When it is necessary to install or replace electrical networks inside a home, the question often arises - what type of conductor to use for this, with one monolithic core or a large number of woven metal hairs. Let's look at how stranded wire differs from single-core wire in composition, design and flexibility class, what the features of each of these types are, what to choose when it comes to organizing electrical wiring in the house, and also what methods of connecting wires exist.
Comparison of wires of the same cross-sectional area, but of different structures - single-core and multi-core Source volk1.ru
Wires - device, composition, flexibility
Conductors for installation of household electrical wiring are a copper or aluminum conductor covered with an insulating layer based on PVC, polyethylene, rubber or fluoroplastic. Moreover, according to their structure, they are divided into 2 main types:
- Single-core . These are, as a rule, rigid conductors consisting of a monolithic cylindrical or sector rod. One of the most important characteristics of electrical conductors is bending resistance. This category is characterized by the minimum value of this indicator. For example, copper products can withstand about 70-90 cycles, while aluminum analogues are not able to withstand more than 10 kinks.
- Stranded . They are a twist of a large number of thin metal hairs, the number of which can vary widely - from 7 to several hundred. Multicore wires are made according to the principle of a metal cable. Moreover, the thinner the wires included in its composition, the higher the bending resistance. For example, for copper specimens belonging to flexibility class 5, its value can reach 30 thousand cycles.
A multi-core cable is a twisting of conductors with a smaller cross-section Source habb.md
Recommendation! Using stranded wires, it is convenient to connect terminals in sockets, as well as sockets in lamps - where single-wire analogues often break. The softness and flexibility of such conductors makes it possible to use them to connect to the network various types of electrical appliances that are characterized by an unstable position during operation, such as a vibrating washing machine, a constantly moving electric stove, a drill.
Flexibility classes and their differences
Whether a conductor belongs to a particular flexibility class shows how much it can bend during operation without irreversible changes in the structure. According to this indicator, wires are graded into 6 categories. At the same time, class 1 means the highest rigidity, class 6, on the contrary, the greatest flexibility.
The flexibility class and conductor structure, as a rule, have a direct relationship. The higher the flexibility index, the greater the number of cores and vice versa.
The flexibility of the wire depends on the type and cross-sectional area Source strojdvor.ru
A good example is two wires with a cross section of 1 mm2 of the 3rd and 5th flexibility classes. The first is made of wires with a diameter of no more than 0.43 mm, the second - no more than 0.21 mm. Thus, the number of cores in a 5th class specimen will be greater than in a 3rd class analogue.
Types of cable
Depending on the operating conditions, flexible multi-core cables are divided into subtypes, which have both their own characteristics of use and differ in markings.
Power cables
The transmission of three-phase current from industrial enterprises is carried out using power cables, including flexible ones with PVC insulation. They are used for stationary installation in electrical networks where the rated alternating voltage is 0.66 kV. 1-6 kV in accordance with GOST 16442-80 for connecting non-stationary machines and mechanisms.
Note! A polyvinyl chloride coating provides low cost, but also the possibility of use in various weather conditions, since special additives to the plastic compound provide it with frost and heat resistance.
The marking is represented by the abbreviation VVG (vinyl-vinyl-naked). Depending on the features, it is supplied with additional symbols:
- VVG-P - flat cable, PVC insulation and sheath, without protective cover;
- VVGng(A) - round cable, PVC insulation, PVC sheath of reduced flammability;
- VVG-Png(A) - flat, PVC insulation, PVC shell of reduced flammability;
- VVGng(A)-LS - insulation, like the shell, is made of PVC, which has a reduced fire hazard, low smoke and gas emissions.
You might be interested in this: Features of the SIP-2 cable
Power cables withstand any temperature changes
To protect against mechanical damage during cable production, armor is used, which consists of two galvanized steel strips or intertwined steel wires, which are necessary to isolate the core from possible mechanical damage. This product is used both when laying underground power lines and in open spaces where mechanical damage is likely.
Reservation scheme
Armored power cables are marked with the letter code VBSH (vinyl-armor-hose) with additional symbols indicating the peculiarity of this cable:
- VBShv - cable armored with two galvanized steel strips, with a PVC protective hose;
- VBShvng(A) - armored with two galvanized steel strips, protective hose made of low-flammability PVC;
- VBShvng(a)-LS - armored with galvanized strips with PVC insulation and a protective hose of reduced fire hazard.
Note! Additionally, they can be marked with a digital code indicating the number of cores and cross-sectional size, for example, 4×1.5 - marking a four-core cable with a cross-section of 1.5 mm².
Wires
The main difference between a wire and a cable is the way it is laid; it cannot be used underground or underwater. They also have one or more aluminum or copper cores and PVC insulation. Wires with copper conductors are characterized by increased electrical conductivity, higher ductility and are more often used in household power supply than in industrial power supply.
Stranded copper wires in PVC
Marked with an alphanumeric code with the following designations:
- P - wire;
- B - PVC insulation;
- G - flexible.
The numbers indicate the number of cores and their cross-section.
Wires of grades PV1, PV2, PV3, PV4 are copper with polyvinyl chloride insulation, where the numbers indicate the flexibility class.
- PPV - two or three-core, flat with PVC insulation (used in lighting systems laid on walls);
- PVA - copper with twisted conductors in PVC insulation (used in everyday life as an extension cord, as well as for connecting household appliances, for example, vacuum cleaners);
- PBPP, PUNP - copper with PVC insulation, containing two or three cores (used in low current devices).
Cables for information transmission
The main characteristics of cables for information transmission include their flexibility, moisture resistance and low resistance of the conductor itself, which ensures data transmission with minimal delays. This applies to television, communication channels, etc. Therefore, cables with copper conductors in PVC insulation are most often used for these purposes.
For your information! RK-75, produced in accordance with GOST 11326, is often used as antenna cables that must provide high-speed signal transmission for radio and television. RK-75 has one or more copper cores and PVC insulation, which allows it to be used outdoors.
RK-75 are suitable for connecting antennas
Among the multi-core RK-75, the following modifications are distinguished:
- RK 75-2-13M. It consists of a stranded inner conductor insulated with solid polyethylene from the outer conductor, which is a braided copper wire. This radio frequency cable is used in television for transmitting satellite and cable television signals, as well as as a connection for video surveillance systems. The PVC shell allows it to be used both indoors and outdoors;
- RK 75-3-34M is a cable used in radio frequency communications, consisting of a multi-wire inner conductor and a braid of copper wires, separated by insulation made of porous polyethylene foam with white PVC insulation.
You may be interested in this Features of the heating cable
Important! The service life of such cables is 12 years.
The cables used to transmit digital information with minimal electromechanical interference are so-called twisted pair cables. Used primarily in computer networks and represents a physical medium for data transmission.
A twisted pair is a system of insulated conductors twisted together and combined into a single shell. Depending on the operating conditions, twisted pairs are produced in various modifications. They come in both shielded and unshielded, with the number of pairs from one to one hundred and in various shells.
Twisted pair cable is suitable for connecting a modem
The following concepts are used in labeling:
- F/FTP, S/FTP, S/STP - cables shielded with foil and/or braid;
- U/UTP - unshielded.
Types of shells are designated as follows: PVC shell - PVC, PVC shell fire-resistant, UV-resistant - FR-PVC.
Polyethylene (PE), polypropylene (PP), high-density polyethylene (HDPE) and low-density polyethylene (LDPE) coatings can also be used.
Special twisted pairs include the following:
- FR-LSZH - do not emit smoke and do not support combustion;
- Plenum - self-extinguishing cables that do not ignite again. Used in air ducts.
LED and electroluminescent
For decorative purposes, flexible LED and electroluminescent wires are used.
An LED cable is a flexible wire with a copper core that conducts current. Along it there are additional wires with multi-colored LEDs connected in series at a distance of 2 cm.
LED wires are more for decoration
Electroluminescent wires are thin cords made of polyvinyl chloride, inside of which there are copper conductors coated with a special substance - electroluminescent phosphor. The glow appears due to the effect of electroluminescence when exposed to alternating electric current. The central wire of such a cable is wrapped around a second contact - two wires, while the electroluminophor is covered with a thin layer of dielectric.
Note! The entire structure is enclosed in a PVC shell, which can be either transparent or colored.
Special types
Special-purpose cables and wires are designed specifically for operating conditions that differ from the average. These include both high humidity and abnormal weather conditions, as well as the aggressive environment in which the products are located.
Special cables are needed for aggressive environments
Marine cables intended for operation in conditions of high humidity can be produced either in PVC insulation or in a rubber sheath. Depending on the technical conditions, they are produced with increased fireproof properties, in which combustion does not spread in the bundles.
For rolling stock they are produced mainly in a cold-resistant PVC shell and are used in the operation of trolleybuses and rail transport.
You might be interested in Description and characteristics of wire SIP-4 4x16
When carrying out geophysical work, cables are used that can withstand the temperature range from −40 °C to 50 °C.
Features of single-core and stranded wires
In order to choose a stranded or single-core wire that suits the operating conditions, as well as a suitable connection method, you must first consider the main pros and cons of each of them.
1-core conductors are classified as stationary. This means that they can only be installed in conditions where during operation they will not be subjected to various types of mechanical loads - and above all, bending.
In addition, they are characterized by the following number of features:
- Minimum resistance per kilometer of wire.
Thus, a copper monolith with a cross section of 1 mm2 has a value of about 18 Ohms. At the same time, a stranded wire of class 5 flexibility of a similar area gives a resistance of 19.5 Ohms.
1-core wire is ideal for laying electrical wiring in a groove Source samelectrik.ru
See also: Catalog of companies that specialize in electrical work of any complexity
This phenomenon occurs due to two patterns. There is a direct relationship between cross-sectional area and resistance - the smaller the first, the higher the second. In addition, although all conductors are twisted into a common core, their contact is nevertheless mechanical. Because of this, the resistance value inevitably increases.
- Ease of connection.
There are several basic options for how to connect single-core and stranded wires; consider their features for copper specimens:
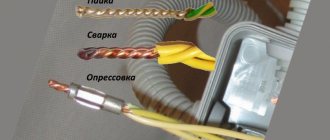
- Screw . A monolithic wire for this method is more preferable than a stranded wire - the cross-section is not reduced, and individual hairs are not squeezed out of the contact point.
- Clamping . When using WAGO type terminals, a single-core wire fits perfectly, which cannot be said about a multi-core analogue.
- Welding . The monolith is welded perfectly. On the contrary, individual thin hairs are easily damaged or torn off by an arc.
- Soldering . Typically used for small cross-section conductors. In this case, preference is given to the multi-core option due to the specifics of the technology.
- Pressing . The method is difficult to implement for a large-section monolith unless special equipment is used.
In addition, 1-core wire is inexpensive, which is especially important when laying a large network.
The stranded conductor, for its part, has the following number of features:
- High flexibility . This property is all the more relevant for installation, the higher the cross-sectional area.
- Ease of installation . A flexible stranded conductor or cord allows you to install electrical wiring in almost any environment.
- The need to use special tips for convenient switching. The solution is inexpensive brass connectors, the installation of which is possible without special skills.
- Possibility of easy connection using WAGO terminals after crimping.
Connecting Stranded Wires Using WAGO Terminals Source dowsingandreynolds.com
Advice! To finally understand and decide which cable is better, multi-core or single-core, it is necessary to take into account the conditions of its future operation. If you do not plan to move the electrical wiring or influence it in any way, then you can choose the 1-wire option. On the other hand, for portable equipment or when the wire will constantly change position, it is better to give preference to a multi-core modification.
Where and how to use the cable correctly
Flexible cable has a lot of modifications, which has led to its widespread use both in industry and in everyday life. Depending on the technical characteristics of a particular product, a copper stranded cable can be used in various conditions where increased elasticity of the wire is required, connecting the mechanism to the source of electric current.
When using such cables, you need to take into account its multi-core nature, which affects the connection methods in the outlet or in the distribution panel. Before installation, it is necessary to terminate the cores using special crimp-type lugs.
What is an ending
Important! In the absence of a special tool, the termination of the cores can be done by conventional soldering.
Thus, flexible copper stranded cable in PVC insulation can be of different types, which are used in various spheres of human life. Even in aggressive environments, it can last for decades. The main thing is to choose the right type and marking.
Rules for choosing between single- and multi-core wires
When choosing between a 1-core or stranded wire option, you must first take into account the conditions of their use:
- Multi-core is better suited for connecting moving devices. It is also ideal for laying in cable ducts, as it bends well when cornering.
- For standard electrical wiring, as well as in the groove, it is better to use a monolith, since during operation it remains in one position and better withstands mechanical loads.
- On automatic panels and RCDs, it is better to use a 1-core conductor, as it is well held in place and is not damaged when replacing the machine.
When assembling an electrical panel, a 1-core conductor is most often used Source samelectrik.ru
- In control panels it is permissible to install the cable version that corresponds to the type of fastening.
- For information communications (telephone, Internet, video), special single-wire conductors are used. The equipment can be powered either through a multi-core cable or through the wire itself.
- For working power tools, a cord is used - a stranded wire with a braid.
- In audio equipment, acoustics and high-frequency circuits, single-wire braided conductors or stranded soft wires are used to prevent the transfer of current to the surface of the conductor.
Bolted connection is the simplest and most reliable way to connect conductors made of different metals Source remontbp.com
On a note! Often, when installing wiring in a house for the first time or replacing it, the question arises about which wire is better - stranded or single-core - for the quality of power supply to electrical appliances. In fact, for a household electrical network with a voltage of 220 V and a frequency of 50 Hz, only the features of laying the electrical route and the conditions of its subsequent operation are decisive.
Video description
Watch in this video which is better for wiring a house – single-core or stranded wire:
- Connection strength . This is true for any electrical wiring, and even more so for installation options when the wire is under tension. In this case, the contact strength must be equal to or greater than the conductor itself.
A poor-quality connection or weak contact leads to an increase in the resistance of the circuit section and, as a result, to heating of the conductor. The latter in turn increases resistance. As a result, the contact quickly weakens and heats up excessively. This is what causes most household fires due to faulty electrical wiring.
Video description
Video review of ways to connect wires:
- Pressing . The ends of the wires are pressed with special pliers and sleeves. The technology is used to connect both types of conductors, as well as their combinations.
- Welding . To use the method, a welding machine is required. The idea is to melt the ends of twisted conductors. The technology makes it possible to connect an unlimited number of conductors at one point.
- Soldering . Suitable for connecting 1-core wires of small cross-section. It is also used for multi-core cables and a combination of both types, but in this case the technology becomes somewhat more complicated.
Note! Conventional twisting is not a technically correct, much less safe, way to connect wires. Due to constant temperature exposure, the dimensions of metal conductors will fluctuate. Over time, this will lead to weakening of the contact, increased resistance and heating.
Characteristics of flexible copper multicore cable in PVC insulation
Increased flexibility is achieved by:
- instead of aluminum, copper is used, which has a lower resistance and allows the use of a smaller cross-section;
- the use of two or more cores creates greater elasticity.
like Note! The flexibility index of copper wire is determined according to GOST 22483-2012.
Advantages and disadvantages
Flexible multi-core cable has become widespread due to its high performance characteristics:
- high corrosion resistance allows it to be used without replacement for 30-35 years;
- the plasticity of copper allows you to lay the wire along a radius without creases;
- the dielectric coating made of polyvinyl chloride is durable, wear-resistant, and has good resistance to chemical environments;
- The electrical conductivity of copper is 1.7 times higher than that of aluminum, which makes it possible to use wires with a smaller cross-section.
Despite the many advantages, this cable also has disadvantages:
- the cost of copper is several times higher than the cost of aluminum, which affects the price of wires;
- due to its high density, copper wire is almost three times heavier than aluminum;
- they cannot be connected by ordinary twisting; special terminal clamps must be used;
- PVC coating, when heated, releases hydrogen chloride, a harmful halogen, so the wires should not be heated above 70 °C.
Important! Halogen is harmful to both humans (causes suffocation) and metals (promotes corrosion).
Briefly about the main thing
Wires for arranging a household electrical network are divided according to structure and composition into 2 main types - single-core and multi-core. They differ primarily in the number of cores under the insulating layer, flexibility and operating conditions. The higher the flexibility class of the conductor, the softer the wire and the better its resistance to bending.
Single-core or stranded wiring wires can be connected in the following accessible and safe ways:
- With squeezes.
- Welding.
- By pressing.
- Soldering.
1-core wires have lower resistance and are convenient for connection in most available connection methods. Stranded ones are more flexible, but require a special approach for switching. Therefore, each of them has its own advantages in choosing for different applications.
Design features of soft cables
Soft or flexible cables are produced with copper stranded conductors in rubber or plastic insulating materials. Depending on the number of copper wires in the core, the flexibility class of the conductor is determined. Core flexibility classes are regulated by GOST 22483-2012. In accordance with GOST, 6 classes are distinguished.
Read more about flexibility classes in the article “Multi-wire flexible cable”
“Soft” cables and wires use cores starting from the 2nd flexibility class. For stationary installation, cable grades such as low-wire VVG (2nd class of flexibility) can already be classified as “soft”, and their installation is easier than installation of the same VVG with a monolithic core, but as a rule, multi-wire VVG is produced with a cross-section of more than 16 mm2 (according to GOST 31996-2012)
In accordance with GOST 24334-80, cables can be divided into degrees of flexibility: flexible, increased flexibility and especially flexible. The degree of flexibility largely depends on the flexibility class of the cores. An important factor in softness is the material of insulation and shells. Insulation based on rubber or silicone has proven to be more “obedient” in frosty conditions. The temperature range is usually -40/-50…+50C. In more severe conditions, special cold-resistant rubber is used, which can withstand temperatures up to – 60C.
In addition to insulation and sheath, a cable can have screens, braids, fillers, cores, etc. and the final set of soft cable design elements will depend on the brand.