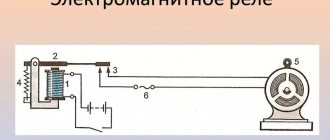
First, just a little general information. The supply line can optionally be single-phase, when there are only two wires, or three-phase, when there are four wires, three phase wires and one neutral wire. The generators that produce electricity are designed in such a way that they only have three coils. Therefore, if in the technical specifications you indicate a power of up to 5 kW, you will be powered from one coil, ask for more, then from three coils at once.
How to carry out three phases in a private house? If it is technically possible, you need to request (declare) such a connection. True, along the way from the generator to you there will be a transformer that reduces the high-voltage voltage to household values, so you will get not 380, but the original 220. But you will have as many as three phases of 220 volts! In the latter case, from the panel with circuit breakers in the house, three network lines will immediately go, each with a voltage of 220 volts and a power of 3.5 to 5 kW, depending on the installed circuit breaker.
Connection and wiring diagrams, taking into account the presence of three phases, may be different, depending on the needs and the presence of buildings on the site, but the general principles are, of course, the same. Below is my personal version:
Connection diagram for three phases of a private house and outbuildings on the site
By the way, both in the bathhouse and in the utility room, automatic switches (fuses) are also necessary. Installed at the same current as with the central input, in these buildings they will operate faster in the event of a faulty load due to losses in the supply line.
Is it possible to cover a house with vinyl siding in winter?
Wiring in the bathhouse and steam room: rules and recommendations
This winter, I already felt the advantage of three-phase water supply , when the dog Bob, having played enough in the first snow, wrapped in a blanket, warmed himself by the oil radiator in the change house, additionally pointing his muzzle at the heated air coming from the fan heater. There was no need to be afraid that the fuse would trip due to overload when working with a high-power power tool by connecting to a temporary socket with a different phase.
Why do you need a temporary socket?
Well, of course, not because of the dog. When the walls and windows are already in place, there is a roof over your head and a subfloor has been laid, but only the interior decoration is missing, then the time comes for a temporary outlet inside the house. And each time it is extremely inconvenient to drag the extension cord out of the change house. Although the outlet is called temporary, it must be made like a real one, according to all safety rules using a circuit breaker.
The distribution board diagram includes the following components:
A residual current device (RCD) is a device that monitors leakage current in the electrical network. This device opens the contacts if the differential current value (i.e., the difference in current between the phase and neutral conductors) exceeds a critical level. The RCD includes elements designed to measure and compare currents passing through the electrical network and to open the circuit.
The residual current device is designed to prevent fires caused by worn-out wiring and to protect people from electric shock. It can only be installed together with a circuit breaker.
Residual current devices are characterized by the number of poles (2, 4), leakage current (from electric shock - 30 mA), as well as the rated load current. All characteristics are indicated on the inside of the device.
Features of a three-phase network
A three-phase network is in most cases found in production and is intended for the operation of large three-phase consumers that have electric motors and are designed for 380 V power supply. Accordingly, in everyday life this version of the electrical network allows you to power a three-phase load, for example, a hob or oven, the power of which can be more than 5 kW.
In the case of three-phase wiring, alternating current is supplied through three phase wires (L1, L2 and L3), and returns through the neutral (N). There is also a ground wire (PE). In this case, between each phase and zero the voltage is 220 V, and 380 V passes between the phases themselves.
In a three-phase network, it is necessary to distribute the load proportionally, eliminating phase imbalance. For example, if the input power is 15 kW, then each phase will have 5 kW, respectively.
Note!
Phase imbalance is an asymmetry of currents and voltages that occurs for various reasons. Most often this is due to improper distribution of loads. For example, when one or two phases are operated with an excessively high load, and the third phase has minimal consumption.
Connecting 380 volts in a private house: diagram and some requirements
Having a connection project in hand, you can begin basic calculations: how much material, equipment and instruments will be required. Also determine the dimensions of the electrical panel and all its constituent devices and elements.
The three-phase connection of a detached house is as follows: four wires, one of which is zero, and the other three are working phases, supply voltage to the house from the transformer.
The principle of this connection is based on: all the conductors have the ability to connect to the water device of the entire building, and only from it does electricity flow to the multi-tariff meter and then to the distribution board. From this power panel, which is located on the facade of the house, wires go for internal connection of all rooms.
The connection diagram determines the location of the following elements:
- Switches;
- Sockets;
- Stabilizing devices;
- Stationary equipment.
The most important thing is to make the correct and competent connection of all input cables, common lines and additional electrical panel devices. This device is important and necessary for the entire three-phase system circuit. Before installing a switchboard, you need to know some of its features. This device must be located only in a freely accessible place, and its model must correspond to the type of room. Its compliance with the electrical wiring of the entire house also plays a very important role.
Distribution Rules
As is obvious from the above, the answer to the question of how to distribute the load across phases in a private house lies in the even division of consumers into all current-supplying conductors. A popular method is to connect a separate group of sockets in rooms to a separate phase wire. Moreover, subsequent grouping occurs in such a way as to optimize the load on the network. Lighting is connected using a similar principle; the load distribution across the phases of the conductor must be uniform.
Three-phase distribution diagram for power supply to a cottage Source samelectrik.ru
The above image shows the correct 380 volt, 3 phase connection. The private house, the electrical supply diagram of which is presented, is “wired” correctly, taking into account all the requirements.
Diagram of the correct connection of an electrical panel for a country house Source samelectrik.ru
The following image shows the correct wiring of a 380 volt 3 phase electrical panel. A private house, the technological connection diagram of which is shown in the picture, is connected correctly, which reduces the likelihood of circuit breakers turning off as a result of network overload.
Electric installation work
We will not dwell in more detail on the preparation of documentation for connecting the power supply; this is a separate topic. Our task is to determine the materials and devices for external installation work, which, although they are an intermediate stage in the connection, are the most important, since they are related to human safety.
Single-phase or three-phase input?
For both three-phase and single-phase networks, the permitted power is indicated in the technical specifications. This can be 15 kW for both options, that is, the benefit of a three-phase network is not in power, but in the possibility of using an input cable of a smaller cross-section and reducing the load, since the current is distributed over 3 phases. Therefore, in a three-phase network, the rating of the input circuit breaker will be lower.
But the input distribution board will be increased in size, since the meter itself is larger than a single-phase one, and the circuit breakers occupy 3-4 modules. Three-phase RCDs also have larger dimensions. This is a disadvantage of three-phase input into the house, but it is not very significant compared to such advantages as the ability to connect asynchronous electric drives, electric boilers, heaters, and electric stoves in the house.
To avoid phase imbalance from powerful electrical receivers, the electrician-installer must distribute the load as evenly as possible. The operating voltage of a three-phase network is 380V, therefore, in order to eliminate the risk of fire and electric shock, it would be a good idea to install a three-pole additional circuit breaker right before entering the house. This prevents short circuits at the input.
External connection and electrical panel
When connecting a private house to the power supply, an air input is most often used (which is also indicated in the technical specifications) with the installation of an electricity metering cabinet (SHUE) to eliminate cases of electricity theft and problems with the commercial registration of electricity supply.
According to the standards, the input cable must have a cross-section of at least 16 mm2 if the core is aluminum, and 10 mm2 if the core is copper, at a distance from the support pole of 25 m. For a distance of less than 25 m, the cross-section of the aluminum wire is 10 mm2, copper - 4 mm2 .
If you have decided on the method of connection from the pole to the house (aerial or underground), as well as the type and cross-section of the cable, then it remains to figure out exactly how the wire is connected to the house, from where further wiring to the devices is made.
The wire cross-section is selected according to the PUE based on the long-term permissible current. For aerial input, the most common cable is VVG or VVGng (modern version), as well as cable AVVG and SIP (self-supporting wire). By the way, for underground input, VBBbShv or AVBbShv cable is most often used. As you already understand, the presence or absence of the letter “A” means an aluminum core.
The value of the cable cross-section and the long-term permissible current for it are taken from the PUE. The optimal cross-sections for the input cable are 10, 16, 25 mm2, with a maximum permissible current, respectively: 50, 70, 85A (for underground input), and 80, 100, 140A for air input. For example, to a copper wire with a cross-section of 10 mm2, you can connect a power of 15 kW for a voltage of 230 V and from 30 kW for a voltage of 380 V.
Sequence of correct installation of an electrical panel
To ensure that the electrical panel in your home is installed correctly, you should use only high-quality electrical products, as well as consumables. Only after installation is completed, operating voltage is supplied to the panel.
The correct assembly of a three-phase electrical panel has the following sequence:
- Installation of an introductory machine. The device rating must cover the maximum power consumption. Since 3 phases will be brought into the house, the voltage between them will be 380 V, it is necessary to install a three-pole circuit breaker. To save money, it is not recommended to install 3 single-pole circuit breakers and connect them with a special strip. The input machine is installed in the upper left corner of the shield and is marked accordingly.
- After the introductory machine, it is necessary to install an RCD. The rating of the device must correspond to the rating of the input switch. You should also pay attention to the cut-off current - the lower this indicator, the faster the RCD will turn off the network. There are differential circuit breakers that include protective functions against short circuits and shutdown the network when a leakage current occurs (RCD and standard switch). It is easier to use such a product, but its cost is quite high.
- To the right of the RCD, at a short distance, a zero bus is mounted. Modern busbars provide a plastic dielectric between the copper strip and the shield body. This is done so that if the zero burns out and a phase gets on it, the electrical panel does not end up under life-threatening voltage.
- Measuring instruments and voltage relays can also be placed on the strip with the input circuit breaker, RCD and zero bus. If you install a voltmeter and an ammeter in a three-phase network, then you must select products that display both linear and phase loads. And also capable of showing data on each phase separately.
- The lower DIN rail contains automatic switches for power and lighting lines. In order not to get confused and not constantly look at the rating of the machines, lighting line products should be located at a short distance from the power switches.
After assembling the shield, you can mount it to the wall and connect the wires from consumers to the machines. An example of an electrical panel diagram, the number of machines can vary depending on the wishes of the owner.
If the electricity metering panel with a voltage of 380 V is not located on the street, then it is first installed in front of the input machine. But installing a device to monitor electricity consumption in the house is inconvenient, so inspectors (to save time and the absence of owners) must take readings on the street.
Single-phase and three-phase connection
There are many technical differences between single- and three-phase connections. For example, a three-phase connection is made using four or five wires. Of these, three are phase, through which current is supplied, and the remaining two are the neutral wire and grounding. In some cases, one common wire is used for neutral and ground.
When connecting using a single-phase circuit, two or three wires are used. This corresponds to phase zero and grounding. Using two wires means that neutral and ground are on a single conductor. Knowing the number of phases in advance, you can make calculations of the permissible power and determine the amount of electrical equipment that can be simultaneously connected to the network on each line.
Read also: Circles for a small grinder diameter
In the case of a single-phase connection, all the supplied voltage is concentrated on one line, which often leads to overloads. The thickness of the wires on the internal lines of a home network is much higher than those used in a three-phase circuit. This is due to the higher load that falls on only one line. Taking into account all of the above factors, when installing power supply for a private home, preference is most often given to three phases.
Types of three-phase sockets
Depending on the connection diagram used for the device that will be powered from a three-phase outlet, four or five wires need to be connected to it. In rare cases, it can be three or seven pieces - in the first case, when the control circuit and grounding are made separately, and in the second, when enhanced protection is used.
For each of these methods, its own socket is selected, with a certain number of contacts. An exception is the case if only three phases need to be connected to the device, but this happens extremely rarely. Here we take a four-pin plug, one of the contacts on which remains empty. You should not buy three-pin sockets that are available in stores - in fact, they are household ones, designed for 220 volts - phase, neutral and ground. They are similar to three-phase ones, since they can connect loads with a current of up to 32 Amperes.
The dimensions of three-phase sockets are usually quite significant, so these devices are not intended for mounting inside the wall, but are screwed externally onto dowels or a stand made for them.
Four-pin sockets
They are the most common in everyday life and in production, in networks where the neutral wire also serves as a ground wire and is connected to the device body. The socket is a base that is mounted on a wall or stand and then a protective cover is put on it.
The design of the sockets and the location of the terminals may differ, so if you plan to connect several devices to one socket, then it would be a good idea to ask the store which of them are constantly on sale.
When connecting, you need to be careful with the zero - in appearance this contact looks like all the others, but is marked with the corresponding icon on the base of the socket or its cover.
The wires are connected to the contacts using a bolted connection. Since most often the contacts themselves are made of brass, the use of aluminum wires is acceptable. If desired, you can use metal washers to be on the safe side.
Five-pin sockets
They are used in modern electrical circuits, where the protective, grounding zero is connected separately from the working zero, which requires a separate contact on the socket. Although only one wire is added compared to four-pin sockets, five-pin sockets are significantly larger in size. Considering that fairly rigid cables are often connected to them, they must be well secured to the wall.
The design of the box, the location of the terminals and their shape may differ, so it is better to select standard models so that, if necessary, you can freely find a replacement.
When purchasing, it is advisable to pay attention to the method of connecting the wires - if it is a bolt, the tip of which presses the wire to the contact, then over time it may break at the point of attachment. A solution to the problem may be to choose a socket model with other fastening methods or use wire lugs with which the cores are crimped
In general, if you need to use bolt clamps, then nothing bad will happen - you just need to check the contacts more often.
Grounding options
Grounding serves to protect a person from the harmful effects of electric current if the voltage is uninterrupted. The bottom line is that when a person touches a damaged section of the circuit, and thereby comes under dangerous voltage, the electric current flows along the path of least resistance. In this case, grounding is performed with the least resistance so that the electric current does not flow through you, but through the grounding system into the ground. But for this, the grounding system must be performed in accordance with the rules.
Ground loop
If the area near your house has enough area for a grounding loop, then it is necessary to perform it. In this case, at least three vertical electrodes, at least 2 m long, are driven into the ground. The distance between them should be no less than their length itself. They must be driven into a trench, the depth of which must be at least 0.5 m.
Using horizontal metal rods, they are connected by welding and brought out to the building, after which they are brought to the input device of the house. After installing the grounding, the current resistance is measured. If it does not correspond, then additional electrodes are driven in until the grounding resistance is brought to the required value.
Features of a single-phase network
Before putting into operation, any cottage or holiday village, as well as an apartment building, is connected to the local power grid, which is three-phase. Next, one of the three phases or all three phases is allocated to a specific consumer (a plot with a house or an apartment). Let's understand what these two types of electrical wiring are.
As a rule, in apartments or country houses, consumers are supplied with power through a single-phase network with a capacity of 5 kW. In this case, an electrical circuit consisting of three wires is introduced into the house: phase (L), neutral (N) and protective (PE) or grounding. The current flows to the consumer through the phase wire, and returns through the neutral. The protective conductor is used to prevent electric shock.
Features of the arrangement of the distribution panel
A single-line diagram of a 15 kW 380V metering panel (as a special case) is the most common option for constructing this part of the power supply system. When arranging it, the following configuration options are considered, taking into account the differences between single-phase and three-phase power supplies:
- Using standard single-pole circuit breakers and RCDs (one for each phase) as protective equipment.
- The use of only 4-pole differential devices in the circuit.
- Installation of two-pole circuit breakers in the panel, supplemented with a cross-module and an RCD.
- Installation of single-pole linear circuit breakers together with a 4-pole RCD and cross module.
Each of these options, if there is space in the panel, is suitable for arranging and connecting a full-fledged three-phase power supply system. The choice of a specific set of switching devices depends on the preferences and financial capabilities of the owner of a country home.