VVG-P).
When ordering a cable, the following must be indicated sequentially: its designation with the necessary additions, the number and cross-section of the cores, the operating voltage in kilovolts separated by a dash. The letters “ozh” in brackets next to the core cross-section indicate the unambiguous design of the cable with monolithic cores, for example
Example: VVG-T 3x25(ozh) - 0.66 - VVG cable in tropical design with three monolithic cores with a cross-section of 25 mm2 for a voltage of 0.66 kV/
VVG cables can have from one to six cores with a cross-section from 1.5 mm2 to 240 mm2. The range of core cross-sections depending on their number and operating voltage of the cable is given in the table.
| Number of cores | Nominal cross-section, mm 2 | |
| cable 0.66 kV | 1 kV cable | |
| 1,2,3,4 | 1,5 — 50 | 1,5 — 240 |
| 5,6 | 1,5 — 25 | 1,5 — 25 |
Two-core VVG cables must have cores of the same cross-section. Three-, four- and five-core cables must have all conductors of the same cross-section or one conductor of a smaller cross-section (grounding or neutral conductor). Six-core VVG cables must have four cores of equal cross-section and two wires of smaller cross-section. The cross-sections of neutral conductors (in the case of a smaller cross-section than the main ones) and grounding conductors, depending on the cross-section of the main conductors up to 50 mm2, are given below.
| Main veins | 1,5 | 2,5 | 4 | 6 | 10 | 16 | 25 | 35 | 50 |
| Zero core | 1,5 | 1,5 | 2,5 | 4 | 6 | 10 | 16 | 16 | 25 |
| Grounding conductor | 1,0 | 1,5 | 2,5 | 2,5 | 4 | 6 | 10 | 16 | 16 |
The most common among VVG cables with conductors of unequal cross-sections are cables with three main and one neutral conductor (the so-called “three plus”).
Two- and three-core VVG cables with a cross-section up to 16 mm2 inclusive can have a flat design. In round cables, the insulated cores must be twisted, and twisting with an alternating change in direction is allowed.
Cores with a cross section of up to 50 mm2 are round in shape. Cores up to 16 mm2 are made only monolithic; over 16 mm2 can also be twisted from individual wires (number of wires: at least 7 for sections 16, 25 and 35 mm2; at least 19 for sections 50, 70 and 95 mm2).
The insulated conductors must have a distinctive color, while the insulation of the neutral conductors should be blue, and the insulation of the ground conductors should be yellow-green. Digital marking of cores is also allowed.
To increase mechanical stability in VVG cables intended for installation in the ground, the empty space between twisted insulated conductors should be filled with bundles or a mixture of insulating materials.
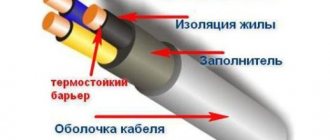
The sheath must be applied in such a way that it can be easily separated from the core insulation. To do this, a Mylar tape can be laid between the core insulation and the sheath. The shell color is predominantly black.
The nominal and minimum values of the radial insulation thickness for VVG cables with a cross-section of up to 50 mm2 for an operating voltage of 0.66 kV and 1 kV are given in the table.
| Cable voltage, kV | Nominal cross-section of cores, mm | Nominal insulation thickness, mm | Minimum insulation thickness, mm |
| 0,66 | 1 — 2,5 | 0,6 | 0,44 |
| 4 and 6 | 0,7 | 0,53 | |
| 10 and 16 | 0,9 | 0,71 | |
| 25 and 35 | 1,1 | 0,89 | |
| 50 | 1,07 | ||
| 1-2,5 | 0,8 | 0,62 | 1,3 |
| 4-16 | 1,0 | 0,8 | |
| 25 and 35 | 1,2 | 0,98 | |
| 50 | 1,4 | 1,16 |
The thickness of the sheath of VVG cables depends on the twisting diameter of the insulated cores under the sheath. The nominal and minimum values of the shell thickness are given in the table.
| Diameter under the shell, mm | Nominal insulation thickness, mm | Minimum insulation thickness, mm |
| Until 6 | 1,2 | 0,92 |
| 6 – 15 | 1,5 | 1,18 |
| 15 – 20 | 1,7 | 1,35 |
| 20 – 30 | 1,9 | 1,52 |
| 30 – 40 | 2,1 | 1,69 |
Conditions for installation and operation of the VVG power cable
Operation of VVG cable at ambient temperatures from -50°С to +50°С. Recommended for installation outdoors, in dry and damp industrial areas. The VVG cable, which has a filling between the cores, made in accordance with GOST, can be laid in the ground under conditions of low corrosive activity of the soil and the absence of significant mechanical loads. Can be laid without preheating at a temperature not lower than minus 15°C. The minimum bending radius during installation must be at least 7.5 times the outer diameter of the cable. Does not propagate combustion when laid alone. The service life of the VVG cable is 30 years.
Scope of application
VVG brand wire is intended for use in household and industrial electrical circuits with voltages up to 1000 Volts. Most often, such a wire is recommended for home electrical wiring when using hidden and open installation methods, as well as when installing behind plasterboard floors.
The limitation on the use of VVG cable is its installation underground, since soft outer insulation will not be able to protect the wire from rodents or mechanical damage that may occur due to soil displacements. If it is necessary to use it for laying underground communications, the cable should be laid in a pipe or other rigid insulation.
Technical characteristics of the VVG power cable
The electrical resistance of the current-carrying cable cores up to 50 mm2 at direct current should be no more than that indicated in the table.
| Nominal cross-section, mm 2 | 1,5 | 2,5 | 4 | 6 | 10 | 16 | 25 | 35 | 50 |
| Core resistance, Ohm/km | 12,1 | 7,41 | 4,61 | 3,08 | 1,83 | 1,15 | 0,727 | 0,524 | 0,387 |
The electrical resistance of the insulation per 1 km of length at a temperature of 20 0C is at least 7 - 12 MOhm, depending on the cross-section of the conductors.
Finished cables must withstand alternating voltage testing at a frequency of 50 Hz for 10 minutes. The voltage is applied between the cores and is 3 kV for cables with a rated voltage of 0.66 kV and 3.5 kV for cables with a rated voltage of 1 kV.
Decoding and marking of VVG
VVG cable stands for “vinyl-vinyl-naked.” But to understand where this name comes from, let's look at some concepts.
The difference between a wire and such a cable primarily lies in the number of cores.
The wire has one core and can be either sheathed (or several) or without it.
Conductors are the conductive metal elements of electrical cables; in the VVG cable they are copper. The presence of a large letter “A” in front of this abbreviation will indicate that the cable contains conductors based on an aluminum alloy.
The veins are:
- single-wire;
- stranded.
When ordering a stranded wire, you must understand that most likely you will be offered a wire with one stranded core. If we need 2 or more cores, then we should order a cable . Moreover, they can be single-wire or multi-wire.
The VVG designation almost always indicates that we are talking about a cable, because the first 2 letters “B” indicate the presence of a polyvinyl chloride sheath of cores, and the letter “G” indicates that they are bare, hence the name: “vinyl-vinyl- naked". Those. Vinyl protection contains each of the cores and the cable itself.
The photo shows a two-core VVG cable, most often used for home electrical wiring.
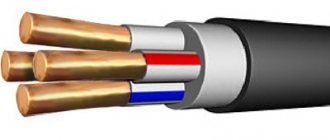
Also quite often, 3-core VVG cables are used if grounding or grounding of a single-phase electrical appliance is necessary.
For 3-phase wiring, use 4-core VVG cables, in which one is zero, or 5-core cables, if a separate grounding or grounding wire is needed.
VVG cables can be either round or flat. The latter have the letter “P” in their designation. Sometimes the conductors are not made in a round shape in order to more compactly fill the sheath in cables with a large cross-section.
Also, in multi-core VVG power cables, one core is thinner than the rest. This is a “zero” that does not carry such a load as phase ones.
After the letter designation in the cable marking there are numbers. We will explain their decoding using the example of a specific VVG 2x2.5 cable, most often used to connect most outlets in houses and apartments. The first number indicates the number of cores in the cable, and the second indicates their cross-section.
Many people mistakenly consider the second indicator to be the diameter of the cores, and this is their cross-sectional area, calculated using the formula for the area of a circle: 2πr². So, the diameter of the cores of this cable will be 1.88 mm.
Requirements for marking power cable VVG
On the sheath no more than every 300 mm the distinctive index of the manufacturer and the year of manufacture of the cable must be applied. For cables with a diameter under the sheath of less than 20 mm, the use of colored marking thread is allowed.
The drum cheek or label attached to the coil or drum must indicate:
— trademark of the manufacturer; — symbol of the cable (full indicating the number of cores and cross-section); — cable length in meters and number of segments; — gross or net weight when delivered in coils in kilograms; — date of manufacture (year, month); — drum or coil number.
The label must bear a technical control stamp and a certification mark.
What to look for when purchasing
With a large selection of products, it will not be difficult to more accurately select the wiring of the required diameter to ensure the operation of electrical appliances of a certain power, which will save money when designing and installing wiring.
When purchasing a product, you should carefully check the quality of the product's insulation. The cable must have a smooth cut with insulation that securely wraps around the cores. The shell material should not have any smudges or signs of drying out, that is, it should be elastic without cracks.
You might be interested in: Types and types of cable channels for electrical wiring and their installation
To obtain complete information about the product, you should read the certificate of conformity and then rely on the technical data. Based on the operating conditions, along with the wires, you should also purchase the necessary accessories that provide additional protection when laying the cable.
Weight and dimensions parameters of the VVG power cable
The approximate external dimensions and weights of individual cables with a cross-section of up to 50 mm2 for packaging and transportation purposes are given in the table. The given values may differ for cables of different batches and manufacturers by 10% less or more.
| Cable cross-section | External size value for packaging and transportation purposes, mm | Weight value for packaging and transportation purposes, kg/km |
| Flat cables | (a x b) | |
| 2x1.5 | 5 x 7.5 | 70 |
| 2x2.5 | 5.5 x 8 | 90 |
| 2x4 | 6 x 9.5 | 140 |
| 2x6 | 7 x 10.5 | 180 |
| 3x1.5 | 5 x 9.5 | 95 |
| 3x2.5 | 5.5 x 11 | 135 |
| 3x4 | 6 x 13 | 200 |
| Stranded cables | Diameter | |
| 3x1.5 | 8 | 90 |
| 3x2.5 | 9,5 | 135 |
| 3x4 | 11 | 200 |
| 3x6 | 12 | 260 |
| 3x10 | 14,5 | 410 |
| 3x16 | 17 | 590 |
| 3x25 | 20,5 | 810 |
| 3x35 | 23 | 1300 |
| 3x50 | 27 | 1700 |
| 3x4+1x2.5 | 12 | 230 |
| 3x6+1x4 | 14 | 310 |
| 3x10+1x6 | 16 | 480 |
| 3x16+1x10 | 19 | 650 |
| 4x1.5 | 8,5 | 110 |
| 4x2.5 | 10 | 170 |
| 4x4 | 12 | 240 |
| 4x6 | 13 | 320 |
| 4x10 | 16 | 510 |
| 4x16 | 19 | 750 |
| 4x25 | 23 | 1150 |
| 4x35 | 26 | 1550 |
| 4x50 | 31 | 2200 |
| 5x1.5 | 9,5 | 135 |
| 5x2.5 | 11 | 205 |
| 5x4 | 13 | 300 |
| 5x6 | 14 | 405 |
| 5x10 | 17,5 | 630 |
| 5x16 | 21 | 950 |
| 5x25 | 26 | 1450 |
| 5x35 | 29 | 1900 |
| 5x50 | 35 | 2700 |
Weight and dimensions of the packaged electrical cable
The dimensions of the drum or coil, as well as their weight, depend on the purpose of packaging (storage or transportation). These parameters can be found on the websites of cable manufacturers or their regional dealers. As practice shows, the declared dimensions and weight may have a deviation of around 10%.
Operating conditions:
- First of all, you need to adhere to the temperature regime. According to the technical characteristics, VVG can be operated in the temperature range from -50°C to 50°C. Short-term heating of the cable to a temperature of no more than 90°C is allowed.
- When laying an electrical cable, it is impossible for its temperature to drop below -15°C; this can lead to the “fragility” of the PVC material from which the protective sheath and insulation are made. In this case, heating will be necessary.
- Humidity threshold no more than 98%.
- When laying, bending less than ten diameters of the electrical cable is not allowed.
- Compliance with operating conditions guarantees the service life of VVG cable products up to 30 years.
VVG power cable load currents
Permissible load currents for cables with a cross-section of up to 50 mm2 laid in air are indicated in the table.
| Nominal cross-section of cores, mm2 | Permissible load current, A | ||
| With two main cores | With three main cores | With four main cores | |
| 1,5 | 24 | 21 | 19 |
| 2,5 | 33 | 28 | 26 |
| 4 | 44 | 37 | 34 |
| 6 | 56 | 49 | 45 |
| 10 | 76 | 66 | 61 |
| 16 | 101 | 87 | 81 |
| 25 | 134 | 115 | 107 |
| 35 | 166 | 141 | 131 |
| 50 | 208 | 177 | 165 |
Number and shape of conductors
All cables can be divided into two categories - single-core and multi-core.
Diagram of a three-core VVG cable. Each copper core is protected by a color-coded PVC sheath, and the entire bundle is protected by another outer insulation
The number of conductors under the outer sheath of the cable is from 2 to 6, while the cross-section of the cores can be any - from 1.5 to 250 mm².
For home electrical networks, products with neutral and grounding conductors are more often used. The insulation of the first is painted blue, the second is yellow-green.
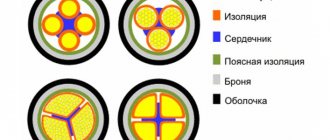
On the market, in addition to round, there are also segmented shapes of conductors. It is advisable to use it in the manufacture of large-diameter cables for compactness, so that there are no voids between the individual cores.
If the current-carrying conductors have a round shape, all the free space between them can be filled with plastic compound - a material whose properties resemble cable insulation
In VVG products of small diameter - up to 25 mm - internal filling may not be used.
Available methods for quality control of VVG power cable
Control methods are presented that, while not strictly complying with GOST, allow preliminary conclusions to be drawn about the quality of the cable if the measured values differ significantly from the regulated ones. The final conclusion about the cable's compliance with GOST can be made only after testing the cable in a specialized laboratory using strict methods and in the volumes specified in the standard.
Visual inspection The following can be checked: the number and color of cores, the number of wires in the core, the integrity of the insulation and sheath and the ease (without damage) of their separation.
Measuring structural dimensions Can be checked using suitable measuring instruments: insulation and sheath thickness. Measuring the diameter of the wires dpr and calculating the cross-section of the core using the formula 0.785dpr2N (where N is the number of wires in the core) is not a strict method for controlling the cross-section of the cores, because confirmation of cross-section compliance is electrical resistance, however, a significant deviation of the calculated cross-section from the nominal (more than 10%) may serve as a basis for doubts about the quality.
Measuring the electrical resistance of current-carrying conductors. It can be carried out on a finished cable with an ohmmeter with a suitable measurement limit (for cables with a small cross-section at a normal length in a coil or on a drum it can be several Ohms) and recalculated to a length of 1 km. If the cable has twisted cores, the obtained values should be reduced by 1.02 times. Particular attention should be paid to making good contact with the test leads.
Winding test after exposure at low temperatures If you have a large freezer compartment of a household refrigerator with temperatures down to minus 150C, you can check the quality of the cable sheath with an outer diameter of up to 20 mm. To do this, a piece of cable approximately 1.2 m long, rolled for compactness into a ring with a diameter of at least 40 cm, is placed in the freezer for 45 minutes, after which it is removed from the chamber and, in no more than 5 minutes, is wound onto the cylinder (drum) in a full turn first in one direction, then in the opposite direction. The material of the cylinder (drum) can be any - wood, plastic, metal. The diameter of the cylinder (drum) should be 15(Dн + d) ±5%, where Dн is the outer diameter of the cable in mm (for flat sheath thickness), d is the diameter of any of the main insulated cores in mm. A high-quality shell should not have cracks or tears.
Explanation of the VVG cable abbreviation
Let's start our conversation about this type of cable by deciphering the abbreviation of its name. After all, the name alone can already say a lot about the structure and scope of application of this conductor.
Decoding the abbreviation VVG
- In the marking of any wires and cables, the first letter may be “A” . It says that the cable is made of aluminum. If it is not there, as in our case, then this indicates that the cable is made of copper.
- The first letter “B” tells us about the conductor insulation material. In our case, this is polyvinyl chloride or, as it is sometimes called, vinyl.
- The second letter is again “B” . It tells us that the cable, in addition to direct insulation, also has an additional sheath. As you might guess, it is also made of vinyl.
- The letter “G” tells us that the cable does not have a protective sheath or, as it is also called, armor. Thanks to this, the product is more flexible and has less weight. Although this reduces protection from mechanical damage.
VVGz cables
- In addition to these basic abbreviation letters, you may find additional symbols at the end. Therefore, so that they do not confuse you, let’s talk about them too. The first of them is “z”. This letter indicates that the space between the sheath and the cores is filled. Typically, threads made from the same polyvinyl chloride or other non-hydrophobic synthetic fiber are used for this.
- You may also come across the abbreviation “ozh”. It tells us that the cable is made of a single-wire core. Now we will not go into details, but will cover this issue in the description of the cable structure.
VVGp cables
- VVG cable and deciphering its name may confuse you if you see the letter “p” at the end. But there is nothing scary here, this abbreviation refers to the flat shape of the cable structure.
- In addition, you may come across the symbol "T" , which indicates a tropical cable design. Well, the abbreviation “ng” tells us about the degree of non-flammability of the cable. Usually after “ng” there are other symbols that reveal this property to us in more detail.
Explanation and scope of application of VVGng cables
Note! Additionally, after “ng” the conductor’s non-flammability class may be indicated. It is designated by the symbols "A" to "D". The higher the order of the letter, the higher the non-flammability class. In addition, the abbreviation may contain symbols indicating the release of cable combustion products. For example, “LS” indicates low smoke emission, and “LT” indicates low toxicity of gases released during combustion. Other combinations are possible.