What equipment is needed for welding copper wires?
To weld prepared copper cables you will need an inverter and electrodes.
Features of copper: fluidity, high thermal conductivity, ability to absorb gases - require experience and skill from the performer.
Electrodes used
For welding copper wires, two types of electrodes are used: carbon or graphite with a copper coating:
- the destruction temperature of the electrode material is more than 3800ºС, and copper melts at 1080ºС, which allows their repeated use;
- rapid heating of the rod material to the copper liquefaction temperature;
- During welding, the carbon rod does not stick to the wires;
- 5-10 A is a sufficient, although small, current for a stable arc discharge.
Features of using carbon electrodes
The electrodes are made from black electrical carbon pressed into a rod shape. Its ends are beveled. Even with a very low welding current, a high temperature occurs at the tip of the electrode.
A carbon electrode is used when it is not possible to weld with a graphite element. You need to work very carefully to prevent the insulation from overheating. Carbon electrodes are commonly used in low power welders.
When working with carbon electrodes, the following features must be taken into account:
- the welding site is fragile , can oxidize and have a porous structure;
- Due to the high arc temperature, the electrode is consumed faster;
- It is more difficult to work with a carbon rod electrode than with a graphite electrode ; practical skills are required.
Approximate cost of carbon electrodes on Yandex.market
Graphite welding electrodes
Graphite electrode rods are gray in color with a slight metallic tint. The crystalline structure of carbon is not subject to oxidation. When welded, crystalline graphite forms a corrosion- and temperature-resistant compound. These electrodes are advantageous to use and are cheaper than carbon electrodes. The rods do not crack and last a long time.
If necessary, it is possible to replace it with improvised graphite products - brushes from commutator motors, rods of disassembled batteries. In the case of using a readily available graphite replacement without copper plating, an alligator clip is used instead of a conventional holder.
Approximate cost of graphite electrodes on Yandex.market
Graphite electrodes are more often used with inverters that regulate the welding current.
Inverters
For welding, a DC or AC device with a voltage in the range of 12-36 V is suitable; current adjustment is required.
The choice of model is based on the intended modes of use of the device: from half-hour work without a break to many hours of intensive work.
If the device will be used infrequently, then a model that provides a maximum welding current of 150 A and a power of about 500 W is suitable. This is enough for welding strands with a cross-section of 20-25 mm².
Approximate cost of inverters for welding on Yandex.market
Selecting Electrodes
Graphite or carbon electrodes are used to connect copper conductors.
Working with the second type of contacts is associated with the following features:
- The melting point is 3800 °C.
- Welding is performed using direct current with straight polarity.
- The efficiency of the electric arc is low.
- It is possible to connect cables with solder supplied directly to the welded joint.
- The consumption of the carbon electrode is increased at high temperatures.
- A high temperature arc is created even when low current is applied.
The welding process with graphite electrodes has the following subtleties:
- Graphite is not consumed during operation.
- Copper's resistance to oxidation increases.
- Non-copper-plated electrodes are used. To do this, the wires are twisted tightly and clamped with a holder. Welding is performed in a standard way.
- During operation, a reliable connection is formed. To do this, the conductors are twisted tightly, the remaining ends are cut to increase the strength of the seam.
We recommend reading: How to properly cook carbon steels
Recommended welding current modes for different conductors
The magnitude of the welding current depends on the cross-section size and the number of strands in the twist: the thicker the twisted bundle, the greater the current value must be set on the welding machine:
- 2 cores, cross section of each 1.5 mm² - 70 A;
- 3 cores, cross section of each 1.5 mm² - 80-90 A;
- 2-3 cores, cross section of each 2.5 mm² - 80-100 A;
- 3-4 cores, cross section of each 2.5 mm² - 100-120 A.
The specified welding current modes are indicative. Wires from different manufacturers differ in chemical composition and declared cross-section, and welding devices also differ in their characteristics. Therefore, it is better to select the value of the welding current practically on a small section of the same wire. When choosing a mode experimentally, the optimal one will be when the arc is stable and the tip of the electrode does not stick to the welding site.
For modern inverter-type devices:
- stable welding discharge , ensuring high-quality welding work;
- When welding, liquid metal does not splash;
- the arc does not blind the welder due to the low melting point of copper;
- inverters are not heavy, their dimensions are small , which allows them to be carried to the installation site on a belt.
Characteristics of welding machines
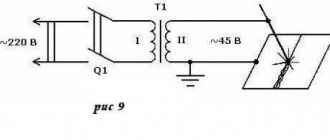
To weld wires with your own hands, use units with a voltage of less than 20 V; use transformer or inverter devices that produce a low-power arc.
Inverter type
Welding with an inverter is convenient, which is explained by its compact size and optimal preset parameters. The controls make fine-tuning easy.
Unlike transformer units, inverter units are lightweight. The method of application is similar to that of other devices. When choosing, take into account the possibility of adjusting the current strength within 40-200 A.
This simplifies the process of forming a welding arc and minimizes the amount of interference. The inverter method is suitable for a novice welder.
Transformer welding
To connect wires at home, it is sufficient to use current-regulated devices. The load must be at least 400 A. To form a strong weld, heating to 1080 °C is required.
We recommend reading Features of welding metal with galvanization
The electrodes are connected according to a straight polarity circuit. This method helps maintain a stable welding arc. A step-down transformer is used for soldering all types of copper cables. It is permissible to use the device for work in a junction box.
Welding is performed after de-energizing the electrical wiring. The current strength is selected taking into account the cross-section of the cores.
Requirements for homemade products
When performing one-time work, it is not necessary to purchase expensive equipment. It is better to use homemade devices that have a simple structure. The device circuit includes a transformer, monitoring and control elements, ground, and clamp. The first component is the basis of the welding equipment.
You can purchase a transformer or assemble it yourself. The number of turns and the cross-section of the winding are calculated taking into account the input and output current indicators.
A homemade welding machine must have the following technical characteristics:
- transformer type – step-down;
- input voltage range – 12-48 V;
- Current control limits are 40-150 A.
The homemade device is being improved by adding the function of welding twists with alternating voltage. To do this, a diode bridge is introduced into the circuit. It maintains a stable arc. The finished device is protected by a durable case that prevents damage to the device due to mechanical stress.
The transformer is connected to the cables of a holder made of mass clamps, which are played by heavy pliers.
Preparatory work
Before you start working with the wires, you need to check again that there is no voltage on them.
For further work you will need a knife or special cutting tools, emery cloth, solvent, pliers or pliers, insulating tape or heat-shrinkable tubing. If heat-shrinkable tubing is used for insulation, it is very convenient to use a hair dryer, which gives a tight fit with the film.
To obtain a high-quality connection, preparatory work is carried out in the following sequence:
- Carefully remove a section of the insulating coating of at least 7 cm from the core for a core with a cross section of 1.5 mm² . If the wires are thicker, then for every 0.5 mm² of core diameter, reduce 5 mm of insulation. The cutting is carried out along the conductor with a knife or a special tool - a stripper;
- bare areas of the wire are cleaned with emery cloth;
- the surface of the conductors is degreased with acetone or white spirit;
- carefully, so as not to damage the wires, twist them into a flagellum with your hands or pliers , trying to ensure they fit snugly against each other;
- use wire cutters or mounting scissors to cut off the end of the harness to align the wires.
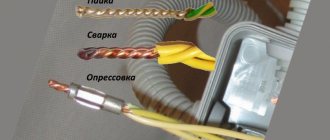
Wire welding algorithm
For safe work you will need gloves, protective welding glasses, and special clothing. You need to check again that there are no flammable objects under the welding site. Once you are completely safe, you can start welding:
- a radiator clamp is placed on the twist near the insulation to remove excess heat from the copper conductor and protect the insulating coating from melting;
- the “ground” of the welding inverter is also attached there;
- mains power is connected to the welding machine;
- the holder with the electrode is brought to the end of the twist;
- the arc melts the copper , and a droplet-shaped bead forms at the end of the twisted wire;
- The welding process takes 1-2 seconds.
After the weld has cooled, the twist is placed in a heat shrink tube or wrapped with insulating tape.