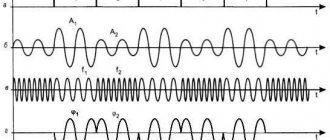
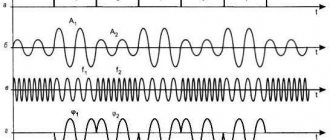
Soldering stations are mainly used in professional environments, although anyone can purchase them. This is quite powerful equipment that is suitable for many different operations, including the restoration of complex equipment. The station can include not only a standard soldering iron, but also a hot air dryer.
In addition, any station has a so-called control module and galvanic isolation from the network. The presence of galvanic isolation minimizes possible negative consequences from soldering (black smoke or electric shock).
The soldering station is also distinguished from ordinary soldering irons by its temperature stability during operation, which is critical when soldering printed circuit boards.
Contact and non-contact
Now soldering stations are presented in a significant variety.
They can be divided into groups according to several parameters. For example, they are contact and non-contact. A contact station is an ordinary soldering iron that has direct contact with the surface when soldering, equipped with an electronic control and temperature control unit. That is, this is the most standard variety, which is suitable even for beginners.
Contact stations, in turn, can be divided into two subtypes depending on the solder used. Some models use only lead-containing solders, while others also use lead-free solders.
In the latest modifications, the heating element has a power of up to 160 watts. In this case, increased power is absolutely necessary, because the melting temperature of lead-free solders is quite high.
As for contactless stations, they can be used, among other things, for operations with microcircuits. A non-contact soldering unit can be hot-air, infrared or combined, and each of these three types has its own principle of operation.
From the history of soldering and metallurgy
There is information that soldering was used in Mesopotamia already 5000 years ago. Selected Sumerian swords from 3000 years before Christ were collected using the indicated method. Incorrect soldering process leads to disastrous consequences. Scott's expedition to the South Pole was lost due to the fact that the containers soldered with tin lost their fuel supply. A little knowledge in the field of metallurgy could radically change the course of history. After all, Scott reached the pole first and was already returning... Therefore, a scientific approach is important.
A welding society is registered in the USA. This is an official organization that deals with specific issues of joining metals. Anyone can check it on aws.org. The American Welding Society was a non-profit organization founded in 1919 to study and describe the welding and brazing processes. The publications of the mentioned society are full of science-intensive definitions.
American Welding Society logo
AWS employs over 73,000 people and consists of 22 departments, divided into 250 sections, scattered around the world. Thanks to this organization, knowledge regarding welding and soldering is constantly systematized and kept fresh. The American state began to experience its first difficulties during World War I, when the speed of creating military equipment was greatly affected due to the lack of standards. President Woodrow Wilson sought the help of Professor Comfort Adams to create a special committee to deal with the issue.
On March 28, 1919, AWS was born. In its first year of existence, the organization grew to 217 members and acquired its own publications and headquarters. In the first years, the society lived from fees in favor of its own magazine. Today the society is engaged in training world professionals, continues scientific publications, and accredits specialists.
Infrared devices and hair dryers
First, a strong air flow generated by the compressor, passing through the heating coil, acquires the desired temperature, and then a stream of hot air is directed to the soldering area. The hot air station makes it possible to solder in hard-to-reach areas with simultaneous heating of several surfaces at once. Any hot air installation has a power that is sufficient for soldering with any type of solder, both with and without lead.
Hot air soldering has wide application, for example, in the field of repairing household electrical appliances and mobile phones. However, it is almost impossible to install and dismantle microcircuits (even in BGA format) with thermal air installations - this is a serious limitation.
Infrared-type stations must have a heating element in the form of an infrared emitter made of ceramic or quartz. And thanks to this, infrared installations have some advantages over their thermal air counterparts:
- soldering of complex-profile components is possible;
- there is no need to look for a nozzle for a hot air gun for a specific microcircuit;
- During soldering, no radio components are blown away by heated air flows from the printed circuit board;
- The soldering area heats up very evenly.
Infrared stations are not cheap and are considered equipment for true professionals. Beginners in soldering and radio electronics for the most part do not use such devices.
A few words should be said about combined soldering stations. They are called that because they combine several types of equipment in their design, for example, a soldering iron and a hair dryer.
Types of soldering stations
You can find many models of soldering stations on the market; they differ in functionality and, of course, price. You can try to classify them by type and technological capabilities.
Digital and analog
Control modules on soldering stations can operate using digital or analog circuits.
For stations controlled by analog equipment, temperature stabilization occurs as follows - that is, the heater operates until the core is heated to a certain temperature. When it is reached, the power will turn off. As the temperature drops, the heater will turn on again and continue to heat the tip. The soldering iron control system includes a set of electronic components and a temperature sensor. It is they who generate the signals that turn the heating of the relay on and off.
Analog soldering station
The main advantage of the analog system is its low cost, but at the same time, a significant disadvantage is the lack of accuracy of operation and this often leads to overheating of the soldering iron. This causes excessive heating of parts and rapid wear of the soldering iron tip, which leads to its frequent replacement.
Digital soldering station
Digital stations operate under the control of a controller, which contains a program that regulates the operation of the device. The digital control system shows much better results than the analogue one, in particular, in accurately maintaining the specified temperature parameters.
Induction devices
In an induction-type soldering station, the soldering iron is heated due to high-frequency currents; the tip is heated to the so-called Curie point.
Induction soldering devices
Once it is reached, the properties of the ferromagnetic coating change and heating stops.
Contactless stations
Stations of this class are used for repairing and dismantling circuits; in addition, with their help, it is possible to implement microcircuits with a large number of contacts.
Various principles are used in the operation of such stations:
- hot air;
- infrared;
- combined.
Combined soldering stations combine other types of equipment, for example, a hot air gun and a soldering iron.
Lukey 852D+ contactless soldering station
In appearance, such a device is similar to a soldering iron, which is equipped with an electronic temperature control unit.
Contact stations can work with two types of solders - tin-lead and lead-free.
Lead-free solder
Tin-lead solder
The latest stations are distinguished by the fact that their kit includes a soldering iron with a power of 160 W. This is because lead-free solders have a high melting point. Such stations are equipped with a power regulator, and this allows them to be used for working with solders with a low melting point.
Desoldering Stations
Existing soldering devices can be divided into mounting and dismantling. The first group includes those that solder parts on the board, but not every one of them can be used to disassemble any soldered structure.
To perform dismantling work, special stations are used. Such equipment includes a compressor, which is used to remove solder from the work area. That is, solder, heated to a certain temperature, is sucked off the surface of the board and collected in a separate container.
Desoldering station
In addition, in practice, installations are used that can be used for assembling boards and for dismantling them. The set of such devices includes soldering irons with different power.
Combined hot air soldering stations
Thermal air devices are used as a basis for assembling combined installations. These models are widely available on the market. Essentially, this is a complex consisting of a thermal hair dryer and a soldering iron.
There are many modifications of devices of this type; they differ from the basic model in the brand of supercharger. An air turbine is installed in the handle of the hair dryer. This decision made it possible to exclude the air supply hose from the station. Working with the station has become more comfortable. In addition, the station comes with a built-in power supply. This device may include smoke absorbers, a desoldering gun and a device for soldering with lead-free solders.
Soldering station 852D+
Combination stations include a compressor that can supply air to the work area or pump it out from there. With its help, the solder falls into a special container. This can be useful when installing microcircuits into devices.
Infrared soldering stations
Soldering devices of this class were developed to solve difficult technological problems. Among them there are also:
- installation and dismantling of elements of different sizes;
- lowering the heating temperature of elements made of polymer materials;
- eliminating the need to use a large number of attachments for installation work, which are adapted to work with different models of microcircuits.
Stations of this class are increasingly used for the repair and maintenance of computers and other equipment.
Any IR station is a complex of components and equipment consisting of:
- preheating devices;
- upper heating device;
- table for fixing the board being processed;
- a block responsible for temperature control and containing temperature sensors and a microcontroller in its design.
IR stations can be called the optimal solution for working with large boards, for example, motherboards.
The upper heating device has high power and this allows it to remove large boards. The lower heating device prevents deformation of the PCB, which can occur as a result of local heating.
A type of infrared soldering station
The design of the table is designed to securely fasten the board being processed, and the pre-installed temperature control system adjusts it quite well at certain control points.
The task of an employee operating a station of this class comes down to setting temperature conditions. All other work is transferred to the station.
IR devices can be classified according to the type of heater - ceramic and quartz. Ceramic devices use elements that have a high mean time between failures and reliability. Quartz ones are less inertial and provide a uniform heating area.
Soldering iron with ceramic heater
The use of infrared stations ensures uniform heating of the work area.
Stations of this type are highly expensive and are classified as professional equipment.
Analog and digital
It is also possible to classify soldering stations depending on the temperature stabilization mechanism and the operating principle of the control units. Based on these parameters, the following types of modern soldering stations are distinguished:
- analog;
- digital.
For analog models, the heating element is turned on until the soldering iron warms up to a certain temperature, then the power stops. When the temperature drops to a preset level, the heating element turns on again and continues heating.
The advantages of analogue stations include their affordable cost. A disadvantage of such models is considered to be low accuracy of operation, which sometimes leads to overheating of the soldering tip and radio components.
A digital soldering station is characterized by the fact that the heater is controlled and controlled using a PID controller. And this regulator, in turn, is controlled by a program embedded in the microcontroller. In general, the digital temperature stabilization method is much more accurate than the analog method.
Design and principle of operation
Soldering equipment consists of the following elements:
- Control module. This unit is equipped with a temperature control chip and a step-down transformer. It is thanks to this module that the user can independently select the heating temperature.
- Soldering iron. The main element of the tool, which is connected to the control module.
- Stand. Needed to secure a heated soldering iron when it is not in use.
Some models are additionally equipped with thermal tweezers, a hair dryer and a compressor.
Assembly and dismantling
It is also possible to divide all soldering stations into assembly and desoldering stations.
Assembly stations are any stations that perform soldering of parts. However, not all of them can unsolder any element from the overall structure.
For such purposes, special dismantling stations have been created. Their design includes a compressor that works to suck out solder. That is, the heated solder is removed from the working surface into a special container.
There are also assembly and disassembly installations for soldering that perform both functions at once. They are equipped with both mounting and dismantling soldering irons (by the way, they have different capacities).
Temperature regulation
The method of regulating the temperature of a soldering iron tip or the air flow of a soldering gun can be done in two ways. Relatively cheap soldering stations implement analog control.
Its essence lies in the fact that when the set temperature is reached, the power to the soldering iron is turned off, and after cooling to a certain level, the voltage supply is resumed. This method has low temperature maintenance accuracy.
Devices belonging to the higher category of professional soldering stations use a digital control method. This function is performed by so-called proportional integral-differential controllers.
This scheme is characterized by low inertia and high accuracy of temperature stabilization. This happens due to the fact that digital controllers respond not only to temperature, but also to its time derivative, that is, to the rate of its change.
Repair
In addition, in specialized literature and on the Internet there are references to repair soldering stations. They are used to carry out repairs of all kinds of electronic devices or in those industries where it is necessary to independently or simultaneously perform various operations related to soldering.
In other words, a multifunctional repair soldering station is a single installation that combines several tools for different purposes.
Plus, there are 2 in 1 and 3 in 1 soldering stations. 2 in 1 models combine the functions of a hair dryer and a soldering iron. A 3 in 1 soldering station also contains a power supply.
And one more addition. Almost all soldering machines run on electricity. But some are interested in whether there are gas soldering stations. In fact, there is some confusion in terms here.
To perform significant volumes of work on construction sites or in public utilities, powerful devices with stationary gas cylinders are sometimes used to solder thick copper pipes. Of course, they can be called soldering stations, but in fact they are just large and powerful gas burners.
What to look for when selecting and purchasing
The quality of soldering is directly and strictly dependent on the parameters of the soldering equipment and its design features, and all this is extremely important to take into account when purchasing.
Power
First of all, you need to pay attention to the number of functions and modes in which the station operates, as well as the rated power consumed and produced.
To repair printed circuit boards and install elements that are sensitive to static electricity, soldering irons with a power of 24 to 40 watts are used.
To work with power buses and conductors, soldering irons from 40 to 80 watts are needed. Soldering tools of 100 Watts and more are usually used for large-sized structures made of non-ferrous metal, which, in principle, have significant thermal conductivity.
Equipment
The equipment also plays an equally important role here; in particular, you should pay attention to the number of tips in the factory kit. The stings may differ from each other in shape and edge area.
These characteristics are noticeably reflected in the final soldering. The larger the area of the end of the tip, the better the heat transfer.
The presence or absence of an indication of the tip temperature on the screen is also an important parameter. All other things being equal, it is better to choose a model in which such an indication is present.
Even the weight and dimensions of the soldering station are of great importance. After all, sometimes during repairs you have to hold the tool in your hands for several hours.
Also, when choosing a soldering device for yourself, it is worth asking whether it is possible to replace spare parts if they break down and how easy it is to find and buy these spare parts.
Flux selection
It should be added that in the future, for work, the owner of the soldering machine will have to constantly purchase consumables, such as flux. And here, too, it is important to make a wise choice.
The functional purpose of the flux is to prevent oxidation of the surfaces being soldered.
There are a lot of brands of flux in stores, but they are almost always based on the same ingredients. This can be pine or spruce rosin, an alcohol solution of rosin, or a special soldering acid (it is considered the most powerful and active).
Soldering process: solder, flux, technological modes
Not everyone immediately understands why a soldering station is needed. For most, it's just a convenient stand. We argue that the technological regime often determines the success or failure of an event. Soldering is the process of joining two metals using solders without melting. Flux is actively involved in the process, the tasks of which include removing the oxide film, improving wettability properties, and others. There are a number of conditions for solder:
- The strength of the future connection depends on the solder.
- The alloy used in this capacity must well wet the metal being joined.
- Diffusion inevitably occurs at contact points; the process should not reduce strength.
In detail, it is convenient to display the characteristics of solder in the form of temperature diagrams, similar to those that illustrate the conditions of steel. It turns out that a mixture of two metals, regardless of the percentage composition of the composition, has the same solidification point. But final melting occurs at different temperatures. For example, when mixing silver and copper, an alloy is formed with a component ratio of 72:28, and the melting point (liquidus) is as close as possible to crystallization (solidus). This ensures the homogeneity of the solder during operation. Otherwise, its mobile fractions are separated at relatively low temperatures.
Soldering process
All this leads to inhomogeneity, which complicates the soldering process. Solder for which the liquidus and solidus differ too much is recommended to be preheated a little higher than the required level. Many difficulties await a person who does not handle the technology correctly. List of phenomena affecting the soldering process and reducing quality:
- Hydrogen embrittlement is inherent in steels, copper and silver. The essence of the phenomenon is that metal oxides are reduced by hydrogen atoms, which easily penetrate the crystal lattice. The resulting water inside creates enormous pressure, destroying the metals in the weld area. Copper is more difficult than anything else, but steel can be pre-conditioned for a while at temperatures up to 100 degrees Celsius to get rid of hydrogen.
- In steels (and other alloys) containing chromium, metal carbide is actively formed during soldering. As a result, the corrosion resistance of the seam is sharply reduced. Carbide tends to be deposited in certain parts of the crystal lattice. It is possible to straighten the process by heating to 1000 - 1130 degrees, which will force the connection to dissolve again, but for most soldered seams this approach is unacceptable. Instead, heating is applied only to 870 degrees, followed by cooling in an oven to 540 degrees.
- During thermal stress during soldering, cracking of the metal is often noticed. To avoid this, annealing is often used instead of hardening. They try to make prefabricated connections without mechanical stress at the seam points. Heating is done gradually. The other side of the coin is that massive parts are brought to condition as quickly as possible. In this case, the heating during soldering does not have time to capture the entire volume, which significantly reduces the voltage. The key becomes the right technology. The correct choice of solder plays a role.
Alloy for the job
- Nickel cracks when heated in the presence of sulfur. This is caused by the formation of low-melting sulfides deposited along the grain boundaries of the crystal lattice. Such metal cannot be restored. The problem is solved by adding chromium to the alloy and thoroughly cleaning the environment from any impurities of substances containing sulfur (oil, paint, grease, etc.). For a similar reason, compounds with a phosphorus component are not used for soldering iron and nickel.