The massive replacement of incandescent lamps with LED lamps is due to the economic benefits of such a solution. Light Emitting Diodes (LED) provide high luminous efficiency (up to 150 lm/W) with significantly lower power consumption. The watts of incandescent and LED lamps differ greatly: for incandescent lamps it is 40 W, 60 W, 100 W, and for LED lamps it is 7 W, 9 W, 15 W, and it can be difficult to figure out what the correct ratio is between them.
We will tell you how to choose an LED lamp by power - after reading the article, the conversion will become clear to you, and you will be able to independently calculate what power of an LED lamp is suitable for a cafe, cottage, office, industrial or administrative building.
Simple calculation of the required luminous flux power of LED lamps
In this article we look at replacing incandescent lamps with E27 and E14 sockets. Conversion formula: to simply calculate the required power of an LED lamp, you need to divide the power of the incandescent lamp by 6.5.
That is, to replace a 60 W incandescent lamp with LED power, it can be calculated using the formula: 60/6.5=9. We need a 9 W LED lamp. And some manufacturers of high-quality lamps have enough 7 W.
There is an error in this formula, but as a first approximation it will give you approximate information about how much power LED light bulb you need. After reading the article to the end, you will understand what this error is associated with and why any recalculation will be approximate. 1. Luminous flux power - measured in lumens (Lm). This value indicates how bright the light bulb is. 2. Power consumption - measured in watts (W). This value means how much electricity the light bulb consumes from the network.
When replacing incandescent light bulbs with LED ones, a lamp with approximately the same luminous flux power (in lumens, Lm) is selected so that the illumination level does not deteriorate after replacement. And the electrical power consumed from the outlet (in watts, W) will become several times lower.
Factors due to which the recalculation will be inaccurate: 1. The luminous flux power of incandescent and LED lamp models with similar characteristics always differs from each other, up or down. 2. The luminous power or luminous flux indicated in the characteristics of LED lamps are correct only for high-quality bulbs. For cheap, low-quality products, these figures are far from reality.
Comparison of design features
The first models of lighting lamps using a tungsten filament to emit light appeared at the end of the 18th century. Structurally, an incandescent lamp has two terminals on the base, to which a filament is connected, which is connected in series to the electrical network.
Rice. 1: incandescent light bulb design
The operating principle of these lighting sources has not changed to this day:
- Air is pumped out of the glass flask to create an environment close to a vacuum;
- when a light flux voltage is applied to the filament, the fiber is heated to a red-hot state;
- Due to the absence of particles in the surrounding space that create an obstacle to the free exit of heated electrons, quite intense light radiation occurs.
Over more than a hundred years of use of this technology, only the shape of the design and the efficiency of the filament have changed.
The first LEDs, as a source of at least some visible light flux, appeared in the 60s of the last century. And only in the current century have they learned to assemble semiconductor elements into matrices for organized LED lighting.
Structurally, the LED lamp resembles the Ilyich lamp, but unlike the latter it contains:
- several semiconductor elements;
- capacitor;
- microcircuit (current stabilizer).
2: LED lamp design All these parts are located in a standard housing and are necessary for stable operation of the device. The principle of operation is based on the release of elementary particles when electric current passes through a pn junction.
Ratio of luminous power in watts of incandescent and LED lamps
A simple method for converting the power of LED lamps to incandescent lamps when replacing looks like this:
1. Find its luminous flux power in the technical characteristics of the old incandescent lamp. For example, for a 60 W incandescent light bulb it is 615 lm (the value may vary among different manufacturers).
2. View the luminous flux power of LED lamp models with a suitable E27 or E14 socket (luminous flux indicators may also differ between light bulbs from different manufacturers).
- A 7 W LED lamp has a luminous flux of 600 lm.
- Power 9 W – 720 lm.
- Power 10 W – 750 lm.
3. Select an LED lamp with a luminous flux power close to the required one. In this case, with some reserve, LED light bulbs with a power consumption of 8 W or 9 W are suitable for us.
Let's consider recalculation for other most common lamp powers.
A 100 W incandescent lamp has a luminous flux of 1360 lm. The nearest options for LED lamps:
- A 15 W LED bulb has a luminous flux of 1350 lm.
- A 20 W LED bulb has a luminous flux power of 1600 lm.
As a result, a 15 W LED bulb will be suitable to replace a 100 W incandescent lamp.
If we consider the correspondence in terms of luminous flux from LED lamps, we get:
- A 7 watt LED bulb is equivalent to a 40 watt incandescent bulb.
- A 10W LED bulb is equivalent to a 60W incandescent bulb (but produces a higher lumen output of 750 lumens versus 615 lumens for an incandescent bulb).
- A 15 watt LED bulb is equivalent to a 100 watt incandescent bulb.
For ease of selection, all options are summarized in a table that corresponds to the power of LED lamps compared to incandescent lamps.
Rules for choosing LED light sources
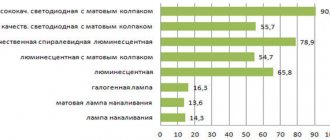
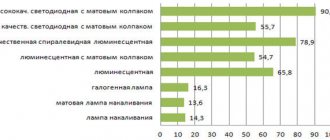
When purchasing LED H4 diodes, first always pay attention to Lumens, this indicator indicates what kind of luminous flux this device emits. For many years, we were guided only by how much energy (W) 36, 18, 60 or 100 an artificial light source consumed, without thinking about what their radiation was
Lumen is the light emission coefficient, which allows us to obtain information about how much lighting we will receive at the output.
Label for LED H4 lamps
What should be indicated on the packaging that contains the device and what should the user take into account when choosing a lighting source, how is this indicator measured?
The Federal Trade Commission, for the convenience of consumers and to understand the difference between Watts and Lumens, has proposed a new label for new generation light sources. This label will allow people to purchase the devices they need (18, 36, 60). Just like a simple label placed on food products, packaging for lighting products will make users aware of what they are purchasing. The new label indicates: the type of bulb, the radiation, the cost of using the device per year and the shade of the glow from warm white (with a slight yellowish glow) to cool white (with a blue glow).
Table of correspondence between the power of LED lamps and incandescent lamps
| № | Incandescent lamps | LED bulbs | ||
| Power consumption (W) | Luminous flux power (lm) | Power consumption (W) | Luminous flux power (lm) | |
| 1 | 25 | 300 | 360 | 4 |
| 2 | 40 | 580 | 600 | 7 |
| 3 | 60 | 615 | 720 | 9 |
| 4 | 75 | 935 | 990 | 11 |
| 5 | 95 | 1250 | 1150 | 13 |
| 6 | 100 | 1360 | 1350 | 15 |
| 7 | 150 | 2150 | 2700 | 30 |
| 8 | 200 | 2950 | 4700 | 50 |
The table shows the luminous flux power indicators of lamps presented in the retail network. It is recommended to clarify these indicators according to the technical characteristics of the manufacturer of the lamps you are using or intend to buy.
Let's look at a couple of examples of selecting the power of LED lamps using this table.
A 75 W incandescent lamp provides a luminous flux of 935 lm. According to the table, the closest in brightness will be an 11 W LED lamp, giving a luminous flux of 990 lm. To select a replacement for a 100 W incandescent lamp, we determine its luminous flux: it is equal to 1360 lm. We are looking for an LED lamp with a similar luminous flux power: an LED lamp producing a luminous flux of 1350 lm has a power consumption of 15 W.
DRL and DNAT
In industrial and street lighting, DRL and DNAT lamps are used, which have decent light output. With such high power consumption, the E40, E40 base is used.
- DNAT is sodium arc tubular;
- DRL is a mercury arc fluorescent.
Their lm/watt efficiency is at the level of simple LEDs, but their service life is 3-4 times lower. In addition, light output decreases faster than with LED lighting.
Table of analogues for sodium
| DNAT | LED analogue | Lumens |
| DNAT 70 | 50W | 4.600 |
| DNAT 100 | 75W | 7.300 |
| DNAT 150 | 110W | 11.000 |
| DNAT 250 | 190W | 19.000 |
| DNAT 400 | 350W | 35.000 |
Table of analogues for mercury
| DRL | LED analogue | Lumens |
| DRL 125 | 65W | 6000 |
| DRL 250 | 150W | 13000 |
| DRL 400 | 250W | 23000 |
| DRL 700 | 450W | 40000 |
| DRL 1000 | 600W | 58000 |
Modern LED analogues of lamps with good diodes, for example Osram Duris, have a service life of about 100,000 hours. The power supply will fail faster than the LED chips. A good power supply (driver, converter) with Japanese components lasts up to 70,000 hours. Much depends on the capacitors, which lose their capacity and the power parameters of the LEDs change.
Luminous output and differences in the operating principle of incandescent and LED lamps
As you can see, incandescent lamps at similar brightness, that is, luminous flux power, consume more energy. The ratio of power consumption to luminous flux power is called luminous efficiency, which is measured in W/lm (watts per lumen).
Luminous efficiency is an indicator of the efficiency of lamps, indicating how many watts of electrical power need to be spent to obtain a unit of brightness of its glow. A 60 W incandescent lamp has a luminous efficiency of 10 W/lm. Its analogue, a 9 W LED lamp, has a luminous efficiency of 80 W/lm. As you can see, the luminous efficiency of incandescent lamps is several times less than the luminous efficiency of LED lamps. This LED lamp is 8 times more economical than an incandescent lamp.
Why is there such a difference? This is due to the differences in the operating principle of incandescent lamps and LED lamps.
| The glow of incandescent lamps is caused by a hot filament in a vacuum in a glass bulb. Heat is the cause of large energy losses in incandescent lamps. | The glow of LED lamps occurs due to photoemission, the optical emission of LEDs when current is passed through. LEDs heat up much less, and they also have less energy loss. |
Conclusion
LED lighting systems are rapidly replacing incandescent lamps and energy-saving elements from the market. The economics of operating LEDs outweigh even the higher investment costs due to low energy consumption and long service life. The payback period for new lamps is several months, and prices for LED lamps are constantly falling as technology develops. This also makes the payback period even shorter.
Energy-saving lamps have lost the competition due to low environmental friendliness and difficulties with disposal. In the coming years, we can expect complete dominance of LED equipment in the lighting market.
Why do you need to replace incandescent lamps with LEDs?
The main reasons why incandescent lamps are replaced with LED ones:
- energy savings: LED lamps consume several times less electricity than incandescent lamps.
- service life and replacement frequency: LED lamps have a much longer service life, and they can be changed less often: - incandescent light bulbs - up to 1000 hours, - LED light bulbs - 20,000-50,000 hours.
Lamp life may vary among individual manufacturers depending on the quality of components used and manufacturing.
The advantages and disadvantages of LED lighting are discussed in more detail in this article. We hope that from this article you learned how to calculate the power of LED lamps when replacing incandescent lamps. If you have any questions about choosing or using LED lamps, call: +7.
Disadvantages of diodes
Much has already been written about the advantages of the product, but diodes also have some disadvantages. Let's look at them in more detail:
- Price. Diode lamps cost up to 10 times more than spiral lamps. However, you should keep in mind the same energy savings.
- Big sizes. Diode lighting devices are superior to competitive markings in all dimensional parameters.
- Not every lamp can be replaced. For example, candles with an E14 base element with a power of 60W, it is simply impossible to choose the most worthy analogue. There may not be physically enough space to install the required radiator, but installing a smaller version may lead to overheating.
The most common complaint is the specific direction of the rays. Light fluxes are directional in nature. The rays do not illuminate the side elements well; light travels best along a parallel plane.
- Color rendition. Color rendering parameters reach 80. Only spiral devices and natural lighting have a higher value.
The disadvantage is that when a powerful product is working, its color barrier is “eaten up”, resulting in a shade mixed with the colors of the interior.
VIDEO: Comparison of LED lamps
general information
The white LEDs that are used today first appeared in 1996. However, only in 2005 they began to be used specifically as a lighting source. This type of light bulb is energy saving.
The luminous power of LED lamps is their main characteristic . It shows the energy efficiency of this type of lighting. The power of LED lamps is measured in watts. Manufacturers are gradually trying to increase the quality of the glow without changing their power. That is why the consumer receives a high-quality lighting source, but at the same time saves energy. For comparison, you can use an incandescent light bulb with a rating of 100 W. A LED with the same level of illumination will have only 12 W.
How to recycle lamps?
Many electrical appliances require special disposal. For example, fluorescent, sodium, halogen and metal halide devices contain mercury, which is harmful to nature and human health. Therefore, they cannot be disposed of as household waste by simply throwing them in the trash. They should be taken to special recycling centers.
LED lamps, classic and retro incandescent lamps do not contain mercury and other harmful substances. Therefore, they can be thrown into solid waste bins.
Advice! Although LEDs and incandescent bulbs are safe, you can recycle them in a way that is good for nature. To do this, hand over broken lamps to a recycling and recycling facility.
Types of diode light bulbs
The first criterion for dividing is the material of the case:
- Glass (frosted or transparent);
- Aluminum;
- Plastic;
- Ceramics.
By type of base:
- Screw (letter designation – E);
- Pin (letter designation - G).
Thus, the following types of LEDs can be distinguished:
- E14 (bulbs with a smaller diameter base, suitable for some lamps);
- E27 (regular, which are suitable for installation, for example, in chandeliers, where the socket is designed for incandescent light bulbs);
- G4 (can be used, for example, to illuminate pictures).
- GU5.3, G9 (replacement for halogen bulbs);
- GU10 (used for built-in lamps that serve as lighting, as well as in hoods);
This list shows only the main types.
Measuring stand
What measuring instruments I used: lux meter and adapted built-in tester.
The photo studio lamp is turned on through a tester, which shows the power consumed by the light bulb (voltage and current as well). A meter from the lamp on the sofa there is a photodetector and a TASI lux meter. The lux meter shows the illumination. The lamp is installed. We screw in the lamp, measure the illumination a meter from the lamp and the power consumption. Photo by the author The photodetector is positioned so that the light rays fall on it perpendicularly. The illumination is measured directly under the light bulb.
Photodetector and luxmeter. On the luxmeter display we see the illumination given by the tested light bulb at a distance of 1 m. Photo by the author
It is impossible to measure the luminous flux produced by a light bulb at home without special equipment. Therefore, I made the assumption that the strength of the luminous flux is proportional to the illumination. In any case, I will be able to compare the illumination provided by an incandescent lamp with the illumination of its LED counterpart.