Types of cables and wires and their purpose: description and classification + explanation of markings Meanwhile, it is not at all necessary to describe all types of cables and wires and their purpose. It is enough to have an idea of labeling standards and be able to extract the necessary information from the characteristics in order to select the appropriate option from the variety of cable products according to its purpose.
Let's consider the main points on how you can learn to distinguish electrical wires among an array of such products, and also provide descriptions of the most popular wires and cables.
Structural basis of the cable product
The design of the cable or electrical wires determines the technical and operational characteristics of the product. Actually, the design of cable or wire products is, in most design variations, a fairly simple technological approach.
Classic version:
- Cable insulation.
- Core insulation.
- Metal core – solid/bundled.
A metal core is the base of a cable/wire through which electric current flows. The main characteristic, in this case, is the throughput, determined by the cross-section of the core. This parameter is influenced by the structure - solid or bunched.
Such a property as flexibility also depends on the structure. In terms of the degree of “softness” of bending, stranded (bundled) conductors are characterized by better properties than single-core wires.
The structural design of the current-carrying part is traditionally represented by “beam” or “solid” (monolithic). This has implications, for example, in relation to flexibility properties. The picture shows stranded/bundled wire type
The cores of cables and wires in electrical practice, as a rule, have a cylindrical shape. At the same time, it is rare, but there are several modified shapes: square, oval.
The main materials for the manufacture of conductive metal cores are copper and aluminum. However, electrical practice does not exclude conductors whose structure contains steel cores, for example, a “field” wire.
While a single electrical wire is traditionally built on a single conductor, a cable is a product where several such conductors are concentrated.
Wire design
The wire can consist of one or several cores, it can be either bare or with insulation. The wire strands are laid parallel to each other and twisted into a bundle. Power copper wire is often found as part of indoor electrical lines, and bare versions are used to transmit energy to power lines and laid over the air.
The wire design resembles a cable one, but here everything is much simpler.
Conductor
Performs the function of conducting current. Basic requirements: minimal heating, flexibility, resistance to corrosion, good electrical conductivity and low cost. The core of the flexible power wire is made in the form of a wire made of aluminum or copper, which is characterized by classes from 1 to 6. The higher the level, the better the product can withstand bending load.
Wire and cable insulating component
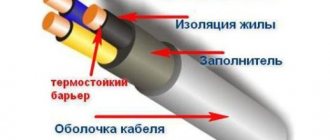
An integral part of cable and wire products is the insulation of the metal current-carrying base. The purpose of insulation is quite clear - to ensure an isolated state for each current-carrying core, preventing the effect of a short circuit.
The insulating material in most cases is polyvinyl chloride, which has shown in practice quite acceptable qualities in the construction of widespread electrical networks.
Depending on the purpose of the cable (wire) products, the insulating part may have different designs.
The dielectric material can be:
In addition to purely electrical protection, the insulating material also provides mechanical protection, protecting the electrical wire (cable) from moisture and other destructive factors.
There is also a special insulating construction applied to electrical wires and cables, giving the products "armored" or "anti-chemical" properties.
Special design - “armored”, reliably protects the internal structure, prevents moisture penetration, acts as a buffer against mechanical overloads
What is the difference between cable, wire and cord?
In order to understand the difference between a cable, a wire and a cord, a basic knowledge of electrical engineering is sufficient.
Unlike wires, cables are more widely used in difficult operating conditions. Reinforced with increased protection against mechanical and aggressive damage, the cables can be laid even under pressure, including under water. In mines and fire hazardous areas, at objects with increased corrosive activity, only cables are used.
Wires are laid only inside electrical distribution devices. If you need to connect outside them, use cables.
The main difference is stated in GOST 15845-80. According to the standard, the wire does not have insulation of thin-bearing cores. A strand of conductors or a single conductor may be insulated into a sheath, but may not have one. The same GOST states that, unlike a wire, in a cable all thin-bearing cores have their own insulation.
The main difference between a wire and a cable is the presence of insulation. If bare conductors are covered with an insulating sheath or if there is no insulation, then you have a wire. If each conductor is insulated, then it is a cable.
If you go into details, the cable looks like a protected wire. It contains one or more conductors carrying current, each of which is in its own insulation; in addition, the cable is covered with a protective outer layer.
Bare wires are used only for transmission along power lines; they are practically not used in domestic conditions.
Inside, the cable space is filled with a special compound or threads that are needed to prevent the conductors from sticking together. This simplifies cable installation and maintenance.
The service life also differs: cables are more durable in use than wires. The average service life of a quality cable is about 30 years, while wire will last half as long.
As for the difference between a cord and a wire or cable, a cord is essentially a cable or flexible wire for connecting to electrical appliances. The cords are resistant to bending, they have increased fracture resistance, and only stranded copper cores are used inside them, the cross-section of which does not exceed 4 mm².
Distinctive features of cable and conductor
Often, in non-professional practice, the term “cable” is equated to any type of electrical wire. Meanwhile, the concepts of “cable” and “wire” should be distinguished. And, first of all, the separation involves the factor of transmitted power.
A cable is a product whose structure combines at least three conductors in insulation, additionally protected inside the shell with a special material - parchment, rubber, lead, etc.
Wire is a product consisting of one, maximum five conductors (cord), in the latter case, united by a common casing.
Classic power cable structure: 5 – protective sheath of the assembly; 4 – armored layer; 3 – common shell of current-carrying metal conductors; 2 – insulation of the conductors themselves; 1 – metal conductor
The priority use of cables is industrial and economic facilities. Wires are actively used in everyday life, as well as in other areas.
Separately, bare wires that do not have insulation should be highlighted. The main use of such products is in the installation of centralized power lines.
Lived in the electrical wiring
A core is a metal wire, the core of all cables and wires. It is she who passes current through herself. The cross-section of the core and the number of wires of which it consists determine its parameters. According to the number of wires included in its composition, the cores are:
- monolithic - consisting of one wire;
- multi-wire - in them several wires are twisted together.
The more wires there are in the core, the easier it is to bend it, and the further choice of cable or wire depends on the flexibility of the core. For example, single-wire conductors are used for wiring in apartments; to replace the cord in equipment, wires with multi-wire conductors are needed.
Based on their composition, the cores are divided into aluminum and copper. We talk about the advantages and disadvantages of both types of cores.
Aluminum conductors
The advantages of aluminum cores include:
- strength and lightness - aluminum wire weighs half as much as copper wire;
- low price.
According to the provisions of the PUE, it is prohibited to use aluminum wires with a cross-section of less than 16 mm².
Disadvantages of aluminum cores:
- aluminum quickly oxidizes upon contact with air;
- if you bend an aluminum wire several times in the same place, it will break at the bend;
- high thermal conductivity, due to which aluminum quickly overheats
Thus, despite their strength and lightness, aluminum conductors have several significant disadvantages.
Copper conductors
The advantages of copper conductors include:
- electrical conductivity - in this parameter copper is second only to one metal - silver;
- oxidation resistance;
- strength.
Disadvantages of copper cores:
- high price;
- high density.
We recommend choosing a cable based on your needs and capabilities: cables with an aluminum core are distinguished by their lightness and they are cheap. Copper ones are more expensive, but at the same time they have excellent electrical conductivity with low resistance.
Basic types of electrical wires
Electrical network wires are classified based on load power and application conditions. For everyday use, the use of the following types of wires is typical: PBPP, PBPPg, APUNP, PPV, APPV, APV, PV1 - PV3, PVS, ShVVP.
Type #1 - PBPP wire (flat)
A product with a polyvinyl chloride insulating sheath, under which a solid copper core is hidden. This electrical material is manufactured with conductors with a cross section of 1.5 - 6.0 mm 2.
The flat design is a fairly convenient type of electrical conductor for use in household construction of power lines. Thanks to the copper current-carrying part, it is possible to connect a powerful load
It is allowed to use PBPP wire in ambient temperatures from -15°C to +50°C. The wire is designed for the installation of networks with a voltage not exceeding 250 V. The traditional use of PBPP is the installation of socket lines in the domestic sector. This wire is often used to organize wiring in an apartment.
Type #2 - modification of PBPPg
In fact, the product is presented in the same design as described for the PPPP, with the exception of one nuance, which is indicated by the letter “g” of the standard marking.
This nuance lies in the more pronounced properties of flexibility. In turn, improved flexibility properties are provided by the core structure of this type of wire, which is “bundled” and not solid.
A modified version in a two-wire version, which uses the structure of a “bundle” current-carrying part. This option is also popular in households
Type #3 - aluminum conductor APUNP
The presence of an aluminum conductor under the insulation is directly indicated by the product marking - the first symbol “A”. This product is produced in the core cross-section range of 2.5-6.0 mm 2.
Electrical aluminum wire is the simplest design of all existing options. It has a low price on the market, but at the same time it has low quality
This type of conductor is not recommended for use by professional electricians. The only advantage of this brand is its low cost. However, for the construction of temporary low-load circuits it is quite acceptable to use.
Type #4 - two-three-wire PPV
A product of a two- or three-conductor configuration, where the current-carrying conductors are placed under PVC insulation and held next to each other by means of an insulating jumper based on the same polyvinyl chloride.
At first glance, this type of wire resembles a glued pair. However, the connection of the pair is maintained by a PVC jumper running along the entire length at the point of contact of the insulation
Wire strands (copper) can have a cross-section in the range of 0.75-6.0 mm.
According to the technical specifications, operation is maintained at frequencies up to 400 Hz at voltages up to 450 V. Temperature limit -50/+70°C.
Type #5 - variety under the APPV brand
In fact, the same type of performance as demonstrated by the PPV brand, with the exception of the presence of aluminum conductors instead of copper conductors. It is manufactured in different sections, starting from a section of 2.5 mm 2.
Almost a complete analogue of PPV, if you do not consider the material of the current-carrying part. This modification uses aluminum wires, which reduces the cost of the product, but somewhat reduces the performance
This type of electrical wire is widely used in a wide variety of installation cases. It is allowed to use APPV for open-type wiring devices.
Type #6 - APV aluminum with PVC insulation
It is produced in two configurations of cores - single-cast or bundled (multi-core).
At the same time, the single version is represented by products where the cross-section range is 2.5-16 mm 2, and the multi-core version is available in the range 25-95 mm 2.
A variation of “bundled” aluminum is another type of the whole variety of electrical wires, which is used quite often in the practice of constructing electrical lines
This is one of those modifications that can be used in high humidity conditions. A wide temperature range is supported - from -50°C to +70°C.
Type #7 - modification PV1 - PV5
In fact, it is an analogue of automatic reclosure, but is produced exclusively with copper conductors. The difference between indexes 1 and 5 is that the first option is a product with a solid core, and the second option is, accordingly, multi-core.
We can say that there is an automatic reclosure design, but the conductors are made exclusively of copper. In all other respects, the difference is practically unnoticeable. A specific type used for specific circuit designs
This variety is often used when assembling control cabinet circuits. Supplied with multi-colored insulation.
Type #8 - PVC patch cord with PVC insulation
A type of conductor representing the configuration of an electrical cord. Available with a number of cores 2-5 in the cross-section range 0.75 - 16 mm. The structure of the cores is multi-wire (bundled).
A constructive version of the “cord” for household electrics. Indeed, this “cord” is often used to connect relatively powerful household appliances. Provides a convenient connection option due to color separation
Designed for operation in networks with voltages up to 380 V at a frequency of 50 Hz.
A special feature of the PVS design is a high degree of flexibility. However, the temperature regime is somewhat limited - from -25°C to +40°C.
Type #9 - flat cord SHVVP in PVC sheath
Another variety in a “corded” design. A variation in the number of wires united by a PVC sheath is supported, in the amount of two or three.
A flat two-wire “cord” is a pair of conductors enclosed in a polyvinyl chloride sheath. There is also a configuration with three conductors and a multi-core structure of the current-carrying part
The main application is the domestic sphere, outdoor wiring. Operating voltage up to 380 V, core structure - bundle, maximum cross-section 0.75 mm 2.
Cable design
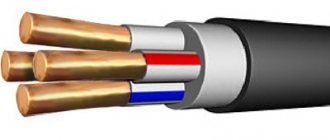
A cable is a flexible electrical product designed to transmit electricity or a radio signal from one network element to another. The main difference between a cable and a wire is the presence of its own insulating sheaths for each of the cores, and the entire structure is enclosed in a common layer of dense material.
Current-carrying cores of multi-core power cable
For manufacturing, wire made of copper, steel, aluminum, as well as alloys with low or high resistance is used. The diameter of the cable core varies from 1 to 10 millimeters. The main requirement for the element is good electrical conductivity, which affects the permissible load current or signal loss coefficient (in data cables). It is the electrical conductivity that determines the choice of cross-section and the number of cores.
The most popular materials of internal components of power flexible cable:
- Copper has the highest conductivity of all metals except silver. Compliance with processing allows you to obtain wire of any thickness and length by machine rolling. To protect against corrosion, copper is coated with tinning.
- Aluminum ranks third after silver and copper in terms of electrical conductivity. Due to its relatively low cost and virtually inexhaustible reserves in nature, aluminum often replaces the scarce red metal in cable products. The disadvantage that limits the scope of application is the lack of resistance to damage due to bending.
The price of a copper power cable is much higher than that of an aluminum cable. This is explained by a wide range of applications, scarcity of metal, high reliability and durability.
Insulating shell
The coating is intended, firstly, to create a dielectric gap in simple and power cables with copper and aluminum conductors. Secondly, it performs the function of stabilizing geometric dimensions - this is important for radio frequency products. It is worth noting that the material, thickness and density of the insulation affect the operating voltage limit.
Types of materials:
- polyvinyl chloride;
- dielectric rubber;
- cable paper impregnated with a special composition;
- polyethylene.
The most common material for insulating shells in products for general industrial use is PVC.
Electrical screens
Shielded power cable is a product protected from interference generated by operating electrical appliances. Screens are made in the form of a braid of aluminum wire, tape or foil. The element reduces the impact of the electromagnetic field and improves the quality of the transmitted signal.
Outer protective covering
Before buying a power cable, it is worth considering in detail the design options for the outer insulating sheath, since this parameter determines the scope of use and affects the choice of installation method.
The following types of insulation materials are distinguished:
- Metal - provides complete long-term protection from moisture.
- Polymer plastic compound - temporarily prevents water from penetrating into the structure. During operation, the liquid gradually diffuses through the plastic, which leads to a decrease in resistance.
- Rubber and PVC are equivalent in efficiency to metal.
There are specialized products, the shells of which are made of technological materials, for example, VVGng and VVGng LS power cables. The peculiarity is that when the maximum permissible temperature is exceeded, the product does not burn, does not melt, and does not emit acrid smoke or poisonous gas. Fire-resistant power cables are laid in strategically important facilities: at nuclear power plants, airports, medical facilities and other buildings where it is important to prevent smoke in the event of an accident.
Types of electrical cables
If we consider exclusively cables for power electrical circuits, the main types here are the following power cables:
- VVG;
- KG;
- VBBShv.
Of course, this is not a complete list of all existing cable products. However, using the technical characteristics as an example, you can form a general idea of the electrical cable.
Execution under the VVG brand
Widely used, popular and reliable brand. The VVG cable is designed to transmit current with a voltage of 600 - 1000 volts (maximum 3000 V).
The product is manufactured in two modifications, with current-carrying conductors of a solid structure or a bundle structure.
Product from the category of electrical cables, noted as popular and often chosen as the material for constructing electrical power lines
According to the product specification, the range of core sections is 1.5 - 50 mm. PVC insulation allows the cable to be used at temperatures of -40…+50°C.
There are several modifications of this type of cable products:
- AVVG
- VVGng
- VVGp
- VVGz
The modifications are distinguished by a slightly different design of insulation, the use of aluminum conductors instead of copper conductors, and the shape of the cable.
Power flexible cable type KG
The design of another popular cable, characterized by a high degree of flexibility due to the use of a bundle structure of current-carrying conductors.
Design of the KG brand flexible power cable for four working current-carrying conductors. The product has high quality insulation and demonstrates good technical characteristics
The design of this type provides for the presence of up to six current-carrying wires inside the shell. Operating temperature range -60…+50°С. Mainly, the KG variety is used to connect power equipment.
Cable
Unlike a wire, it has one or more cores, each of which is enclosed in insulation and covered on top with a protective sheath made of polymer plastics, rubber or metal. In addition to external insulation, sometimes called cambric, cables use various types of fillers that serve as additional protection from external influences. Some species are also protected by metal strips twisted into a spiral. In this case, the cable is called armored. Such types can rarely be seen during residential work, but in private houses for underground installation they are used quite often.
Cable VVGz
Types of copper wires
Among the electrical cables, the following types are distinguished:
- PUGNP (PBPPg). The cores consist of very thin wires. The last letter of the abbreviation “g” means flexible cable;
- PUNP (PBPP). Single-core cable with protective PVC insulating layers. It can consist of 1-4 wires with a small cross-section. More often, such wires are used for supplying housing to lighting fixtures;
- PPV. Single-core copper cable with single-layer insulation, designed for hidden wiring or laying through a corrugated hose or cable duct;
- APPV. A cable similar to the product described above only has an internal aluminum core;
- PVS. A common electrical cable with PVC protective insulation. Consists of twisted wires with a sector cross-section. Often laid for power supply to housing;
- SHVVP. An electrical cable consisting of conductors of both copper and aluminum, connected by terminal blocks. Mixed wires are used in household electrical appliances.
WIRE GRADES
| Brand | Core cross-section, mm | Number of cores | Characteristic | Application |
| Automatic reclosing | 2,5-120 | 1 | Wire with aluminum core, polyvinyl chloride insulation | For installation of power and lighting networks in pipes and channels |
| APPV | 2,5-6 | 2; 3 | Wire with aluminum conductors, polyvinyl chloride insulation, flat, with dividing base | For installation of power and lighting networks on walls, partitions, hidden wiring, in pipes, channels |
| APR | 2,5-120 | 1 | Wire with aluminum core, rubber insulation, braided with cotton yarn. impregnated with anti-rotten composition | For installation in pipes |
| APPR | 2,5-6 | 2; 3 | Wire with aluminum conductors, rubber insulation | For laying on wooden structures of residential and industrial buildings |
| APRN | 2,5-120 | 1 | Wire with aluminum core, rubber insulation, in a non-flammable sheath | For laying in dry and damp rooms, in channels, outdoors. |
| PV-1 | 0,5-95 | 1 | Wire with copper core, polyvinyl chloride insulation | For installation of power and lighting networks in pipes and channels |
| PV-2 | 2,5-95 | 1 | Wire with copper core, polyvinyl chloride insulation, flexible | For installation of power and lighting networks in pipes and channels |
| PPV | 0,75-4 | 2; 3 | Wire with copper cores, polyvinyl chloride insulation, flat, with a separating base | For installation of power and lighting networks on walls, partitions, hidden wiring, in pipes, channels |
| ETC | 0,75-120 | 1 | Wire with copper core, rubber insulation, braided with cotton yarn, impregnated with anti-rotten composition | For installation in pipes |
| PVS | 0,5-2,5 | 2; 3 | The wire is flexible, with twisted with copper conductors, polyvinyl chloride insulation, polyvinyl chloride shell | For connecting household electrical appliances - washing machines, vacuum cleaners, extension cords |
| PRS | 0,5-4 | 2; 3 | Flexible wire, with twisted copper cores, rubber insulation, rubber sheath | For connecting household electrical appliances - washing machines, vacuum cleaners, extension cords |
| PUNP (PBPP) | 1,5-4 | 2; 3 | Wire with copper core, polyvinyl chloride insulation, polyvinyl chloride sheath | For laying in lighting networks, installation and connection of low current household appliances appointments |
| MGS | 0,05-0,12 | 1 | Installation wire, flexible with copper core, with silk insulation | For stationary and mobile installation of intra-unit and inter-unit connections in electronic and electrical devices |
| MGSHV | 0,12-1,5 | 1 | Installation wire, flexible, with copper core, with combined silk and polyvinyl chloride isolation | For stationary and mobile installation of intra-unit and inter-unit connections in electronic and electrical devices |
| TRP (noodles) | 0,4-0,5 | 2 | Wire with copper core, polyethylene insulation, with dividing base | For open and hidden wiring of telephone network |
Power cables (Table 46)
Table 46. Technical parameters of power cables of types VVG, VB and VK
| Trademark | Cross-section of current-carrying conductors, mm2 | Number of conductors | Operating voltage, kV | Climatic performance | Notes |
| VVG | 1,5; 2,5; 4; 6; 10; 16; 25; 35; 50 | 1; 2; 3; 4 | 0,66/1 | UHL, T | — |
| 1,5; 2; 5; 4; 6; 10; 16; 25 | 5 | ||||
| VVGz | 1,5; 2,5; 4; 6 | 2; 3; 4 | 0,66/1 | UHL, T | |
| VVG-P | 1; 1,5; 2,5; 4; 6 | UHL, T | |||
| VVGng-LS | 1,5; 2,5; 4; 6; 10; 16; 25; 35; 50 | 1; 2; 3; 4 | 0,66/1 | IN | Permissible core heating temperature - +70 °C. During operation - +160 °C with short circuit |
| VVGng-LS | 1,5; 2; 5; 4; 6; 10; 16; 25 | 5 | 0,66/1 | IN | Cable with reduced smoke and gas emissions |
| VBBShv | 10; 16; 25; 35 | 2; 3; 4 | 0,66/1 | UHL, T | Cable with reduced smoke and gas emissions |
| VBBShvng-LS | 10; 16; 25; 35 | ||||
| VKbShv | 1,5; 2,5; 4; 6 | 2; 3; 4 | 0,66 | UHL | Armor made of galvanized steel wires |
Color indication of wire insulation
This is an important insulation function. All TPGs are enclosed in a sheath of different colors, so you don’t have to guess which core comes out from different sides of the cable. In addition, color marking carries an information load. In different types of cable, the cores have different colors. However, as a rule, in three-core they are white, yellow and red.
Standard color coding for three-core wire
White is taken as a phase, red - zero, yellow or yellow-green - ground wire. With a different scale, the stable binding color is considered to be yellow-green TPG, and other colors, as a rule, are distributed according to the taste of the chain installer. The main thing is to remember or write down which color belongs to what, so as not to make a mistake later.
Standard color coding for five-core cable
Inside the cable itself, under the outer sheath, the insulated conductors are sprinkled with chalk to improve their sliding and prevent the TPG from sticking together.
These articles may also be of interest to you:
- Wire routing
- Wire connection methods
- Selecting a cable for electrical wiring
- What are cables, wires and cords made of?