After electrical installation is completed, the issues of ensuring the safety and protection of the connection during further operation of the wiring become a priority. In the process of laying electrical networks, special attention must be paid to compliance with technology and quality standards when laying and connecting cables, because these sections of electrical wiring are the most vulnerable. To prevent burnout and emergency situations, insulation and heat-shrinkable tubing of different categories are used.
Heat-shrinkable tubing is an elastic product made of thermopolymer material that is subject to heat shrinking. That is, the length and diameter are affected by temperature; the source of temperature can be hot water, air or fire.
A distinctive feature of the tubes is the increased transverse compression value compared to the longitudinal compression. This means that the diameter of the heat-shrinkable tube can decrease several times (from 2 to 6), and the maximum increase in length is 20%.
General information and scope of application of heat shrink tube
The production of heat-shrinkable tubes at the plant is carried out from a special heat-shrinkable material, which changes dimensions several times depending on the degree of temperature increase. The product is influenced by the surrounding elements - water, flame, air. If one end is heated, the dimensions of the heat shrink tube will increase only in this area, and the other end will remain in the same size range. As the diameter decreases, there is a proportional increase in the thickness of the thermopolymer walls, as a result of which the insulating characteristics of the heat-shrinkable tube for insulating electrical wiring also increase.
Heat shrink tubing HERE is capable of shrinking in size under the influence of temperature and tightening around the wire. HERE is used in the following areas:
- performing electrical installation work to ensure reliable electrical insulation. Heat shrinkage has many advantages over conventional electrical tape, especially when there are a large number of connections;
- marking of cables and electrical wiring - in this case, heat-shrinkable tubes are used as cambrics;
- providing anti-corrosion protection of connections in many areas;
- a means to ensure the mechanical stability of operating mechanisms. Thus, heat-shrinkable tubes are often used on conveyor rollers and rollers;
- In production, thermotubes provide reliable protection of connections from the aggressive effects of external factors, including precipitation.
Scope of application of the device
Heat-shrinkable tubes are characterized by a high degree of elasticity, resistance to various negative environmental factors, and increased tensile strength, due to which they are actively used for:
- insulation of the current-carrying zone of wires and functioning units under voltage;
- providing protection at the connection points of cable lines or conductors;
- fastening lugs for connecting purposes and couplings on the cable;
- designing markings on wires;
- hermetically sealed protection of cable bundles in the longitudinal direction with a special heat-shrinkable tape;
- preventing violations of the integrity of wires under the influence of the temperature factor;
- ensuring ergonomic handles on equipment and creating conditions for safe operation of various tools.
Advantages and disadvantages
Heat-shrinkable tube has the following advantages:
- due to its tight fit, it does not move under mechanical influence;
- Using and installing heat shrink tubing is a simple task that you can easily do yourself;
- large selection of materials and diameters of heat shrink tube;
- after shrinking, the heat-shrinkable tube HERE acquires additional strength and rigidity at the connection point;
- When choosing which is better - heat shrink or electrical tape, heat shrink definitely has advantages in terms of technical characteristics and a longer service life.
DIY installation
To properly install the tube, you must adhere to a number of rules. At the preliminary stage, perform the following actions:
- Select the appropriate size and brand of heat shrink tube.
- Determined by the amount of material.
- Study the available offers on the market.
- Prepare the working tool.
Note! The choice of tool is especially important, since for different brands of heat shrink the difference in operating temperature can be more than a hundred degrees.
The following tools can be used to install the tube:
- construction hair dryer;
- heat gun;
- portable gas burner;
- gas soldering iron;
- propane torch;
- infrared burner.
Installation of heat shrinkage is carried out in the following sequence:
- Dirt, dust and any foreign particles are removed from the conductors.
- The heat shrink is cut into pieces of the required length.
- Next, the prepared section of heat shrink must be put on the entire wire.
- Using a hair dryer, torch or soldering iron, heat the heat shrink.
The best equipment option for installing heat shrink is a heat gun. It is possible to set the desired shrinkage temperature, which facilitates the installation process.
The heating and installation operation is carried out according to the following algorithm:
- Tubes with a large cross-section are first heated to 50% of the nominal temperature required for shrinkage. The same applies to wide flexible tapes. Heat shrinks with thin walls or small diameters do not require preheating.
- Cut the required length of the tube using regular scissors. You need to cut carefully so as not to leave any unevenness on the edges of the product.
- The tube is slightly stretched and put on the desired area.
- Heat the heat shrink to the nominal temperature using a heat gun or other heating tool. The temperature must not be exceeded, as in this case the surface will be deformed.
- After heating, you need to let the material cool. At this time, no mechanical influences should be exerted on the structure.
Some useful tips for installing heat shrink tubing:
- In the case of heat shrinks of large length or diameter, it is better to start heating from the middle part of the product. Next, the burner is moved towards the edges.
- If it is unclear whether the length of the tube is sufficient, it is recommended to start warming up from the end of the product where the communication plug, wire tip, etc. is installed.
- If heat shrink is installed on a metal base with high thermal conductivity, this surface must be thoroughly heated before installation.
- There should be no sharp edges on the surface to be coated.
- There is no point in stretching heat shrink tubing that is not long enough. The consequence of such actions will be the loss of heat shrink strength and dielectric properties.
Types of heat shrinkage
Types of thermopolymer heat-shrinkable tubes HERE are distinguished based on the production method and the material used:
- polyolefin. They are made from chemically or radiation-glued polyethylene, to which dyes, components to impart plasticity, and fire-fighting substances are added. Most tubes are manufactured using this method; they are designed for a temperature range from -50 to 125 degrees. The material is also resistant to benzene and oxidizing agents during short-term contact;
- elastomers based on synthetic rubber. A characteristic difference is resistance to temperatures up to 175 degrees and the presence of oil and petrol resistant properties, however the price is often too high, which hinders the growth of popularity;
- heat shrink for wires made of thermoplastic polyvinyl chloride. The material provides a high level of insulation, but a small operating temperature range from -20 to 80 degrees;
- polyester has a high level of chemical resistance and resistance to mechanical damage. The material is ideal for the manufacture of thin-walled products;
- fluoropolymer - require complex technological processing, provide unique chemical and physical characteristics;
- products made from silicones are characterized by plasticity and non-toxicity, but are not resistant to organic solvents.
Also classified HERE according to installation method:
- adhesive heat-shrinkable tube, in which a layer of glue is applied on the inside, providing a high degree of tightness and tightness. This type also provides protection against moisture ingress;
- HERE without an adhesive layer for standard connections where there is no need to ensure tightness.
Decorative ones are distinguished by color for an additional decorative effect, and it is recommended to use transparent standard heat shrink in places where it is necessary to check the tightness of the connection.
Depending on the thickness of the walls, they are distinguished: thin, medium and thick walls.
For specific tasks, special types of heat shrink with additional functions are produced, for example, heat shrink with solder, with a corrugated surface, high electrical density, specific cold shrink material and others.
What are heat-shrinkable products made from?
Thermal tubes, in addition to polyethylene, are also made from the following polymer materials:
- synthetic fluorinated rubber (fluorine rubber);
- polymers of the polyolefin group;
- polyvinyl chloride;
- polyvinylidene;
- polytetrafluoroethylene (Teflon);
- polyethylene terephthalate (polyester).
The operating temperature range of heat-shrinkable products also depends on the material (the range is huge: from -60 to +260 degrees).
Characteristics and differences
The main parameters that characterize a heat-shrinkable tube are:
- heat resistance;
- shrinkage coefficient in the range from 200 to 600%;
- diameter of the heat shrink tube before and after exposure to temperature;
- oil resistance;
- chemical inertness;
- ability to withstand voltage up to 1000V;
- petrol resistance;
- resistance to ultraviolet radiation;
- anti-flammability properties;
- shrinkage temperature and operating range.
Products can be produced in round, oval and compressed shapes, which does not affect installation. Note that thin-walled heat-shrinkable tubing is mainly produced in an oval or flattened shape.
Properties
All the working properties of heat-shrinkable tubes are manifested thanks to the thermopolymers from which they are made. Under the influence of elevated temperatures, they can be easily heat-shrinkable, that is, they change their shape - they shrink or expand. That is, it is enough to put the pipe on some object and heat it with a special hairdryer or a regular lighter. As a result, its size will instantly decrease, and shrinking, it will tightly fit the object. The most important thing is to prevent overheating, otherwise bubbles will appear in the tube and it will lose its physical properties.
Radiation and chemical effects on the polymer during the production process lead to the release of hydrogen atoms and the fusion of molecules of the polymer substance. This results in a durable, cross-linked material with increased thermal stability. When heated, it becomes more elastic, but does not melt, but simply changes its shape. After heating, a correctly selected material acquires a so-called shape memory, with the help of which the configuration is restored after reheating.
Diameter before and after
Heat shrink for wires changes its size as the temperature rises. For this reason, the manufacturer's name indicates the size before and after heating. For example, if the name indicates HERE NG 40/20, then 40 mm is the internal diameter before shrinkage, 20 mm after. When connecting cables of different sections and diameters, heat shrinks with large coefficients are required.
The amount of shrinkage must also be taken into account when choosing the length of products. For high-quality tubes, shrinkage along the length is no more than 5-7%, and for Chinese tubes it is about 20%.
When choosing a large-diameter heat-shrinkable tube, you need to pay attention to both shrinkage parameters. The higher the degree of shrinkage, the thicker the walls of the tube become after heating, which as a result significantly increases the density and strength of the connection. Thick-walled products have optimal shrinkage rates.
Shrinkage
Installing a tube with your own hands at the junction of the wires is quite simple; this is exactly the case when special skills and the invitation of a professional are not required.
The most important thing is not to forget to put it on one of the conductors before they are connected into a common electrical unit.
And then follow a certain sequence:
- The tube must first be heated to half the required temperature. In the case of thin-walled products, this point can be neglected, but for a tube with thick walls and a large diameter, it must be completed.
- Pull the tube over the connection and begin heating. Try not to exceed the temperature specified by the manufacturer. If you use a heat gun, this is easy to do by setting it to the desired degrees. Please note that if the required temperature is exceeded, the material may overheat, and the tube may melt or curl, or shrinkage may occur in waves. Heat from the middle of the product being attached.
- When the central part lies firmly on the joint surface, begin to alternately move the heat source in both directions. Constantly and evenly move the flame or air flow from the middle to the edges to avoid overheating in any one place.
- Correct shrinkage is smooth and there should be no bulges or bumps on it. If you are using a glue tube, pay attention to the fact that after shrinking is completed, glue should appear at the edges. Allow the installed heat shrink to cool completely.
How to use heat shrink, watch the following videos:
Selection by color
Colored decorative heat shrink tubing is convenient for marking because a small ring of a distinctive color is placed over the insulation at the end of the cable. Here are the basic rules for using colored tubes:
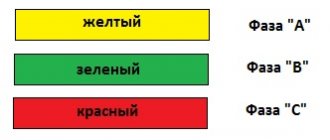
- in the wiring of DC electrical circuits, red is used on the plus and black on the minus;
- on the ground wires - a yellow-green tint;
- in a three-phase electrical circuit - red, yellow and green colors in phases.
Thanks to the wide range of colors, heat-shrinkable tubes can be used as a decorative material.
Necessary tool
In order for heat shrink to work as intended, it must first be heated. This means that any heating sources will be needed. It can be:
- industrial dryer;
- heat gun;
- a gas burner running on propane-butane (the main thing is to set it so that the flame is soft and yellow);
- ordinary household hair dryer;
- lighter or matches.
The main thing is to create a stream of hot air or an open flame. In some emergency cases, when nothing is at hand, they even lower the tube into boiling water.
The best option would be an industrial hair dryer or a heat gun, because these devices are safe and easy to use, and you can use them to regulate the temperature. The kit also includes additional attachments that facilitate the installation process in hard-to-reach places. But such a tool is not cheap; buying it just to insulate the wire connections in the junction box is not economically profitable. It will be good if you can rent or borrow it.
What are cambrics used for in electrical engineering?
The purpose of the tube is to insulate the electrical network, since the connection must be closed using welding, bolts, soldering, sleeves or terminal lugs. The cambrics are put on the products, then the edges are covered with electrical tape. The free edge is heated and pressed with pliers.
Thermocembric, in addition to its intended purpose, is used in the following cases:
- restoration of the insulating layer of wiring with direct and alternating current;
- contact markings – other colors are clearly visible on the white tube;
- ensuring cable protection from breaks or damage;
- masking connection points when installing electrical wiring;
- additional insulation of substation areas;
- preventing the edges of a printed circuit board from contacting each other.
Anglers use cambric to secure floats and hooks or even as bait.
Using different types of installation
Heat-shrinkable tubing has an important feature determined by its design. The method of attachment will depend on this:
- Tubes with an adhesive layer. The inner surface of the product is covered with a base in the form of glue. Therefore, during the shrinkage process, a higher sealing is ensured due to a better fit.
- Tubes without glue. In this embodiment, the tightness is created solely due to the tight grip of the wires.
A type of adhesive tube is heat shrink on solder. Such tubes have red rings - these are thickened heat shrinks with an adhesive-based layer. When heated, the rings begin to shrink, which ensures a strong fixation on the wire sheath. This option protects against moisture and mechanical rupture.