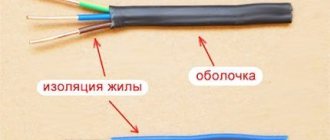
Physically, an electrical cable is an assembly consisting of one or more conductors with their own insulation, additional shielding, assembly protection, and an overall protective covering. A conductor (core) is a material that can transmit electricity through itself. The most commonly used conductors in cables are copper and aluminum. These metals are characterized by good electrical conductivity and long service life. Another advantage of these conductors is that they are recyclable. That’s why today the question of where to scrap a cable in Moscow is so popular. End-of-life electrical cables and wires can bring material income to those who collect and sell them, as well as reduce the cost of energy consumption in the production of primary conductor metals.
Prices for cable reception
| Cable type | Price per kg, rub. |
| Copper cable 1.5-4 square | 70-150 gross or up to 320 for contents. |
| Copper cable from 6 square | 300-330 copper yield |
| Internet cable (twisted pair, utp), telephone cable in plastic | 80-140 gross or up to 320 for contents. |
| Coaxial cable (corrugated feeder, thin ones are not accepted) | 300-360 copper yield |
| Power cable (contact) | 305-370 for copper yield |
| Copper cable with lead sheath | 120-160 gross |
| Aluminum cable with lead sheath | 45-55 gross |
| Aluminum cable (power) | 60-80 for aluminum yield |
Properties of electrical conductors
Electrical conductors have mobile electrically charged particles, which in metals are called "electrons". The moment an electric charge interacts with a metal, its electrons begin to move and transmit electricity. Metals with high electron mobility are good conductors, while metals with low electron mobility are used as insulators. Various conductors are used in electrical wiring and in the manufacture of electrical cables, but copper and aluminum continue to be the most common. These can be used to produce:
- Single-core cables, which, as the name suggests, have one conductor or strand that carries the electric current, as well as an insulating layer that protects against short circuits and electric shocks.
- Stranded is a combination of several single-core electrical wires that have one insulating and protective layer.
Copper conductors: copper is one of the oldest metals mastered by mankind. Copper was used by Ben Franklin and Michael Faraday in their experiments with electricity, and was first used in inventions such as the telegraph, telephone and electric motor.
With the exception of silver, copper is considered the most common conductive metal and became an international standard, which was adopted in the 13th century. The international standard was created for the purpose of comparing other copper conductors. According to it, annealed pure copper has 101% IACS conductivity.
In addition to excellent conductivity, this metal has characteristics such as tensile strength, thermal conductivity and lack of thermal expansion. Advantages of copper cables:
- Low resistance.
- Excellent ductility – elongation of molar alloy from 20 to 40%.
- High strength at high temperature stresses.
- The flexibility of copper is 1.8 times higher than aluminum - this suggests that cables with a copper core are more resistant to bending.
- Good stability and corrosion resistance.
- High current carrying capacity: Due to its low resistivity, copper cable has a cross-section that is approximately 30% larger than the permissible current carrying capacity of aluminum cable.
- Low voltage loss.
- Low power consumption: Since the resistance of copper cable is lower than aluminum cable, its power loss is also lower.
- Resistance to creep - deformation of a metal under the influence of a changing load. Copper is resistant to expansion and contraction, so its connections do not weaken and therefore do not overheat or spark.
What is a wire
A wire is a product of the radio engineering industry, consisting of a conductive core and insulation.
The core can be made of copper, aluminum and other metals, and the insulation can be made of dielectric materials. First, let's figure out why wires are thick and thin?
Have you ever noticed that an iron and an electric kettle have a larger wire diameter than a cell phone charger? The Joule-Lenz law is to blame for everything. All electronic consumers “eat” current.
From the article work and current power, we know that power is the product of current and voltage, that is, P = IxU. Therefore, to find out the current strength, you need to divide the power by the voltage in the outlet. If my iron has a power of 1400 Watts, then I=P/U=1400/220=6.36 Amperes will be consumed by my iron.
A wire is like a hose.
The hose can only withstand a certain amount of water pressure. If we apply too much water pressure, the hose will break into pieces! To prevent this from happening, you need to take a larger diameter hose. The situation is exactly the same with wires. The more current flows through the wire, the thicker it should be. That's why our iron and electric kettle have thick wires. These wires will carry a high current, while the charging wires will carry a low current. Therefore, in order to save expensive copper, wires for charging mobile phones are made thinner.
Here is a small sign showing how much current can be passed through a copper wire for a long time:
Cables with aluminum core
Although copper has high throughput, flexibility, and low creep resistance, aluminum has some important advantages. This metal has 61% of the conductivity of copper, while it is 30% lighter than its competitor - this means that a bare aluminum wire will weigh half as much as copper with a similar electrical resistance. Aluminum is a cheaper conductor than copper, and when using aluminum cables there is no current fluctuation that usually occurs due to conductor resistance. Due to their light weight, aluminum wires are often used when installing high-voltage overhead power lines, as they require fewer support towers.
In addition to the above conductors, other metals such as gold, silver, tungsten and alloys can be used in the production of cables. Each of them has its own advantages and disadvantages and is used depending on the purpose of the cable.
The core is the basis of any wire and cable
It is the core that conducts current. It can be solid or consist of a different number of wires. Aluminum, copper, aluminum-copper and nichrome are used to make cores. Recently, copper wires are most often used. Nichrome conductors have also appeared in home installations. This is an alloy with increased resistance, and when electric current passes through such a core, it becomes very hot. Nichrome conductors are most often used for certain purposes, for example when installing heated floors. Materials for making cores Aluminum is considered an excellent material for making cores. This metal is very light, inexpensive, has good conductivity and heat dissipation, as well as chemical resistance. But it also has its drawbacks. Aluminum wire is not flexible and breaks easily, even if you bend it just a few times. Therefore, aluminum wires are used exclusively in stationary wiring where there are no sharp cable bending angles. Another significant disadvantage of this material is that it reacts with oxygen to form aluminum oxide (a refractory, dark-colored substance) that does not conduct current. The metal surface oxidizes and this can seriously impair the flow of electrical current. As a result, overheating and short circuits occur at the junctions of mechanisms and conductors. And one more drawback: aluminum can only be a good conductor if the material is chemically pure. And this is very difficult to achieve. It is worth noting that ordinary unrefined copper conducts electricity 1.5 times better. Although copper also has its pros and cons. The high conductivity of this metal has already been mentioned; moreover, it does not form dielectric oxides when interacting with air. Copper is a very flexible metal, which is important for the production of thin wires. The main disadvantage of this material is its high cost. In addition, copper weighs quite a lot. Finally, when copper comes into contact with aluminum, a galvanic couple is formed, and the current generated during this process destroys the contact. In everyday practice, this should be taken into account and when connecting two cores made of these materials, use special terminals. The third material used in the manufacture of cores is aluminum-copper. It is not a physical alloy of two metals, since heavy copper does not alloy very well with light aluminum. The material is a mechanical alloy. Moreover, the latter takes up only 10% of the total volume of the product. Aluminum copper has all the positive qualities of aluminum and copper, but is still inferior to conductors made of pure metals in terms of the sum of indicators. In addition, the production of this material is quite expensive. Cross-section of cores According to the configuration, the cross-sections of the cores are flat and sector. The cross-section of the conductor is the most important characteristic of the conductor, because the degree of its conductivity will depend on it. All conductors have information about the cross-section of the conductor, but sometimes it is useful to double-check the area of the conductor yourself. There is a simple way to do this - using a regular ruler or caliper, you need to measure the diameter of the core. Then calculate its area using the formula. The diameter of the wire in electrical installation terminology is classified by gauge: the smaller the latter, the larger the diameter. It is more difficult to calculate the cross-sectional area of a stranded core. You can twist the core very tightly, maintaining its round shape, and then take measurements with a ruler. It is also recommended to measure the diameter of an individual wire with a caliper, and then multiply the resulting number by the number of wires and calculate the area using the formula. Although all the necessary information can be obtained from the sales consultant. Number of wires in the cores A core in the form of a solid wire is called single-wire, or monolithic. Rigid monolithic conductors are used for installation of distribution boards, where increased rigidity is required from the conductor. A core in the form of several thin wires twisted together into a bundle is called multi-wire, or flexible. Its flexibility depends on the number of wires in the core: the more wires per unit cross-section, the more flexible the conductor. There are flexible cores and cores with increased flexibility. The latter are used to make household cords. Stranded wire bends very easily, so it is convenient to work with. Insulation of conductors To insulate current-carrying conductors, a special dielectric material is used: glass, ceramics, various plastic materials (polyvinyl chloride), as well as celluloid, etc. Today, insulating polymers are considered the most common. They protect a person from electric shock, and the conductors themselves - from contact with each other in the cable and from external influences (mechanical, temperature, chemical, etc.). There are a lot of materials for insulation, but for installing house wiring there is a special set of wires and cables with a certain type of insulation. The insulation includes the insulation of the conductor (conductor) and the outer sheath, which covers the outside of the wire and serves as additional protection. The main characteristic of an insulation material is its electrical strength. This is the current value at which an energy charge can penetrate a 1 mm thick layer of insulation. For example, all cables have multiple dielectric strength for safety reasons. Such insulation can only be broken through mechanically or when the current in the circuit is repeatedly exceeded, as well as due to wear. The insulation must be resistant to heat. The higher this indicator, the more intense heat the insulation can withstand without losing its properties. Some conductors are equipped with frost-resistant insulation, others with insulation with increased mechanical strength. The stronger and more resistant the insulator material, the better the quality of the conductor. When choosing a cable, you should pay attention to its external texture: a well-crimped cable holds its shape, and its outer sheath does not lag behind the insulation of the cores. The most common insulator is polyvinyl chloride (PVC). This soft and flexible white plastic is chemical resistant. In addition, it is non-flammable and can be easily cut with a sharp tool. Its main disadvantage is low frost resistance, although more improved varieties of this material have appeared recently. In addition, when heated, this material begins to release hydrogen chloride (HC1) and dioxins. These substances are very harmful, and upon contact with water they form hydrochloric acid. If a person constantly inhales such fumes, this terrible, corrosive acid will form in his bronchi and lungs. Rubber, which is made from synthetic or natural rubbers, is an excellent insulator. It is used in the production of flexible and frost-resistant cables. Another dielectric with good frost resistance is polyethylene. It is also able to withstand aggressive substances. The heat-resistant insulator is silicone rubber, which after combustion forms a dielectric protective film. In addition, it is a very elastic material. Impregnated paper also has good current-insulating properties, but this material is flammable and therefore requires additional protection from high temperatures, that is, the presence of an outer shell. Carbolite is also used to make conductors - a plastic that is resistant to high temperatures, but quite fragile. Information cables are additionally protected by screens - metal foil, which reflects electromagnetic signals and equalizes the electric field inside the conductor itself. For high voltage power cables that are buried in the ground, a protective cover made of metal is used to protect the wiring from mechanical stress. Additionally, protective cushions are installed above and below the armor to protect the system from aggressive environmental influences. In addition to all of the above, insulation performs another important function - it plays the role of an indicator. In other words, all conductive wires are enclosed in a sheath painted in a certain color. For example, black indicates phase, red or blue indicates neutral, and yellow-green indicates ground. The distribution of colors in the wiring can be anything, but the stable color always remains yellow-green, indicating only grounding. The main rule for a home electrician is to remember when installing wiring which indicator is responsible for what. A three-core cable always has black, yellow-green and red (blue) wires. Inside the cable itself, under the top layer (cambric), all insulated cores are additionally sprinkled with talc, which prevents them from sticking together.
Insulators
Insulators are synthetic materials that are used to insulate electrical wires and perform the following protective functions:
- from electric shock;
- from mechanical damage;
- from moisture;
- against the harmful effects of various substances.
The insulation in the cables has its own marking, thanks to which you can immediately determine what type of material we are dealing with. Most often used for insulation:
- regular tires G;
- silicone gum Gs;
- Halogen-free material N or H;
- cross-linked polyethylene XS;
- organofluorine plastic Zb;
- multivitamin coating Y;
- heat-resistant polyvinyl coating Yc.
Cables subject to high mechanical loads that can destroy the insulation are additionally protected and reinforced with metal armor. Armor can be made of galvanized steel, bronze or aluminum. It is used both for screen (signal insulation of power cables) and for internal or external insulation.
Main types of wires
The most important factor when choosing an electrical wire is the power of the connected household appliance. In everyday life, the most commonly used types of electrical wires are PUNP, PPV, PVS, ShVVP and others.
Flat wires
All cables from this group have similar characteristics and purposes.
- PUNP - a flat conductor with protection and copper single-wire conductors of the PBPP brand (can also be called PUNP) has a cross-section from 1.5 sq. mm to 6 sq. mm. PVC is used as external and internal insulation. Operating temperatures – from -15° to +50°С. The minimum bending radius is 10 diameters. Operates at voltages up to 250 V and frequency 50 Hz. The main use is lighting group, sockets.
- PBPPg - Already by the name you can understand the distinctive feature of this conductor - its flexibility. The multi-core structure allows you to reduce the bending radius to 6 diameters. Other characteristics are similar to PBPP.
- APUNP - The wire with the designation APUNP is a single-wire aluminum conductor. Section 2.5 – 6 sq.mm. The remaining characteristics are similar to the PUNP wire. The cable is rarely used, as it is prohibited according to the provisions of the PUE. Has a low cost.
All listed flat wires can only be used in lighting. For other purposes, it is better to purchase other conductors.
With jumpers
The main representatives of this group are PPV, APPV. PPV is easy to identify by the characteristic jumpers between the cores, which are made of PVC, like the insulating layer. Consists of 2-3 single-wire cores with a cross-section of 0.75 -6 sq. mm. Operates at voltage 450 V and frequency up to 400 Hz. Operating temperatures from -50°С to +70°С. The insulation is resistant to fire, alkalis and acids. Can be used at 100% humidity. The minimum bending radius is 10 diameter sizes.
An analogue of the described conductor is an APPV with aluminum conductors. The cross section starts from 2.5 sq. mm. These types of wires are suitable for lighting and power group.
Single-core
reclosing is made of aluminum and is a single-core conductor with a cross-section of 2.5 sq. mm. up to 16 sq.mm. single-wire and 25-95 sq. mm. for multi-wire structure. PVC is used as insulation, allowing operation at 100% humidity and temperatures from -50°C to +70°C. There are no restrictions on use.
Also representatives of single-core electrical installation products are PV1 and PV3. The numbers in the marking indicate the flexibility class. The wire used is a single-wire copper core with a cross-section of 0.75-16 sq. mm. or stranded with a cross section of 16-95 sq. mm. Soft wire PV3 is actively used in places where frequent bends and transitions are required.
Conductors for electrical cords
PVA is a copper wire with a multi-core structure, having a cross-section of 0.75-16 sq. mm. The insulation is multi-colored for the convenience of the master, the shell is white. Operates at a frequency of 50 Hz and a voltage of 380 V. Has a high level of flexibility. Designed for approximately 3000 bends or more. Operating temperature range from -25°C to +40°C. The PVSU modification is used from -40°С to +40°С.
SHVVP is a copper stranded conductor for connection, consisting of two or three stranded conductors. The cross section is 0.5-0.75 sq. mm. Not used for laying electrical wiring inside walls. The main application is lighting group and low-power household appliances.
Power cables
For internal and external installation of electrical wiring, crimped power cables are used. The most common is the domestic VVG. It is used to transmit current with voltages up to 1000 V. There are various modifications of wires with single-wire and multi-wire conductors with a cross-section of up to 240 sq. mm. External and internal insulation is made of PVC. Maximum operating temperature +40°C, humidity 98%. The most popular modifications include AVVG (made of aluminum with single-wire conductors), VVGng (non-flammable), VVGz (with filling between insulation made of rubber shavings or PVC threads). The minimum bending radius for all modifications is 10 diameters.
NYM
The European analogue of VVG is NYM. It is more reliable as it is made of high quality materials and has undergone more stringent testing. The intended purpose is a household cable for sockets or lighting. Maximum voltage 660 V. Bending radius is 4 diameters. Operating temperature range from -40°C to +70°C. NYM should not be used when exposed to direct sunlight and should not be laid directly into concrete.
The flexible cable KG consists of 1-6 stranded copper cores. It is designed to operate at voltages up to 660 V and frequencies not exceeding 400 Hz. Rubber is used for internal and external insulation, giving the wire additional flexibility. Operates at temperatures from -60°C to +50°C. Area of application – connection of powerful installations (welding machine, heater, generator). It is expensive, so VVG cables are more often used in everyday life.
VBBShv – copper conductor with single or multi-wire conductors. Has a cross section of up to 240 sq. mm. The insulation is made of PVC material. Under the lower shell, armor is created from two metal strips. Can withstand loads up to 1000 V and temperatures from -50°C to +50°C. The following modifications are usually used - AVBBShv (made of aluminum), VBBShvng (non-flammable), VBBShvng-ls (no smoke or corrosive gas emission during smoldering).
Conductors for transmitting information
Connecting telephones, computers, television antennas is done using special cables for transmitting information.
The RK75 antenna cable consists of a single- or multi-wire copper core. The cross section is 1 sq. mm. The insulating layer is made of polyethylene and shielding braid. External insulation is made of cambric. Used for transmitting low-current high-frequency signals.
Computer twisted pair cable is used to connect a PC to a local network. It consists of 4 or 8 wires that are intertwined with each other in pairs. For additional protection, a breaking thread is installed. There are different types of cables with and without shielding, which are used for different purposes.
Telephone wires are low current. They allow you to install telephone lines in the house or lay them between substations.
Specialized cables
To work in non-standard conditions, conductors with special characteristics are used. These include the heating wire PNSV. Made from steel and galvanized. For insulation, heat-resistant PVC or polyethylene is selected, which retains its properties in the temperature range from -50°C to +80°C. They operate at a load of 220-380 V. The main area of application is the creation of heated floors.
VPP – copper cable with a cross-section of up to 25 sq. mm. has double insulation made of polyethylene or PVC. Operates up to 660 V. Capable of operating under sudden pressure surges and temperatures from -40°C to +80°C. Typically used to power pumps that are lowered into wells.
RKGM is a copper single-core power heat-resistant installation cable. The cross-section reaches 120 sq. mm. Operates at voltages up to 600 V. Silicone rubber is used as insulation material. The outer shell is made of fiberglass. Properties are maintained at temperatures from -60°C to +180°C. Scope of application: places with elevated temperatures (baths, saunas, electric ovens).
Recycling after use
Despite the long service life of the cables (from 15 to 30 years), they all need to be replaced after this period has expired. After this, the cables must be disposed of and recycled. Searching for wires and delivering them to scrap metal collection points allows us to partially solve the problem of obtaining primary raw materials. Collection points accept scrap:
- household;
- control;
- power;
- special cables.
The price per kilogram of scrap is determined:
- The quality of supplied raw materials.
- The percentage of a particular metal.
- Purity – the amount of contaminants and oxides.
- The integrity of the sheath, as well as the complexity of further processing of cable scrap.
- Volume of recyclable materials - the more cable scrap is handed over, the higher the price per kilogram.