The power and current cable cross-section calculator will help you calculate the minimum cable cross-section required for safe operation of electrical wiring to avoid overheating, insulation melting, short circuits and fires.
- Indicate the source data (current or power), voltage, conductor material (copper or aluminum), type of wiring (open or closed in a pipe), number of wires (when laying communications in a pipe);
- Note additional conditions (wire length, permissible losses);
- Click on the “Calculate” button and save the resulting parameters.
The cable cross-section calculator works online and offline. Please note: it is for guidance only and cannot guarantee 100% accuracy of the calculations. However, the more valid data you enter into the appropriate fields, the higher the match rate will be.
Related regulatory documents:
- PUE-7 “Rules for electrical installations”
- SP 76.13330.2016 “Electrical devices”
- GOST R 50571.5.52-2011/IEC 60364-5-52:2009 “Low-voltage electrical installations. Selection and installation of electrical equipment"
- GOST 31946-2012 “Self-supporting insulated and protected wires for overhead power lines”
- GOST 31947-2012 “Wires and cables for electrical installations for rated voltage up to 450/750 V”
- GOST 6323-79 “Wires with polyvinyl chloride insulation for electrical installations”
- GOST 31996-2012 “Power cables with plastic insulation for a rated voltage of 0.66; 1 and 3 kV"
- GOST 433-73 “Power cables with rubber insulation”
Expert opinion
It-Technology, Electrical power and electronics specialist
Ask questions to the “Specialist for modernization of energy generation systems”
The resistance of a copper wire Zero high-voltage wires have a difference compared to conventional high-voltage wires with polymer conductors R in them is measured in Ohms and tenths of Ohms, while in ordinary ones it is in thousands. Ask, I'm in touch!
Online calculator: calculation of cable cross-section by power TABLE
- Length of cable
. The longer the wire, the greater the current loss observed in it. This again occurs as a result of an increase in resistance, which increases as the length of the conductor increases. This is especially noticeable when using aluminum wiring. When using copper wires to organize electrical wiring in an apartment, the length, as a rule, is not taken into account - the standard margin of 20–30% (for hidden wiring) is more than enough to compensate for possible increases in resistance associated with the length of the wire. - Type of wires used
. There are 2 types of conductors used in household electricity supply - copper or aluminum based. Copper wires are of better quality and have less resistance, but aluminum wires are cheaper. In full compliance with the standards, aluminum wiring copes with its tasks no worse than copper, so you need to carefully weigh your choice before purchasing a wire. - Electrical panel configuration
. If all the wires supplying consumers are connected to one circuit breaker, then it will be the weak point in the system. A heavy load will lead to heating of the terminal blocks, and non-compliance with the rating will lead to its constant operation. It is recommended to divide the electrical wiring into several “beams” with the installation of a separate machine.
Selecting cable cross-sections
For large calculations, you can use a specialized calculator on the help site or appropriate software. The following algorithm is used to sequentially calculate operating parameters using the formulas:
- when transmitting power P = 1,600 W to a connected load in a line with a voltage U = 220 V, direct current (I) is determined as follows: I = P/U ≈ 7.27 A;
- resistance of a copper conductor (in both directions) with a length of 800 m and a cross-section of 2.5 mm square: R = (2*I*p)/S = (2*800*0.0175)/2.5 = 11.2 Ohm ;
- voltage losses in this path: ΔU = (2*L*I)/((1/p)*S) = (2*800*7.27)/((1/0.0175)*2.5) = 11,520/ 142.86 = 80.63 V.
What is electrical resistance
If necessary, the last expression can be easily converted mathematically to select the cross-sectional area of the conductor based on the total value of the connected load:
S = (2*I*L)/((1/p)*ΔU.
In the example considered, the voltage loss is more than 36%. This result indicates the need to adjust the calculation of conductor resistance. According to current standards, it is permissible to reduce the control parameter by no more than 5%. By increasing the diameter of the wire, you can get the desired result. With a cross section of 19 mm square. the voltage will decrease to 209.41 V (4.81%).
Taking into account the increased resistance of the aluminum wire, proportional changes in losses are assumed. By performing a similar calculation, you can get a recommended cross-section of 31 mm square. The use of such a conductor under similar conditions will reduce the voltage to 209.2 V, which will ensure compliance with the standards - 4.92%.
For your information. You can use a multimeter to check the calculated data. Measurements are performed in the appropriate range, taking into account the amplitude of the signal, alternating (direct) current.
Measuring cable resistance with a multimeter
When connecting an AC power source, the calculation algorithm becomes more complicated. For such initial conditions, use the formula:
ΔU = ((Pa * Ra + Pр * Ri) *L)/ U,
Where:
- Pa (Pр) – active (reactive) power;
- Ra (Ri) – relative active (inductive) resistance of the line in Ohms per kilometer.
For certain conductor materials, the initial data is taken from the reference book. By analogy with the mentioned standards, the voltage reduction should generally not be more than 5%. Additional restrictions are applied taking into account the characteristics of electrical networks and connected consumers (from 1% to 12%). The current rules are clarified according to the text of the latest edition of the PUE.
The above calculation results convincingly confirm the advantages of lower resistivity of copper wire. When using an aluminum analogue, the amount of material for transmitting electricity with standard losses increases significantly. For a comprehensive analysis, the best indicators of copper in terms of strength and flexibility should be taken into account.
Aluminum is less expensive and lightweight. But when working with this material, vibration effects and movements during operation should be excluded. Bends are designed with particular care to maintain the integrity of the conductor. Electrical contact is disrupted by the formation of oxides on the surface of products made from this metal.
For your information. In certain situations, free space for laying the route will mean a lot. In terms of space saving, copper has the advantageous parameters.
Selection of conductor cross-section based on permissible heating
As the current increases, the temperature of the conducting metal increases. At a certain level, the protective insulation layer made of polymers is damaged. This causes short circuits and flame formation. Dangerous situations are prevented by correct calculation of the cross-sectional area. The method of laying (joint/separate) has a certain significance.
Selection of cable products taking into account heating
Selection of cross section based on voltage loss
As shown in the calculations, with a long route length it is necessary to take into account the voltage reduction and the corresponding energy losses. In large projects, the entire current circuit with switchgear and connected loads is considered.
Selection based on acceptable losses
To accurately determine suitable cable products, the characteristics of the operating process are considered. They make the necessary reserves to prevent emergency situations when connecting new consumers and voltage surges in the power supply network.
How to calculate cable cross-section by power: formula
1️⃣ First step. The total power of all electrical appliances that can be connected to the network is calculated:
2️⃣ Second step. Then the rated current in the circuit is determined:
3️⃣ Third step. At the last stage, tables are used in accordance with the PUE (Electrical Installation Rules).
Table of copper cable cross-section by current according to PUE-7
Table of cross-section of aluminum cable by current according to PUE-7
In the Electrical Installation Rules, 7th edition, there are no tables of cable cross-section by power, there is only data on current strength. Therefore, when calculating sections using load tables on the Internet, you risk getting incorrect results.
Resistivity
Resistivity is constant and is a property of the substance from which the conductor is made. Units of measurement r - ohm*m. Often the resistivity value is given in ohm*mm sq./m. This is due to the fact that the cross-sectional area of the most commonly used cables is relatively small and is measured in mm2. Let's give a simple example.
What kind of lighting do you prefer?
Built-in Chandelier
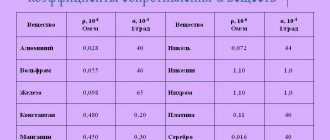
| Metal | r, ohm*mm. sq/m | γ, m/(ohm*mm. sq.) | α, 1/°С |
| Copper | 0,018 | 57 | 0.0043 |
| Aluminum | 0,027 | 35 | 0.0045 |
| Steel | 0.13 | 7.7 | 0.00625 |
| Nichrome | 0.98 | 1.01 | 0.0003 |
| Metal | r, ohm*mm. sq/m | γ, m/(ohm*mm. sq.) | α, 1/°С |
| Copper | 0,018 | 57 | 0.0043 |
| Aluminum | 0,027 | 35 | 0.0045 |
| Steel | 0.13 | 7.7 | 0.00625 |
| Nichrome | 0.98 | 1.01 | 0.0003 |
Expert opinion
It-Technology, Electrical power and electronics specialist
Ask questions to the “Specialist for modernization of energy generation systems”
Wires for electrical wiring. Calculation and table of permissible cross-section of electrical wires. Within reasonable temperature limits around a certain point, the dependence of the resistivity of metals on temperature is described as: Ask, I'm in touch!
How to find out the resistance of 1 meter of copper wire
After finding out all the factors that influence the resistance of a copper wire, you can combine them in the formula for the dependence of resistance on the cross-section of the conductor and find out how to calculate this parameter. The mathematical expression is as follows: R= pl/s, where:
You may be interested in this: Learning to read electrical diagrams
To calculate S, in the case of a cylindrical wire, the formula is used: S = π ∙ r2 = π d2/4 ≈ 0.785 ∙ d2, here:
If the wire consists of several cores, then the total area will be equal to: S = n d2/1.27, where n is the number of cores.
If the conductor has a rectangular shape, then S = a ∙ b, where a is the width of the rectangle, b is the length.
Important! You can find out the diameter of the section using a caliper. If it is not at hand, then wind the measured wire around any rod, count the number of turns, preferably there should be at least 10 for greater accuracy. After this, measure the wound part of the conductor and divide the value by the number of turns.
Cable resistivity table
I didn’t understand anything =) Apparently, when calculating voltage loss and when calculating short-circuit currents, we must take into account the resistance of the conductors, as under normal conditions.
Expert opinion
It-Technology, Electrical power and electronics specialist
Ask questions to the “Specialist for modernization of energy generation systems”
Video about the use of aluminum wires Also note that any metal conductor has inductance created by the conductive core and capacitance created by the insulation. Ask, I'm in touch!
Concepts and meaning of resistance
The electrical resistance of materials is widely used and taken into account in electrical engineering. This value allows you to set the basic parameters of wires and cables, especially with a hidden method of laying them. First of all, the exact length of the laid line and the material used to produce the wire are established. Having calculated the initial data, it is quite possible to determine the diameter and cross-section of the cable being measured.
Compared to conventional electrical wiring, resistance parameters are of critical importance in electronics. It is considered and compared in conjunction with other indicators present in electronic circuits. In these cases, incorrectly selected wire resistance can cause a malfunction of all elements of the system. This can happen if you use a wire that is too thin to connect to the computer's power supply. There will be a slight decrease in voltage in the conductor, which will cause the computer to operate incorrectly.
The resistance in a copper wire depends on many factors, and primarily on the physical properties of the material itself. In addition, the diameter or cross-section of the conductor is taken into account, determined by a formula or a special table.
Table
The resistance of a copper conductor is influenced by several additional physical quantities. First of all, the ambient temperature must be taken into account. Everyone knows that as the temperature of a conductor increases, its resistance increases. At the same time, the current decreases due to the inversely proportional dependence of both quantities. This primarily applies to metals with a positive temperature coefficient. An example of a negative coefficient is tungsten alloy used in incandescent lamps. In this alloy, the current strength does not decrease even at very high temperatures.