LED lamps - device features
LED light bulbs are very popular and in demand; they are gradually replacing similar devices with incandescent filament from the market. Despite the significant cost, many apartment owners strive to purchase diode lamps, since they have a significantly longer service life, efficiency and reliability.
Compared to incandescent lamps, the design of diode devices is somewhat more complex. Let us highlight the main elements and describe their purpose:
- The base is made of brass and plated with nickel, which prevents corrosion and promotes reliable contact with the cartridge.
- The polymer base of the base part is coated with polyethylene terephthalate to protect the device body from electric shock.
- Driver – is implemented according to the circuit of a galvanically isolated modulator of an electric current stabilizer. The main purpose of the driver is to ensure stable, uninterrupted operation even during network voltage fluctuations.
- Radiator – made of anodized aluminum alloy. Required for effective removal of thermal energy from the remaining elements of the light bulb.
- A printed circuit board made of aluminum on a heat-conducting mass guarantees the required operating temperature of the chips by removing heat to the radiator directly from the chips.
- Chips - in fact, this is the lighting mechanism, in other words - diodes.
- The diffuser is a glass hemisphere, the level of light dispersion of which tends to the maximum.
LED lamp device
The principle of operation of LED lamps for the common man is quite complex and confusing. In short, glow occurs as a result of the release of photons due to the constant change and recombination of electrons, followed by a transition to other energy layers. The uninterrupted flow of the process is ensured by the semiconductor materials of the chips. To ensure optimal operating conditions for the entire device, various resistors or current-limiting mechanisms are used.
Some manufacturers today are trying to introduce improved technologies for creating a glow, in particular, using special diode bridges. The cost of such light bulbs is slightly higher compared to other LEDs, but the quality fully corresponds to the price.
Because of the switch, when the light is off, the LED light glows
Currently, a huge number of electrical devices that have long been known and familiar to everyone are equipped, for ease of use or control, with additional elements that cannot work correctly together in one electrical circuit.
These devices include a switch in which an LED is installed for convenience. In this case, normal operation of such a switch and LEDs is impossible. Therefore, some work is required.
Troubleshooting work:
- Switch modification;
- Replacing the switch.
As mentioned earlier, the LED installed in the switch is connected to the network through a resistor for optimal operation. In turn, the resistor, constantly giving off the accumulated charge to the LEDs, makes them glow.
Therefore, in this situation, the best solution would be to remove the LED from the switch circuit. This is done quite simply. The switch is disassembled and, using wire cutters, the LED and resistor are bitten off.
The best solution to get rid of this problem is to remove the LED from the switch circuit
It is worth noting that if you have a regular switch, you can use the second method. Just replace it.
Note! Carry out all electrical installation work only when the mains voltage is turned off.
To do this, you need to turn off the circuit breaker in the distribution panel. After this, using a set of screwdrivers, disassemble the switch, disconnect it from the live conductors and install a new one.
Causes of emergencies
The most common reason for electrical failure is the desire to save on materials, because this way you will spend less money. Cheap materials can later lead to wiring failures and fires.
The second reason is old wiring. People replace old wiring in an apartment every 15-20 years, and sometimes even much later. During this time, the cable insulation is destroyed and the connections in the junction boxes are weakened. As a result, light may be lost. Now that powerful electric stoves and boilers have appeared, the cross-section of the cores should be no less than 4 mm2. In this regard, the old wiring is not able to withstand such current loads. If you are interested, then you can read about marking electrical wiring in the house.
The third reason is improper electrical installation. Even if you recently rewired your home or apartment, it may already be faulty. The technician may have made incorrect wire connections for you, or the conductor insulation may have been damaged during installation. As a result, a current leak will occur and household appliances will fail.
Another reason could be improper use. For example, pulling a plug from a socket results in a situation where the socket falls out of the wall. Damage to the cable may occur when driving a nail into the wall.
Causes of malfunction may also include flooding of the apartment, failure of household appliances. If necessary, you can read about installing wiring under a suspended ceiling.
Here are the types of electrical wiring faults in apartments and houses:
- Insulation damage. As a result of this, a current leak will occur, and if you do not have an RCD in the panel, then electric shock cannot be avoided. Such a breakdown can be eliminated by restoring the integrity of the insulation or simply replacing the damaged area.
- Damage to the current-carrying conductor. It can occur as a result of careless installation or repair work. Aluminum conductors are very fragile, so you need to twist them with a screw clamp as carefully as possible, because if they break, the power will be lost.
- Due to an incorrectly selected core cross-section or poor contact in the strands, insulation melting may occur. Such a malfunction can lead to a fire in a house or apartment. This problem can be resolved by replacing the cable with a more powerful one.
- Failure of household appliances. If your electrical appliances are shocking or you smell a burning smell, it means your household appliances are faulty. In this case, an electric shock or electrical fire may occur.
- Poor contact in places where wires are connected to machines, sockets, or poor contact in twists. In this case, the cores heat up and the insulation melts. And as a result, a fire occurs in the electrical wiring. The malfunction can be eliminated by tightening the clamps or periodically checking all connections.
- Failure of switches and sockets. On average, an electrical product has a service life of no more than 10 years. If the socket is old, then when connecting the plug, overheating may occur, which can cause a fire. If the switch wears out, it simply stops working.
- Burning of the neutral wire in the panel. This is the most dangerous electrical wiring fault. As a result, there may be a danger of electric shock to a person. Such a breakdown can be eliminated only by restoring contact, and the danger can be prevented by installing a voltage control relay.
Lamp glow when the load is off
There are several likely factors that could explain why the lighting element is still lit after being disconnected from the power source, albeit dimly:
- Problems with electrical wiring, in particular, poor-quality insulation on one of the sections of the circuit.
- The LED lamp is connected to a backlit switch.
- Poor quality emitters used in the design of the light source.
- Functional features of the lamp.
If the emitters burn when the switching device is in the off position, it is recommended to first consider all other factors except the first, since it is problematic to determine the area of hidden wiring that is weak in insulation.
To do this, conditions are created under which a circuit breakdown occurs (high voltage is applied for 1 minute). The problem area, due to which the diode lamps glow after the load is turned off, will have to be opened: the integrity of the wall is compromised if the wiring is laid using the gating method.
A very common situation occurs when energy-saving light sources function differently when connected to a backlit switching device. The problem here lies in the fact that the lighting element installed in the switch completes the circuit, which means it passes a small current. It powers the diode lamps when the lights are off.
The problem of cheap LED products is no less common. If a product of low quality at an affordable price was chosen, and usually the connection between these factors is direct, then there is a high probability of an error in the soldering board. But it happens that the emitter, although dimly, burns due to the functional features of the design.
In particular, we are talking about the processes that occur in the resistor when a load is applied to the lamp: this element accumulates energy as current flows through the circuit, and after the load is turned off, it maintains the glow in the emitters.
Members
| This section do not quote any sources . |
Current members
| Former members
|
[7]
LED lamps glow after switching off: troubleshooting
If the reason for the glow of LED lamps is a backlit switch, then in this case you can do without altering or replacing it. To do this you need to do the following.
In order to troubleshoot the problem you must:
- Select a capacitor;
- Integrate a capacitor into an electrical circuit.
First of all, an additional element in the form of a capacitor is selected. This circuit is known to many, but when designing it, one mistake is made, which leads to the failure of the capacitor.
This is an incorrect device selection based on voltage. It is known that a current with a voltage of 220 Volts is used for the public network. This indicates that this voltage is active.
Note! The value of the effective voltage is equal to the maximum voltage (amplitude) divided by the root of two.
This suggests that when a maximum voltage value occurs in the network, the capacitor may not withstand the load and fail. Therefore, to install capacitors in a 220 Volt circuit, it is best to use capacitors with a rated voltage of 630 Volts and a capacitance of 0.1 µF.
If the reason for the glow of LED lamps is a backlit switch, then in this case you can do without altering or replacing it
Once the correct capacitor has been selected, you can begin installing it. To do this, you need to solder two wires about 5 cm long to its contact legs. Next, the device is mounted in the circuit. Installation is carried out in parallel. Polarity is not required.
Mount the capacitor in the junction box, to the wires going to the lighting device, or to the contacts of the cartridge.
Causes of bad light
If your headlights aren't bright enough, it's most likely due to one of the following:
- damage to contacts;
- the lampshade is clogged or damaged;
- in a faulty or old light bulb;
- in cloudy glass;
- due to improper lighting adjustment.
If the low beam headlights are dim, but you have no complaints about the performance of the high beam ones, then most likely you should look for the cause in the outgoing contacts, incorrect adjustment or a bad light bulb. Since if there were problems with the lampshade, any light would not work well.
If one headlight burns brighter than the other, it means that the fault must be looked for in its device.
Now that we've looked at the possible reasons why your headlights are dim, it's time to talk about how to make your headlights shine brighter.
Why does the lamp glow or blink?
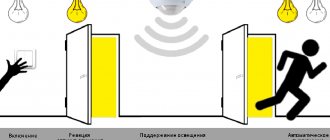
One of the most common reasons is the backlight on the switch. LEDs are sensitive to ultra-low currents and interference, and the backlit switch elements allow weak currents to pass through, even when the state is “off”. The second, also very common reason, is that the switch opens zero instead of phase. A broken zero, as a rule, has a capacitive coupling with the surrounding wiring and due to this, parasitic currents arise.
The situation when the switch breaks zero is ubiquitous in Soviet-era wiring. This phenomenon is so common that sometimes it seems as if it was done on purpose. Let me remind you that in the “correct” electrical wiring, the switch must break the phase. A broken zero, by the way, causes the indicator screwdriver attached to it to light up. Similar to an indicator screwdriver, a light bulb sometimes only needs a fraction of a milliamp to produce a faint glow.
Why do some lamps glow dimly and others flicker? This is usually due to the design of the lamp driver, which is hidden in the base. It is believed that a flashing lamp has a better driver, while a smoldering lamp has a cheaper driver. It’s difficult to say about reliability here; both burn out.
The lamp lights up after turning off - solutions to the problem
Having decided why the LED light is on when the light is off, you can move on to solving the problem. The following is a list of basic recommendations, depending on the causes of this phenomenon. If dim light is associated with purchasing a product at an affordable price, but of low quality, then the advice here is very simple - you need to go to the nearest store and buy a high-quality light bulb from a reliable manufacturer.
If the problem is the backlight in the switch, there may be several solutions. You can act logically and, following the example of the first point, go to the store for a switching device that does not have backlighting. Another option is to cut off the power wire that controls the backlight. To do this, you will need to open the switch, which is done quite simply and quickly; even beginners in this matter will be able to disassemble and reassemble the device on their own in a few minutes. If you cannot do without backlighting, then you can just install another resistor in the circuit, which will prevent the accumulation of energy.
The main thing is to find the cause of this glow, after which you can begin to take action.
Isolation, as noted earlier, causes the greatest difficulties in solving the problem. If you do not want to violate the integrity of the wall, then you can try to go the other way. Its essence is to connect an additional load (relay, resistor, incandescent lamp) in parallel with diodes that do not stop burning. The only condition is that the resistance of the connected additional device must be less than that of the LED lamp. Due to the weak resistance, the connected element will not light up, and due to the redirection of current, the LED lamps will also not light up after turning off.
So, we told you why LED bulbs light up when the switch is off, and also that solving such a problem is not so difficult. The main thing is to find the cause of this glow, after which you can begin to take action.
How to fix the problem
If the LED lamp lights up when the light is off, how to fix it? There are different solutions. It all depends on the nature of the problem itself.
- For example:
- A cheap, low-quality LED lamp always glows in the dark after it is turned off. To eliminate this problem, it is necessary to replace it with quality products from a trusted manufacturer.
- If the lighting element is on because an illuminated switch is used, then this problem can be solved in different ways.
- For example, the easiest way out is to change the switch in the house to a regular one, without backlighting. You can simply cut off the specific wire that powers the backlight. This can be done after opening the switching device. But there is another way out - to preserve this function, it is enough to place a resistor in parallel on a certain section of the electrical circuit.
- If the LED light is on and the reason is in the wiring, then it will be extremely difficult to solve such a problem. To eliminate it, you need to find the location of the current leak. But this may entail certain difficulties. But when the light turns off, the bulbs will not light up.
A variety of methods can solve the problem of the glow of emitters with diodes so that they do not glow at full intensity when the switch is turned off. The main thing is to understand the root cause of the problem. We hope you now understand why the LED lamp glows after turning off and what to do to correct the situation!
Removing the backlight will be the easiest and fastest solution to this problem. To do this, it is necessary to disconnect the wires from which the backlight is powered, after first opening the switch cover.
Alternatively, you can also cut off this wire, but first be sure to find out where the power wire is so as not to get confused.
Having done this, no current will flow to the charging capacitor, after which the lamp will no longer glow dimly or blink; If you want to avoid this problem, then before purchasing a switch, pay attention to the presence or absence of backlighting. If it is not there, then the main problem will not appear; A good option would be to connect a regular lamp in parallel; using this option will prevent the energy-saving light source from burning when turned off. This is achieved due to the fact that the current to recharge the capacitor goes to the filament; There are switches that have mandatory backlighting needed for some purpose.
What to do in this case, and what actions to take?
This is achieved due to the fact that the current to recharge the capacitor goes to the filament; There are switches that have mandatory backlighting needed for some purpose. What to do in this case, and what actions to take?
A good solution to eliminate this problem would be to connect a resistor in parallel, which will help create additional resistance in the desired section of the electrical circuit. The main advantage of this method is its cheap price; you can purchase a resistor in absolutely any radio equipment store.
It is worth noting that the resistor will not negatively affect the normal operation of the LEDs. But when the switch is turned off, the backlight will work, and accordingly the resistor will consume current, which goes to charge the capacitor. Also don't forget to insulate the resistor, the best way to do this is to use heat shrink tubing.
Using the glow for good
Let me make a reservation right away: only “smoldering” lamps will do; it’s unlikely that it will work with blinking ones. I personally witnessed the long operation of lamps in this mode, but I do not rule out that these experiments can significantly shorten the life of the lamps. There are too many different lamp designs and not enough data to make clear conclusions.
So, a weak glow can be used as a feature, an additional lighting option. A night light in the corridor, a romantic twilight in the room - “smoldering” can be used effectively. The main thing is to learn how to properly control this glow.
Good results will be achieved by proper “correct” wiring and switches without backlights. That is, when the lamp is turned off, it does not glow at all.
The same capacitor, but connected in parallel with the switch, can make it glow. Also, capacitors of 0.047-0.1 µF for 400-600 volts are suitable. Here you may have to select a container for the desired glow. For convenience, you can use a two-key switch instead of a single-key switch: the first key must be connected according to the standard circuit, and the second through a selected capacitor. You will get two modes - normal and night light!
If the lamp glows initially, you can try connecting a capacitor in parallel with the lamp to eliminate it, and another capacitor, but of a larger capacity, to the second switch key. In general, you will have to experiment. But overall, I think this idea is quite interesting.
In all my experiments with the “night light” I used non-dimmable lamps. The photo below shows two types of cheap lamps that “smolder”.
How to solve the problem of dim light
Recommendations may vary depending on the size of the problem:
- If you initially purchased a cheap LED lamp, then it is possible to eliminate the glow only by installing a product from a reliable manufacturer and of high quality.
- When the problem lies in the backlit switch, it can be eliminated in different ways. The simplest solution is to change the switching device to a model without backlight. You can also cut off the corresponding backlight power wire; this is done after opening the switch. But in some cases it is important to preserve this function. Then you need to install a resistor in parallel on the desired section of the circuit.
- The hardest problem to fix is the one in the wiring. To do everything correctly, of course, it is recommended to find the source of the leakage current. But, as already mentioned, this will entail other difficulties. But as a result, when the light is turned off, the diode lamps will not light up. But you can go another way, a simpler one. To do this, a load (incandescent lamp, resistor or relay) is connected in parallel with the diodes that light up. It is important that the resistance of this element is less than that of LED emitters. As a result, the leakage current will flow, for example, to an incandescent lamp. But due to the slight resistance it will not burn.
As you can see, there are many ways to solve the problem of diode-based emitters, which, although dim, still shine when turned off. It is necessary, if possible, to determine the most likely cause of this phenomenon.
Illuminated switch
The most common reason for a lamp to glow after being turned off is backlit switches.
Inside such a switch there is an LED with a current-limiting resistor. The LED lamp glows dimly when the light is turned off, because even when the main contact is turned off, voltage continues to flow through them.
Why does an LED lamp burn at full heat and not at full power ? Thanks to the limiting resistor, the current flowing through the electrical circuit is extremely insignificant and insufficient to light an incandescent electric lamp or ignite fluorescent lamps.
The power consumption of LEDs is tens of times lower than the same parameters of an ordinary incandescent lamp. But even a small current flowing through the backlight diode is sufficient for the LEDs in the lamp to glow weakly.
There can be two lighting options. Either the LED lamp lights up continuously after turning off, which means that sufficient current flows through the LED backlight of the switch, or the light flashes periodically. This usually happens if the current flowing through the circuit is too small to cause a constant glow, but it recharges the smoothing capacitor in the power supply circuit.
When sufficient voltage gradually accumulates on the capacitor, the stabilizer chip is triggered and the lamp flashes for a moment. Such blinking must be definitely combated, no matter where the lamp is located.
In this operating mode, the lifespan of the power board components will be significantly reduced, since even the microcircuit does not have an infinite number of operation cycles.
There are several ways to eliminate the situation when the LED light is on when the switch is off.
The simplest is to remove it from the backlight switch. To do this, we disassemble the housing and unscrew or bite off with wire cutters the wire going to the resistor and LED. You can replace the switch with another one, but without such a useful function.
Another option would be to solder a shunt resistor in parallel with the lamp. According to the parameters, it should be designed for 2-4 W and have a resistance of no more than 50 kOhm. Then the current will flow through it, and not through the power driver of the lamp itself.
You can purchase such a resistor at any radio store. Installing the resistor is not difficult. It is enough to remove the lampshade and fix the resistance legs in the terminal block for connecting the network wires.
If you are not particularly friendly with electricians and are afraid to “interfere” with the wiring yourself, another way to “fight” backlit switches can be to install a regular incandescent lamp in the chandelier. When turned off, its spiral will act as a shunt resistor. But this method is only possible if the chandelier has several sockets.