Nowadays, electrical wiring is carried out using wires with different insulation colors. And the point here is not about some fashion trends or the beauty of the product itself, but about the safety and ease of use of this electrical wiring.
After all, colored insulation can perform two functions simultaneously - protection against electric shock or protection against short circuits by applying insulating material to the conductor, and with the help of the color of this very insulating material, it helps the electrician determine the purpose of this conductor.
To avoid confusion, all color colors were reduced to a single standard, described in the PUE.
Color marking can be done both along the entire length of the conductor and at the connection points of the conductors or at their ends. To do this, colored electrical tape or heat-shrinkable tubes (cambrics) can be used.
In this article we will look at color marking in single-phase and three-phase circuits, as well as in DC circuits.
Wire colors in a single-phase network
Different colors of wire insulation become most relevant when the installation of electrical wiring is carried out by one person, and repairs and maintenance are carried out by another. The main purpose of color marking is to make it easy and quick to determine the purpose of any of the wires.
Phase wire colors
According to the PUE, phase wires in a single-phase electrical network can have the following insulation color - black, red, brown, gray, purple, pink, orange, white, turquoise. This color marking is quite convenient - when you see a wire with this color of insulation, it becomes clear that you have a phase in front of you (but it is still better to double-check, since in practice there are cases when the marking is not observed).
Zero working conductor or neutral
The neutral or neutral working conductor (N) is usually made with a wire with blue insulation.
Neutral protective conductor and neutral combined conductor
The neutral protective conductor (PE) has a yellow-green insulation color. The combined neutral and working conductor (PEN) has a blue color with yellow-green marks at the end, or vice versa - a yellow-green color with blue marks at the end.
If you do not have a wire of a suitable color, then installation can be done with a wire of any color (except for the protective PE conductor that is colored) by marking the ends of this wire with colored electrical tape or heat-shrink tubing, which have a color indicating the purpose of the conductor. You can also mark the ends of the conductor with the desired color in the case when the installation has already been carried out with a conductor of a different color.
Below are the colors that indicate phase, neutral, protective and combined conductors:
Electric tires: brief description, markings
6g. Designations for the type of current and voltage
Note. If it is impossible to use the basic designation, then use the following designation.
3. m
DC wire line with voltage
U
, for example:
a) two-wire 110 V DC line
b) three-wire DC line, including the middle wire, with a voltage of 110 V between each outer conductor and the middle wire 220 V between the outer conductors
Note. It is allowed to indicate the frequency value to the right of the alternating current designation, for example:
AC in the frequency range from 100 to 600 kHz
5. Alternating current with number of phases m
, frequency
f
,
6. Alternating current with number of phases m
, frequency
f
, voltage
U
, for example:
a) alternating current, three-phase, frequency 50 Hz, voltage 220 V
b) alternating current, three-phase, four-wire line (three wires, neutral) with a frequency of 50 Hz, voltage 220/380 V
c) alternating current, three-phase, five-wire line (three phase wires, neutral, one protective wire with grounding) with a frequency of 50 Hz, voltage 220/380 V
d) alternating current, three-phase, four-wire line (three phase wires, one protective wire with grounding, serving as a neutral) with a frequency of 50 Hz, voltage 220/380 V
Expert opinion
It-Technology, Electrical power and electronics specialist
Ask questions to the “Specialist for modernization of energy generation systems”
Designations for general use. GOST 2.721. Part 2 In electrical diagrams, passports, and even on the equipment itself, conductors and contacts for connection are often marked with letters. Ask, I'm in touch!
Colors of wires and buses in the AC network for a three-phase connection
To maintain the correct phase rotation when connecting three-phase consumers of electrical energy, color marking of buses and cables is also used. This makes life much easier for installers and repairmen, since by the color of the cable or bus, you can determine the phase that is connected or will be connected to this cable or bus. Unlike single-phase consumers, where the phase wire can be made of cables with different insulation colors (list above), for three-phase consumers the colors that can be used to indicate phases are strictly regulated by the PUE.
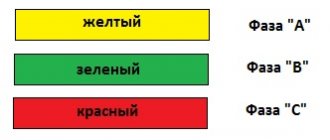
For a three-phase connection, phase A should be indicated in yellow, phase B in green, phase C in red. Zero working, protective and combined conductors have the same color as with a single-phase connection.
It is permissible to color code cables and buses not along their entire length, but only at the points where cables or buses are connected, as shown in the figure above.
Also, color codes may comply with the international standard IEC 60446 or may use the coding adopted within the country by the relevant regulatory documents. For example, in the USA and Canada, different color codes are used for grounded and ungrounded systems. Below is a table showing the color coding of cables and busbars in different countries for comparison:
Types of material for manufacturing
Made from aluminum, copper and a mixture of aluminum and steel. The former are characterized by high electrical conductivity, corrosion resistance, low weight and low cost. Busbars made of aluminum and steel are particularly durable, elastic and ductile, but have low electrical conductivity. Copper has high resistivity and excellent thermal and electrical conductivity.
Aluminum as the main material for manufacturing
Colors of wires and buses in DC circuits
DC circuits typically use only two buses, namely plus and minus. But sometimes DC circuits have a middle conductor. According to the PUE, buses and wires are subject to the following markings in DC circuits: positive bus (+) - red, negative (-) - blue, zero operating M (if available) - blue.
Classification by section shape
The busbar duct is classified, in addition to the topic of how busbars are designated for direct current, according to the material of manufacture, design, insulation and geometric shape of the section. The result is copper, aluminum, steel-aluminum, flexible, rigid, insulated or non-insulated, as well as rectangular, two-way and three-way, box and tubular.
It has flexibility and a high degree of tension. Equipped with a vibration damper and a flexible jumper responsible for temperature tension.
Conductors with a flat rectangular cross-section have good heat conductivity. Their disadvantage is that they are difficult to assemble and have an unevenly distributed current.
Note! Box-section devices are used where there is a mains voltage of 10 kilovolts. Used in turbogenerators.
The tubular cross-sectional shape is the most effective. It has good thermal conductivity and durability. Capable of evenly distributing the electric field and preventing the appearance of corona.
Flat variety for solid chain
Changes in color marking of buses and wires
In the Russian Federation, GOST R 50462-92, which regulated the identification of conductors in electrical networks using digital and color designations from 01/01/2011, was replaced by GOST R 50462-2009, which has quite significant differences from GOST R 50462-92 and has some contradictions with PUE 7. Below is a table containing recommendations for color marking of busbars and cables in accordance with GOST R 50462-92:
What it is
This is the connecting element of a power system or installation that allows the creation of one equivalent point. Defined according to GOST of 2007 as a connecting conductor having low resistance. The combination of such components is a busbar. It is mounted on insulating supports and placed in the electrical system channel. It must have the main quality - high resistance to electric shocks with thermal and dynamic overloads.
Definition from the textbook
PUE-7 clause 1.1.30
The alphanumeric and color designations of tires of the same name in each electrical installation must be the same.
Tires must be marked:
1) with alternating three-phase current: buses of phase A - yellow, phase B - green, phase C - red;
2) with single-phase alternating current, bus B connected to the end of the power source winding is in red, bus A connected to the beginning of the power source winding is yellow.
Single-phase current buses, if they are a branch from the buses of a three-phase system, are designated as the corresponding three-phase current buses;
3) at constant current: positive bus ( + ) - in red, negative ( - ) - in blue and zero operating M - in blue.
The color coding must be carried out along the entire length of the tires if it is also provided for more intensive cooling or anti-corrosion protection.
It is allowed to carry out a color designation not along the entire length of the busbars, only a color or only an alphanumeric designation, or a color in combination with an alphanumeric designation at the points where the busbars are connected. If non-insulated busbars are not accessible for inspection during the period when they are energized, then they may not be marked. At the same time, the level of safety and visibility when servicing the electrical installation should not be reduced.
Source
Letter marking
The letter marking is designed to allow the user to correctly read the diagram, know exactly how the busbars are designated for three-phase alternating current, and determine the type of busbar trunking. Like colors, letters have their own meaning and have a corresponding winding pattern. All existing letters with the meaning of zero and positive branches of the source network are indicated in the figure below.
Note! It is important to note that they are mandatory and regulated at the legislative level.
In general, busbars are a necessary element of any electrical installation, which allows you to reduce the installation area with material consumption and labor costs. They are needed where low active and reactance is required. There is a classification based on material of manufacture, design, insulation and geometric shape of the section. Busbars with single-phase alternating current are indicated in yellow. They are also marked with letters.
Source