A lamp is an artificial light source. Main components: working element (filament body, electrodes, LEDs), base and bulb.
- Incandescent lamp
Halogen lamp- Fluorescent Lamp
LED lamp
View
Incandescent lamp - the main working element is a filament body (usually a tungsten filament) placed in a flask with inert gases. Another name is LON (“general purpose lamp”).
An incandescent lamp is cheap, insensitive to high and low temperatures, resistant to condensation, but consumes a lot of energy at the lowest light output (converts electricity not only into light, but also into heat). This lamp is an outdated option, which is gradually being replaced by more modern models.
Scope of application: household lighting devices, as well as short-term operation in difficult weather conditions (high temperature, frost, high humidity).
Halogen is a type of incandescent lamp. The bulb of such a lamp is filled with gas containing iodine or bromine, which reduces the evaporation of tungsten, therefore increasing its service life. The halogen lamp is compact and provides good color rendering. At the same time, such a lamp is expensive, has high energy consumption and gets very hot.
Scope of application: vehicles (headlights), lighting devices (spotlights, ramps), lighting for photo, video and film shooting, interior design.
Important: The halogen lamp needs to be handled with care during installation as it is sensitive to grease. Even small stains of grease from the skin of the hands cause uneven heating of the lamp, as a result of which it quickly burns out. Gloves or a special suction cup will help solve this problem.
Luminescent - has a tube coated on the inside with a layer of a luminous substance (luminophore) and filled with mercury vapor. When mercury vapor is exposed to an electric discharge, UV radiation is generated, which the phosphor converts into visible light.
The fluorescent lamp is characterized by low energy consumption and long service life. Cons: high price, uneven color rendering, toxicity (due to the presence of mercury).
Scope of application: enterprises, public institutions (schools, offices, hospitals). Such lamps are widely used for lighting apartments.
There are two types of fluorescent lamps:
- compact - lamps with a curved tube (for home);
- flask - made in the form of a straight tube (for offices, shops).
Important: fluorescent light bulbs are disposed of only at special points. If a lamp breaks in a room, you should ventilate the room, then collect the fragments and do a wet cleaning (use products containing chlorine).
LED LED – the main element of such a lamp is LEDs. This lamp is distinguished by even lower energy consumption, the longest service life, and good color rendition. In addition, the LED bulb is shock-resistant and hardly heats up during operation. The main disadvantages are high cost and uneven lighting.
- Smart LED - equipped with a Wi-Fi or Bluetooth module, which allows you to control operating parameters using a smartphone or other mobile device. The user can adjust the brightness and color of the glow, connect the light bulb to the smart home system and light music (color music), and adjust gradual attenuation. These bulbs are more expensive than “regular” LED models.
LED filament - in appearance it resembles an incandescent lamp, and its bulb is also filled with an inert gas. But such a lamp consumes much less electricity and lasts longer. Compared to a conventional LED model, this lamp produces light that is more comfortable for the eyes and provides uniform illumination with reduced power consumption.
Filament lamps are available in a wide range of shapes and sizes, which allows you to choose the best option for classic and modern interiors. The disadvantage is the high price.
LED RGB – equipped with colored LEDs – red, green, blue (RGB), which makes it possible to adjust the color of the lighting. Such light bulbs will be expensive.
LED strip - unlike the previous type, it has a chain of LEDs, reminiscent of a tungsten spiral in incandescent lamps. Thanks to this, the LED strip provides uniform illumination.
Important: fluorescent and LED models are energy-saving lamps.
Types of lamps
Let us dwell on the types of light sources and their performance characteristics in more detail.
With filaments
Incandescent lamps have been known for almost 150 years. The invention was first patented in 1872. As power plants were built, power lines and self-contained generators spread even to remote communities, people came to appreciate light bulbs. The replacement of dangerous and inconvenient kerosene stoves, oil lamps, gas burners and candles with electric lamps revolutionized the way of life. People were able to fully engage in work and study in the evenings and at night, soot on ceilings and walls disappeared, and the number of fires decreased.
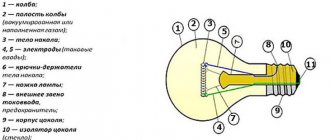
Filament light bulbs consist of:
- a glass flask from which air is pumped out to a vacuum;
- metal base with soldered contacts;
- a tungsten spiral that heats up to 29,000 Celsius under the influence of current.
The products give off a yellowish light. It distorts color perception, adding a fair amount of the yellow spectrum to the surrounding environment. But it creates a feeling of home and comfort. That is why many consumers give preference to this type of lamps, without changing family traditions.
Like any electrical appliance, incandescent lamps have their pros and cons.
- The simplest design and proven production technologies determine the low cost. Products are available for everyone.
- When turned on, the lamps light up instantly, without pause.
- They provide an even light that is comfortable for the eyes, without flickering and not too bright unless you look at the filament itself.
- The durability of products is practically not affected by current fluctuations in the electrical network. You should only beware of sudden changes in filament resistance when the lamp is turned on. If you install a dimmer that provides smooth switching, these bulbs will last much longer.
- The products are highly resistant to environmental influences - high and low temperatures, humidity. They can be used for street lighting, in bathrooms, saunas, and kitchens.
Customers are offered a variety of shapes and sizes of flasks, types of bases. In addition, lamps with colored and frosted bulbs, mirrored and transparent, are sold. They also differ in power, from weak, 5 W, to bright, 200 W.
Now let's look at the disadvantages:
- incandescent lamps have the shortest service life - only about 1 thousand hours;
- with increased energy intensity (this is the most “gluttonous” type available), most of the energy is spent on thermal infrared radiation. The luminous efficiency of the products is very low;
- During operation, both the bulb and the base with the cartridge become very hot. Their temperature reaches 1800. Accordingly, the risk of fires, short circuits, and melting of plastic elements increases. It is not recommended to make luminaires with such lamps from fire hazardous materials. And also install with suspended or suspended ceilings.
Despite their low efficiency and high energy consumption, incandescent lamps are still popular. They are readily installed in bathrooms, storerooms and sheds, in corridors and boiler rooms. That is, where artificial lighting is required from time to time.
Halogen lamps
Strictly speaking, halogen models differ little in design from incandescent lamps known to everyone. They have the same base with a contact, electrodes and a tungsten filament sealed in a bulb. The main difference between the products is the inert gas, halogen, which is pumped inside the flask.
Thanks to this design solution, halogen lamps have a number of undoubted advantages:
- product service life increased to 4000 hours;
- Light output has also become greater, doubling, and energy consumption has decreased. That is, compared to traditional incandescent lamps, halogen lamps have greater efficiency;
- In addition to standard and large-sized models, miniature light bulbs are produced for small devices and flashlights;
- You can choose from products with flasks of different shapes - pear-shaped, in the form of candles and elongated cylinders, reflectors.
Not without its drawbacks:
- Just like traditional light bulbs, halogen light bulbs get very hot. They cannot be installed on suspended ceilings or screwed into lamps with paper, fabric, or down lampshades, to avoid fire;
- this type of product is extremely sensitive to voltage drops, so experts recommend using them in conjunction with stabilizers;
- During installation and operation, the surface of the flask must not be touched with unprotected fingers, only with clean cotton gloves or wrapped in a napkin. Grease stains remaining after such touches lead to rapid burnout.
Not everyone likes the bright, intense light of halogen lamps. Especially if they are installed as central lighting in cozy living rooms or bedrooms. But they are irreplaceable as lighting for cabinets, shelving, and work surfaces. They can illuminate a collection of rarities and interesting things, since the lamps have a high color rendering index and almost do not distort natural colors.
Luminescent
The operating principle of fluorescent lamps (CFLs) was discovered back in 1856. It was then that the first gas-discharge flasks appeared, glowing green under the influence of electric current. Later, the inner surface of the tubes began to be coated with a phosphor containing phosphorus. The familiar bright white light of the lamp was achieved in 1926, thanks to the research of E. Germer. The first lamps looked like oblong tubes with contacts on both sides. And only in 1984, a compact fluorescent lamp with built-in electronic control gear, which is often called energy-saving, was patented. This is not an entirely accurate definition, since reduced energy consumption is also typical for products operating on other principles.
What are the advantages of the products?
- Excellent light output to power consumption ratio. The efficiency of fluorescent products is five times higher than that of incandescent lamps. That is, with a power of 15 W, the device shines like a 75-watt light bulb with a tungsten filament.
- They have a high color rendering index, practically without distorting the shades of surrounding things, finishing materials, fabrics, and decor.
- The service life can be up to 10 thousand hours of continuous operation. However, constant switching on and off quickly damages the product.
- All the energy is spent on creating a luminous flux, so the products hardly heat up. They are fireproof, can be installed with suspended ceilings, and used in lamps with decorative lampshades.
- They feature minimal energy consumption, which means they are economical.
Minuses:
- products operate correctly only at a certain ambient temperature - 18-250 C. That is, they can only be used in heated rooms or in summer. If the thermometer drops below 100 degrees Celsius, the lamps stop working;
- Since mercury vapor and phosphorus are used in the production of lamps, they require careful handling. They are disposed of only at special stations, like mercury thermometers;
- the lamps produce a distinctly flickering light that is tiresome to the eyes. Additionally, the built-in choke may be noisy.
Such lamps are good for lighting work rooms and illuminating corridors.
LEDs
LED lamps became available to the general consumer only at the beginning of the 21st century. Previously, LEDs were used only for street advertising or traffic control, medical equipment and electronics. According to their characteristics, LED lamps are recognized record holders:
- maximum efficiency. With a power of 10 W, the product is equivalent to a 100-watt incandescent lamp;
- average service life is 30-50 thousand hours;
- the devices practically do not heat up, so there is no risk of fire, even if paper or fluff gets on the flask;
- resistance to mechanical damage and shock;
- work at sub-zero temperatures and extreme heat, tolerate high humidity well;
- you can choose any spectrum of light, from piercing bluish to soft yellowish and colorful;
- a huge selection of shapes, sizes and power - from the usual pear-shaped ones to LED strips.
What are the disadvantages of LED lamps?
- The main disadvantage limiting widespread distribution is the high cost. However, this is compensated by a long service life.
- LEDs produce a luminous flux directed forward in the form of a cone. The space behind is not illuminated at all, and on the sides - only partially. Therefore, for diffuse lighting it is necessary to use filters.
This is an ideal type of lamp for street and home lighting. Suitable for any premises: living rooms, technical rooms, bedrooms, kitchens.
Flask
Bulb is a lamp body made of transparent or translucent material (glass, etc.). Marking: the number next to the name of the flask indicates the diameter (mm). The exception is the MR type, where the number indicates a size of 1/8 inch.
Form
A (“pear”) is the standard option that is most common. The most common bulbs are A55; A60; A67.
B and C (“candle”) – used in decorative lighting fixtures, chandeliers, wall sconces. B35 bulbs are common; C35; C37.
- BA and CA (“candle in the wind”).
- CW (“twisted candle”).
F (“torch”) – slightly different from the “candle” in shape and has a larger size.
G (“ball”) – resembles a “pear”, but provides a larger radius of illumination. The most commonly found bulbs on sale are G45; G60; G80.
R (“reflector”) – used for spot or concentrated lighting (tracking lights, for suspended or suspended ceilings). The most common lamps are R39; R50; R63.
- MR (“multifaceted reflector”) - differs from the previous version in shape, is equipped with a pin rather than a screw base, and is used in 12/24 V lamps.
T (“tube”) – used in bulb fluorescent lamps and some LED models. Typically T3 lamps are used; T4; T20; T30; T37.
JC – used in ceiling lamps.
Color
Transparent - gives the brightest and sharpest light. This option is suitable for crystal chandeliers, lamps with transparent shades, faceted parts or pendants.
Matte – reduces brightness, providing softer light. This solution is ideal for children's rooms and matte lampshades.
Colored - produces colored light, used to solve decorative problems, for example, artistic lighting.
Auxiliary criteria
Ceiling lamp
If you are used to using an intricate lampshade or a carved lampshade, think about what percentage of light distortion they will introduce: both in the color of the glow and in the illumination. One way or another, in this context the lampshade acts as an optical filter. The overall appearance of the room depends on whether it is matte, transparent or colored. Depending on whether the lampshade is single or multi-colored - there is a rainbow on the walls. Finally, the material itself from which it is made sets the overall tone of the interior.
Let's imagine that a light bulb with warm light, level 2700 K in color temperature, is installed in a traditional dark beige or yellow lampshade. In this case, the room will be flooded with a “concentrated” warm glow, causing suffocation rather than pleasant warmth. You especially shouldn’t take such risks in the country house or in the kitchen. Unpleasant sensations are guaranteed for you.
A classic crystal chandelier or simply a transparent lamp harmonizes best with transparent light bulbs. The whole point of such lighting devices is precisely in the play of light, and if you put a matte lamp there, the entire desired effect will be lost.
At the same time, a coated light bulb will fit under the matte lampshade. It will immediately scatter the light and will never blind a person in those places where the lampshade itself should be visible through.
Let's not devote too much time to lamps for other places in the apartment. We believe that the basic principle is clear - the light bulb and the lamp must be combined with each other and not cause either aesthetic or physical discomfort to a person.
Base
It’s a little funny to dwell on this criterion, but often buyers take light bulbs from the shelves after reading all the main characteristics and completely forgetting about the type of base. It is all the more interesting that such consumers know exactly the desired color temperature, the required luminous flux, checked the color rendering index in advance, and also inquired about other products from the same manufacturer as the selected product. And only when checking the light bulb at the checkout it turns out that you should have taken the exact same lamp from a nearby rack, but with a different base.
Therefore, let us remind you: the most common base in our country is E27. The overwhelming majority of light bulbs use it. This standard threaded connection is one of the simplest and most reliable at the same time.
In second place is the so-called “minion”, or E14. The socket for it is often installed in sconces and small lamps. However, sometimes the latter type can be found in ordinary ceiling chandeliers. Here it is used to add additional lightness and elegance to the structure.
Sometimes you come across lamps with very small base diameters (E5, E10, E12) or, conversely, larger ones (E40), which are not used in everyday life and are used exclusively for street lighting. However, their scope of application is extremely limited and the consumer is unlikely to be deceived when choosing a light bulb for them.
From time to time, in European-made chandeliers you can also see sockets for a pin base. It is absolutely impossible to forget that you have a pin rather than a threaded connection, but it is quite possible to be deceived by their diversity, even though the choice of lamps for such sockets is significantly smaller (the main ones are , , GU5.3). Sometimes, if you really like a chandelier, it makes sense to even replace the original socket with a more common one and never have to worry about searching for specific light bulbs in the future.
Price
No one has canceled the price factor, but every prudent owner understands: a quality item cannot be too cheap. It’s better to buy a good light bulb once, and then forget about the need to replace it for five to seven years.
We are mainly talking, of course, about modern LED lamps from well-known global manufacturers. If we talk about the long-term perspective of using different types of light bulbs, this type will show the greatest savings, and the usual and beloved incandescent light bulbs will show the greatest wastefulness in relation to your family budget.
Base
The socket is a part of the lamp designed to be fixed in the lamp socket and supply current to it. For normal operation of the lighting fixture, the socket must match the lamp base. Different types of base are not compatible with each other.
The letter in the designation indicates the type of base, and the number indicates its diameter (E) or the distance between the contacts (G) in mm.
E (screw, Edison screw) is the most common option used in household lighting fixtures.
- E40 – for powerful industrial luminaires and street lighting.
- E27 (regular, standard) - for lighting devices designed for 200 V (floor lamps, chandeliers, often sconces and table lamps). Found in lamps with bulbs A, C, F, R63.
- E14 (minion) – for miniature lamps, for example, small chandeliers. Used with flasks C, F, R.
G (pin) – used in halogen and fluorescent lamps (spotlights for walls or suspended ceilings).
- G4 – for small halogen lamps (with JC bulbs).
- G5 – for fluorescent tubular lamps.
- G9 – for 220 V halogen lamps and decorative lamps. Found in lamps with JC bulbs; T5; T8; T12.
- 2G11 – for compact fluorescent lamps.
- GU – for energy-saving lamps (the most common is GU5.3). Used with MR11 and MR16 flasks.
Important: in order not to make a mistake in choosing the right light bulb, since type G models are very diverse, take a burnt-out lamp with you.
R7s (with recessed contact) - used in high-power quartz halogen lamps (high intensity lamp).
In addition to these types, there are light bulbs with base B (pin), P (focusing), S (spot). They are used quite rarely.
Chandelier height and ceiling height
To determine the allowable height of a chandelier for your living room, use the max. height of the chandelier.
Remember that the length of the chain can be adjusted, but the stationary leg cannot be made smaller. Therefore, check the dimensions several times.
After hanging the chandelier, the remaining height is the distance from the bottom of the structure to the floor.
As a standard, 190 cm from the bottom of the chandelier to the floor is considered comfortable. The formula is this: ceiling height - 190 cm = maximum length of the chandelier. This way, you won’t hit the top of your head on the chandelier or accidentally knock it over with your hand.
How to calculate the height of a chandelier + diagram
Another way to calculate the allowable length of a chandelier is to focus on the height of the doorway, which is approximately 2 meters. Those. choose a chandelier no lower than the top of the doorway.
But it’s better not to trust formulas and standard values, but to try on a chandelier for yourself, taking into account personal preferences, the height of the tallest family member, the area and height of the ceilings, etc.
A chandelier cannot be a single light source; complement the functional areas with sconces, floor lamps, accent lamps, etc.
190 cm or the height of the doorway - exactly this amount of free ceiling height should remain after installing the chandelier.
Low ceilings - below 2.5 m
Select the light for the room according to the furniture arrangement plan, taking into account all sizes. The diagram will immediately show what you are dealing with and which segment of chandeliers you should not waste time on.
Ceiling chandelier in a small living room with a low ceiling
High ceilings - more than 3 m
For high ceilings, classic multi-lamp chandeliers on a leg, from 60 cm and above, are suitable. As well as designer asymmetrical designs.
Remember, high ceilings “eat up” light, so the power of light bulbs is increased by 1.5 times the recommended standard power.
Designer asymmetrical chandelier in a large living room with a high ceiling
Expert opinion
Viktor Pavlovich Strebizh, lighting and electrical expert
Any questions ask me, I will help!
Such lighting elements are very diverse in shape and size, due to which they are capable of creating unique effects. If there is something you don’t understand, write to me!
Power consumption
Using this parameter, the efficiency of the light bulb is assessed: the lower the value, the less energy the lamp consumes. In addition, the brightness of the lamp also depends on the power.
Important: different types of lamps differ in brightness, even if they consume the same amount of energy.
To choose the right lamp based on power consumption, consider the size of the room:
- 100 W – small room;
- 120-150 W – medium-sized room;
- 150 W and above – spacious room.
Maximum permissible power of lighting lamps:
- 25 W – night lights;
- 150 W – decorative and spotlights;
- 180 W – mixed lighting fixtures;
- 550 W – general lighting fixtures.
Incandescent, halogen, energy saving or LED bulbs?
Among all electrical installation products, lighting lamps are perhaps the most common and frequently used product in everyday life. However, without paying due attention to the choice of light bulbs, it may turn out that in some cases the lighting turns out to be completely inappropriate, depressing, or, conversely, too cheerful and cheerful for a particular room. How to choose lighting lamps? Differences in lamp types Incandescent lamp Halogen lamp Energy-saving lamp LED lamp Some features of choosing LED lamps Correspondence of incandescent, energy-saving and LED lamps in terms of power Conclusion Which lamps are more profitable to use What savings are obtained from upgrading lighting What is the payback period after replacing incandescent lamps Replacing energy-saving lamps with LED lamps
Colorful temperature
This parameter indicates the color of the lamp (“cold” or “warm” shades). Color temperature is measured in kelvins (K). The higher this value, the “colder” the shade of the lamp light.
Incandescent lamp:
- 2200 K – 40 W lamp;
- 2680 K – 60 W lamp;
- 2800 K – 100 W lamp;
- 3000 K – 200 W lamp, halogen lamp.
Fluorescent and LED lamps:
- 2700-3000 K – “warm” white color;
- 3000-3500 K – “a little warmer than average”;
- 3500-4500 K – neutral white (4500 K – daylight);
- 4500 K and above are “cold” tones of white.
Important: the color temperature cannot be used to judge the color rendering quality of a particular lamp, since this quality is largely determined by its design.
The colors of the glow are selected depending on the style of the room, tasks and individual preferences of the user. For classic styles, it is advisable to use lamps with “warm” tones, and for high-tech – cooler ones. “Warm” shades of light help you relax, while “cold” shades help you concentrate.
Scattering angle
Due to the design features of the lamp, different models may diffuse light differently. In order to form the required direction, various auxiliary optics are often used (matte polycarbonate bulbs, focusing/scattering lenses, etc.).
The angle of illumination of objects really plays a significant role in the feeling of comfort in a room. The higher it is, the larger the area your lamp will be able to illuminate. This indicator is standardized at the official level for various types of activities. For example, a workplace should be illuminated no less than 27°, and a large room should be illuminated no less than 120-130°.
But not all types of lamps are able to provide the required values. The same halogens are limited to 32-38°, which will automatically require the installation of a large number of lamps within one room for overhead lighting. At the same time, the range of operation of LED lamps is much wider. Their range is divided into several parts. Some models are great for directional light and are installed in the makeup area, near the workplace or computer. Others are suitable for illuminating spacious rooms. Among them there are lamps with a lighting angle of over 270°, which allows the most daring ideas of designers to be realized when designing an interior.
In LED lamps, manufacturers can specifically position the diodes so that they emit light in different directions. The leading role in this regard is played by the technology of the light bulb: SMD or filament. For the first type, the determining criterion will be the direction of the LED. It emits a luminous flux solely depending on it, and is not able to cover large spaces. At the same time, according to filament technology, the emitting element is a sandwich consisting of a substrate, LEDs and a phosphor fill. Since the light emitted by the source will in any case reach the phosphor, the limitations associated with the scattering angle are not important for this type of light bulb.
As a technical indicator, the scattering angle value indicates the range in which at least 50% of the maximum amount of light emitted by the lamp is present. Some companies provide a simplified diagram with a visual representation of the direction of the light flux directly on the packaging of their products. The classification of such diagrams is presented in GOSTs: the traditional one is divided into 7 types, but with in-depth study it is much more extensive.
When properly designing indoor lighting, it is the dispersion angle that serves as the key zoning factor:
- to illuminate individual objects or small spaces, light sources with an angle of 30° or 60° are used;
- for overhead light of uniform saturation in large rooms - lamps with a wide angle - 140°, 160° or 180°;
- To solve individual lighting problems, lighting devices with different suspension heights can be used.
It should be noted that the selection of a light bulb for it will also depend on the design of the lamp itself. If you have a lampshade of complex shape, with overlap areas or made of dense material, part of the light flux will inevitably be lost. In addition, the very direction of the lampshade orients the luminous flux, and its elongated shape can slightly narrow the illuminated range. In each specific case, it is necessary to analyze such nuances and select a light bulb taking into account as much information as possible about the lamp, as well as the illumination required for a given zone.
Color rendering index
Color rendition is the correspondence of the natural color of an object to its apparent color when illuminated by a certain light source. The higher this index, the better the colors of the illuminated object are reproduced. To measure the level of color rendering, the index (Ra) is used:
- incandescent and halogen lamps – 100;
- fluorescent lamp – 80-90;
- LED lamp – from 80.
Ra over 90 is considered very good color rendering (grade 1A), Ra 80-89 is considered very good (grade 1B), Ra 70-79 is good (grade 2A), Ra 60-69 is good (grade 2B). Ra 40-59 – mediocre (grade 3), Ra 39 and below – bad (grade 4).
Characteristics and types of light bulbs for the home
The most common types of household lighting devices include:
- incandescent lamps;
- luminescent sources;
- LED bulbs.
Incandescent lamps
Incandescent lamps.
Incandescent lamps are now gradually being replaced from the market by more advanced lighting devices. However, in some cases they remain useful. In particular, such a source can be placed in a public place that is rarely visited.
Pros:
- stability of the glow even with voltage fluctuations;
- lighting close to natural;
- availability;
- the design does not contain harmful components.
Minuses:
- small resource;
- fragile design;
- gradual decrease in light intensity;
- High power models are hard to find.
Luminescent elements
Fluorescent lighting sources.
These are universal energy-saving lighting devices that can be installed in any room. A feature of such equipment is its increased sensitivity to the number of switches on and off per day. It is best to turn on the lamp once and use it for a long time.
Pros:
- long service life of at least 2000 hours;
- increased light output compared to incandescent lamps;
- economical energy consumption.
Minuses:
- include dangerous components that can cause a lot of trouble if leaked;
- with prolonged use, the light intensity gradually decreases;
- operation requires ballasts;
- fragility;
- high price.
LED bulbs
LED light sources.
LED lighting sources seem to be the most modern, completely devoid of the shortcomings of their predecessors. They are not suitable for streets, but they show their best side in houses.
Advanced LED devices boast a spectrum that is as close as possible to sunlight. The flow created is enough for work, rest and other activities.
Pros:
- very high resource from 35,000 to 70,000 hours;
- economical energy consumption;
- convenience.
Minuses:
- high cost of models;
- light differs significantly from daylight, which leads to sleep disturbances and other problems.
Brightness
This characteristic is determined by the luminous flux produced by the lamp in normal mode. Luminous flux is measured in lumens (lm). The higher this parameter, the more space the light bulb can illuminate with high quality. At the same time, as brightness increases, energy consumption and the price of the lamp itself increase. Yes, and very bright light has a negative effect on the eyes and causes fatigue.
Power to brightness ratio.
Incandescent lamp:
- 20 W – 250 lm;
- 40 W – 400 lm;
- 60 W – 700 lm;
- 75 W – 900 lm;
- 100 W – 1200 lm;
- 150 W – 1800 lm;
- 200 W – 2500 lm.
Fluorescent Lamp:
- 5-7 W – 250 lm;
- 10-13 W – 400 lm;
- 15-16 W – 700 lm;
- 18-20 W – 900 lm;
- 25-30 W – 1200 lm;
- 40-50 W – 1800 lm;
- 60-80 W – 2500 lm.
LED lamp:
- 2-3 W – 250 lm;
- 4-5 W – 400 lm;
- 8-10 W – 700 lm;
- 10-12 W – 900 lm;
- 12-15 W – 1200 lm;
- 18-20 W – 1800 lm;
- 25-30 W – 2500 lm.
Types of LED light sources
LED lamps are divided into several groups - according to intensity, type of base and other characteristics.
Intensity compared to incandescent lamps:
- The 25-watt incandescent lamp is replaced by one 5.5-watt LED;
- 40 V - 8 W;
- 70-90 W - 15.
The most important characteristic of any light bulb is the base. LED products have the following types:
- pin G9;
- standard E27;
- E14.
- G4 for small light bulbs used in lighting;
- GU10 for spotlights;
- GU5.3 for chandeliers.
The most common bases are E27 and E14. They are similar, but with different thread diameters.
Life time
Manufacturers indicate lamp life under ideal conditions. Practice shows that this parameter is influenced by the build quality of the lighting device, the stability of the rated voltage, the quality of wire switching, humidity and ambient temperature and some other factors.
- incandescent lamp - 1000 hours (six months), some lamps have a longer life - 3000 hours;
- halogen lamp – 2000-4000 hours;
- fluorescent lamp - 15,000-20,000 hours;
- LED lamp – 50,000 hours.
LED bulbs
These are the most economical lamps to date. The efficiency of an LED lamp is 10 times higher than an incandescent lamp. In terms of service life, this is the most durable lamp and, undoubtedly, the most expensive.
Economical lamps
Such a lamp is constructed from a semiconductor device that produces light in the presence of a constant electric current. A distinctive feature of the LED lamp is the change from alternating electric current to direct current with minimal losses in heat generation, which explains the cost-effectiveness and safety of such lamps.
When choosing an LED, keep in mind that there are two main types of bulbs - matte and transparent. Matte type LEDs have a more diffused light, while transparent type LEDs are brighter, which will be ideal for a crystal chandelier.
When purchasing such a lamp, you should remember that only high-quality LEDs will meet the electricity consumption parameters stated on the packaging. LEDs produced in China have the same efficiency as a fluorescent lamp.
If you have decided to equip your home with LED light bulbs, you need to make the right choice. LED light bulbs have a large number of parameters that affect energy savings, lighting comfort, product costs, etc.
The main ones are:
- luminous flux of products
- scattering angle
- manufacturer
- power
- type of base.
Power
This is the most significant characteristic for buyers. The economical side of lighting depends on the number of watts consumed.
It is important to know that when replacing incandescent lamps with LED lamps, the power of the proposed option must be reduced by 5 times. Those. , if a 75 W light bulb can be replaced by an LED lamp with a power of no more than 15 W.
For an apartment or a house, you need to opt for LED lamps with a power of 6 to 8 W, because they illuminate the room better than the 60 W “Ilyich bulb”.
A few words worth mentioning about tension. The bulbs operate on 12 and 220 V. The former are used for rooms with high humidity, for example, installing lighting in the bathroom. It would be wrong to buy 12-volt light bulbs with the expectation that they consume less electricity.
Colorful temperature
In order to spend time in a room comfortably, you should not give preference to LED lamps with bright daylight; these often find their use in industrial premises and offices.
Preferred, in this case, would be a range from 2700 to 3000 Kelvin , due to the fact that this temperature range demonstrates the yellowish glow of the usual sunlight. The color on the packaging is usually indicated in words. Look for models that say “warm white” or “soft white.”
Base type
When choosing an LED lamp by base type, you must choose the option that was before. For example, when a regular E27 threaded base is screwed into a chandelier, you need to buy an LED with exactly the same thread.
If you decide to install a spotlight, you must choose a lamp with a GU 5.3 base. The following thread types are used in nightlights and sconces: E27 and E14 (Mignon).
The shapes of LED lamps are varied: round, elongated, pear-shaped. Your choice in this case should be based on your taste and design of the lamp.
Important for LED bulbs is the presence of a heat sink, which removes the temperature from the LED block. If the proposed model does not have a cooling system in the form of an aluminum ribbed surface, you should not buy such a light bulb.
It happens that manufacturers of inexpensive products install a radiator in the form of a plastic outlet. Experts do not recommend buying such products, because plastic has many disadvantages and, in comparison with aluminum, it does not have such high cooling efficiency. It is worth remembering that frosted bulbs do not allow you to see the presence of a radiator.
Work resource
The reason is that over time, LEDs undergo a process of degradation, and the quality of their glow deteriorates.
When choosing, it is better to start from the warranty period, which ranges from 3 to 5 years. This means that if a light bulb breaks during this time period, it must be replaced with a new one free of charge.
Scattering angle
This parameter must be taken into account when buying LED light bulbs for your home. The nature of the lighting will depend on whether the LED lamp is equipped with a diffuser lens and whether it is coated on the inside with phosphors. Look at the location of the LEDs; if they are in the same plane, the lighting will be narrowly focused, and the multi-level placement of the diodes will provide diffused lighting.
An important characteristic is the color rendering coefficient, which receives little attention. For good bright lighting, this indicator should be at least 80. A value of 95 is considered high, but the price for such a model will be much more expensive. Indicate the color rendition on the product packaging.
Packaging or how to recognize a fake?
The packaging, which indicates the following parameters, will tell you a lot about the quality of the product:
- power
- base type
- color rendering coefficient
- manufacturer information
- warranty period
- Colorful temperature
- light flow
- barcode.
If, when looking at the packaging, you couldn’t find most of the parameters with your eyes, you should doubt the quality of such products.
When giving your preference to one or another LED lamp, you should pay attention to the product itself: all fastening elements must be made without irregularities, gaps and roughness.
Manufacturer
The company is a manufacturer - the information is quite important to the consumer. The quality of the products we purchase depends on the manufacturer. I would like to say that both foreign and domestic companies produce highly reliable products.
Manufacturers of LED lamps for home
Advantages of LED lamps:
- profitability, because such a lamp has a minimum electricity consumption, and the high cost is paid off by small bills for light
- duration of operation (5-10 years)
- heat transfer is at a minimum . LED bulbs practically do not heat up, which provides the necessary safety. This is very important when you need many light sources.
- high degree of strength. The body of such light bulbs is made of plastic, which prevents the risk of breaking and injury from small fragments
- does not contain mercury vapor
- no problems with disposal
Flaws:
- high cost, but considering the long term, they are the most profitable.
- requires special lamps. For long lamp operation, strict adherence to the permissible power of the lighting device and its power is necessary.
LED lamps have the fewest disadvantages
Recommendations for selection and operation.
LED lamps are a real breakthrough in the development of lighting systems; they are increasingly popular when choosing home lighting devices.
Be sure to pay attention to the power of such a lamp. When replacing incandescent lamps with LED lamps, you can use a simple but effective method of dividing the power by 8. This means that an “Ilyich light bulb” with a power of 60 W will be replaced by an LED with a power of 7.5 W.
Choose the right lamp light spectrum
Color spectrum
- Consider the price of the lamp. Quality cannot come cheap. A low price is a sign of a low quality product, the service life of which will not be long, and the desired savings will not be achieved. It is better to buy a product from a well-known manufacturer, preferably a European one.
- Pay attention to the LED pulsation during operation. The presence of pulsation or flickering will indicate the poor quality of the rectifier in the lamp power supply. The light emitted by such a lamp can cause vision impairment.
- Check the base holder and the quality of the radiator, because... These parameters are responsible for the life of the lamp.
A very necessary purchase for your home will be an LED lamp with a built-in motion sensor and night mode. In the dark, the lamp automatically turns on the standby lighting, and when a person appears, it turns on full brightness.
This option will be ideal for lighting a technical room, as well as a corridor or a bathroom.
At the end of the article, I would like to say a few words about the quartz lamp. Such a purchase will become a reliable assistant for parents during the season of the spread of infectious diseases. Its purpose is to stop the infection. This lamp can treat skin diseases, as well as joints, diseases of the nervous and respiratory systems. The choice of such lamps is huge. They differ in technical characteristics and range of procedures.
Analogue LON
This parameter evaluates the brightness of different types of lamps, comparing them with an incandescent lamp. The power consumption of light bulbs is a kind of standard by which the capabilities of other types of lamps are determined. For example, a fluorescent lamp with a 100 W analogue corresponds in brightness to a 100 W incandescent lamp, while consuming 25-30 W. The following lamp is marked: “Analog LON 100 W.”
The incandescent lamp equivalent makes it possible to compare different types of lamps with each other.
Fluorescent Lamp
In fluorescent lamps, to put it very simply, it is not any body that shines, but gas. A current passes through the mercury vapor, producing ultraviolet radiation, which the phosphor (a special substance on the bulb) transforms into visible light. It is fluorescent lamps that are called energy-saving in everyday life, although from a technical point of view, any modern light sources other than an incandescent lamp are such... even a halogen lamp.
Pros:
- economical electricity consumption;
- light output is five times higher than that of an incandescent lamp (a 20 W light bulb shines as much as 100 W);
- long service life, especially with infrequent switching on and off;
- various shades of light;
- scattered light.
Minuses:
- more expensive than incandescent lamps;
- larger than them;
- potential toxicity;
- incomplete spectrum of radiation harmful to vision;
- color distortion (over time, manufacturers eliminate the defect);
- strong flicker (with double network frequency);
- high energy consumption when turned on (less than incandescent lamps);
- do not work well at low temperatures;
- slight turn-on delay;
- deterioration of performance over time;
- the difficulty of recycling (you can’t just throw it away, and there are almost no collection points);
- There may be difficulties with the dimmer.
Functions
Brightness adjustment - makes it possible to change the brightness of the light bulb using dimmers that change the operating voltage. This feature is most often used in incandescent lamps, while other types of lamps are not always compatible with dimmers.
Fluorescent and LED models require special dimmers. The disadvantage of this option is the dependence on an external device (dimmer). In modern RGB LED models, brightness adjustment is carried out using a built-in regulator - in this case, an external dimmer is not needed.
Important: the ability to adjust brightness (dimmer compatibility) is indicated in the characteristics of halogen, fluorescent, and LED lamps.
Color control – allows you to select the color of the RGB LED lamp or strip.
Scenario/schedule support – allows you to configure the lamp to operate according to a specific lighting scenario (template)/schedule. Scenarios differ from each other in brightness and color temperature of light; they can be static or dynamic. The schedule makes it possible to control the time the light bulb turns on and off, and set operating modes at certain times.
Threaded base
This type of base has been used since the time of Edison and is marked with the letter E after the first letter of his last name. The spiral thread allows you to quickly screw in the bulb and achieve tight contact. Threaded sockets come in diameters from 5 to 40mm.
E14 "Minion". A small type of base popular in everyday life for use in miniature lamps and various sconces. Most often, such bulbs illuminate the corridor, toilet and bathroom, separate areas of the kitchen and reading areas in the bedroom and living room.
E27. The most common base for home use is medium-sized. Now with such a base they produce not only incandescent lamps, but also more economical fluorescent and bright halogen lamps. Such a base is most often found in chandeliers, pendant lamps, floor lamps and large sconces.
Remote control
Wi-Fi – allows you to control the settings of the “smart lamp” from anywhere in the world.
Bluetooth – makes it possible to work with a “smart lamp” from a relatively close distance.
Remote control – allows you to control the light bulb from a distance. Such a device is usually found in RGB LED lamps with brightness adjustments or color settings.
Important: when choosing a lamp, be sure to check its serviceability. To diagnose a light bulb, testers with light or sound indication are used.
Types of socles
When choosing an LED lamp for an apartment, be sure to pay attention to the base.
Most often in everyday life they are used with an E27 socket, which in one feature article was wittily called “well, like an ordinary light bulb.” It is with this base (with a thread and a diameter of 27 mm) that most of the incandescent lamps we are familiar with are produced.
A little less often, but also very often used, is the base - e14, it is also threaded, but of a smaller diameter (14 mm), it is called “minion”. Lamps with such a base usually have a power of 15 to 60 watts, are used in wall and table lamps, and are sometimes used for chandeliers with a large number of arms.
For suspended ceilings, lamps with GX53 and GX70 sockets are often used. Their feature is a pin mount, as well as the small height of the light bulb itself - 28 mm, ideal for built-in lamps. You can also use a GU10 base for mounting ceiling lighting; they are also considered pin-type, but have thickenings at the ends of the contacts.
Lamps with a g9 socket also have a pin mount. Such “microlamps” are widely used for spot lighting in apartments and shops. Lamps with a g4 socket are also used for the same purpose - they are even smaller than g9, the distance between the pins of both is 4 and 9 mm. respectively.
Manufacturer
Products in the mid-price segment and below consist of light bulbs from little-known manufacturers and other low-quality brands: Saturn, Electrum, Foton, and Global. Their main disadvantages are the discrepancy between the power of the light flux and the declared one, unreliable operation (they often burn out quickly), and not the best quality bases.
Excellent quality is provided by the brands Brille, Delux, Maxus, Panasonic, Philips, Eurolamp, Osram, Economka, Verbatim. It is worth noting that these brands have different “strengths”. For example, the best LED lamps are made by Philips, Osram, Maxus and Verbatim. They are the most economical and reliable. And among fluorescent lamps, the Maxus brand gives up its leading position to the Economy brand. And almost every type of light bulb has its own leading manufacturer. It is necessary to study comparative tests and reviews carefully and in detail.
Correspondence of incandescent, energy-saving and LED lamps in terms of power.
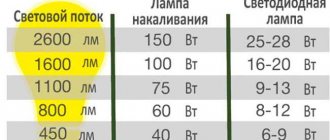
When it comes to replacing incandescent lamps with compact fluorescent lamps or LED lamps, the average consumer has the main criterion - equivalent power. If you don’t want to delve into this issue, you can simply tell the consultant “I need to replace a 100 W incandescent lamp with an energy-saving one.” Most likely, the buyer will be offered a lamp with a nominal power of 20 or 23 W, or an LED lamp with a power of 12-14 W. How are the powers of different types of lamps related to each other? The easiest way when replacing an incandescent lamp with a compact fluorescent lamp is to divide the power of the first by 5. Thus, a 100 W incandescent lamp can be replaced with an energy-saving 20 W lamp without loss of illumination. And when moving to LED lamps, you should divide the same 100 W by 8. Then the LED lamp, equivalent to an incandescent lamp, will have a power of 12 W. The table with calculated powers when replacing lamp types looks like this:
| LN, W | CFL, W | SDL., W |
| 30 | 6 | 3 |
| 40 | 8 | 5 |
| 50 | 10 | 6 |
| 60 | 12 | 7 |
| 70 | 14 | 8 |
| 80 | 16 | 10 |
| 90 | 18 | 11 |
| 100 | 20 | 12 |
| 110 | 22 | 13 |
| 120 | 24 | 15 |
* LN - incandescent lamp; CFL - compact fluorescent lamp (energy saving); SDL - LED lamp. It would seem that everything is simple. However, an equally important characteristic of a lamp is the luminous flux received from it. The higher the lamp power, the higher the luminous flux. And if a full equivalent of the one being replaced is required, then this indicator cannot be avoided. Thus, one more column needs to be added to the lamp power correspondence table, which will reflect exactly the luminous flux, which is measured in Lumens. Based on it, you can absolutely say that a lamp with such a luminous flux and such power will fully meet your requirements. The dependence of the flux (amount of light) on the lamp power is almost linear and, having the luminous fluxes of lamps of common ratings, it is easy to calculate this value for lamps of less popular powers:
| LN, W | CFL, W | SDL., W | Lumen |
| 30 | 6 | 3 | 300 |
| 40 | 8 | 5 | 400 |
| 50 | 10 | 6 | 550 |
| 60 | 12 | 7 | 700 |
| 70 | 14 | 8 | 850 |
| 80 | 16 | 10 | 950 |
| 90 | 18 | 11 | 1100 |
| 100 | 20 | 12 | 1200 |
| 110 | 22 | 13 | 1350 |
| 120 | 24 | 15 | 1500 |
* Lumen - luminous flux. * Please note that the luminous flux value is always written on the packaging of any modern lamp. At least on energy-saving and LED packaging - for sure.