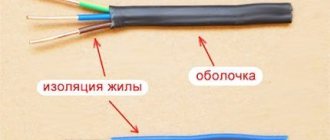
The transmission of electrical energy and the connection of consumers can be carried out using electrical cables in both round and flat versions. Each type of wire is used in different situations, installation and operating conditions, so it is important to understand how a flat cable differs from a round cable for its correct (including from an economical point of view) application.
In household electrical installations, both types of cable are often used. For example, cable brand VVGng exists in two versions: VVGng and VVGng-p (the “P” symbol at the end of the product marking indicates that it has a flat shape). Such products are used when connecting stationary electrical installations in residential and industrial buildings, including in dry and damp rooms, as well as when laying cable lines in the absence of a threat of cable damage.
Based on a comparison of the design features of the round VVG cable and its flat version, it is clear that they differ:
- The plane of laying of current-carrying conductors: VVGng-p has conductors arranged in one plane, while VVGng conductors are laid in planes parallel to each other;
- The number of cores in the common sheath and their cross-section: for a flat cable, due to its design features, the number of cores cannot be more than three pieces and each of them can have a maximum cross-section of 25 mm2, but for a round cable under one common sheath there are from 1 to 5 cores, and the cores themselves can have a round or segmental cross-section up to 500 mm2;
- Flat cables do not have a protective shield or armor due to the fact that the protective material cannot be flat and tends to be rounded.
Also, the two types of these cable products differ in their resistance to mechanical stress, namely torsion. Operating a flat cable under constant twisting forces means that it will only be twisted up to a certain point, after which the cores and insulation of such a conductor may be damaged. The round cable can operate under torsion conditions, when exposed to random bends and movement along one axis. The flat version of the wire can be used in electrical installations that move only along one axis or are stationary.
Replacing wiring in an apartment
How to reliably replace wiring in an apartment.
Wiring hidden in the wall, which cable is better - flat or round. Masters online: 156 Orders per week: 2,148 Offers per day: 901
flat copper 3x2.5 or 2.x2.5 if there is no grounding or it is not needed
VVGng 3x1.5 for lighting VVGng 3x2.5 for sockets
Call a competent team. The shape of the cable does not matter, the main thing is its type.
Leave it to a professional. Cable - copper - 1.5mm - light, 2.5mm - sockets. Flat or round does not matter. The brand and cross-section are important
The old cable needs to be cut and a new light of the same section must be installed. other sockets round flat does not matter, preferably copper
It doesn't matter whether the cable is flat or round. It is important to choose the right sections: for sockets 3*2.5, for light 3*1.5. Usually they buy cable brands VVGng (sometimes with the prefix ls), and NYM. VVG - flat, NYM - round. Keep in mind that VVGng 3*2.5 fits very poorly into 16mm corrugation. And 3*1.5 works great. NYM is in the 16th corrugation. Moreover, half of the practicing electricians believe that stretching NYM in corrugation is reinsurance. Regarding cable manufacturers: NYM buys the production of a well-promoted or Bryansk plant (it is cheaper, but not inferior in quality to Sevkabel). VVG -, Kaluga and Oryol plants.
Thank you, where is the best place to buy a non-counterfeit cable in Moscow?
In residential premises and public buildings VVG ng ls, NYM - for wooden buildings, PUNP - prohibited.
Wiring should be done using NYM 3X2.5 and 3X1.5 cable. Divide into groups: for each room there is a group for sockets and a group for lighting. Each group is protected by an individual circuit breaker (16A sockets, 6-10 A light) Groups in wet rooms and kitchens are additionally protected by an RCD. For washing machine, dishwasher, boiler, etc. It is advisable to install an individual cable and install your own machine. For a hob (or electric stove), install a cable with a cross-section of at least 4 sq. mm (if the network is single-phase) and a 32A circuit breaker. The wire connections are made very well (welding is the most reliable) But high-quality twists and terminal blocks are also allowed. In general, it is dangerous to trust this work to just anyone and the cost is not cheap.
VVGNG or NUM cable in the wall
To lay new wiring, you need to make lowerings for each socket and switch. Then you must decide on the ceiling, if all the ceilings are suspended, then all the wiring and distribution boxes can be run along the rough ceiling. If the ceiling remains zero, then you need to prepare for more grooves. Cable of any shape 3x2.5 to 3x1.5 sockets for light and of course don’t forget about the input cable, it will most likely also need to be replaced
I beg your pardon, but when in 3-5 years you get tired of the suspended suspended ceilings and want to drop them, change the wiring again to hide the junction boxes and cable?
Yes, and the old wiring remains in the wall; it is not necessary to remove it if you completely turn off the power
Hello Natalya, I’m reading this and couldn’t resist commenting. The question is as meaningless as most of the answers. Electrical wiring can be reliably replaced by a Master with a capital letter, who will know and love his work, and then the questions “which cable is better” simply will not arise. It so happened that electricians were and will be done by ignoramuses, because for access to the Master you have to pay twice and expensively. IMHO.
Yes, they are all just having fun here))) Some simply amaze with ignorance and lack of knowledge. Well, I would respectfully advise the hostess to focus on choosing a MASTER, and not on technical subtleties. Don't mind your own business! ))) No offense.
Natalya, only an excellent electrician can reliably replace the wiring. He will also help with the choice of materials. General requirements: cable - NYM or VVGng LS GOST. 3x1.5 (lighting) 3x2.5 (sockets) 3x4 (oven, hob), 3x6 (input), flat round doesn’t matter (I use flat, it’s easier to put in grooves); machines 6-10A (lighting), 16A (sockets), additionally for RCD sockets (differential circuit breakers), for s/u differential circuit breakers with a leakage current of 10 mlA, manufacturers: Schneider, Legrand, ABB, Siemens (choose according to your budget, but do not save much - this is your safety!!), it is advisable to make connections by twisting + welding in junction boxes installed on the walls (must be accessible for maintenance) And another tip: before installing in the kitchen, it is advisable to call a designer and draw up a project for the future set, otherwise It’s almost impossible to guess the position of the sockets, and in general, start by arranging the furniture on paper, this will make it easier to decide what and where. Good luck with the repair
Pyryshev Dmitry Mikhailovich - competent approach! +1
Thank you, reputation is more important than anything.
so as not to spend a lot of money on installers and materials, throw the main cable to the boxes in each room with a 4x4 cable (light phase, socket phase, zero, ground) or 3x4 if there is no grounding, and then throw everything with the usual 3x2.5 and 2x1.5 ( the earth is not needed for the world; all this is profanation).
Cable for electrical wiring in an apartment - 300 brands and 5000 varieties
Which side should we start with? A person who is far from electrical installation will grab his head. And there is something to grab onto. Because there are not just a lot of cables and wires, they literally cannot be counted, like Don Pedro in Brazil. Even professional electricians sometimes get overwhelmed and confused by the abundance of manufacturers and products.
The choice of wire for electrical wiring in an apartment is not only a question of the cost of repairs. A much more important point is that the wiring must ensure the “delivery” of electricity to any corner of the apartment and be safe, that is, not “bite” with current. And also be fire resistant and reliable.
Attention!
The key to reliable electrical wiring is finding the right electrician. A specially trained technician must do electrical work and select cables for wiring in an apartment! Who has access to electrical installation work and practical experience.
We will briefly talk about cables and wires, their cross-section, markings, materials and types. We will explain what is suitable for home wiring and what cannot be used. So that you are aware of what your electrician is doing and why.
What is the difference between round and flat cables?
Very often, when designing electronic and automation systems, the issue of cable selection is a “secondary” issue for many engineers. However, later, when it turns out that a properly selected cable system can save production costs, increase the service life and reliability of the device, and, importantly, maintain signal quality.
Unplanned equipment downtime is unacceptable in any industry. Therefore, power supply systems are the “arteries” of modern technology. In modern automatic systems, moving devices (robots, cranes, etc.) create a lot of problems for engineers who must make a decision - which cable is better to use, round or flat? Let's consider several criteria that need to be taken into account when choosing.
Applications
Depending on the market and operating conditions of the products, round and flat cables are used. Round cables have long been an industry standard and are used in most industrial and automation systems and range from simple manufacturing systems to alternative energy applications.
Flat cables are not as widespread and are more of a "point" solution, and can be used for power and control and measurement signals in medical equipment, civil aircraft and other specific categories. Flat or scalloped cables are also in high demand in the overhead crane market for companies that do not want to use spools in their solutions.
Performance criterion
Electrical characteristics
- Electromagnetic interference (EMI) consists of both external and internal sources. Internal EMI protection varies and is highly dependent on cable design. If engineers work with individual shielded pairs in a flat cable, this will ensure crosstalk pair pairing and communication protection.
It is very difficult to place a general shield on a flat cable because the shielding material tends to be rounded - it cannot be in a flat format. This makes external EMI protection for flat cables very difficult and virtually impossible, since this method of protection can only provide better external EMI protection for round cables.
- Crosstalk: This is an uncontrolled coupling of signals between two transmission circuits. Similar to EMI protection, using a variety of pair lengths in a flat or round cable increases crosstalk immunity.
- Attenuation: Ultimately determines the maximum signal cable length and conductor resistance, which affects the voltage drop across the power component. In most cases, the attenuation is worse when using a flat cable. The use of high quality insulation and proper placement in the ground can improve attenuation, leading to the need to select a flat design. Some industries produce high performance (low strength and weakened) flat cables.
Unfavorable working conditions
These electrical products are exposed to many environmental factors, which can lead to deterioration of the cable quality if the materials were incorrectly selected during manufacture. Some of these conditions include ultraviolet, oil, radiation, abrasion, high or low temperature and friction. Knowing these factors in advance will greatly influence the choice of material properties (polyimide / polyethylene foam, etc.) for conductor insulation and cable sheath materials (polyurethane).
Most PVC or PTFE used in round cables can be applied to withstand many of these harsh environmental conditions while maintaining their flexibility. Flat cables that are extruded with silicone will be able to withstand high temperatures. However, silicone is a softer material and does not provide much resistance to abrasion and friction, which can lead to internal failures.
Cable design and production
Round cables are designed to maximize space within the minimum required cross-sectional area. This allows them to be used in most openings for automation systems or when connecting various types of electrical machines, which may be a problem for a flat cable with an extended cross-section, that is, a square pin and a round hole.
The space occupied during installation and its convenience play an important role, and here round conductors have an advantage, since it is much easier to make a round hole than a rectangular one. However, when using flat cables, it is possible to stack them on top of each other to save space, which is not possible when using round ones.
In addition, flat cables must be weighed and balanced to ensure smooth movement. This is also necessary for round conductors only when they are installed in a cable route. They require only fillers and tapes to ensure concentricity.
The weight and flexibility of the cable design optimizes ergonomic performance for the end user, especially when it is a portable device:
Finally, special equipment is required to encapsulate all the planar components in one cable. Cable production equipment is standardized to produce round cables, so additional tooling translates into additional production cost for customers.
Cable components and accessories
When installing electrical wiring, you need not only a cable, but also a whole list of equipment, components, electrical installation products and accessories. To determine the exact quantity, the electrician always makes a wiring plan or diagram. But, now we are speaking in general, so we will name an approximate list of additional elements.
Naturally, everything is selected according to the room conditions, load and type of hidden wiring. After all, it can be both in the wall and in plasterboard structures. An experienced electrician will take into account all the details and issue a list or go to purchase the goods with you.
Dependence on operating conditions
Modern industrial realities require cable products to be protected from many adverse factors, and not just one. For example:
- Wear and cut resistance: Because conductors can wrap around spools and be pulled along concrete surfaces with sharp edges, which can damage the outer insulation layer. Therefore, the outer layer must have good rigidity (polyurethanes have a good reputation).
- Low elongation under high tensile load: This is achieved by a double-wall extrusion process combined with an aramid braid (Kevlar/Vectran) between them to relieve mechanical stress on internal components. This type of design minimizes tensile stress on the internal conductors, reducing fatigue and early failure.
- Using a durable element in designs reduces dependence on copper, thereby reducing the overall amount of copper, which ultimately reduces cable size, weight and cost. These types of designs are virtually impossible with flat cables, which rely on silicone and PTFE to seal multiple conductor components.
There are a large number of options available when designing an electrical system. Engineers must do a lot of work to find the best option that will meet the mechanical and electrical requirements of the device. The correct choice of cable design gives all parties confidence in the reliable and long-lasting operation of the system.
KG, VVG and NYM: we understand the types of cable and choose the appropriate one
Content
If you come to the store and look at the cables, it will not be easy to immediately understand which one to choose. In appearance they are not much different. Only the keen eye of a professional electrician will pay attention to the number of cores, sheathing and markings. Our article will help you understand the main types that are common today in residential, office, commercial and industrial premises.
Each location has different wiring requirements. For example, in a car wash it must withstand high humidity. Street lighting in the cottage area must be done taking into account the effect of ultraviolet radiation and low temperatures on the cable. For internal electrical wiring, its non-flammability and low smoke generation are important. Do you already know what requirements apply to your facility? Then explore our selection and make the right decision.
Cables for electrical wiring of an apartment 380 Volt
If your apartment is powered by a voltage of 220/380 Volts, then all of the above cables with only five or four cores are used.
These cables will most likely be recommended to you by professional electricians. Don't be fooled by cheap prices and advice from left-wing electricians. Do not use PUNP cable for electrical wiring of the apartment. Remember, the cable for electrical wiring of the apartment is not used for one day and not only the operation of household appliances, but also your safety depends on it.
©Ehto.ru
Articles on the topic
Similar
KG – designed for harsh conditions
Perhaps the best solution for outdoor use is a cable marked KG. It has an insulating layer of rubber based on natural rubber. Moreover, such insulation is used both outside and for the cores themselves. This helps the product maintain high flexibility even in severe frost, and also makes it resistant to ultraviolet radiation - the shell does not crack. Withstands high air humidity. It is suitable for outdoor lighting of cottages, private houses, and enterprises. Can be used in car washes and production areas. It is often the basis for creating extension cords and powering equipment.
Understanding the labeling
- K – cable
- G – flexible
It has copper cores - from 1 to 5 pieces. The cross section can be up to 95 square meters. mm. For example, the 3x4 marking means that the cable is three-core and the cross-section of the cores is 4 square meters. mm. There are also additional letter designations: t – the cable is suitable for tropical zones and rooms with air humidity up to 98%; n – non-flammable with oil-resistant insulation; chl – resistant to cold, withstands frosts down to -60 °C.
VVG – a safe solution for residential premises
If you ask electricians what is the most common type of cable for residential buildings, they will answer - VVG. This is the most popular solution for internal electrical networks and closed electrical installations with voltages up to 1 kV. The maximum service life is 30 years. This type of cable replaced PVS as more reliable. But at the same time, this is one of the most budget options on the market, which is why it is in such great demand.
Understanding the labeling
- B – PVC core insulation
- B – PVC outer sheath
- D – there is no external armor or other additional protective layers
NYM – confidence for many years
This is a German analogue of the VVG cable. Only it is manufactured in accordance with the German standard DIN VDE Normenleitung. It is characterized by high reliability, safety and long service life - up to 40 years. It is most often chosen for installation in apartments, cottages, office buildings, commercial and industrial premises. Many manufacturers offer frost-resistant cables, the operating temperature of which can reach -50 °C. Therefore they are suitable for installation in unheated rooms. Also, the NYM sheath is not afraid of ultraviolet radiation, unlike VVG - you can install the cable where direct sunlight hits. It is also easy to cut without special tools, which electricians appreciate.
Understanding the labeling
- N (normenleitung) – manufactured according to VDE standard
- Y (ysolationsschicht) – polyvinyl chloride insulation
- M (mantelleitung) – there is an outer shell
This type of cable can have from 1 to 7 copper cores. The cross section can reach 6 square meters. mm. You can find a product marked ls (low smoke), which means reduced smoke production when heated. The letter J indicates the presence of a yellow-green protective ground conductor. If there is no letter after the name or the letter O , this means there is no grounding conductor.
PBPP wire
This is a flat electrical wire with two or three solid copper cores. The outer protective layer and conductor insulation are made of PVC. The cross-sectional area of the conductors is from 1.5 to 6 square meters. mm. The operating temperature of the product is from –15 to +50 °C with a network voltage of up to 250 V. The electrical wire PBPP (PUNP) is used when installing lighting systems and power outlets. There are modifications of this product: PBPPg and APUNP. The letter “g” in the marking means that this wire is flexible and its current-carrying conductors are multi-wire. The modification with the first letter “A” is a wire with aluminum conductors.
PBPP wire has become very widespread, as it is excellent for connecting lighting, installing electrical sockets and switches, as well as for solving other electrical problems. This product is a truly universal conductor of electric current, which is highly popular due to its excellent quality. PBPP wire is recommended for use when carrying out electrical work in a private house, apartment or country house.
Important! Basically, PBPP brand wires of all modifications are used in home and household networks. They are great for installing indoor wiring, but should not be used as a replacement for power cables. When purchasing these products, be careful, as mislabeling of wires of these brands is quite common!
What to consider when choosing a cable
Within each described category there are subtypes, and you have probably already decided on the most suitable cable for your requirements. But there are also general tips that guide your purchase.
- First, consider the voltage. In a household network its value is 220 - 230 V, in an industrial network - 380 V and higher. Here you will find a cable for both needs. The main thing is to pay attention to the number of cores.
- Secondly, calculate the cross section. It depends on the type of gasket - open or closed, current strength and connected power. If you do not know these parameters, it is better to contact an electrician. And according to his calculations, order the required cable.
- Thirdly, pay attention to which document the cable is made from. In Russia this may be TU or GOST. If the installation will take place at an enterprise where the parameters of the electrical network are strictly controlled, it makes sense to give preference to GOST.
- Fourthly, calculate the length and decide how it will be more convenient to buy the required quantity. Manufacturers offer cable in a coil, coiled, on a reel and cut to individual lengths.
- Fifth, consider the country of production. You can purchase products from China, Russia, Europe and the USA. Products differ in price, workmanship and warranty.
If you need advice on selection, please contact our managers. They will help you choose the right cable and guide you in terms of parameters, price and delivery time. And if you are ready to make your own choice, go to the catalog and buy through the website. Here you will find electrical installation products and other products in the “Electrical and Lighting” category. Therefore, you can do turnkey electrical installation by purchasing everything on one site!
Characteristics of wires and cables that you should pay attention to when choosing
Let us immediately clarify that we are talking about a household power cable or wire with a voltage of 220/380 V for transmitting electric current in a home network. We are not currently considering all other types such as heating, television, computer and others.
The general list of characteristics looks like this:
Material and design
According to the composition of the vein
, cable products are divided into copper and aluminum. Copper products are more reliable, the resistance is lower, the current is higher, and the heating is less when compared with aluminum of the same cross-section. In addition, copper oxidizes less and is more ductile, which means the cable lasts longer without loss of properties and characteristics.
Attention!
Wiring aluminum cables in an apartment is prohibited according to the requirements of the PUE (electrical installation rules).
By design
single-core (single-wire) and multi-core (multi-wire) cables and wires are produced. Single-core varieties are more rigid and inflexible, especially with a large conductor cross-section.
Answering the question “which wire to use for wiring under plaster,” we can say that theoretically a single-core single-wire copper cable is also suitable. Plaster will create additional protection for such a conductor. But in fact, no one lays a single-wire home electrical network.
Multi-wire single-core cable is softer and more flexible. It tolerates bends and turns well and is suitable for both open wiring and hidden wiring under plaster. It is the three-core single-wire that is now used for laying in apartments.
Attention!
Do not confuse cables in which each core consists of one conductor with wires where the core is made of several conductors.
Multi-wire cable products are prohibited for permanent installation in an apartment due to the high fire hazard. Read more about them in the block “which wires should not be used for electrical wiring in an apartment”
Cable cross-section for wiring in an apartment
It is measured in “squares”, that is, square millimeters and shows the throughput. For a copper cable, one “square” carries 8-10 Amperes of current, for an aluminum cable only 5 A. For safe operation, the conductor should be selected with a reserve of carrying capacity, which ensures heating of the wire within the permissible value, or, more simply, so that it does not “float” under the load. insulation. In addition, with hidden wiring, it must be taken into account that it is cooled less efficiently, which means that the cross-sectional reserve must compensate for this.
Attention!
Do not confuse the cable cross-section with its diameter, these are two big differences! The diameter can be measured with a ruler, or better yet, with a caliper. And then substitute it into the formula and calculate the cross-sectional area.
Also remember that the choice of cable for wiring in an apartment is always rounded up. If the calculation results in 2.3 “squares”, a two and a half cable is selected, not two “squares”.
Ideally, the cross-section should match the marking on the cable tag, but in fact it often differs to a smaller extent. Small discrepancies are acceptable because the cable is certified by resistance, not by wire cross-section. If the discrepancies are significant, it is a marriage. An experienced electrician will see it visually, and you can measure the diameter of the core and calculate the cross-section for interest or to help a friend who independently decides to buy a cable for apartment wiring.
Some electricians advise using a cable with a rating higher than the calculated one. For example, 4 “squares”, instead of 2.5, to cover the “shortage” of the section, if there is one. But then you will have to calculate the wiring protection accordingly and install the correct machines and RCDs.
Core insulation thickness
Simply put, there is a range of thicknesses where the insulation must “fit” so that the wiring serves reliably and there are no problems during installation. Whether the manufacturer violated the technology cannot be determined without a micrometer unless you tinker with the cables every day. Therefore, if there is no experienced electrician nearby, you should only buy cables from well-known brands in trusted stores.
Shell thickness
The sheath encloses the cable over the insulated cores, secures them and protects them. It is made, like the core insulation, from PVC plastic or polymer, but is thicker. For multi-core cables, the thickness is 1.8 mm, for single-core cables - 1.4 mm. Deviations in a smaller direction are also possible, but insignificant.
The insulating shell is a mandatory element. For any residential wiring cable, even with minimal power, double insulation is prescribed. That is, first on the core, and then on top of it. This ensures the safety of people and protects the conductor itself from damage.
Marking
This is the inscription on the cable sheath for installing electrical wiring in the apartment. It contains all the necessary information for selection. The inscription is printed or extruded during the manufacture of cable products. It should be clear, contrasting, and easily readable.
The labeling indicates:
The inscription is applied along the entire length of the conductor at small intervals.
On the price tag and in catalogs of online stores, they usually do not indicate the year of manufacture and manufacturer and write the marking in the form VVGng(ozh)-0.66 kV 3x1.5
or
VVG, VVGng cable 3x1.5.
It stands for three-core copper cable with a core cross-section of 1.5 “square” (3x1.5), single-wire core design (ozh). Insulation and sheath made of PVC compound (VV), flexible cable (G), non-flammable (ng). Rated voltage 660 Volts.
Remember!
The letter designation of the cable brand begins with the core material; for aluminum the letter A is always indicated, for copper
the
letter is not indicated, therefore all cables of the VVG brands of all modifications have a copper conductor.
Core colors
What you need to know about the color is that it is either a solid color or a stripe is applied to the sheath along the entire cable, approximately a millimeter wide. This is the standard. Everything else, in the form of smears, spots, stripes across it, is from the evil one. And he says that strange people were making the cable in some basement.
There is a table for the colors of the cores that any experienced electrician knows. It describes what shade the main conductors are denoted by - phase, neutral, grounding. This was done for convenience during installation, in order to see where to connect which conductor. Phase and working conductors may differ in color, but the “ground” is always “painted” yellow-green.
Package
Standard for all types is a coil or drum. The coils are sold to stores and wound onto drums for wholesalers, builders and other large buyers. In any case, a label with a description is attached to the cable.
The contents of the tag repeat the information on the inscription on the shell with some additions. It states:
If you come to buy a cable for wiring in an apartment in a whole bay of 100 m, you will receive a tag along with it. But if they cut off a piece for you, they won’t give you the label, you can just look at it.
Certificate
Needed to confirm that the cable is of high quality. Typically, products have 2 documents - a certificate of conformity, which is responsible for the suitability of the cable as an electrical installation material, and a fire safety certificate. You can ask the seller for them to review. The documents must be filled out indicating GOST standards for the cable and have a valid period, for example, until the end of the current year. As a rule, the documentation indicates specifications (technical conditions) in accordance with GOST and for cable products this is equivalent to compliance with GOST.
State
This is the appearance of the power wire. Pay attention to how the cable looks, because bruises, strong kinks, and compression hide an internal defect. The veins may be broken and even shorted to each other. It is clear that such material cannot be laid, therefore, do not be lazy to inspect the cable in the store, even before paying for your own purchase.
Which cable is better for home and apartment?
Today we will try to cover the topic of choosing the right cable for your home network. What calculations should be made? What are the distinctive features of different cables? How to calculate everything, avoid unnecessary expenses and new repairs?
So, let's start with the fact that when receiving electrical energy from the supplier, we undertake to use it in accordance with certain rules, called the rules for the use of electrical installations (RUE).
PUE, 7th edition, valid in Russia, prohibits the use of aluminum conductors in household electrical networks. Accordingly, copper cable is by far the most reliable and practical conductor used in apartments and houses of residents of our country.
Selecting the section and markings
When choosing a wire cross-section, it is necessary to determine its intended purpose and the estimated load that it will carry. A cross-section of 1.5 mm is excellent for mounting lighting elements and switches, but for sockets and cables that will carry a large load, a larger cross-section is needed.
As for the marking of copper wires, they are:
• SHVVP – multi-wire copper conductors, covered with insulating polyvinyl chloride plastic compound, enclosed in a PVC sheath; • PVC – multi-wire copper conductors, covered and enclosed in a PVC sheath; • VVG, VVG-P – copper MONOLITHIC conductors, covered and enclosed in a PVC sheath (P – flat); • VVGng – similar to VVG, but with increased fire resistance (non-flammable), used for joint, group installation and with increased fire hazard; • PVZ – one multi-wire core, PVC insulation.
As for practical application, we recommend using VVGng brand wire for wiring and power plants.
Why is VVGng cable better than alternative markings?
So, we will try to outline in order the undeniable advantages of the VVGng cable for installing electrical wiring in an apartment and a residential building.
• The rated current load with the same cross-section of conductors for VVGng is higher than for multi-wire ones (by 30-40%); • PVS and ShVVP are produced according to the household standard, VVGng – to the industrial standard; • for VVGng the current strength during a short circuit is normalized (tests are being carried out), PVS and ShVVP are not; • when installing VVGng and connecting to contact terminals, thanks to monolithic conductors, no tinning or ferrules are required, unlike stranded analogues; • operating temperature range of VVGng from –50 to +50, and for PVA and ShVVP from –15 to +50; • VVGng 5 years warranty and service life 30 years, PVS and ShVVP 2 years warranty and service life 10 years.
Here are the main reasons to choose VVGng cable for laying hidden or open wiring. Depending on where your grounding is located, a two or three-wire wire is selected for single-phase alternating current.
We also recommend choosing a round or flat cable depending on the intended installation method. If you are making channels in the wall, then flat wire is better because it requires less depth to lay.
Is there a difference where to buy VVGng cable?
Every professional electrician will be able to use a tester to detect the difference between VVGng cables of different prices with the same cross-section. With what it can be connected? Some unscrupulous manufacturers dilute copper with iron, which makes the cable harder and conductivity worse.
This situation occurs in spontaneous markets with uncertified “Chinese” products. Therefore, we recommend purchasing cable from suppliers that are consistent, reliable and have a good reputation. A large selection of VVGng cables made in accordance with GOST on the windows of our online store Elektrik.ru.
Choose a GOST or TU cable?
In a separate article, we looked at the differences between GOST and TU cables. In short, any cable is manufactured according to the technical specifications of the plant (abbreviated as TU). This means that the manufacturer declares certain conditions that the cable meets (resistance per 1 km of cable, sheath and insulation materials, filler, type of metal, etc.). At the same time, each plant has the opportunity to obtain compliance of its plant’s specifications with the state standard (abbreviated GOST). If a plant receives GOST for its products, this means that the cable production plant’s specifications comply with the GOST standard. In common people, the cable that does not pass certification is called TU (because the cable complies with the Technical Conditions of the plant, but does not comply with GOST), and the cable that has passed certification is called GOST (that is, the plant’s specifications comply with GOST). Very often we are asked the question - what to take, GOST or TU? This decision remains primarily yours. We, for our part, believe that the optimal cable in terms of quality-price ratio is the VVGng GOST cable - that is, a flat cable without filler, but made in accordance with GOST. It is more than enough for household needs.
Installing wiring in the house: how to choose the right cable?
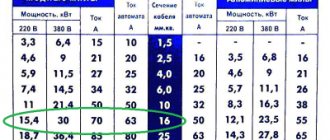
We understand the classification of wires and choose a cable to suit your needs. The summary table will allow you to quickly select the wire cross-section based on the current load.
Laying electrical wiring is one of the most important stages of home renovation. If you select the wrong current-carrying cable, the wiring may overheat and melt, and in some cases lead to a fire. We will tell you about the most popular types of cables used for wiring and explain how to choose the right wire cross-section. In this article, we will consider exclusively wire with copper conductors, since aluminum is falling out of popularity due to its low electrical conductivity compared to copper.
Express method: how to choose a good cable?
Below we provide a detailed method for selecting a cable. But what to do if you don’t have time to study GOSTs, tables, or any mathematical formula confuses you. Then we proceed according to a simplified method.
Of course, this is a greatly simplified technique. For those who are not too lazy to figure out the details, we offer a more efficient algorithm.
Classification of cables for wiring
Each cable consists of several copper cores of a certain cross-section. In turn, the cores in the cable can be single-wire monolithic or multi-wire. Each core is enclosed in a protective sheath made of rubber, polyethylene or PVC plastic. Note that any cable used for electrical wiring has at least two layers of insulation: the first envelops the core, and the second collects all the conductive wires into a bundle.
The most popular types of wires for wiring in a house and apartment are:
- VVG
- NYM
- PUNP
Let's look at what these types of cables are and where they are used.
VVG cable
The VVG cable is used for wiring in networks with voltages up to 1 kV. The number of cores in the bundle can be from 1 to 6. The letters VVG are deciphered as follows:
- B - the first layer of PVC insulation.
- B - second layer of PVC insulation.
- G - insulation without an additional protective layer (armor).
Additionally, some types of VVG wire may have the designation “ng”. These letters mean that the wire is flame retardant. Thus, if a high temperature occurs due to a short circuit, the wire will melt, but will not burn. We recommend using this type of VVGng wire for installing electrical wiring in an apartment.
There are also VVG types with the designations “P” and “Z”.
- P means that the wire in the wire is flat;
- 3 - that the space between the cores and the outer insulation is filled with PVC plastic.
Here is an example of a flat flame retardant cable REXANT VVG-Png-LS 3x2.5:
The advantage of the VVG cable is the ability to use it in conditions of low and high temperatures from -50 to +50 degrees. Also, in comparison with other types, it is much cheaper. For example, VVGng 3x2.5 costs on average from 35 - 40 rubles per 1 m, and NYM 3x2.5, which has similar characteristics, costs about 55 - 60 rubles. If the house is large, the difference in wiring costs can reach a couple of thousand rubles.
VVG wire cores can be single- or multi-wire. Multi-wire ones are more flexible than single-wire ones, but they are also a little more expensive. Single-wire ones have a cross-section from 1 to 50 mm 2, and multi-wire ones from 16 to 240 mm 2. It is worth noting that for residential wiring, cables with a cross-section from 1.5 to 6 mm 2 are usually used.
The bending length of the VVG wire (at turns in the groove) is equal to the cross-section of the entire bundle multiplied by 10. That is, if you have a wire with a cross-section of 5 mm, then the bending radius should be at least 50 mm.
Cables for information transmission
In addition to electricity, cables transmit information signals. Recently, many new types of information conductors have appeared. If 10–15 years ago there were only telephone and antenna cables, now with the development of computer technology there are many more types of information conductors. Most of them are too specialized and are of interest only to narrowly specialized specialists. For a home craftsman, it is enough to know and be able to use only a few types. We will consider them.
RG-6 coaxial cable
Antenna cables
. Today, RG-6, RG-59, RG-58 or Russian analogues of the RK 75 series are most often used. RG-6 is a coaxial cable for transmitting high-frequency signals for electronic equipment, television or radio. It consists of a central copper core with a cross-section of 1 mm², surrounding polyethylene foam insulation, an aluminum foil screen, an outer conductor of tinned copper braid and a PVC sheath. Widely used for transmitting cable and satellite television signals. It has many technical characteristics regarding transmitting signal frequency, resistance, shielding, etc.
Cable RK 75
For example, the designation in the name of the cable RK 75 means that the conductor resistance is 75 Ohms. This information is intended for specialists. In short, we can say that this cable is ideal for transmitting a video signal from an antenna or video camera to a receiver (TV) and distributing the video signal to several sources.
Coaxial cable with lug
RG brand
cables come in many varieties and differ from each other in certain characteristics, such as conductor resistance, resistance to temperature and shock loads, signal decay time, type of screen, etc.
Sectional view of cable RK 75
Computer cables
.
They are used to build computer networks. The cable with which computers connect to the Internet or to each other is exactly what is known to all computer scientists - twisted pair
. Consists of one or more pairs of wires intertwined in pairs, which is done in order to improve signal reception or transmission.
twisted pair
Each conductor is enclosed in PVC or propylene insulation. The outer shell is also made of PVC. The cable can be additionally equipped with a waterproof polypropylene sheath.
Twisted pair section
There is a breaking thread in the twisted pair design. With its help, the outer sheath can be easily removed from the cable, opening access to the conductive wires. Depending on the type of cable, various protection options are possible:
- UTP, or unprotected, without a common shield for pairs of wires;
- FTP, or foil, with an aluminum foil screen;
- STP, or secure, with a common shield made of copper mesh, in addition, each twisted pair is surrounded by a separate shield;
- S/FTP, or foil, shielded with a common foil shield, in addition, each pair is additionally enclosed in a shield.
RJ-45 tip for connecting to a computer
In addition, twisted pair cables are divided into categories based on the number of pairs combined into one cable. The most common type used for computer networks is the CAT5e category. It consists of 4 pairs of wires of different colors. Data transfer speed - up to 1 Gb/s when using all pairs. You can see such a cable used as a telephone wire of category CAT1 or CAT2, that is, consisting of 1 or 2 pairs of wires.
Twisted pair with a connector for connecting to a computer, protected by a PVC sheath
NYM cable
The NYM cable is applicable in networks with voltages up to 0.66 kV. The number of conductors in the bundle is from 2 to 6. In addition to the current-carrying conductors, there may be a yellow-green grounding conductor. Although the cable is mostly used for indoor wiring (it is afraid of ultraviolet radiation), it can also be used for outdoor installation if it is placed in a protective sleeve (plastic pipes, boxes, etc.). NYM stands for as follows:
- N - standard type wire (German classification).
- Y - sheath of cores made of PVC plastic.
- M - there is an outer shell (most often also made of PVC).
Additionally, the wire may have the symbol “J”, which indicates the presence of a grounding conductor in the harness. It is worth noting that NYM is initially manufactured with insulation that does not support combustion, so you should not look for the letters “ng” in the marking. However, unlike VVGng, the NYM cable can withstand lower temperature loads, so it is better to use it for single installations rather than for group installations. It is manufactured with a cross section from 1 to 35 mm 2.
The advantage of this cable is its durability - German-made wire can last up to 40 years (VVG is about 30 years). But the Russian analogues of NYM are not as durable, no matter how the manufacturers convince them of this. NYM can be used in rooms with high humidity up to 98%, so it is convenient for wiring in baths and saunas.
The bend radius length for NYM wire will be four cross sections. Thanks to this, passing “turns” while laying cables in ditches will be easier than with VVG. However, this and other factors significantly influence the high cost of the wire (compared to other types). Here is a relatively inexpensive two-core wire Pan Electric NYM 2×1.5 (100 m):
Is the VVGng cable on?
By the way, in practice the difference between VVGng and VVngLS cables is not so small. As the technologists directly responsible for the production of these products say, when the VVGng cable burns during testing, it is simply impossible to stay in the room.
For some reason, many people confuse the abbreviation “ng”, thinking that it guarantees the “non-flammability” of the cable. In fact, it means that the product does not support or spread combustion after the source of fire is removed from it. But the cable itself, when exposed to flame and other factors (short circuit, overload), even burns and melts.
When the VVGngLS cable is on, everything is much more comfortable and safer. This does not mean some kind of large-scale fire, but some kind of local fire. For example, in a place where the insulation was accidentally damaged during installation.
There are many ways to protect yourself from such fires at the very initial stage. One of the latest, not yet widely introduced into our apartments, is the installation of special spark-proof devices. The fire is localized at the spark formation stage.
PUNP cable
This is a budget type of cable for electrical wiring. It is a flat two or three-core wire with a core cross-section from 0.75 to 6 mm 2. PUNP stands for as follows:
- P - wire.
- UN is universal.
- P - flat shape.
Also in the abbreviation the letter “G” is sometimes found, which means that the wire is flexible. Its main advantage is its low cost compared to VVG and NYM.
There is an opinion among electricians that PUNP wire is prohibited for manufacture and use. Indeed, on June 1, 2007, a ban was introduced on the use of TU 16.K13-020-93 by members of the Elektrokabel association. However, manufacturing plants continue to produce and sell PUNP. In Russia they can be purchased freely.
Concerns about the use of PUNP are well founded. Statistics of fires caused by electrical wiring fires showed that in 60% of cases the source of fire was the PUNP cable type. The reason for this is that TU 16.K13-020-93 states that during the manufacture of wires, a deviation of 30% from GOST 22483-77 in the cross-section of current-carrying conductors is allowed. This means that, for example, a wire with a nominal cross-section of 4 mm 2 may well be 2.9 mm 2 or even less.
In general, whether to buy PUNP or not is up to you. In any case, if you have the means, it is better to purchase a wire of good quality once and not be afraid of a fire.
Telephone cables and wires
Telephone wires
are divided into 2 main types. The first ones are intended for laying several (up to 400) subscriber lines. The second type is used for wiring in a separate apartment or house.
TPPep: 1 - core; 2 — polyethylene insulation; 3 - core; 4 - fastening winding; 5 - waist insulation; 6 - screen
TPPep
- the main
type of cable for laying telephone lines
designed for a large number of subscribers. The cable consists of two wires twisted into pairs. TPG made of soft copper wire, cross-section 0.4 or 0.5 mm², covered with polyethylene insulation. In some types of cable, pairs are combined into groups of 5 or 10 pairs. The outer shell is also polyethylene or vinyl. The letters “e” and “p” in the name stand for film screen.
There are varieties of cable armored with tapes, or filled, in which the space between the sheath and the cores is occupied by a hydrophobic seal. In a word, this is a cable for telephone communication in an apartment building; it is intended for installation in almost all conditions: underground, in cable ducts or by air. To conduct a telephone line to an individual subscriber and distribute it indoors, the following types of telephone wires are used.
Telephone wire TRV
TRV
-
single or double pair telephone distribution wire
. This is a flat wire with a divided base, a copper core, single-wire, with a cross-section of 0.4 or 0.5 mm². Number of cores - 2 or 4. PVC insulation. Designed for conducting telephone lines indoors. Operates at temperatures from –10 to +40 °C. Humidity should not exceed 80% at a temperature of +30 °C.
TRP wire
TRP
— the characteristics coincide with the expansion valve. The only difference is the insulation; for TRP it is made of polyethylene. Compared to expansion valves, the wire is more resistant to the external environment and can be laid outside buildings.
Wire SHTLP
SHTLP
-
telephone flat cord
with copper stranded conductors. The core insulation is made of polyethylene. Insulated TPGs are covered with a PVC sheath. Number of cores - 2 or 4, cross-section - from 0.08 to 0.12 mm². Used for conducting lines indoors and in telephone sets. Highly flexible wire.
Wire PRPPM
PRPPM
-
a flat wire
with a dividing base and single-wire copper conductors with insulation and a polyethylene sheath. There is a modification of PRPVM, the shell of which is made of PVC. Number of cores - 2, core cross-section - 0.9 or 1.2 mm². It is used when laying a telephone line outdoors, on aerial supports, in the ground and along the walls of buildings. Resistant to temperature influences, operating conditions - from –60 to +60 °C.