Home » Electrical wiring » Wires and cables » Types of cable and wire insulation
Most recently, we looked at marking cables and wires, but our subscribers still have many serious questions about insulation. Therefore, in this article we decided to talk in detail about what types of cable and wire insulation exist at the moment. Let's look at the most popular insulating materials and highlight the most popular ones.
Situations requiring additional insulation
Insulating wires is usually necessary after making connections between individual lines to ensure safety from electric shock. In this case, the following situations occur when insulating material is needed:
- If a separate section of the cable line’s protective layer is damaged. This will allow you not to replace the entire conductor, but only to insulate the damaged protection layer.
- When located in close proximity to the electrical equipment housing, unprotected current-carrying conductors.
- For marking wires of the same color.
- For bundling separately lying thin wires.
Insulating joints of electrical wires
Wire insulation and requirements for it
The definition of insulation in electrical engineering, which is given in a popular online encyclopedia, is unlikely to be fully applicable to wire insulation. From our point of view, wire insulation can be called its dielectric shell (structural element), which prevents the penetration of electric current through it and protects:
- a person (user) from electric shock; internal conductors:
Types of insulating materials and their scope of application
Depending on the planned operating conditions and the type of connection of the conductors, various types of insulation can be used. Let's look at the most popular options.
Insulation tape
Insulating tape is the most affordable and popular way to protect current-carrying conductors. The scope of its application directly depends on the material of manufacture.
Polyvinyl chloride
The tape is available in widths from 10 to 20 mm. Adhesion to the protected surface is ensured by a special adhesive compound applied to the inner surface of the tape. Manufacturers produce products in various colors. The positive basic properties of PVC electrical tape include:
- strength;
- adhesion to many types of surfaces;
- ability to withstand significant temperatures - up to 120 degrees Celsius;
- withstand increased voltage;
- elasticity;
- high level of fire safety;
- resistance to external factors: moisture, alkali, acid.
Among the disadvantages, the loss of useful properties when used in subzero temperatures stands out.
PVC insulating tape is widely used in the electrical industry, as well as in everyday life. Electrical tape for wiring with voltage levels up to 1000 Volts can last a long period of time.
Note! If necessary, it is allowed to insulate high-voltage cables. According to the recommended performance indicators, one layer is capable of providing safety at a voltage level of 660 V.
In addition to these cases, the material is actively used for the repair of pipelines, household appliances and packaging of goods.
Types of PVC insulating tape
Cotton
The basis of the product is cotton material with the addition of rubber, on the inside of which an adhesive solution is also applied. Some manufacturers use fiberglass as the base material. Tapes are produced with a width from 15 to 50 mm. Positive characteristics include:
- high strength;
- increased wear resistance;
- thermal stability;
- low cost.
The negative aspects of cotton insulating material include:
- risk of ignition due to overheating;
- liquid absorption.
Fabric insulating tape TESA
The main area of application of CB electrical tape is the protection of electrical wiring with voltage levels up to 1000 Volts. It is recommended to use it exclusively in closed and dry rooms. In electrical installations of higher voltage it is used as an additional means to increase the frost resistance at the junction of conductors.
Application of rubber insulation
In industrial applications, rubber sheathing is often used to insulate cables. Its positive qualities include:
- Moisture resistance.
- Elasticity.
- High resistance.
- High temperature resistance.
Rubber insulation is made on the basis of natural and synthetic materials. High-quality synthetic braid has better performance - it ages longer, withstands the effects of aggressive chemicals and negative temperatures. The rubber bends easily, so the wires can be laid in any conditions. But over time, the rubber insulation ages, cracks and begins to conduct current. In high temperature environments, it is recommended to use vulcanized rubber for insulation. Rubber insulated cables are most often used where cable flexibility is required. These are power cables of cranes, descents to control panels of crane beams. Connecting welding transformers, both from the power side and from the low voltage side to the electrode “holder” and the neutral wire.
Thermal shrink tubes
Heat shrinking is a modern and more reliable method of insulating conductors. Heat-shrinkable tubes are available in various diameters and lengths (up to one meter). They are not collapsible and not universal, so they must be selected for a specific conductor diameter. During the installation process, the original cross-section narrows almost in half. This ensures a secure fit to the protected surface.
Special polymers are used to make thermotubes: polyethylene, silicone, and so on. To improve the adhesion performance with current-carrying conductors, hot-melt adhesive is additionally used in the internal cavity of the tube. At the same time, they can be easily used in various climatic conditions, withstanding exposure to aggressive environments.
Heat shrink tubing for wire insulation
The operating temperature range of standard heat shrinks is from - 50 to + 125⁰С, but products are produced that can withstand up to 260⁰С. Thanks to the use of special polymers, manufacturers produce the following types of heat shrinks:
- heat resistant;
- with increased strength;
- semiconductor;
- corrugated;
- fluorescent.
The scope of application of thermotubes is very wide. With their help, cable insulation with voltage values up to 110 kV can be restored.
Wire insulation - what materials are there?
Before you begin the process of insulating wires, you need to prepare all the necessary tools. Before starting work, you need to turn off the voltage in the apartment (house) using automatic switches.
Today, the following materials for insulating wires and cables can be noted:
PVC electrical tape
PVC electrical tape . (Pictured above) It is highly resistant to environmental damage. In a humid room it does not become limp and does not even come off over time. However, it is better to use it only in dry rooms, so the service life of this insulating material will be longer and more reliable.
PVC electrical tape
HB electrical tape
HB electrical tape . It is considered quite good material, even better than the previous version. Because it is much more resistant to moisture and other loads. It can be used in more extensive areas of application, for example for connecting wires in a car. And the quality of cotton is superior to PVC.
HB electrical tape
Heat shrink tube (HERE)
Heat shrink tube (HERE). The best option, we would recommend using it everywhere. The most reliable degree of insulation under water, underground and finally in the car. It is easy to install and has a long service life. HERE is considered the best material at the moment.
Heat shrink tube (HERE)
PPE caps
PPE caps. They are used extremely rarely, often in cases where it is necessary to insulate the twist. The properties are similar to heat shrink tubing.
PPE caps
Heat shrink tubing
Heat shrink tubes. This method is a modern and more reliable way of insulating conductors. Heat-shrinkable tubes are made in various diameters and lengths (up to one meter). Since they come in a universal size, they must be selected for a specific conductor diameter. During the installation process, the original cross-section narrows almost in half. This ensures reliable fixation to the protected surface.
Heat shrink tubing
The materials from which thermotubes are made are special polymers: polyethylene, silicone, etc. To improve the adhesion performance with current-carrying conductors, hot-melt adhesive is additionally used in the internal cavity of the tube. In addition, they are easy to operate in various climatic conditions and can withstand exposure to aggressive environments without problems.
Types of heat shrinks:
- heat resistant;
- with increased strength;
- semiconductor;
- corrugated;
- fluorescent.
Liquid wire insulation
Liquid insulation of wires . Another option for materials for proper wire insulation. It is used to restore the protective layer of current-carrying conductors, the operation of which takes place in conditions of high humidity or in direct contact with water. Polyurethane compound is used as an insulating material. It is poured into a pre-prepared coupling through a special bandage. Rubber seals are installed at both ends of the coupling.
Liquid wire insulation
Positive properties of the coating:
- Has high resistance to external adverse factors;
- ability for dialect coverage;
- vibration resistance;
- can withstand exposure to ultraviolet radiation;
- ease of application of repair work;
- ductility and thorough coating of the wire in hard-to-reach places and bends.
Negative properties of the coating:
- toxicity;
- high price;
- volatility of the liquid. It is not economically consumed when opening a sealed jar.
Characteristics of liquid electrical insulation:
- has the appearance of a viscous substance, a stretchy substance;
- Available in three forms - in a tube, a jar and in the form of a spray;
- Application is carried out with a brush, with the exception of a spray.
The type of cable insulation is used based on the design features of the cable and the mains voltage at which it will be operated:
- for sheathed cable products with a direct voltage of no more than 700 Volts, and a rated alternating current of no more than 220 Volts for single-phase networks (380 Volts in the case of three-phase networks);
- for unsheathed cables with direct voltage not exceeding 700 Volts, and rated alternating current up to 220 Volts (380 Volts for three-phase networks);
- and for sheathed and non-sheathed cables with direct current ratings of no more than 700 - 1000 Volts, and alternating current from 220 to 400 Volts (for three-phase networks at 380 and single-phase at 220 Volts);
- for cables with direct voltage up to 3600 Volts and alternating current ratings from 400 to 1800 Volts;
- for cables operated under constant voltage conditions of 1000 - 6000 Volts with alternating current values of 400 - 1800 Volts.
Liquid insulation coating
Liquid insulation for wires is used to restore the protective layer of conductors that are operated in conditions of high humidity or in direct contact with water. Polyurethane compound is used as an insulating material. It is poured into a pre-prepared coupling through a special bandage. In this case, rubber seals are installed at the ends of the coupling.
Liquid electrical insulation for wires
Terminals for isolating wiring connections
The products are a contact part, which is placed in a dielectric housing. Available in the form of pads and caps. Fixation of current-carrying wires can be done with screws or clamps. This option is perfect for forming contact connections in a junction box with your own hands.
Insulated crimp terminal
The disadvantages of the terminal connection include:
- increasing the volume of wiring at the contact point;
- exposure to moisture.
Preliminary stage of work
Before you start insulating wires yourself, it is recommended that you carefully familiarize yourself with safety precautions and work rules. This procedure can only be carried out when the power supply is de-energized. However, a disabled machine is not a guarantee of safety. Immediately before starting work, you should check the absence of voltage with a special indicator. In the future, you will need to clean the surface to be treated from dirt, dust, and so on.
De-energize the electrical network before starting work
Preparation of the treated surface
Not only the service life, but also the safety of operation depends on the quality of preparatory measures at the site where the insulating layer will be applied to the conductor. To remove damaged insulation, it is better to use a specialized tool. This will prevent damage to the protective varnish and the surface of the conductor itself, but its cost is quite high. It is not advisable to purchase such a tool for one-time work.
The following are the most affordable methods for stripping insulation at home:
- It is recommended to use a soldering iron to clean the protective coating of old wiring. After warming up the tool, the required surface is heated until the insulating shell melts. Later it is removed using gloves.
- Removing insulation using a knife with a sharp blade (a stationery knife is recommended). The knife must be held parallel to the current-carrying conductors, preventing it from being raised to a vertical position. After making a longitudinal hole, the insulation is carefully removed and cut off.
Stripping wires from insulation
Optimal thickness - insulation
| Graph of the dependence of the reduced S, capital K and operating E costs on the insulation thickness. |
The optimal insulation thickness depends on the properties of the insulating material: the lower the thermal conductivity coefficient, the thinner the insulation thickness, and vice versa.
The economically optimal insulation thickness, corresponding to the lowest operating costs, is determined by comparing the costs of depreciation, repair and maintenance of insulation with the cost of heat lost to the environment.
Determining the optimal insulation thickness is a technical and economic problem and, in general, very difficult, since in addition to the insulation thickness, several more parameters have to be optimized: temperatures at the outlet and inlet of thermal stations, the number of thermal and pumping stations, etc. However, in practice, taking into account design experience and operation of hot oil pipelines, the optimization problem can be simplified.
When calculating the optimal insulation thickness taking into account operational losses from drying out products with conventional battery cooling of chambers, its value turns out to be so large that it is not possible to practically use such values. In other words, the fight against shrinkage of products, especially in the southern regions of the Soviet Union, cannot follow the path of simply extinguishing external heat inflows by increasing the thickness of the insulation.
Thus, the optimal insulation thickness depends on the temperature difference between the inside of the device and the environment, the number of hours of loss per year, the thermal conductivity of the insulation and the heat transfer coefficient. Determining only the optimal insulation thickness without taking into account the quantitative change in the Sp / ( 6) function in the minimum zone is insufficient to make a final decision. It is necessary to consider not the optimal point of 60pt, but the optimal zone within which a certain insulation thickness can be accepted, taking into account its normalized thickness, the availability of certain materials, technical and economic indicators of thermostatic devices, energy costs and other factors.
In order to find the optimal insulation thickness corresponding to the minimum total costs, we determine these costs using the last equation for insulation layers of different thicknesses.
| Nomogram diagram for determining the maximum permissible value. |
Direct determination of Yain and the optimal insulation thickness by differentiation is very difficult here, and therefore the calculation is carried out using a computer.
In these cases, additional tests and calculations must be carried out to determine the optimal insulation thickness. For example, for corded cables, INSULATION crush tests are carried out.
In most Western countries, when energy prices rise, the optimal insulation thickness is recalculated and, if necessary, increased. Such work is also necessary in our conditions.
Based on the data below, we will determine, firstly, the optimal insulation thickness and, secondly, which of the options for insulating a liquefied gas storage tank will be cost-effective.
Next, having determined the cost of depreciation of refrigeration and energy equipment, as well as the insulation itself, you can find the optimal thickness of the insulation of the external contour of the refrigerator, which should meet the minimum annual costs associated with external heat inflows.
| Final distribution matrix. |
A number of economic problems in the field of design and operation of equipment used in gas separation can be successfully solved by conventional methods of classical analysis (selection of the optimal insulation thickness, assessment of the comparative economic efficiency of various types of heat exchangers, selection of the optimal size of enterprises, etc.
The process of using electrical tape to form a protective coating
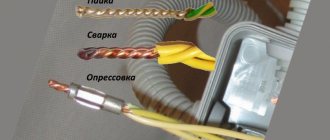
The procedure for applying the protective layer of electrical tape depends on the type of surface being treated. If you plan to insulate the junction of two conductive wires, it is recommended to adhere to the following sequence:
- Twist and solder.
- The electrical tape is applied at an angle, catching a small portion of the main insulation towards the end of the twist.
- At the next stage, you will need to carefully bend the twist so that it is parallel to the main protective coating.
- Another layer of electrical tape is applied, but this time towards the factory insulation.
- The applied electrical tape is pressed with hand force and the excess material is cut off.
To restore the protective coating on a solid conductor, it is recommended to perform the following steps:
- The tape is laid at an angle, capturing part of the main insulation towards another undamaged area.
- Next, the insulating material is applied in the opposite direction.
- The electrical tape is carefully pressed with your hands, followed by removal of excess material.
Insulation tape
Insulating electrical wires with electrical tape does not lose its relevance. Insulating tape is inexpensive and is sold at any hardware store in a wide variety.
It must be wound at an angle, starting from the edge of the original wire insulation. With a parallel connection, an empty winding tube is made at the end of the twist, bent and continued movement in the opposite direction.
Common PVC insulating tape melts when exposed to high heat, but does not allow moisture to pass through. Cotton insulating tape, on the other hand, can withstand high temperatures, but dries out over time and can peel off when wet.
PVC is also used to make cambrics - tubes for insulating wires and cables. In order for the tube to fit tightly, you need to choose the correct diameter of the tube.
How to properly insulate twisted wires, watch the video:
The procedure for forming an insulating coating using heat shrinkage
The process of installing a thermal tube begins by putting it on one of the ends of the wires being connected. Only after this they are twisted. It is recommended to select the size of the heat shrink so that approximately one centimeter of the main insulation is covered.
Subsequently, the insulating tube is pulled over the connected area and heated. To do this, you can use a hair dryer or a lighter. It is recommended to heat from the edges to the center.
Note! The heat shrink should not be allowed to overheat, otherwise it will lose its insulating properties.
Heat shrink tubing
The material from which these tubes are made is polymer. I note that it is best to use this type of shell on low-voltage equipment, when the voltage is not higher than 1 kV.
In order to use this method of creating a casing for electrical wiring, you need to follow some steps:
- First you need to prepare a piece of heat-shrinkable tubing. To do this, measure the exposed section of the electrical wire, after turning off the electricity. We cut off a piece of tube, it is better if it is a little larger than needed. About 2-3 centimeters.
- Next, take a piece of tube and put it on the end of one of the wires.
- After completing the second step, you need to twist the wiring.
- The last step is to transfer the heat-shrinkable tube to the junction of the wiring and use a hair dryer to secure the result.
After these steps, the heat shrink tube will be pressed tightly against the wiring. If you don't have a hair dryer, a lighter will do. It should be carefully kept at a small distance from the junction of the wires.
There are different tubes. It all depends on the desired temperature that the tube must withstand, as well as on the voltage. To find out the characteristics of the tube, you need to look at the markings that manufacturers put on at the factory for the manufacture of these products.
There are tubes of different diameters, colors, and also for certain cable sections. This plus allows you to select the most suitable heat shrink tube.
General understanding of insulation resistance
The determining indicator that influences the formation of leakage currents and the formation of single-phase or phase-to-phase short circuits of conductors is the insulation resistance. It shows how insulated the conductor is from the ground and neighboring conductors.
Depending on the brand of cable used, standard resistance values are provided. They may vary based on specific climatic conditions. A megger is used to record the readings. In order to identify weak points, the specified value is periodically monitored. The timing of the inspection is established in accordance with the PUE. Extraordinary insulation tests are carried out in the following cases:
- during commissioning;
- after repair work;
- in case of contact with the protective layer of water or when it overheats.
For high-quality formation of a protective coating of current-carrying conductors, it is recommended to use appropriate types of insulating material. In this case, be sure to follow safety regulations. For short-term insulation of conductors, you can use tape.
Features of PVC cable insulation: advantages and disadvantages
PVC-insulated cable is usually laid in buildings rather than outdoors, since it is not designed to withstand severe frosts and the harmful effects of ultraviolet radiation. However, a number of modifications have been developed that can withstand temperatures down to -60 °C. To protect from the sun, the cable is laid in pipes.
These power cables with plastic insulation are highly resistant to damage and do not ignite. The addition of plasticizers such as talc, calcium carbonate and kaolin increases their elasticity and resistance to frost.
PVC-insulated cable has a number of advantages:
- excellent throughput;
- high permissible load current (compared to analogues with paper insulation - 30% higher);
- environmental Safety;
- low weight, medium diameter and large bending radius allow the cable to be used on difficult routes;
- high thermal resistance current during short circuit (up to 250 °C);
- insignificant insulation losses (0.001).
There are two disadvantages that need to be highlighted:
- under the influence of ultraviolet rays, the aging process is activated;
- there is no resistance to high temperatures.