To provide lamps and equipment on the site with electricity, a separate branch is laid from the house along the street. However, not every wire is suitable for this, due to the specific factors affecting it - heat, cold, wind, precipitation, sunlight, soil pressure. Therefore, we will consider which cable to use for wiring outdoors through the air and in the ground, what are its features and the requirements for it, what types there are, what markings are applied to them, as well as what are the main options and rules for their installation.
Universal NYY cable for outdoor wiring Source alicdn.com
Outdoor cable - what is it, features, requirements
To ensure reliability, safety and durability of the external electrical network, a cable is used instead of a conventional conductor. Its main features are as follows:
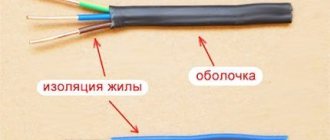
- The design is an assembly of several cores (usually from 2 to 4), covered with an individual insulating sheath and a common outer one.
- The insulating coating can have several layers of different materials - rubber, polyethylene, PVC, metal.
- Multilayer insulation provides reliable protection of the structure from external destructive factors, thanks to which the network can be carried out not only through the air, but also in soil and water.
- The sheath can significantly strengthen the cable, even giving it armored properties.
Unlike a cable, a wire for street electrical wiring is a single metal wiring. It may be covered with an insulating coating or bare. Moreover, in both cases, the cores can have a monolithic or multi-hair structure. The latter option is more resistant to mechanical damage and almost never breaks down due to all kinds of kinks during installation and operation.
Requirements
When laying a cable along the street, it is necessary to take into account the negative factors affecting it - these are:
- Temperature changes. Under the influence of heat in summer, the insulating shell softens, and in winter, on the contrary, it hardens. To avoid destruction under the influence of this type of influence, the insulation material must have sufficient resistance for this - be both elastic and durable.
- Wind load. The stronger the wind, the more the cable will be subject to tearing and stretching. Therefore, its structure must include elements and materials that can withstand this kind of element.
The cable must have a reliable fastening and withstand strong wind loads Source bazar2000.ru
- Ultra-violet rays. Direct solar radiation contributes to the structural destruction of the wire sheath. Without special properties, the insulation will become brittle over time, while other factors (wind and temperature) will accelerate these processes.
Note! A cable for outdoor installation can have both copper and aluminum conductors. The former are significantly more expensive than the latter, however, they are more resistant to loads, conduct current better, and last twice as long.
Types of insulating materials and their scope of application
We've decided on the contact connections - now let's figure out how to insulate the wires? For household use, there are usually two options - insulating tape or heat shrink. But each of these materials has a lot of varieties and areas of application. So let's look at them in more detail.
Insulation tape
Let's start with the most common and time-tested material - insulating tape. This material is applied to the conductor by winding it around the conductive part. But the properties of this product depend on the material of manufacture. And there are not so few of them.
PVC electrical tape
So:
- The most common option is PVC electrical tape. It is made of polyvinyl chloride film, on the surface of which a special adhesive composition is applied. This solution should ensure good adhesion of the tape to most types of materials.
- In our country, PVC electrical tape with a thickness of 0.1 to 0.2 mm is produced. The composition of the adhesive solution and the base of the sleeve also differ. In addition, the color range of such electrical tape, which in Soviet times was only blue, has recently expanded.
- This material can be used to insulate any type of connection. The insulation resistance of such electrical tape, according to standards, is tested at a voltage of 1000V.
Note! In practice, when insulating high-voltage installations, it is generally accepted that one layer of such insulating tape provides protection up to 660V. That is, to insulate a cable under voltage of 6 kV, at least 6 layers should be applied.
HB electrical tape
- Cotton duct tape is another option. It is made on the basis of fabric on which a special adhesive solution is applied. In our country, raw rubber production waste is often used for this. This gives the product additional tightness after drying.
- CB insulating tape is used as the main insulating material in electrical installations up to 1000V. In electrical installations above 1000V, it is often used to give the connection additional properties. For example, if we need frost-resistant insulation on a wire.
Note! PVC, CB and many other types of insulating tapes must be applied at a temperature not lower than -10⁰С. But for some types of electrical tape, operation after the adhesive solution has dried is allowed at lower temperatures.
Epoxy electrical tape
- There are also so-called epoxy tapes. They are elastic, wear-resistant, but their main advantage is high temperature resistance. This tape can normally withstand temperatures up to +155⁰С.
- Mica tapes have even higher heat resistance. They are often used to insulate parts and assemblies of electrical machines. In addition to thermal resistance, such tapes are also fire resistant.
- Fiberglass tapes demonstrate maximum temperature resistance. They are able to withstand temperatures up to +200⁰С.
- In addition, there are other types of electrical tape. But in everyday life they are used extremely rarely, so we will not dwell on them in more detail.
Heat shrink
Now let's talk about heat shrink tubing. The main feature of this material is that it compresses under the influence of temperature. This ensures reliable fixation and uniform adhesion of the material over the entire surface.
Types of heat shrinks
- But if you think that heat shrink is no different from each other, then you are deeply mistaken. The most common heat shrink, with double shrinkage. It is mainly used for insulating wires.
- If it is necessary to ensure more reliable fixation of heat shrinkage to the surface, then materials with glue on the inner surface can be used. This glue is also hot-melt, and when heated, it fills the smallest voids between the tube and the surface.
- If you don’t know how to insulate the wires in a car, then there are special oil- and gas-resistant tubes. Regular PVC electrical tape may be useless in this case. She does not tolerate exposure to chemically active substances well. But chemically resistant heat shrinkage copes with this perfectly.
The photo shows heat shrink with glue
- For use at elevated temperatures, special high-temperature tubes are used. Depending on the material of manufacture, they can withstand temperatures up to +260⁰С. For comparison, conventional heat shrink is intended for operation at temperatures from -50⁰С to +125⁰С.
- By the way, heat shrinks are successfully used not only for low-voltage networks. There are special high-voltage heat shrinks. They can be used in electrical installations up to 110 kV.
High Voltage Heat Shrink
In addition, there are also various types: non-flammable, anti-tracking, semiconductor, self-extinguishing, fluorescent, with increased strength, with a corrugated surface - and many other heat shrinks. The list of such materials is constantly growing.
Rules for applying insulating materials
All these additional properties are of course good. But first of all, we are interested in ensuring that the wire insulation at the connection point is not inferior in resistance to the main insulation. To achieve this, the insulating material must be applied correctly.
Method of installing insulating tape
The method of applying insulating tape largely depends on the type of connection and, of course, the shape of the object - but there are general rules.
Let's look at all these aspects:
- Before applying electrical tape to the surface, it should be prepared. To do this, the wire should be wiped. The insulation and live parts must be free of moisture, oil and dust. All this reduces the adhesion of the tape to the surface.
- Our further actions depend on the type of wire connection. If the wire is connected by soldering or pressing, and does not have twisted branches, then apply electrical tape as follows. We attach the edge of the electrical tape to the part of the conductor that has insulation. The instructions advise doing this at a distance equal to the width of the electrical tape. Then, wrapping the wire with insulating tape at a slight angle, we pass to the edge of the wire with insulation opposite from the junction.
- Here we securely fix the electrical tape with one or two turns around the wire, without an angle of rotation, and then go in the opposite direction. With one or two wraps we fix the tape on the original side and cut off the excess. After this, we press the place where the insulation is applied with our hand to level the surfaces and remove air.
Applying electrical tape to a wire
- If we have a connection made by welding with a twisted branch. In this case, with one or two turns, tightly fix the electrical tape on the insulated surface of the wire. Then, using rotational movements around the wires, we isolate the connection at an angle to the edge and above. We need the electrical tape to extend at least half its width beyond the joint.
- After this, we bend the protruding edges and fix them with the next turn along the edge of the connection. Using rotational movements at an angle, we return to the edge of applying the electrical tape. We fix it with one or two turns and trim the edges.
Applying electrical tape to a twisted connection
Heat shrink installation method
With heat shrink everything is much simpler. It is used only for connections by pressing and soldering. If welding is used, the connection point must be pressed tightly against the wire with the existing insulation. But let's talk about everything in order.
Heat shrink installation
- So we have two wires. Before connecting them, you should cut the heat shrink to the required length and put it on one of the wires. The length of the tube must be such that after making the contact connection and moving it to this place, the tube protrudes at least 3 to 5 wire diameters beyond the insulated surface.
- After making the connection, move the tube and securely fix it in the required position, as in the video. After this, using a special hair dryer or just a lighter, heat the tube.
Heat shrink for twisted connection
During the heating process, the tube decreases in size and tightly fits the contact connection. We check that after shrinking the tube, its edges lie on the surface of the wire insulation, and there are no exposed parts. This completes the installation of heat shrink.
Electrical wiring markings
When choosing materials for arranging an external electrical network, the brand of wire for street wiring is not the least important. The letter designations used in the marking have the following meaning:
- 1st position – core material. A – aluminum, AC – lead-braided aluminum, AA – aluminum with aluminum coating. Copper is the default, so it is not highlighted with a separate letter in the marking.
- 2nd position – appointment. M – mounting, K – control, P – flat, MG – mounting with flexible core, Ш or П (У) – installation.
Cable marking diagram Source stroychik.ru
- 3rd position – material and type of insulating shell. P - polyethylene, V and BP - polyvinyl chloride, NR - non-flammable rubber, K - nylon, S - fiberglass, Sh - polyamide silk, ME - enamel, N - non-flammable, L - varnishing, F - metal, B - armored.
- 4th position – design features. G – flexible, O – braid, T – for inside pipe installation, B – armored with tape, K – armored with round tape, P – flat.
Next to the letter marking there may be 3 digital designations. The first of them shows the number of cores (absence means a monolithic structure), the next one shows the cross-sectional area, and the final one shows the voltage rating.
See also: Catalog of companies that specialize in electrical work of any complexity
Conclusion
Now you know how to insulate wires and how to do it correctly. And you probably have a natural question, so what type of insulating material is better?
There is no clear answer to this. Heat shrinkage performs well during operation, and its installation is much faster.
At the same time, not in all cases it is possible to perform insulation with its help, and the cost of such a connection is a little more expensive. Based on this, you can independently choose how to insulate the wires.
Types of electrical cable
For laying external wiring on the street, the following main types of electrical wires are used:
- SIP. This is a standard street power cable with a rating of up to 1000 V. The cable contains a group of aluminum conductors with an individual insulating sheath. A characteristic feature is the outer shell is black. The advantage is reliability and compactness for aerial installation.
SIP cable for external wiring Source etm.ru
- AVBbShv and VBBbShv. Armored cable conductor based on aluminum and copper conductors, respectively. Designed for laying electrical networks in the ground without an additional protective structure. Pros: steel shell, different shades of core shells, heat and moisture resistance, 30-year service life. Cons: inconvenient installation due to increased rigidity.
- NYY. Universal cable for outdoor and indoor use. It is equipped with both copper and aluminum conductors. It is carried out both in the air and in the ground. Advantages - water and fire resistance, colored core insulation, black PVC sheath, durability up to 30 years. Produced by many manufacturers, meets international requirements and competes well with VBBShV.
- NYM. Another universal conductor. It is characterized by increased resistance to UV radiation. Characteristic features: resistance to thermal changes and exposure to open flames, strength, water resistance, round cross-section. The cable can be laid in plaster and concrete.
Structure of various types of cables for outdoor wiring Source samelectrik.ru
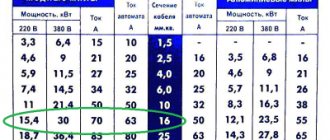
On a note! When choosing a cable for organizing an overhead or underground external electrical line in a country house or area near a house, it is necessary to take into account the internal cross-section of the conductors - the wiring must correspond to the total and actual power consumption of the devices and the voltage rating, taking into account the material of the wires. The parameter must be selected quite accurately. Each extra mm2 significantly increases the cost, and its insufficient value will lead to constant heating, as well as a high risk of melting and ignition of the insulation.
Cable for lighting in an apartment
Installing cables for lighting in an apartment does not require the use of protective structures, as when laying them outdoors. Cable wiring can be laid either openly, for example, in special gutters, trays or boxes, or mounted in walls, in the ceiling or under the floor. Therefore, choosing a cable brand usually comes down to determining the required cross-section, shape, degree of flexibility of the wire and its cost.
Among the most commonly used brands of cable for apartment lighting are VVG, NYM, PV, PPV and PUGNP in various designs (for example, with the indices “ng”, “ng-LS” or “ng-FRLS”). The technical characteristics of these products are similar, while VVG and NYM are more rigid, and PV, PPV, PUGNP are easier to bend at the desired angle. An additional criterion for choosing a brand, in the case of laying open wiring, may be the color of the cable. The optimal cross-section suitable for connecting a lighting system in an apartment is 1.5 mm2. Installation of cable products with a much smaller or larger cross-section can cause an overload or a significant change in resistance at the connection point, which can lead to overheating or even fire of the wiring.
Alternative wiring
When organizing an external electrical network in conditions of shortage or absence of main types of conductors, it is permissible to use alternative ones:
- PVS. Flexible conductor with PVC insulation, equipped with 2-5 cores.
- VVG. Flat cable with double sheath, equipped with 1-5 internal conductors.
- PV, APV, PV1, etc. Acceptable for external installation - but subject to installation in protective pipes, casings, corrugations. The main disadvantage is the single shell.
- VBBbvng. Fire-resistant flexible cable, equipped with 1-6 cores.
To lay the cable in the ground, a trench 0.5-0.7 meters deep is prepared Source ytimg.com
Reference! The longer the power line, the higher the current loss due to the resistance of the wiring material. Therefore, the longer the network, the larger the cross-section of the cores should be. To calculate the parameter, special formulas are used.
Cable laying options and their features
There are 3 main ways to lay a cable in a country house or adjacent area of a private house - laying it by air on the street, installing it along the facade of a structure, and burying it in the ground. Each option has its pros, cons and application features:
- Air. To conduct a line over the air, a SIP cable is most often used, less often a VSG cable. The wire sheath is made of cross-linked polyethylene and is not destroyed by sunlight, wind and temperature changes. The first type of cable has aluminum conductors, the second has copper conductors.
The advantages of this method are high speed of installation, ease of inspection and maintenance. The disadvantage is the impact on the design of the territory, the need to use a durable and resistant to external factors conductor, and sometimes the mandatory installation of a steel installation cable.
Aerial cable wiring on an installation cable in a protective corrugation Source samelectrik.ru
- Along the façade. The method is used when it is necessary to connect equipment located on external walls - most often a lamp. However, it is not necessary to use a durable self-supporting cable to lay the network. Since it will not hang freely in the air, but will rest on the facade.
At the same time, such a conductor will need all the protection from destruction. Therefore, protective corrugation based on polyamide or metal is used for installation. Materials must also be resistant to sunlight and temperature changes.
- Underground.
The method is suitable when it is necessary to conduct an electrical network over a sufficiently long distance. It has the following number of advantages:
- Unaffected by UV radiation and wind.
- Does not affect the design of the territory.
- Does not interfere with the operation of the site.
It also has some disadvantages:
- There is a high probability of damage due to soil pressure and shifting layers.
- The line can also be affected when developing the soil on the site - digging a well, a trench for a foundation, etc.
- Impact of biological factors – damage by rodents.
- Getting wet due to rising groundwater or flood waters.
Rules for laying street cable
When laying cables externally, the following minimum safety rules must be followed:
- The distance from the cable to the door is at least 2.5 m, and to the window and balcony – from 0.5 and 1 m.
- The minimum height of the overhead line to the ground surface is 2.7 m.
- For overhead installation, SIP-4 conductors are recommended.
- For laying in the ground, it is better to use cables of the VBBShV or AVBBShV brands.
- To lay the electrical network between structures, corrugated cables, cables or self-supporting types of cables must be used.
Important! Outdoor wiring connections should be made exclusively in sealed junction boxes, and should be approached exclusively from below through rubber seals.
Briefly about the main thing
An outdoor cable for conducting electricity across a site consists of one or more cores, each of which, in addition to the common one, has an individual insulating sheath. Unlike a conventional conductor, such a cable must reliably withstand wind, temperature changes, and solar radiation.
When choosing a cable for specific application conditions, its properties must be taken into account - for which the marking is used. It indicates the type of core material, purpose, shell material, design features. The most commonly used types of outdoor cable are:
- SIP.
- AVBbShv and VBBbShv.
- NYY.
- NYM.
As alternative options, PVS, VVG VBbvng, PV, APV, PV1 and other wires can be used. For external cable wiring, three methods are used - overhead, along the facade and underground. When laying electrical wiring, safety rules must be followed.
Connecting wires with an Easy-Protect coupling
And finally, a universal product has appeared that makes it easy to use wago clamps now not only in dry buildings, but also in wet rooms and even outdoors.
This thing is called Easy-Protect gel coupling.
Don’t be alarmed by the word “coupling”; there is nothing complicated about installation here. These products are produced by Cellpack (a joint venture of Germany and Switzerland) and consist of two halves.
One is apparently made in Germany, the other in Switzerland, after which everything is put together in China