The technology of sintering neodymium alloys, developed as a result of long-term research and experiments, makes it possible to create powerful magnets used in a variety of fields. Achieving high adhesive strength was not easy, but the developers did everything possible to give the world such a powerful alloy. The strength of a neodymium magnet is so high that it is simply impossible to find competitors for it. It should be noted that this is a record figure, which no one has yet managed to exceed. Existing traditional alloys lost this race - the power of a neodymium magnet and its safety in operation remained unattainable parameters for them.
How to calculate the strength of a magnet?
It is impossible to measure adhesion force indicators with special instruments, since in this way only one magnetic field can be measured, so manufacturers conduct laboratory tests using one of two methods:
- A supermagnet is placed between two thick steel plates and the static tensile force is measured.
- Determine the force to tear off one of the poles of the magnet by placing it on a metal surface 2 cm thick at an angle of 90 degrees.
Main factors influencing calculations
In the characteristics of neodymium products from our online store of magnets Poland-magnit, indicators of adhesion force are noted, which gives an idea of the operational capabilities of each Polish magnet, but is not a system unit. It should be noted that to accurately determine the power of neo-magnets, many factors should be taken into account:
Let's look in more detail using examples.
The power of the magnetic assistant is directly proportional to the weight, i.e. The more effort it takes to tear the magnet off the plane, the greater its weight. Please note that the units of measurement for this force are kilograms/force, not kilograms.
Contact area
The power of a neodymium magnet must be calculated taking into account its size and shape. Let's look at an example: let's take two products of the same class N35 with parameters 25 * 20 mm and a weight of 76.09 g, 30 * 10 mm and a weight of 54.79 g. Considering only the masses of supermagnets, let’s compare their powers: 76.09/54.79=1.38. Therefore, neodymium 25*20 is approximately 38% stronger than 30*10.
Now let’s try to compare the pull-off forces taking into account the area of contact with the surface: a 25*20 magnet has an indicator of 20.65 kg/s, and a 30*10 magnet has an indicator of 20.65 kg/s. Let's find the quotient of these values: 20.65/17.87=1.155. Those. supermagnet 25*20 is stronger than 30*10 by almost 16%. This means that a fairly large difference in mass is compensated by the area of contact with the plane. Consequently, the shape and size of a neodymium magnet are no less important when calculating power than its weight and class.
The catalog of our online store contains magnets from Poland of class N42, which have various parameters and are of high efficiency, reliability and quality.
Physical characteristics or class of neo-magnet
When calculating the pull-out force, you must also take into account the class of the supermagnet, which indicates the magnetic energy. The higher the energy value, the greater the force required to tear the neodymium from the plane. Note that products of different classes with the same linear characteristics have different powers from each other. For example, two magnetic assistants of classes N35 and N45 with the same parameters of 30*10 mm have forces to lift off the surface of 17.87 kg/s and 22.92 kg/s, respectively, and their difference is approximately 28% (22 .92/17.87=1.28).
Tangential component
Please note that by “pull force” we mean the maximum force (directed perpendicular to the neo-magnet) that is required to lift neodymium from a perfectly flat surface. If you change the angle of inclination and try to disconnect the supermagnet from the surface, then you need to apply less force, since a tangential component will appear in the formula for finding the value of the force, depending on the cosine of the angle of the applied force.
The power of powerful magnets - examples
Neodymium super magnets are truly impressive. When confronted with their power for the first time, people express admiration and surprise. In order to be convinced of their capabilities, you need to pick up a small neodymium magnet, attach it to a smooth and clean metal surface, and then try to tear it off. If you choose a 5x3 mm disk magnet for these purposes, then you will have to apply a force of 0.5 kg to tear it off. Small magnets are often found in magnetic badges that adhere securely to garments without damaging the fibers. It will be much more difficult to tear off a 45x15 mm disk magnet from the same surface, since the adhesion force in this case will be 65 kg. Magnetic disks with dimensions of 70x50 mm have the greatest strength - these are one of the largest disk-shaped neodymium magnets.
Magnetic field strength of a permanent magnet
For magnet users, how to confirm the grade and magnetic properties is still a problem. Most users cannot independently obtain the value of the basic magnetic parameters. In this case, the best solution is to measure magnetic properties relative to each other. The relative measurement of magnetic properties includes magnetic field strength, magnetic flux, and magnetic moment. Magnetic flux and magnetic torque tests of different specifications require a different test coil, and it is for this reason that magnetic field strength is the most popular testing method among relative measurements.
Search Magnet Care
To use a search magnet for a long time, it is important to properly care for it. There are no special requirements for processing the coating, but you need to wipe it with a dry cloth and clean it of small adhering metal particles.
The magnet is a fairly reliable tool; its service life depends on the characteristics of its use. Over a decade, it loses no more than 1% of power.
Do not hit or heat the device. When exposed to temperatures above 80 °C, it will lose its magnetic properties and turn into a useless piece of metal.
Important! The design negatively affects the operation of electronics; the damage radius depends on the power. When searching for artifacts, you should keep smartphones and laptops at a safe distance, and it is better to store search magnets in special bags (more details below).
Demagnetization of search magnets
Even the most powerful magnets lose their properties over time. Ferrite products will last for several decades, but neodymium products will last 200-300 years.
Causes of involuntary demagnetization:
- Heat. When heated above 80 ⁰C, the magnet will completely lose its attractive force. Only some models have increased resistance to temperature changes and can withstand up to 200 ⁰C.
- Strong blows. Mechanical impacts on a magnet (impact, falling from a height) deprive it of its value.
- Errors when cutting and drilling. Strong pressure when processing a magnet with a grinder can lead to loss of characteristics.
- Impact of external factors. When exposed to a magnetic field with an induction of about 3-4 Tesla, the magnet can be demagnetized.
It will be possible to restore the lost properties only in large-scale production using an industrial magnetization installation.
How to calculate the magnetic field strength of a magnet?
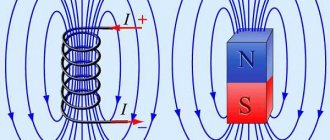
For a simple magnet shape, we can calculate its approximate magnetic field strength using Biot-Savart's law.
For cylinder shape:
Where Br is the residual induction of the magnet; X is the air gap between the test point and the magnet surface.
For block shape:
Where Br is the residual induction of the magnet; X is the air gap between the test point and the magnet surface.
For ring shape:
Where Br is the residual induction of the magnet; X is the air gap between the test point and the magnet surface.
According to the above equation, the value of the magnetic field strength depends on the degree, size and measurement location of the magnet. It should be noted that the measured magnetic field strength value of a nickel-plated magnet will be lower than the Biot-Savart simulation value due to the shielding effect of ferromagnetism. Nickel plated.
For multi-pole magnetization and difficult conditions, the designer will study its strength and magnetic field distribution using finite element analysis (FEA or FEM) software, and then accurately evaluate the magnetization state and flux distribution of the entire magnetic circuit system. Finite element analysis is a powerful tool during the magnetic product development phase.
Diamagnetic???
Sometimes they mistakenly think that a diamagnetic material
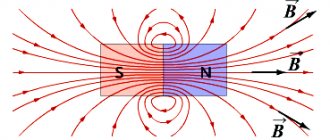
. But this is not true. A diamagnetic material actually weakens the magnetic field. But it weakens the magnetic field only in the thickness of the diamagnetic itself, inside the diamagnetic. Because of this, many people mistakenly think that if one or both magnets are immured in a piece of diamagnetic material, then their attraction or repulsion will weaken.
But this is not a solution to the problem. Firstly, the field lines of one magnet will still reach another magnet, that is, the magnetic field only decreases in the thickness of the diamagnetic, but does not disappear completely. Secondly, if the magnets are immured in the thickness of the diamagnetic material, then we cannot move or rotate them relative to each other.
And if you just make a flat screen out of a diamagnetic material, then this screen will transmit a magnetic field through itself. Moreover, behind this screen the magnetic field will be exactly the same as if this diamagnetic screen did not exist at all.
This suggests that even magnets embedded in a diamagnetic material will not experience a weakening of each other’s magnetic field. In fact, where the walled magnet is located, there is simply no diamagnetic material directly in the volume of this magnet. And since there is no diamagnetic material where the walled magnet is located, it means that both walled magnets actually interact with each other in exactly the same way as if they were not walled up in the diamagnetic material. The diamagnetic material around these magnets is as useless as the flat diamagnetic shield between the magnets.
Neodymium magnets - adhesion strength and other parameters
The next real breakthrough became possible thanks to the discovery of the beneficial properties of neodymium. Deposits of this rare earth element are found in just a few countries, including China, Australia, Canada and Russia. In addition, the percentage of metal in the total mass of rocks is very small, which leads to its high cost. For one kilogram of pure substance they pay about $100 on the world market.
By combining a rare earth element with iron and boron, scientists managed to create a neodymium magnet, the magnetic field of which was several times more powerful than that of its ferrite counterparts and tens of times more powerful than that of the very first magnetic devices made of steel. To date, there is no material that can compare with this kind of alloy in terms of adhesive strength. In addition, it had another important advantage - an unprecedentedly high resistance to demagnetization, weakening by a little more than 10% over 100 years.
Surprisingly, despite the impressive parameters, a strong neodymium magnet was relatively inexpensive, which industrialists quickly appreciated. Where possible, they began to replace previous generations of magnets with neodymium, thereby increasing the efficiency of the equipment.
This kind of magnetic alloys also has its disadvantages. These are, first of all, relatively low thermal stability, fragility and serious susceptibility to corrosion.
In most cases, the magnetic field of a neodymium magnet is maintained only at a temperature not exceeding +80 °C, but on the other hand, it has been possible to develop grades of alloys that today can already operate at +200 °C. The same applies to strength characteristics. They were increased, firstly, by adding polymer impurities, which impart elasticity to the material, and secondly, thanks to protective coatings that protect against chips and aggressive environments. All the products did not affect the field of the neodymium magnet, but significantly extended the service life of each product.
Features of transportation and storage
When using search magnets, you need to follow several recommendations regarding transportation and storage:
- The unit must be kept in a special non-magnetic container. A wooden box or a special bag with shielding is perfect.
- The structure should be moved very carefully, keeping a distance of several meters from electrical equipment and machinery. A strong magnetic field will harm gadgets and computer devices.
Bags for magnets
Bags for search magnets with shielding are an indispensable accessory for any treasure hunter. It is made of wear-resistant material with sewn-in steel plates to isolate the magnetic field. A person will be able to move the unit without the risk of accidentally magnetizing it in the wrong place.
The bag is quite durable and perfectly protects the magnet from external damage, simplifying transportation.