the structural elements of the protective device.
The main ones include:
- Differential transformer;
- Group of releases (thermal and electromagnetic).
Each element performs specific tasks. Let's take a closer look at them.
A differential transformer is a device with several windings, the number of which directly depends on the number of poles.
Its task is to compare the load currents in each of the conductors. If the indicators diverge, a leakage current appears, which is sent to the starting element.
If the parameter is above a certain level, the device turns off the electrical circuit by separating the power contacts of the difavtomat.
To test the functionality, a special button is provided, most often signed as “TEST”. It is connected through a resistor, which is connected in two ways:
- Parallel to one of the existing windings;
- Separate winding for the transformer.
After the button is triggered, the user artificially generates an unbalance current. If the difavtomat is working, it should turn off the circuit. Otherwise, conclusions are drawn about a malfunction of the device.
The next element of the automatic machine is the electric release. Structurally, it looks like an electric magnet with a core.
The purpose of the element is to influence the tripping mechanism. The electromagnet operates when the load current increases above the set level.
Most often this happens when a short circuit occurs in a low-voltage network. The peculiarity of the release is that it operates without a time delay. It takes a split second to turn off the power.
Unlike an electromagnetic one, a thermal release does not protect against short circuits in the circuit, but against overloads. The unit is based on a bimetallic plate through which the load current flows.
If it is higher than the permissible value (the rated current of the difavtomat), gradual deformation of this element occurs. At a certain point, the bimetal plate gradually bends.
At a certain moment it acts on the shutdown element of the protective device. The time delay of the thermal release depends on the current and temperature at the installation location. As a rule, this dependence is directly proportional.
The lower limit is written on the casing of the difavtomat (indicated in mA). In addition to the leakage current, the rated current of the release is also indicated. We'll talk about the device labeling in more detail below.
About connection diagrams for differential automatic machines
Scheme 1
The difavtomat (input) is placed at the input and protects all the necessary elements of one electrical group.
Scheme 2
Guarantees more reliable electrical safety of the room. The machine performs the function of protecting the installed electrical group by turning it on/off in/from the circuit.
In the first situation, wiring with supply voltage is connected to the upper terminals, and loads from different electrical groups are supplied to the lower ones. These groups are separated from each other by automatic switches. But this scheme also has a significant drawback - a general shutdown of all network groups if at least one of them has problems, malfunctions or breakdowns, and the machine is also turned off in emergency mode.
To avoid a false signal coming from a differential circuit breaker installed at the input, in residential premises due to current leakage, they resort to switching devices whose settings set the leakage rate to 30 mA. As a rule, this is true for houses with old wiring.
And yet, in our time, in most cases, the second scheme is used as a higher quality, convenient and reliable one, which will protect in case of emergency situations with the help of a difavtomat. It is usually used only in rooms where there are increased requirements for electrical safety (children's rooms), or in rooms where humidity is increased (kitchens, bathrooms, showers). This will provide protection and guarantee the safety of all electrical groups of the general network.
Of course, in order to achieve maximum results and efficiency, a separate automatic switch is needed for each electrical group. Thus, if one machine is triggered, the electrical circuit as a whole will not be completely de-energized.
This is very practical and meets electrical safety requirements. The benefit of such a connection (protection of the necessary electrical groups when connecting several electrical appliances) is obvious.
If you use this method, you can achieve a reliable and uninterrupted electrical supply. But from the point of view of pricing policy, this method of organizing diffautomats is an order of magnitude more expensive than using one device to protect the entire electrical network.
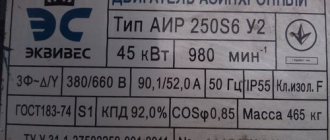
How to decipher the symbols on the case?
It was already noted above that all the necessary information can be found on the body of the differential machine.
Having studied the basic parameters, it is easier to decide whether the device is suitable for solving specific problems.
The most important designations include:
- RCBO is an abbreviation, a shortened version of the full name (“residual current circuit breaker”).
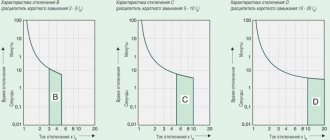
- C25 - rated current parameter. Here C is the characteristic of the dependence of time and current, and 25 is the maximum current of the difavtomat, exceeding which is unacceptable.
- 230 V is the rated voltage at which the device can be used (for a household network).
- In 30mA—leakage current parameter. When 30 mA is reached, the RCD operates.
- A special sign that confirms the presence of the RCD function and the type of RCBO. Based on the presence of the designation, a conclusion is drawn about the ability of the differential machine to respond to direct or alternating pulsating current.
Also on the body of the protective product is a schematic diagram. It may not tell the average person anything, so there is no need to pay attention to it.
Also on the external part of the device there is a “TEST” button, which is necessary for periodic monitoring of the serviceability of the device in the RCD part. We have already discussed the features of checking using this element above.
What should you consider when choosing differential automatic machines?
Options:
- differential current (similar to RCD);
- rated current (similar to automatic machines);
- switched current, designed for a specific device.
Advantages and disadvantages of products
The key advantages of diphatomats are:
- compact dimensions;
- ease of installation of electrical wiring;
- saving time and money.
A certain disadvantage is the difficulty of determining the cause of deactivation.
How to connect the device?
Before connecting the difavtomat, it is worth understanding the type of electrical wiring.
The following options are possible here:
- Network type - single-phase or three-phase. In the first case, the rated voltage will be 220 Volts, and in the second - 380.
- Availability of grounding - there are networks with or without grounding.
- Place for installation. Most often, RCBOs are installed in an apartment, but installation on each separate group of conductors is possible.
Taking into account the considered conditions, it is necessary to decide how to connect the protective device. It is worth remembering that a difavtomat may have a number of design differences.
Let's look at the main connection methods in the panel:
- The simplest option. A popular method is to install one differential circuit breaker that protects the entire chain. When choosing this option, it is advisable to buy a difavtomat with a high rated current in order to take into account the load of all consumers in the apartment. The main disadvantage of the scheme is the difficulty of finding the location of damage when the protection is triggered. In fact, the problem may be hidden in any of the wiring sections.
In the above diagram you can see that the “ground” comes separately and is combined with the ground bus. All conductors (PE) from electrical appliances are connected to it. The key is the connection of the “zero”, which is removed from the automatic machine. Its combination with other “nulls” of the electrical network is prohibited. This is explained by the difference in current values passing through each of the neutral conductors, which is why the differential machine can operate. - Reliable protection. This is an improved option for connecting a protective device, thanks to which it is possible to increase the reliability of the network and simplify the task of finding faults. The peculiarity is the installation of a separate difavtomat for each group of wires. Consequently, the protective device will only work in a situation where a problem occurs in the controlled section of the circuit. Other areas will continue to operate as normal. Unlike the previous scheme, it is much easier to find a fault in the event of a short circuit, leakage or overload in the network. But there is also a drawback - large financial costs associated with the need to purchase several automatic machines.
- Circuit without grounding. The options for connecting the difavtomat discussed above imply the presence of a protective “ground”. But in some houses or on a summer cottage there is no ground loop at all. In such networks, a single-phase network is used, where there is only a phase and a “zero”. In this situation, the protective device (AVDP) is connected according to a different principle.
If you also do not have a “ground” in your low-voltage network, it is advisable to completely change the wiring in the house before installing the difavtomat. Otherwise, there may be a leakage current in the network, which will trigger the RCD. - Scheme for 3-phase network. In cases where it is necessary to install a differential device in a three-phase circuit (for example, in a modern apartment, house or garage), an appropriate AVDP is required. The principle of construction here is the same as in the previous case. The difference is that four wires need to be connected at the input and output.
Specifications
The following technical characteristics of the machines can be distinguished:
- Operating current. The value of the current strength that, flowing through the automatic circuit breaker, does not cause it to operate.
- Time-current characteristic. Indicates the ratio of the actual current passed through the machine to its rated value. Characterizes the degree of sensitivity of the machine’s operation.
Switching operating leakage current. Available in ratings 10 mA, 30 mA, 100 mA, 300 mA, 500 mA.- Operating voltage. There are devices used to operate in an electrical network of 220 and 380 volts.
- Breaking capacity. Threshold value of short circuit current. The amount of current that a device can switch off without affecting its components. Marked on the front side in a rectangle, it has the values 3000 A, 4500 A, 6000 A, 10,000 A.
- Current limiting class. The value is determined by the speed of the device’s response to an emergency situation. Classification occurs in three classes, from 1 to 3. The device is marked in the middle of the square with a number corresponding to the class.
- Type of differential protection control. It can be electromechanical or electronic.
- Type of differential protection. It depends on what type of leakage current the machine operates with. AC type operates with a sinusoidal signal. Type A for sinusoidal and constant signal.
- Number of poles. Each pole is an input for a power line. The quantity depends on the type of network. Devices are available with a number of poles from two to four.
- Temperature Range. Most often used from -25 to +40 C. It is indicated by a snowflake on the device body.
For what reasons can a difavtomat work?
When using a protective device, it is important to understand in what cases it may operate.
Taking these nuances into account, it is worth making a decision about the cause of the problem (short circuit, leakage current, etc.).
Let's look at each option in more detail:
Tripping without load.
Older homes with poor wiring have serious insulation problems.
The latter is worn out and there is a high risk of leakage currents, the magnitude of which can vary taking into account many parameters - the presence of nearby animals, humidity level, and so on.
In such a situation, the AVDP may trigger falsely.
The cause of the problem may be:
- Damaged insulation;
- Presence of twists;
- Miscalculations in the location of distribution boxes;
- Electrical accessories.
To identify the cause, a wiring audit is required. You need to start with diagnosing the location of the damage.
For example, if the automatic switch goes off when the light bulb is turned on, the problem must be looked for in the lighting circuit.
If the AVDP is triggered after connecting some device to the outlet, you should make sure that this device is working properly.
When the “zero” and “ground” are short-circuited.
If for any reason the N and PE wires touch each other, there is a high risk of the differential circuit breaker tripping. Common places for short circuits are in the electrical box or in the outlet box.
Read on the topic - effective ways to protect electrical appliances using special devices.
The triggering logic is based on the operating principle of the device. If neutral and ground are combined, the current is split between the two conductors. Accordingly, there is no equality of currents in the differential transformer, and it perceives this fact as a leak.
This problem is often encountered by novice craftsmen who do not have the proper experience in servicing the automatic machine.
- At the moment the load is turned on. If the AVDP operates when the load is connected, the problem must be looked for in the insulation. It is unsafe to use wiring with such a fault, so it is recommended to call a specialist and deal with the problem. If you ignore it, there is a high risk of one of your family members becoming energized or causing a fire.
- During voltage surges . The logic of the difavtomat is designed in such a way that a shutdown can occur in the event of an increase in voltage. True, not all devices have this option, but only those with an electronic circuit. In addition, the protection can work during a short circuit inside the consumer, because the automatic circuit breaker can turn off in this type of accident.
Read on the topic - how electric current acts on the human body.