RCD (residual current device) is designed to prevent dangerous effects on humans and animals of electric current when touching live and other parts of energized devices and electrical installations. The next important function of the device is to prevent fires when leakage currents appear on the ground. The protective effect is manifested by turning off the power supply in the following situations:
- short circuit of the body of an electrical appliance under voltage through the body to the ground;
- contact of current-carrying elements with grounded non-current-carrying parts of electrical installations as a result of insulation damage;
- change of grounding (PE) and neutral (N) conductors in the electrical circuit.
RCDs also protect networks from power surges. To do this, a nonlinear resistance is connected to the neutral at the input of the device and the phase at the output. The differential current flows through it when the voltage increases above 270 V, after which the RCD turns off.
Safety devices differ in types and operating principles. One of the most practical is a selective RCD, which provides targeted disconnection of groups of loads. Its feature is a reduced speed response characteristic (type S or G). It is installed closer to the source, has a residual trip current rating of 100 or 300 mA and ensures that the next conventional RCD located in front of the consumer will trip first.
Thus, modern protection of electrical networks is based on identifying faults and disconnecting individual sections from systems operating in normal modes.
How does the RCD work?
RCD is also called residual current switch. The purpose remains the same: to turn off the circuit when a current leak occurs. The main element of the device is a toroidal transformer with several turns of neutral and phase wires connected back to back. The resulting magnetic field during normal operation of the device remains equal to zero. A leak into the ground upsets the balance; a voltage arises in the secondary winding, upon reaching a certain value the electrical circuit is switched off using the starting and actuating mechanisms.
The RCD requires a PE grounding bus. Otherwise, when potential appears on the body of an electrical appliance due to damaged insulation, there is no current leakage, and if you touch it and grounded metal parts (heating radiator, water pipes), you can receive a noticeable electric shock. In this case, the protective device will work, but it will be better if it occurs from a leak into the ground.
For reliable operation of the protective device, grounding must be installed. When working according to this scheme, the RCD will break the circuit even before it touches the metal body of the equipment or household appliance.
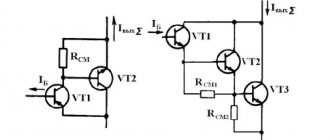
Operating principle of selective RCD
The operating principles of all RCDs listed above are the same. They have one goal - to prevent current leaks in order to avoid fire and electrical injuries. Action diagram:
- The design has a differential type transformer.
- It compares the currents entering it.
- The difference between them is directed to a nearby sensing element.
- If the difference value is greater than the set parameter, then the RCD produces a cutoff.
In fact, this is the basic principle of operation of the device for a single-phase or three-phase network. Disabling occurs according to the same algorithm everywhere.
Types of RCD
RCDs are classified according to the functions they perform:
- AC - response to a suddenly appearing or gradually increasing alternating leakage current.
- A - additionally triggered by a constant pulsating differential current, which can appear unexpectedly or increase gradually.
- B - response to direct and alternating pulsating leakage currents.
- S - selective RCD with additional time delay for shutdown.
- G - similar to S, but with less latency.
Where to install the RCD?
- Public places in buildings where there is no increased risk of electric shock.
- In electrical circuits with a possible risk of electric shock (rooms with humidity above normal, groups of sockets, household appliances, etc.).
- At the main entrance for protection against fire hazard. Usually a selective RCD is installed here.
- In floor distribution boards, in apartment panels, in individual houses.
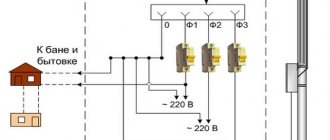
- In radial power supply systems: general selective RCD and separate ones for outlet lines, with a choice of parameters that guarantee selective operation.
- At close protection levels, for example, 10 and 30 mA, 30 and 40 mA, etc., current selectivity of the RCD is unlikely due to the high response speed. For the indicated values, it is ensured if you select a 100mA selective RCD so that there is also a time delay.
- Due to aging of the insulation, there is not always a gradual increase in leakage currents.
- With an instantaneous increase in leakage current due to insulation breakdown, any conventional RCD located in series in the circuit can trip. This occurs due to the rapid and significant exceeding of settings at several stages of protection at once.
Features of the device operation with and without a PE protective conductor
Electric shock to a person can occur as a result of direct or indirect contact. StabExpert.ru reminds that direct contact is a touch directly to live parts of equipment or an electrical appliance, that is, in other words, to a phase wire. Indirect contact is considered to be touching electrically conductive parts that should not normally be energized. In particular, these are the housings of household electrical appliances - refrigerators, washing machines, etc. This means that electric shock due to indirect contact can only occur if the insulation and internal parts of the equipment are damaged and dangerous voltage appears on its body.
In this situation, the difference between power supply systems with and without a protective wire is revealed.
Electrical wiring without a protective wire, this option is found in old houses. Single-phase wiring in this case is performed with only two wires - phase and working neutral. We wrote about this in the topic of grounding a private house.
Electrical sockets in such houses do not have a third protective contact.
What happens without an RCD?
Now let’s imagine what will happen if in such an apartment, which is also not equipped with an RCD, as a result of damage to the insulation under phase voltage, the body of the washing machine ends up in a damp bathroom?
That's right, nothing will happen. But only for the time being. Namely, until someone touches the washing machine and, for example, a water supply pipe at the same time. In this case, a person finds himself under the influence of phase voltage, an electric current will flow through his body and, with a high degree of probability, he will die.
Option 1: No PE wire
Now let’s consider the option when an RCD is installed in the same apartment. In this case, there will also be no reaction to the breakdown of the insulation of the washing machine and the appearance of phase voltage on its body. An RCD can only operate if the washing machine body is accidentally connected to natural grounding (heating, water supply, sewerage pipes). In this case, a certain leakage current will arise, to which the shutdown device will react. But this is a special case, you cannot count on such an outcome. That is, the body of our machine will be energized.
When a person touches the washing machine and the pipe, everything will happen, as in the absence of an RCD. Only in this case, the leakage current flowing through the human body will cause the device to turn off, which will reduce the time of exposure of this current to the body to a fraction of a second. This means that with a residual current device, the level of safety is higher than without it. Although it’s also impossible to say that everything is wonderful, because a person will still get an electric shock.
Option 2. Electrical wiring with protective PE wire
In this case, single-phase wiring is made three-wire. In addition to the phase and working neutral wires, a third, protective PE wire is laid from the panel, which is inserted into the sockets and connected to their protective contact. When connecting electrical appliances to such an outlet, their housing is connected to the PE wire. This radically changes the level of protection of people and equipment. When the insulation of an electrical appliance breaks down and phase voltage appears on its body, a short circuit occurs in such a system and the protection on the supply circuit breaker is triggered. Thus, the presence of phase voltage on the electrical equipment housing is excluded here even in the absence of an RCD.
In the case of installing a residual current device in the presence of a PE protective wire, conditions are created for its guaranteed operation not only when a phase appears on the housing. The RCD will operate reliably when the insulation is weakened, which causes a leakage current that reaches the value of the differential current of the device.
To summarize, the following results can be noted:
- installing a residual current device increases the level of safety both in systems with and without PE protective conductor;
- the greatest efficiency of using RCDs is achieved in the presence of a protective wire, in this case the possibility of even short-term exposure to dangerous voltage on a person is practically eliminated;
- in the presence of a PE wire, the RCD responds to the initial stage of deterioration of the insulation of an electrical device, when the current leakage is measured in milliamps and there are no conditions for the circuit breakers to operate.
The need to use selective RCDs
A selective RCD performs its fire protection function if modifications with a time delay are used - S or G. They are subject to increased requirements for resistance to short circuits, switching capacity, dynamic and thermal resistance, etc.
Typically, a selective fire protection RCD for high leakage current is installed at the main input.
RCDs cannot be used in circuits that cannot be switched off suddenly, as this can lead to emergency situations (fire or security alarms, danger to personnel, etc.).
In addition to RCDs, circuit breakers must have current selectivity. Overloads or short circuits located closer to the area should be triggered first. In this case, the circuit breakers operate before the short-circuit current reaches the limit value. This is necessary to prevent overloading of series-connected sections, since the current passes through the contacts of their protective devices.
What is meant by UDT selectivity?
Kharechko Yu.V. in his book he focuses on the fact that [1]:
“When connecting differential current devices in series, it is necessary to ensure their selective operation during ground faults. The UDT located closest to the ground fault, usually located in the final electrical circuit, should operate first. The second should operate a UDT located closer to the power source, for example, installed at the entrance to the electrical installation of a building or protecting the electrical distribution circuit. Otherwise, if the residual current input device or UDT installed in the distribution electrical circuit is the first to operate, then instead of one final electrical circuit in which a ground fault occurred, the entire electrical installation of the building or part of it, consisting of several final electrical circuits, will be disconnected. »
A similar unwanted tripping will also occur if both residual current devices operate simultaneously. Therefore, when designing electrical installations of buildings, the issues of ensuring selective operation of differential current devices should be given due attention.
Types of selective RCDs
For a selective RCD, it is important to pause so that the general type device located lower in the circuit has time to operate. In this case, the device with a time delay shutdown allows leakage current to pass through itself and does not operate. The delay interval may vary between models. For products marked S, it is 0.15-0.5 s, for example, the RCD 63a 100mA is selective, with the ability to adjust the delay. The best choice will be if they are installed at the input of the apartment's power cable. Some foreign models have even higher time delays. They are designed to disconnect the circuit in the event of a fire hazard. The longer the protection is turned off, the greater the likelihood of the insulation igniting.
When marked G, the device operates within 0.06-0.08 s. The device is quite fast in responding to network problems. It should be installed below the S selective RCD. With two-stage protection, it can be installed at the main input, since the performance of the RCD connected below is still higher.
If there are several groups of loads in the network, a separate protective device is connected in front of each, and a selective fire protection RCD is connected to the input. Then, if one of the lines malfunctions, only that line will be de-energized, while the rest will remain connected. With such a connection diagram it is easier to detect a malfunction. If a conventional RCD turns out to be faulty or does not respond to problems in the circuit, then a selective RCD (300 mA or 100 mA) will trip and disconnect the entire network.
To ensure selectivity, the following instrument settings are required:
- set the response time of the selective RCD, if it provides such a possibility;
- set the required shutdown parameters depending on the magnitude of the leakage current.
The shutdown characteristics of selective RCDs must be at least 3 times higher than the others. Only in this case will the device be guaranteed to work.
What is RCD selectivity?
The main purpose of the selectivity of the protective device is represented by its selectivity, therefore, with this type of automation, exclusively damaged areas are selected, which are cut off from the working electrical network.
In this case, unwanted de-energization of any other operational consumers is excluded.
Selective protective shutdown devices are mandatory for the electrification of modern residential buildings and office premises, warehouse areas and production facilities, apartments and private households.
Thus, selectivity is a property of automatic protection of the electrical network - it operates strictly one by one.
RCD parameters
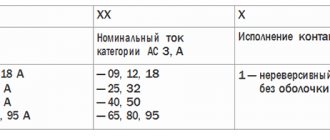
Two time parameters of the RCD are determined by Russian standards:
- shutdown time - the interval from the appearance of the shutdown leakage current ∆i until the moment the arc is extinguished;
- the maximum non-operation time for a type S device is the time interval between the beginning of the occurrence of ∆i and the opening of the contacts.
The last parameter determines the selectivity of the RCD. Its limit value is 0.5 s. It should be taken into account that to protect people, opening should occur within 10-30 ms, to prevent insulation fire - up to 500 ms. Type S selective RCD is widely used where it is necessary to exclude false alarms from the influence of interference or voltage surges.
Based on the speed of disconnection, RCD networks are divided as follows:
- general use - without delay;
- type G - 10-40 ms;
- type S - 40-500 ms.
Leakage currents always occur in electrical circuits. In total, they should not be higher than 1/3 of the nominal ∆i of the device. It is believed that per 1 A of load there is 0.4 mA of consumer leakage current, and per 1 m of phase wire length - 10 μA. The protective device is adjusted according to the total natural leakage current. If this is not done, frequent false positives may occur. It should be taken into account that a device with ∆i=100 mA will no longer protect a person from electric shock.
When designing electrical networks, you may not indicate the type of RCD until experts require it. But you need to justify your choice in advance. It is important that the rated current of the device is higher than the current of the intended load. In addition, the RCD is installed only in a common pair with a circuit breaker. You can install one differential machine instead of two devices. It will cost less, but you need to choose the right parameters.
The RCD protects in two-wire networks where there is no protective conductor. But it only works after touching a dangerous place.
Which fire protection RCD should you choose?
Selective RCD 63A, 300mA is usually installed at the entrance as a fire protection device.
Many people use conventional general-type models, installing 30 mA protection devices in the house. Here the “partial” selectivity function is performed due to the large difference in operating currents. This saves money on price differences. In addition, a conventional RCD provides better safety due to faster response when catching leakage currents. The difference in the behavior of the devices is that the selective device will not turn off first when the differential current is equal to or greater than 300 mA. Such a situation is already extraordinary and there is no question about whether it is worth going to the control panel, which may be located on a street pole. With such a large current, a conventional RCD will probably work if there is an accident on the line. Here it will be clear where to look for the problem.
Thus, the fire protection RCD can be installed either selective or regular.
RCD manufacturers
The Legrand Group is a world-renowned manufacturer of building electrical systems. The leading position is ensured by the highest production culture and large investments in the creation of new electrical products. For Russia, the group supplies the entire range of electrical equipment, from sockets and switches to the most complex control systems.
Selective RCD Legrand is of electronic and electromechanical type (indicated on the front panel). Depending on the version, it is installed on the side or below the circuit breakers. The time delay (0-1.3 s) and sensitivity are adjustable. In combination with automatic machines they are used as highly sensitive or basic protective devices.
Prices for RCDs remain high, like other brands.
The ABB company most fully presents RCDs with the F 200 series - from 16 A to 125 A. For a home network, a 63A RCD, 100mA selective, is sufficient. For leakage currents, a 30 mA device is usually used for household appliances. As fire protection at the entrance to a private house, an ABB selective RCD (63A, 300mA) four-pole for a three-phase network is used, as one of the most reliable. The quality of Legrand brand products is not inferior to it. For an apartment with a single-phase input there will be a two-pole device. The photo below shows an ABB 63A, 300mA selective RCD.
The maximum current that the device can withstand is from 3 to 10 kA (indicated on the front panel). It is a short-term current, not an operating current. The RCD is able to withstand a pause until the machine turns off the circuit.
The company is one of the leading ones, but the prices are very high. Consumers often prefer ABB models because safety costs the most. ABB DDA200 AP-R type A and AC differential block is available. It has a trip delay of 10ms, although it is not an ABB selective RCD. Its tripping characteristic curve is located between selective and conventional RCDs. The device has increased resistance to false alarms compared to general-purpose devices.
The defect rate for the ABB selective RCD, as for other products, is only 2%, due to which there are practically no problems in operation. Electromechanical devices are much more reliable than electronic ones and have advantages in everything, except for the price. RCDs with an electronic actuator are already beginning to appear, which are not inferior in reliability to mechanical ones.
On the market you can find products half the price, but the quality is not inferior to ABB. The company also produces the FH 200 series, which has a slightly lower price, but is significantly inferior in quality to the F 200 products. In particular, it does not have such reliable conductor fastening contacts, which quickly begin to loosen, which affects the quality of work.
If you purchase an ABB selective RCD, then only in specialized stores, and not in dubious places. A counterfeit is dangerous because it is not able to protect a person properly. DIYers pay great attention to modular equipment, the list of which also includes RCDs, due to their high cost.
The domestic group of companies IEK produces about 7 thousand types of products that meet international standards and ensure reliable operation of electrical networks.
High demands are placed on RCDs. On the one hand, they must operate reliably, protecting people from electric shock and wiring from the danger of fire. But at the same time, devices installed at different stages of electrical circuits must act selectively, turning off individual sections. These conditions, as well as GOST 51326.1, correspond to the selective RCD IEK type VD1 63S.
The product group is represented by rated currents of 25-80 A, and differential currents of 100 mA and 300 mA. The products are cheaper than those of famous brands and are widely used as introductory fire-fighting apparatus. In this case, the selectivity of protection is ensured by large values of cut-off currents and time delays for disconnecting circuits.
Selection of protective devices
If electricity is consumed according to a simple circuit, a sinusoidal current flows through the circuit. The leak will have a similar shape and AC type devices can be used here.
Modern household appliances increasingly use phase-cut control circuits. An AC type device will not respond to them and here it is better to use a type A RCD, which also responds to sinusoidal current. The devices can be used together, for example, type AC is suitable for lighting with incandescent lamps, and type A is suitable for sockets to which devices with pulse control can be connected. But if you have to change the lighting to energy-saving lamps with brightness control by phase cutoff, you will also have to replace the device type AC with A. Otherwise it will not work.
In order to separate the operation by levels of electrical circuits, it is necessary to use selective devices. Type S is installed on the main input, type G on the second level, and then instantaneous devices.
The RCD is selected one step higher in rated current than the circuit breaker connected in pair with it, which can operate for a long time when the load is exceeded. If there is a 50 A circuit breaker at the input, a 63A selective RCD will be suitable for it.
According to the requirements of the standards, the nominal values of voltage, as well as continuous and breaking current ∆i are indicated on the front panels of devices. If there is a sinusoid designation, this is an AC type. The presence of two positive half-cycles under it means type A. Selective RCDs are designated by the letters S and G. The rated short-circuit current is indicated in the frame. The device must withstand its increase to the maximum until the machine turns off. Usually the current does not have time to reach the limit value. The RCD disconnects the circuit with a defect in advance, before the conductor heats up and the insulation ignites.
Device types
RCD classification can be carried out according to several characteristics, including:
- rated current value;
- installation of differential current (current leakage);
- type of differential current;
- time delay value;
- number of poles;
- design of the output relay.
Rated current
This characteristic must be selected based on the total load of electrical appliances connected to the protective device. It is better to provide some reserve, that is, choose an RCD whose rated current exceeds the total load by 15 - 20%.
Leakage current
This parameter is of fundamental importance; according to it, all RCDs are divided into two groups.
The first group includes devices
, designed to protect people from electric shock. Since, as already mentioned, a current value of 100 mA and above is considered deadly, devices in this group have leakage current settings less than this value:
- 6 mA
- the most sensitive devices, meeting the standards of the European Union and the USA. Their use in networks with dilapidated wiring leads to unstable operation and frequent outages. In Russia they are practically not used; - 10 mA
- used to connect electrical appliances in high-risk environments, for example, in wet rooms (bath, sauna, swimming pool); - 30 mA
- devices with a similar characteristic are the most common.
Second group
designed for differential operating currents of 100 mA or more. RCDs of this type are designed to prevent fires in electrical wiring if the insulation is broken.
Type of current
Since current transformation occurs in residual current devices, the sensitivity of the RCD is not the same to currents of various types. For this reason, there are several types of RCDs designed to operate in different conditions:
- AC
- devices of this class are designed to work with sinusoidal alternating current, are the most widely used and most affordable; - A
- designed to work not only with sinusoidal currents, but also with pulsating ones; - B
- this type of device has the widest functionality and works with all types of current, including direct current.
In modern household appliances, components such as switching power supplies, inverters and frequency converters are no longer uncommon. The nature of the leakage current in this regard can have not only a sinusoidal shape. And depending on which block of the electronic circuit of a household device loses its insulation with the housing, the situation changes. In this sense, type “A” devices can provide the greatest safety in domestic conditions.
Pictograms that are applied to the housing to indicate the type of RCD.
RCDs of the “AC” type should be considered obsolete and do not fully meet the features of modern household appliances.
Type “B” is used primarily in industrial electrical installations where direct current damage may occur.
Number of poles
Everything is quite simple here. To determine the fact of a leak, monitoring of the phase and neutral wires is necessary. For this reason, in a single-phase network, devices with two poles are used to connect phase and zero, in a three-phase network, devices with four poles are used for zero and three phases.