With rising prices for electrical energy, consumers are increasingly switching to economical and energy-saving lighting devices. The duration of operation of the lamp before it fails, as well as the quality of its glow, also play a major role in savings. Due to these characteristics, halogen lamps have become the most popular.
What is a halogen lamp, device and principle of operation
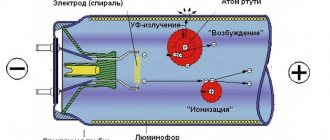
A halogen lamp is one of the varieties of standard incandescent lamps. The main distinguishing feature of its design lies in a special gas - halogen, which is pumped into the flask of the device.
The principle of operation of such a lighting device (as with standard incandescent lamps) is based on the passage of electric current through a filament body and heating of this body until it glows. But thanks to halogen vapor (most often bromine or iodine is used for these purposes), the temperature of the tungsten coil increases significantly and the light output increases. This happens because tungsten atoms, when heated, evaporate and condense on the flask, but iodine or bromine enter into a chemical reaction with tungsten and prevent it from settling. In this case, such compounds quickly disintegrate when heated and tungsten atoms condense back onto the spirals, and this increases the temperature of the filament.
Otherwise, the entire design of the lamp is no different from standard incandescent lamps: a halogen lamp has a bulb, a filament with conductors and a base. At the same time, manufacturers of such devices produce lamps with all types of standard sockets, so the consumer can use such lamps in any lighting device.
Where are halogen lamps used?
Halogen lamps are durable and bright lighting devices that are resistant to temperature and voltage changes. The bulbs of halogen lamps are made of heat-resistant and resistant to mechanical damage quartz, thanks to which this lamp can withstand large temperature changes and can have various sizes from large to miniature. Therefore, they are widely used in lighting devices for cars and other vehicles.
Halogen lamps are often and widely used in everyday life. They are built into various systems of suspended or suspended ceilings, and are also used when installing spot lighting or organizing various types of lighting, installed in chandeliers and various lamps. They are most often used when taking photos and videos using halogen spotlights and other lighting devices based on them.
Linear
This is the oldest type of halogen lamp. It was developed in the 60s of the last century. Such a lamp is a quartz tube, which has leads on both sides. Special wire brackets hold the filament. Despite its small size, the lamp has quite a large power - up to 20 kW and allows for high brightness. For this reason, they are almost never used in everyday life, but they are widely used in floodlighting. True, the latest modifications of linear halogen lamps - halogen flood lamps - are characterized by high durability and can be used with equal success in both indoor and outdoor lighting.
Literally all lamps of this type must be placed horizontally, since a slight deviation in the angle of inclination significantly reduces their service life.
Main types of halogen lamps
Depending on the appearance and method of use, halogen lamps are divided into several main types:
- with external flask;
- capsule;
- with reflector;
- linear.
With external bulb
With a remote or external bulb, a halogen lamp is no different from standard “Ilyich bulbs”. They can be connected directly to a 220 volt network and have any shape and size. A distinctive feature is the presence in a standard glass bulb of a small halogen bulb with a bulb made of heat-resistant quartz. Halogen lamps with a remote bulb are used in various lamps, chandeliers and other lighting devices with an E27 or E14 base.
Capsule
Capsule halogen lamps are miniature in size and are used for interior lighting. They have low power and are often used with bases G4, G5 in a DC network with a voltage of 12 - 24 volts and G9 in an AC network of 220 volts.
Structurally, such a lamp has a filament body located in a longitudinal or transverse plane, and a reflective substance is applied to the back wall of the bulb. Due to their low power and size, such devices do not require a special protective flask and can be mounted in open-type luminaires.
With reflector
Reflector devices are designed to emit light in a directional manner. Halogen lamps may have an aluminum or interference reflector. The most common of these two options is aluminum. It redistributes and focuses heat flow and light radiation forward, so that the light flow is directed to the desired point, and excess heat is removed, protecting the space and materials around the lamp from overheating.
An interference reflector conducts heat into the lamp. Halogen reflector lamps come in a variety of shapes and sizes and have different light emission angles.
Linear
The oldest type of halogen lamps, which has been used since the mid-60s of the 20th century. Linear halogen lamps look like an elongated tube with contacts at the ends. Linear lamps come in various sizes as well as high wattage and are mainly used in various floodlights and street lighting fixtures.
Halogen lamps with IRC technology
IRC halogen lamps are a special type of lighting device of this kind. IRC stands for Infrared Coverage. They have a special coating on the bulb that freely transmits visible light, but prevents the passage of infrared radiation. The coating composition directs this radiation back to the filament body, which increases the efficiency and efficiency of the halogen lamp, improves the uniformity of glow and light output.
Technical characteristics of halogen lamps
To choose the right lamp, you need to know what it will be used for, where it will be mounted and under what conditions it will work. Like any other lamps, halogen lamps have the following important characteristics:
Base type and bulb shape
Halogen lamps are available with any type of base and bulb shape, so there will be no difficulty in choosing a device in this regard. There are options with sockets E14 and E27, as well as specific sockets G4, G9, R7s.
Voltage
Manufacturers of such lamps produce devices for both 220 V AC and 12 - 24 V DC.
Power
An important characteristic of the lamp, indicating the power consumption of the device. Powerful linear lamps range from 100 to 1500 W, capsule lamps from 10 to 35 W, and lamps with an external base or reflector have a power from 20 to 60 W.
Colorful temperature
Halogen lamps typically have an operating color temperature of 2500 K to 3000 K.
Life time
Halogen lamps are quite durable devices compared to standard incandescent lamps. They last from 2000 hours or more, subject to operating conditions.
Features of operation
In order for the lamp to last as long as possible, manufacturers advise not to touch the bulb with your hands, even if they are clean. The fat that remains after touching can cause the lamp to burn out. It is better to wear gloves when replacing. If the temperature inside the flask drops below 250°C, interaction with tungsten will not occur.
Fig. 8 – features of halogen lamps.
As a result, the device will work like an ordinary incandescent lamp. It is also not recommended to install a dimmer. Because of this, the light bulb stops working correctly, since the decrease in brightness is directly related to the temperature of the buffer gas. If a dimmer has been installed, it should be turned on at full power as often as possible. This is necessary for heating to the required temperature and interaction of halogens with tungsten.
This way the filament coil can repair itself. It is important to ensure network voltage stability to extend service life. If voltage surges occur, it is better to install a stabilizing protection unit. For suspended ceilings, lamps without an external bulb are not used; a heated element can melt building materials.
Advantages and disadvantages
Like any device, halogen lamps have both advantages and disadvantages.
Advantages
- Service life is the main advantage of these lamps compared to conventional incandescent lamps. Under proper conditions, halogen lamps last 2000 hours or more;
- Stable glow regardless of lamp life;
- Compact dimensions facilitate use in any systems (including car lighting) and organization of any type of lighting;
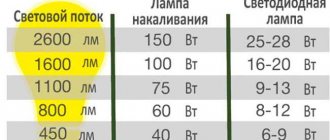
- The luminous efficiency of these lamps reaches 20 Lm/W, which is a good value for incandescent lamps;
- Halogen lamps have good color rendering, the glow is comfortable for the eyes and does not affect vision.
Installation of halogen lamps
Let's look at how to install such a model; step-by-step instruction:
- Turn off the power in the apartment or directly to the lamp you are replacing. Allow the floor lamp to cool;
- Remove the tempered glass cover over the halogen lamp. You may need to remove the clips or screws that hold the glass cover in place;
- Make sure that the markings on the purchased lamp are the same as the old one;
- Use a cotton cloth to remove the old lamp. In most cases, you need to press the light a little and remove the socket.
- Without touching the new light bulb with your hands, carefully insert it in place of the old one;
- Now all that remains is to tighten the screws and glass cover and test the operation.
The differences in the installation of such halogen lamps for the home are the reason for the presence of quartz coating. If you touch it with your hands, you will break the structure. The lamp will not work, or will explode during operation and may harm you with fragments and gas, so be careful.
Photo - Halogen lamps with g9 base
Many owners believe that this is an excellent alternative to home illumination with LEDs or sodium lamps. You can buy halogen lamps for your home at any electrical appliance store; the best reviews are about linear (long) models from Delux G9, German outdoor ones Osram Night Breaker and Lumium. Sales are also made directly at the dealership centers of these companies.
Comparison with other types of lamps
Halogen lamps, of course, do not compare in energy efficiency to LED or fluorescent lamps. In this case, it all depends on the scope of application of the devices. As mentioned above: halogen lamps are resistant to temperature and voltage changes, which in some conditions clearly puts them above LED ones.
But when comparing them with conventional incandescent lamps, the advantages of these lamps are clearly visible. Halogen lamps have higher efficiency and luminous flux at lower power. They are more durable and versatile. High quality of light transmission is another important argument in favor of choosing halogen lamps.