To increase the power of the power grid in private homes, it is necessary to replace the wire. Therefore, we figure out what cable is needed to connect a house to a 15 kW electrical network. Let's consider which wire is best to use, how to introduce it into the house and what types there are. We will also decide what cable is needed for connection via air or ground, what should be the distance from the wire to the ground or other nearby objects.
Power supply input Source infoelectrik.ru
Connection rules
To introduce electricity into a house from a pole, the new rules for connecting which you need to know in order to comply with the law, you need to have the appropriate skills.
The standard power of the connected network for entering a house on private plots is 4-6 kW, but if the owner has permission to build an individual dwelling, then he has the right to connect to a 15 kW network. This is necessary for the convenience of using high-power electrical appliances.
The supply must be carried out according to a design that is made taking into account the technical conditions prescribed individually for the site. Therefore, to connect the electrical network with new power, you need to submit an application to the energy supply company and indicate the required power (15 kW) and voltage (230/400 V). These parameters can be obtained by calculating the total consumption of all electrical appliances.
In the new technical specifications, the supplier company must indicate the permitted power, the size of the cable cross-section, their brand and type, as well as the requirements for protection and connection of the power grid to the house.
Connection to the home Source domelectrik.ru
Independent connection without approval of the project and permission from the energy supplier will entail a fine, but choosing the type of connection and participating in the discussion of the selected materials is recommended for those who understand at least something about this. Laying aluminum cables is prohibited on structures that are susceptible to fire. Therefore, it is necessary to replace it with copper analogues.
The distance from the balcony is required to be from 1 m for insulated and from 1.5 m for bare cables, and from a blank wall - from 20 cm for protected and 1 m for uncoated wires. Also, uninsulated overhead power lines are prohibited from running over buildings for safety reasons.
It is important! Any actions with power lines must be carried out only when the required section is completely disconnected, as well as with the application of portable grounding.
Schematic determination of distance Source www.allremont59.ru
Which cable should I use to connect an 11 kW motor?
The current of an 11 kW 1500 rpm motor is about 22.0 A, the circuit breaker for protection needs to be set to more than 22 * 1.25 = 27.5 A, i.e. somewhere around 31.5 A. The permissible cable cross-section must be at least 4mm2 (35A) for copper according to the conditions resp.
Interesting materials:
What is light diffraction in simple words? What is discrete mathematics in simple words? What is variance in simple words? What is DOS in simple words? What is emf in your own words? What is an economic system in simple words? What is economic theory in your own words? What is an electric field in simple words? What is electrical resistance in simple words? What is electricity in simple words?
Types of cable for a 15 kW network
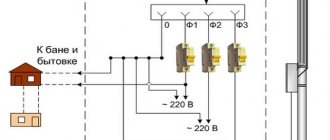
You need to know which cable to use to enter a private house: 3-phase or single-phase. Connecting using the first option implies reducing the load on the network and the rating of the input machine. The disadvantage is that the size of the distribution panel will be larger than with a single-phase connection, since the power switches will occupy 3-4 modules.
Also, three-phase residual current devices are larger in size. But this type of input cable makes it possible to connect asynchronous electrical devices, boilers, electric stoves or heating systems to the house.
Since the voltage in a three-phase network is 380 V, for protection you will need a three-way circuit breaker before entering the network into the house. It will help avoid the risk of fire and electric shock, and also provide protection against short circuits in the electrical network. Wires differ in the material from which the core is made. Copper cables have lower resistance than aluminum cables, but are more expensive.
Sectional view of 15 kW wire Source elektrik-a.su
Cables for power supply differ in the type of input:
- Airy . For this purpose, the AVK, SIP or AVVG (VVG) models are used. They have the ability to transmit current up to 1 kV and withstand temperatures from -50 to +48 ° C. The disadvantage of the air input is the use of jumpers necessary for the normal connection of the cable to the shield. The rules for wiring the electrical network indicate that such jumpers are unacceptable, but if this point is agreed upon by the supplier company, then when the connection is installed, a seal will be placed on it.
- Underground . For this type of connection, AVBbShV (aluminum) or VBBShV (copper) wire with an armored coating, galvanized tape and a protective hose is used. This is necessary to protect the cable from ground fault or mechanical damage.
For each type of connection there are certain connection and installation standards. If the cable is not installed correctly, all electrical devices may be subject to a short circuit or breakage from voltage surges, since improper power distribution leads to inefficient use of the network.
3 phases and zero Source isu.org.ua
See also: Catalog of companies that specialize in the installation of electrical networks
Reasons for replacing the wire
Most people living in the private sector are concerned about why and how to replace the cable from the pole to the house. The supply of electricity to cottages, country houses, and private houses is usually carried out from overhead main lines. Electric poles carry bare wires secured through support insulators. Most of the main lines are long outdated, in a dangerous situation, and also heavily overloaded, because electricity consumption increases every year.
Often in bad weather, due to strong winds, wires break or a short circuit occurs. Organizations whose responsibilities include servicing main lines usually do not immediately come to the scene of an accident, and when they arrive, they generally perform their work poorly. Therefore, the next time unfavorable weather occurs, everything repeats again.
Cable entry underground
If it is possible to connect the power grid through the foundation, then it is recommended to enter electricity into a wooden house or concrete structure underground. To do this, you need to attach a pipe 2 m long above the surface level to the pole. It is needed to protect the cable from people and external damage.
From the base of the pipe it is required to dig a trench with a depth of 0.7-0.8 m if the wire is protected by a pipe sheath and 1 m if it is without it. The connection to the house should also be made through an iron pipe, the edges of which are recommended to be smoothed to avoid chafing of the cable. The holes can be closed with rubber plugs to prevent snow and water from blowing in, and also to increase the thermal insulation of the room.
You can also make a connection from the wire to the panel not through the foundation, but using the wall. To do this, you need a similar pipe, which is installed near a pole with a height of 2 m above the ground. It is installed next to the shield and the wall on the outside of the building.
Fasteners for SIP
To install a line of SIP series cables, use:
- anchor, support and intermediate clamps;
- brackets and mounting hooks;
- yokes and clamps for holding metal tape;
- insulated staples;
- spiral knits;
- die and mounting clamps;
- piercing and branch couplings;
- rollers and auxiliary fittings (for example, protective caps for cut cable lugs).
Clamps
To connect several cables into a single line, special clamps are used that are characterized by increased strength.
The design has an extended clasp that holds the line when branches fall. The clamps are made of plastic that does not lose strength when exposed to ultraviolet radiation or when the temperature drops to -50°C and below. Do not use standard cable ties, which will burst after 6–8 months of being outdoors.
Anchor clamps
To hold the SIP line on the wall, anchor clamps made of aluminum alloy and reinforced polyamide are used. The mounts are designed to withstand exposure to sunlight and low air temperatures. The clamps differ in maximum breaking load, cross-section and number of cores, and are suitable for organizing subscriber branches of power supply lines. The wedge clamp holds the cable and does not destroy the protective insulation.
Brackets
Brackets are used to hold wires on supports or walls. The use of existing structures (for example, mounting loops or reinforcement pins) is not permitted. The clamp is attached to the poles using a metal bandage tape clamped with a yoke. To make the clamp, stainless or galvanized steel is used, the edges of which undergo a machining cycle. The tape is characterized by increased elasticity and is supplied in coils with a length of 25 m. A special tool is required for installation and tightening with a yoke.
The fittings for fixing SIPs are made of glass fiber reinforced polyamide. Products vary in size, configuration and maximum load. The brackets can withstand cooling down to -60°C without loss of strength and are not destroyed under the influence of ultraviolet radiation. Fastening elements are designed for installation at sub-zero air temperatures.
There is reinforced fittings made of aluminum alloy using high pressure casting technology.
Video description
This video shows how to lay the lead-in wire in a trench:
It is necessary to lay the cable through the wall in a metal pipe at a slight angle (protection from water). For a 15 kW power network with this type of connection, it is recommended to use copper VBBShb with a cross-section of 10 mm². It is necessary to avoid crossing the electrical network with water supply lines and gas pipes under the house.
The recess must be placed parallel to the foundation at a distance of 60 cm, and in places where cars pass, the wire must be at a depth of 1.25 m and protected by a pipe. The advantage of this type of connection is the high protection of the cable from external mechanical damage and wear from weather conditions.
The disadvantage of such a connection is that it is labor-intensive and expensive, as well as the inability to quickly replace damaged areas.
Wire that is laid through the wall Source i.ytimg.com
Air cable entry
Electricity can be connected to a country house from a pole using an air inlet. This method involves tensioning the cable from the power line to the panel using anchor bolts on the support. The wire entry must be made no lower than 2 m 75 cm above the ground, and if the height of the structure is insufficient, special pipe racks are used. It can be curved (“gander”) or straight.
If the height of the house meets the standards, then a panel with a residual current device is installed on the wall. The space from the pole to the entry point should be up to 10 m. If it is larger, then it is necessary to install an additional support, which will be mounted at a distance of up to 15 m from the power line.
The branch from the pole is made with a wire with a copper core and a cross-section from 4 mm² (length up to 10 m) to 6 mm² (from 10 to 15 m) and 10 mm² for a cable length of more than 25 m. If the core of the wire consists of aluminum, then it the diameter must be at least 16 mm. If SIP is used to bring electricity into the house, then its connection requires special fittings and an insulator made of glass, polymer or porcelain.
Parameters to consider when choosing a cable
First of all, determine the current loads that will pass through this cable in order to determine the thickness of the wires; professionals call this parameter the cross-section of the wires. Uninitiated people sometimes confuse cross-section with diameter; these are fundamentally different indicators.
The cross-section is considered to be S - the area of the circle of the cut wire.
Typically, private residential buildings and country houses consume 3-5 kW. But it is recommended to use a more accurate calculation method; it consists of summing up the power consumption of all electrical appliances in the house.
Total power consumption table
| Name of household appliances | Power consumption in W |
| Lighting | 800 |
| TV | 150 |
| Fridge | 700 |
| Computer | 50 |
| Boiler for heating water | 1500 |
| Warm floor | 1800 |
| Iron | 700 |
| Sum | 5700 |
By adding up the power of all household appliances, we get the maximum power that can be consumed in a given house: 5.7 kW. Knowing the voltage and power, we calculate the possible maximum load current on the cable wires.
I(current) = P(power)U(voltage) = 5700W/220V = 25.9 A. In order not to waste time studying a complex method for calculating the cross-section of wires with known parameters of power, current and voltage, you need to use tables.
Based on the wire cross-section standards that manufacturers make, calculations were made and compiled into tables, which are available in specialized literature and on Internet resources. Let's use one of these tables for cables with copper wires with one phase, since most consumers in private homes use this connection diagram.
| P – power in kW | 1 | 2 | 3 | 3,5 | 4 | 6 | 8 |
| Current consumption in I, in A amperes | 4,5 | 9,1 | 13,6 | 15,9 | 18,2 | 27,3 | 36,4 |
| Conductor cross- section , mm 2 | 1 | 1 | 1,5 | 2,5 | 2,5 | 4 | 6 |
| permissible cable length , m * | 34,6 | 17,3 | 17,3 | 24,7 | 21,6 | 23 | 27 |
25A – according to the table, corresponds to a wire cross-section of 4 mm2.
Tip #1. Wise consumers always take into account the prospect of a possible increase in household appliances in the house. Therefore, take the next value in the table upward, this is 36A with a 6 mm2 wire.
There are various tables for determining wire cross-sections:
- for copper wires;
- for aluminum wires;
- voltage 220 or 380 V;
- by current or power.
Nowadays, for an ordinary person, in order not to go into details of physical processes and mathematical calculations, it is easier to use the online calculator on this site https://ydoma.info/electricity-vybor-secheniya-provoda.html.
Options with aluminum wires:
| Current loads of wires and cables | |||||
| Conductor cross-section in mm2 | For one wire | With two wires | With three wires | ||
| (aluminum) | Gasket laying method | ||||
| air | air | underground | by air | underground | |
| 2,5 | 23 | 21 | 34 | 19 | 29 |
| 4 | 31 | 29 | 42 | 27 | 38 |
| 6 | 38 | 38 | 55 | 32 | 46 |
| 10 | 60 | 55 | 80 | 42 | 70 |
| 16 | 75 | 70 | 105 | 60 | 90 |
| 25 | 105 | 90 | 135 | 75 | 115 |
| 35 | 130 | 105 | 160 | 90 | 140 |
| 50 | 165 | 135 | 205 | 110 | 175 |
| 70 | 210 | 165 | 245 | 140 | 210 |
| 95 | 250 | 200 | 295 | 170 | 255 |
| 120 | 295 | 230 | 340 | 200 | 295 |
| 150 | 340 | 270 | 390 | 235 | 335 |
| 185 | 390 | 310 | 440 | 270 | 385 |
| 240 | 465 | — | — | — | — |
However, since power lines are laid with aluminum wires, in order to avoid heating and unnecessary losses from transition resistance at contacts with different metals, it is allowed to use a cable with aluminum wire only in sections from the power line to the control panel and electricity consumption meters (meters).
Having decided on the required cross-section of wires in the cable, it is necessary to clarify the route and method of laying it. There are different communication methods:
- by air;
- underground;
- along the walls of buildings;
- along the surface of barrier structures (fences).
Cable calculation
You need to know what cross-section is needed for 15 kW and 380 for input into the house, since with an aluminum and copper core it has different characteristics, and also differs with different connection methods. For open introduction at a voltage of 380 V and a power of 15 kW, a copper conductor with a cross-section of 4 mm² and capable of withstanding a current of 41 A is required, and for an aluminum wire - from 10 mm² and a current of 60 A.
For cables laid in a pipe, copper conductors must have a cross-section of 10 mm², and for aluminum conductors - from 16 mm². The length of the cable depends on the distance of the entry point to the pole, as well as the presence of additional fasteners or supports.
First of all, the wire is connected to the electricity meter Source i.ytimg.com
Laying underground
If it is not possible to lay a cable over the air on a site, it is proposed to consider the possibility of laying it through a trench. The technology is more complex, since you have to dig the ground, plus the cost of the cables is higher.
Almost all models used for underground installation consist of an armored surface made of metal tape. There are two options.
The AVBBShv cable has aluminum wires with PVC insulation, armored with galvanized tape, and the outer side consists of polyvinyl chloride resin. The cores are made both from solid wire and strands. Suitable for line voltages up to 3 kW. Proper operation allows you to save the life of the wiring for 35 years. The structure is well protected from shifts of solid earth, parasites and moisture.
The VBBShv cable is similar in structure to the previous one. The only difference is the copper strands of the conductors. It is used for external wiring along the wall of a building and a concrete fence, in addition to other structures. Due to its differences, it is considered more universal.
Selecting a cable for connecting from a pole is a labor-intensive and serious step. If you do not take it seriously, problems may soon arise that will cost more money to resolve than planned.