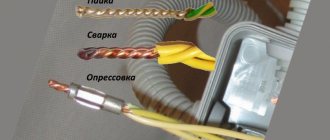
With the development of scientific and technological progress since the second half of the last century, various equipment with moving units and portable devices that were connected to sources of electricity began to appear. The connecting link was the wires, which, due to repeated bending deformations, lost the integrity of the cores and simply quickly became unusable. That's when a durable flexible cable was needed.
Flexible cable
Design
The basis of the CG are conductive conductors made of copper. They are covered with insulation and enclosed in an outer rubber shell. Also in the structure of the wire there is a separating synthetic film, which directly covers the copper conductors.
Flexible power cable
CGs are distinguished by the shape of the strands:
- Midwife;
- Beam.
Stranded twist
This position of the cores is technologically much cheaper for the manufacturer than bundle laying. The conductors in the CG are twisted into separate groups, which, in turn, are twisted into a single core. Extruded polymer insulation is placed on top of it. If technical conditions require shielding, then the cores are wrapped with synthetic tape or foil.
At the beginning of operation, the difference between the outer and inner bending radii has virtually no effect on maintaining the integrity of the copper wire. Over time, metal fatigue accumulates in conductors, which ultimately leads to irreversible deformation. Copper strands bend, forming areas of excessive compression and tension within their structure. After some time, the cable core is destroyed.
Bundle twist
The unique technology of core structuring is that instead of layer-by-layer twisting, the cores are twisted in bundles around an elastic core. Avoiding the formation of multicore layers, they achieve the same bending radius for all conductors.
In the place where the CG bends, the line of action of each core instantly shifts from the inside to the outside of the cable. It turns out that the cores do not compress or stretch separately on the outer and inner sides of the bend.
The KG sheath keeps the cores from unwinding. For this purpose, it is not enough to form a surface insulating layer by pressing alone. Only the internal pressure of the shell can keep the core from unwinding. The rubber outer coating is made using special technology.
As a result, the multicore cable behaves more rigidly in dynamic mode than its standard prototype. However, this achieves the durability of the CG.
Important! For portable electrical installations, only stranded wire is used. Previously, such cables were called cords. Today this name is relevant.
What is cable KGVVng(A)-LS
KGVVng(A)-LS - flexible non-flammable power cable is in demand among consumers, which is easily explained by the ideal ratio of the quality of this type of product to its pricing policy. This product has fairly high characteristics, which puts it at a higher level compared to similar products from other manufacturing companies. The wire of this brand, which has a special plastic polyvinyl chloride insulating coating, is not prone to burning. It is also characterized by a low smoke index, since during the combustion process there is a slight smoke emission, which is confirmed by the ng(A)-LS index in the abbreviation.
Characteristics of flexible cable
Flexible cable channel
The most common use of a flexible cable is to use it to connect a welding machine, a welding electrode holder and a grounding clamp. The technical specifications cover various parameters. They allow the consumer to navigate when choosing cable products that meet certain operating conditions of the CG.
Table of technical characteristics of KG
| Characteristic name | Parameter value |
| Ultimate tensile force | Max – 19.6 Pa |
| Trouble-free service life | 4 years |
| Guarantee | ½ year from the date of sale |
| Release length | 125-150 m |
| Limit bending radius | 8 ø KG |
| Heat Limit | +750 C |
| Operating temperature range | From -400 to +500 C |
| AC voltage limit | 660v |
| DC voltage limit | 1000 in |
| Mains frequency | 400 Hz |
The difference between single-core and stranded wire
You can understand the significant difference between a monoconductor and a multiwire cable by examining their cross section. This allows you to understand how conductive lengths are designed.
Single-core wires differ from other conductors by the presence of one copper core. They are unsuitable for use in conditions of constant deformation. They are bent only a few times during the installation of electrical wiring.
Externally, stranded wires are distinguished by twisted wires with yellow, green and black insulation located under a common rubber sheath.
Answer clearly the question “Which wires are better: stranded or single-core?” it is forbidden. Each wired product is designed for use in certain conditions.
Explanation of abbreviations when marking a flexible cable:
- KG – power flexible cable;
- N – rubber insulation, flame retardant;
- HL - operation at low temperatures (up to -50 °C);
One of the leading materials for flexible cable insulation (CG) is rubber. Rubber is made using ethylene propylene rubber and butyl rubber. A flexible cable with rubber insulation has a certain number of advantages. Firstly, of all types of insulation, rubber can provide the greatest flexibility and resistance to torsion. The bend radius can be more than eight diameters. Secondly, rubber is most optimal for laying cables at high humidity, since it is completely non-hygroscopic. Condensation and precipitation will not affect the operation of the cable. Thirdly, such insulation does not react with alkaline and acidic environments, and is also not affected by oils. The flexible rubber copper cable has one important drawback: constant direct sunlight is harmful to it, so you need to take this into account when choosing.
Types of flexible cable
The figure below shows cross sections of cables of different flexibility classes.
Single-core wire and flexibility classes of multi-core cables
Flexible cable channel
The flexibility class determines how much a single-core or stranded wire can be bent, and how resistant the cable is to this type of deformation. GOST 22483-2012 establishes 6 flexibility classes.
All single-core cables belong to the first flexibility class. The second class is a cable consisting of several conductors twisted together. A multi-core cable with a large number of wires of a certain cross-section is classified as class three or higher.
Note! Regulatory documentation (GOST) strictly regulates the number of wires in a copper multi-core flexible cable. For example, the number of wires in a class 5 cable must be at least seven.
The Russian electrical industry produces several brands of flexible cords:
- KG - the core of a multifunctional cable contains from one to five cores. The wire is covered with electrical rubber;
- KOG - single-core welding conductor designed to power electric welding equipment;
- RPSh, RPSHE – used for control circuits, alarm systems;
- KGNV - a universal conductor can contain up to 27 cores. The wire is enclosed in a PVC sheath;
- HO7RN-F is a multifunctional 24-core cable in a neoprene sheath.
Universal KG
Design features
The core is the basis of the wire and the main conductor of electric current. In accordance with GOST, it consists of several individual copper wires having a round shape.
The insulating coating is plastic polyvinyl chloride with low flammability properties.
Grounding is characterized by a yellow-green color.
Twisting is individual strands intertwined with each other.
The outer covering is plastic polyvinyl chloride with low flammability properties.
Application
The scope of flexible cables is quite extensive. They can be found in any apartment. Almost all household electrical appliances are connected to the electrical network using flexible cords. An electric iron is a movable device that is equipped with a CG. Table lamps, headphones, multi-plug extension cords, televisions - all these devices are connected to sockets with flexible cables.
In industry, machine tools with numerical control (CNC machines) have many moving electrical components. The machines are equipped with multi-wire cable channels. The wiring is designed for operation for 5-10 years, depending on the intensity of the equipment.
There are standard series channels with a limited length of open and closed type. Along with this, products with unlimited length are used. Universal channels can be expanded to any size.
Cable layer
Miniature movable cable managers with flexible wires are used in printers. In the CG of such devices, wires with a thickness measured in hundredths of mm are used.
Additional Information. It is possible to use CG for hidden wiring, but it is not advisable. The wiring diagram of an electrical network made from flexible conductors will cost much more than making it from single-core wires.
Flexible cables are used not only in mobile systems. It is convenient for them to connect contacts in distribution boards and cabinets, where sometimes it is necessary to bend the CG several times; in case of repair work, the cables can be used repeatedly. Connections of signaling devices, control panels of various electrical equipment with power supplies are carried out with flexible cords for control control.
When choosing, you need to pay attention to modifications of cable products. There are wires with flame retardant sheaths, tropical and cold-resistant versions. For domestic needs, the most suitable are CGs in a PVC shell, designed for a voltage of 220 V. If in doubt, you should turn to professionals. They will help you choose the right brand of product and install it.
Areas in which flexible copper cable in rubber insulation is used:
- for operation of welding equipment;
- in ventilation systems and fire extinguishing systems;
- when operating household appliances;
- for connecting industrial and production equipment, electric pumps;
- construction, construction of buildings and many others.
The design of a copper flexible cable consists of conductive conductors, the number of which, depending on the purpose of the cable, can vary from 2 to 91. Insulation made of polyvinyl chloride with reduced flammability, polyethylene, elastomers or variations of polymer compositions is laid on top of the conductors. The top shell is made of rubber, polyurethane, polyethylene or PVC. To enhance resistance to mechanical damage, galvanized steel armor can be additionally used.
Rubber insulation: advantages and disadvantages
Let's look at the main pros and cons of rubber as an insulating and protective coating.
| Advantages of rubber insulation | Disadvantages of rubber insulation |
|
|
To eliminate or minimize shortcomings in the manufacture of rubberized cable sheaths, for example, vulcanization technology is used. The introduction of sulfur atoms or organosilicon substances into the structure of rubber molecular bonds improves the moisture, oil, electrical and fire resistance of rubber.
FLEXIBLE CABLES AND WIRE WITH RUBBER INSULATION FOR GENERAL PURPOSE
8.1. NOMENCLATURE
Rubber-insulated flexible general-purpose cables, produced in accordance with GOST 13497-77, are intended for connecting various mobile mechanisms with alternating voltage up to 660 V with a frequency of 50 Hz. The cables are designed for operation in various atmospheric conditions with a long-term permissible conductor temperature of no more than 65ºС. The list of brands of cables and wires is given in table. 8.1, and the assortment in table. 8.2.
To brands of cables KG, KGN, KPG, KPGS, KPGSN and KPGU, produced for use in areas with a tropical climate in accordance with GOST 15150-69, the T index is added, and to brands of cables KG, KPG, KPGSN and KPGU, intended for areas with cold climate, according to the same GOST - HL index.
In table 8.3 shows the composition of the nominal cross-sections of the grounding and control conductors depending on the main conductors of flexible general purpose cables. For export deliveries, other sections of grounding conductors are allowed.
Table 8.1. Range of flexible cables and wires with rubber insulation and general purpose sheath
| Brand (OKP code) | Cable | Preferred area of application |
| KG (3544410100) | With copper conductors, rubber insulated, rubber sheathed | For bends with a radius of at least 8 D and temperatures from –40 to +50ºС |
| KGN (3544410200) | The same in a rubber, oil-resistant, flame retardant shell | The same applies to conditions where the shell is exposed to disinfectants and aggressive substances used in agriculture, as well as oil at temperatures from -30 to +50ºС |
| CNG (3544410300) | Same as CG, but with increased flexibility | For bends with a radius of at least 5 D and temperatures from –50 to +50ºС |
| KPGN (3544411600) | Same as KGN, but with increased flexibility | The same applies to conditions where the shell is exposed to disinfectants and aggressive substances used in agriculture, as well as oil at temperatures from -30 to +50ºС |
| KPGS (3541450700) | Same as CNG, but with a profiled rubber core | When bending with a radius of at least 5 D when the cable is exposed to shock and crushing loads and temperatures from –50 to +50ºС |
| KPGSN (3544450800) | The same in a rubber, oil-resistant, flame retardant shell | The same applies to contact with the shell of disinfectants and aggressive substances used in agriculture, as well as oil at temperatures from -30 to +50ºС |
| KPGU (3544412700) | Same as CNG, but with increased flexibility cores and rubber filling between them | For bends with a radius of at least 10 D and temperatures from –50 to +50ºС |
| PRS (3555146000) | Flexible wire with twisted cores, rubber insulation in a rubber sheath | For connecting machines and devices to electrical networks of alternating voltage 220/380 V, frequency up to 400 Hz at temperatures from –40 to 65ºС |
| PRSU (3553546000) | The same in a rubber thickened shell | Same |
Table 8.2. Range of flexible cables and wires with rubber insulation for general purposes
| Brand | Number of cores | S, mm2 | ||
| main | grounding | management | ||
| KG and KGN | 1 | — | — | 2,5-120 |
| 2; 3 | — | — | 0,75-120 | |
| 2; 3 | 1 | — | 0,75-120 | |
| CNG | 2 | — | — | 0,75-70 |
| 2; 3 | 1 | — | 0,75-70 | |
| KPGN | 3 | 1 | — | 1,5-10 |
| 3 | 1 | 1 | 1,5-10 | |
| KPGS, KPGSN | 3 | 1 | — | 2,5-120 |
| 3 | 1 | 1 | 2,5-6 | |
| KPGS, KPGSN | 3 | 1 | 2 | 4-50 |
| KPGU | 3 | — | — | 95-150 |
| 3 | 1 | — | 95-150 | |
| PRS | 2; 3 | — | — | 0.5 and 1.5 |
| PRSU | 2 | — | — | 0,5 |
Table 8.3. Cross-sections of grounding and control conductors depending on the cross-section of the main conductors of flexible cables with rubber insulation for general purpose, mm2
| Main veins | Grounding conductors | Control cores |
| 0,75 | 0,75 | — |
| 1,0 | 1,0 | — |
| 1,5 | 1,0 | 1,5 |
| 2,5 | 1,5 | 1,5 |
| 4,0 | 2,5 | 2,5 |
| 6,0 | 4,0 | 4,0 |
| 10,0 | 6,0 | 6,0 |
| 16,0 | 6,0 | 6,0 |
| 25 | 10 | 10 |
| 35 | 10 | 10 |
| 50 | 16 | 10 |
| 70 | 25 | — |
| 95 | 35 | — |
| 120 | 35 | — |
| 150 | 50 | — |
| Note. In CPG and KPGN cables, the grounding conductors and auxiliary conductors have cross-sections equal to the sections of the main conductors, and in the KPGU cable, with a cross-section of the main conductor of 95 mm2, the cross-section of the grounding conductor should be 25 mm2 | ||
8.2. STRUCTURAL ELEMENTS OF CABLES AND WIRES
The conductors consist of copper wires in accordance with GOST 22483-77 according to the designs given in table. 8.4, but the use of cores with a large number of wires is allowed. Current-carrying conductors are insulated with rubber type RTI-1 with a thickness of 0.6 mm with a permissible deviation of 10%.
The main insulated cores have a distinctive color or other type of distinction. By agreement with the consumer, cables can be manufactured without colors or other types of differences in the cores. The grounding conductor, in addition to the grounding conductor of the KPGU cable, has a green-yellow color. For export delivery, the colors of the cores correspond to the table. 8.5.
The insulated main conductors, together with the grounding conductors and control conductors, are twisted in the right direction. Insulated cores of cables KPG, KPGN: three-core with a cross-section of 35 mm2 and more, four-wire with a cross-section of 4 mm2 and more, five-core of all sections, as well as cables KPGS and KPGSN with a cross-section up to 6 mm2 inclusive, are twisted around a round rubber core, and cables KPGS and KPGSN with a cross-section of 10 mm2 and more - around a profiled rubber core. The insulated cores of the KPGU cable (except for the cable with a two-layer sheath) are twisted with a filling of cable yarn or stapled glass yarn and wrapped with a tape of rubberized fabric or synthetic film. In four-core cables, it is allowed to twist the cores around a rubber profiled core.
The twisting steps of insulated cores do not exceed the values indicated in the table. 8.6. The twisted insulated cores of the KGN, KPGN, KPGSN cables are wrapped with a synthetic film strip and a rubber sheath of the RShN-1 type is applied; cables KPG, KPGS, KPGU - type RSh-1. Deviation from the nominal thickness is allowed up to – 20%. The insulated conductors of the PPC and PRSU wires are twisted and a rubber sheath of rubber type RShT-2 or RShTM-2 is placed on them according to OST 16.0.505.015-79. The values of the external diameters of the cables are given in table. 8.7.
The outer diameter of a two-core wire PRSU with a cross-section of 0.5 mm2 is 7.3 mm; three-core wire PRS with a cross-section of 0.5 mm2 - 6.6 mm;
Table 8.4. Design data of current-carrying cores of flexible cables with rubber insulation for general purposes
| S, mm2 | Cable core designs | |
| KG, KGN | KPG, KPGN, KPGS, KPGSN, KPGU | |
| 0,75 | 19*0,23 | 24*0.20 or 19*0.23 |
| 1,0 | 19*0,26 | 32*0.20 or 19*0.26 |
| 1,5 | 19*0,32 | 28*0.26 or 19*0.32 |
| 2,5 | 49*0,26 | 49*0,26 |
| 4,0 | 49*0,32 | 49*0,32 |
| 6,0 | 49*0,40 | 84*0,30 |
| 10 | 49*0,50 | 91*0,37 |
| 16 | 56*0,60 | 84*0,49 |
| 25 | 84*0,60 | 126*0,50 |
| 35 | 133*0,58 | 189*0,49 |
| 50 | 133*0,68 | 266*0,49 |
| 70 | 189*0,68 | 266*0,58 |
| 95 | 266*0,67 | 361*0,58 |
| 120 | 266*0,77 | 266*0,77 |
| 150 | — | 405*0,68 |
Table 8.5. Coloring of cores of flexible cables with rubber insulation for general purposes, supplied for export (cables with a grounding core)
| Number of cores | Core color |
| 3 | Green-yellow, blue, brown |
| 4 | Green-yellow, blue, black, brown |
| 5 | Green-yellow, blue, black, brown, black |
| 6 | Green-yellow, blue, black, brown, black, black |
| Note. Green-yellow insulation color is used only for the grounding conductor. | |
Table 8.6. Twisting pitch of insulated cores of flexible cables with rubber insulation for general purpose is no more than
| Brand | S, mm2 | Twist pitch |
| KG, KGN | 0,75-50 | 16 D |
| 70-120 | 14 D | |
| CNG, KPGN, KPGS, KPGSN | 0,75-50 | 12D |
| CNG, KPGS, KPGSN | 70-120 | 10D |
| KPGU | 95-150 | 14 D |
Table 8.7. External diameter, mm, of flexible cables for general purposes
| S, mm2 | KG, KGN | CNG, CPGN | KPGS, KPGSN | KPGU | |||||||||||
| One main core | Two main cores | Two main conductors and a ground conductor | Three main cores | Three main conductors and a ground conductor | Two main cores | Two main conductors and a ground conductor | Three main conductors and a ground conductor | Three main conductors, a grounding conductor and an auxiliary | Three main conductors and a ground conductor | Three main conductors, a grounding conductor and an auxiliary | Three main conductors, a grounding conductor and two auxiliary conductors | Three main cores | Three main conductors and a ground conductor | Two main cores | |
| 0,5 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 6,3 |
| 0,75 | — | 10,3 | 10,8 | 10,8 | 11,6 | 10,4 | 10,9 | 11,8 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| 1,0 | — | 10,6 | 11,1 | 11,1 | 12,0 | 10,7 | 11,2 | 12,1 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| 1,5 | — | 11,2 | 11,8 | 11,8 | 12,7 | 11,8 | 12,4 | 13,4 | 15,5 | — | — | — | — | — | 8,2 |
| 2,5 | 7,3 | 12,7 | 13,4 | 13,4 | 15,5 | 12,7 | 13,4 | 15,5 | 16,8 | 18,1 | 19,7 | — | — | — | — |
| 4,0 | 7,9 | 13,8 | 15,5 | 15,5 | 16,8 | 13,8 | 15,5 | 16,8 | 18,2 | 19,2 | 21,8 | 22,8 | — | — | — |
| 6,0 | 8,6 | 16,2 | 17,1 | 17,1 | 18,5 | 16,5 | 17,4 | 18,9 | 21,5 | 21,9 | 23,5 | 24,5 | — | — | — |
| 10 | 10,9 | 18,8 | 19,9 | 19,9 | 22,7 | 19,6 | 21,7 | 23,6 | 25,8 | 25,0 | — | 31,6 | — | — | — |
| 16 | 12,3 | 22,7 | 22,7 | 24,0 | 24,6 | 23,0 | 24,3 | 27,5 | — | 29,4 | — | 36,0 | — | — | — |
| 25 | 15,3 | 27,6 | 27,6 | 29,1 | 29,9 | 27,6 | 29,2 | 31,9 | — | 35,0 | — | 38,6 | — | — | — |
| 35 | 16,5 | 30,0 | 30,0 | 31,8 | 34,7 | 30,7 | 34,7 | 37,7 | — | 37,1 | — | 42,7 | — | — | — |
| 50 | 19,0 | 37,0 | 37,0 | 40,1 | 41,3 | 37,0 | 40,1 | 43,8 | — | 44,8 | — | 47,0 | — | — | — |
| 70 | 21,8 | 41,5 | 41,5 | 43,9 | 45,2 | 42,0 | 44,4 | 48,6 | — | 48,8 | — | — | — | — | — |
| 95 | 24,4 | 46,8 | 46,8 | 49,5 | 51,0 | — | — | — | — | 53,0 | — | — | 45,5 | 52,2 | — |
| 120 | 27,6 | 51,2 | 51,2 | 54,3 | 55,9 | — | — | — | — | 58,0 | — | — | 52,8 | 59,2 | — |
| 150 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 60,6 | 66,6 | — |