Why are circuit breakers needed?
There are many reasons why the current in the network may exceed normal levels. This mainly occurs due to excessive load, when the total power of the connected devices exceeds the value that the cable cross-section can withstand. In this case, the machine does not turn off immediately, but only after the temperature of the wire reaches the set level.
If a short circuit occurs in the network, this leads to a multiple increase in current power in an instant, so the circuit breaker immediately reacts to the situation and blocks the supply of electricity.
What types of machines are there?
There are three categories that a network circuit breaker can fall into. Each of them is designed for a specific load, and the differences between the types lie in the features of the design used.
- Modular devices can most often be found in household networks connected to a power supply network with low currents. In the vast majority of cases, they differ in the presence of one or two poles.
- Cast ones are used in industrial networks, where the current power reaches 1000 A. They got their name because their main feature is the use of a cast housing.
- Air circuit breakers can have up to four poles, being able to withstand currents of up to 6300 A. In this regard, they are installed only in electrical circuits to which high-power installations are connected.
There are also differential circuit breakers, these are ordinary switches that have an RCD in their design.
Marking of circuit breakers
Let's see where to look on the body of the circuit breaker, the above-mentioned values of cut-off currents and response times.
Breaking capacity is a characteristic of the reliability of a circuit breaker. For example, in the photo you see a marking of a breaking capacity of 10,000 Amperes. This means that after the machine is triggered with a short circuit current of less than 10,000 amperes, the machine will remain in good condition and can continue to operate after the fault is eliminated.
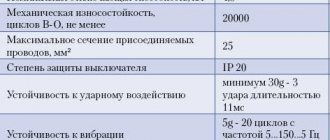
GOST R 50345 defines standard values for the breaking capacity ratings of circuit breakers: 1500 A, 3000 A, 4500 A, 6000 A, 10,000 A.
Current limiting class . A circuit breaker with a current limiter does not allow the short circuit current to reach its maximum value, and the shutdown occurs faster.
The current limiting class is marked with numbers:
Class 2 – reduction of shutdown time by half a half cycle;
Class 3 – reduction by a third of the half-cycle.
At the end of the article, it should be mentioned that the choice of circuit breaker will have to be made from the following AZ ratings for mounting on a DIN rail:
Related articles: Electricity metering in an apartment
Releases and their varieties
The release is the key element of any circuit breaker. It has the function of blocking the power supply if the current exceeds the permissible value. At the same time, there are two types of such devices that can be equipped with a circuit breaker - thermal or electromagnetic.
The latter are distinguished by the fact that with their help, almost instantaneous operation of the protective system is achieved, and the section is immediately de-energized as soon as the occurrence of a short circuit is detected. The design includes a coil with a core, which, under the influence of a strong current, is drawn inward, which is why the tripping element is constantly activated.
As an additional device, zero releases are often installed, which turn off the circuit breaker if the voltage is below the permissible limit.
There are remote-type devices that not only block, but also return the energy supply without the need to go to the electrical panel yourself. However, these options significantly increase the overall price of the equipment.
Pros and cons of air machines
Among the advantages are the following:
- Such devices have been used for a long time, so there is plenty of experience in their operation and repair.
- More modern devices (for example, SF6 gas) cannot be repaired.
But there are also disadvantages, for example:
- It is necessary to have additional pneumatic equipment or a compressor.
- When switched off (especially during an emergency) it makes a lot of noise.
- Installation requires a large space - the device has quite large dimensions.
- Do not install in dusty or damp areas. Therefore, additional measures have to be taken to reduce dust and humidity.
The difference between machines by the number of poles
The complete set of circuit breakers includes up to four poles. To purchase a suitable device, it is enough to understand the types of electrical machines, the purpose and characteristics of each of them:
- One pole. Designed for safety in the electrical network that supplies power to regular outlets and lighting in the home. Installed on the phase wire, excluding the capture of the neutral wire.
- Two poles. They are connected to a circuit that supplies power to household appliances that require high energy consumption. This category includes electric stoves, washing machines and others.
- Three poles. They are installed in semi-industrial networks that provide power to powerful devices such as well pumps or installations for a car workshop.
- Four poles. They ensure network safety from overloads and short circuits, allowing you to connect four cables to it at once.
Devices are selected only depending on their area of application.
Circuit breaker parameters
The characteristics of circuit breakers are another indicator by which they differ from each other. First of all, craftsmen pay attention to how sensitive the protective equipment is to current surges. It is enough to look at the corresponding marking to understand how the device will react to an increase in current. Some immediately cut off access to power, while others operate with a delay.
Depending on the sensitivity, the marking also changes:
- A. The most sensitive and effective devices that instantly turn off the power supply as soon as an increased load is detected. They are not used in household networks. The main area of application is circuits that provide power to high-precision equipment.
- B. When the current exceeds the rated value of the power, the machine turns off the power with a slight delay. In the vast majority of cases, the scope of application of these devices is lines into which expensive household appliances are connected.
- C. The most popular version of machines for domestic use. When such equipment detects an excess of current, they do not immediately turn off the power supply, but with some delay. Thanks to this, if the difference is insignificant, the load can normalize itself, without requiring a forced shutdown of the entire room.
- D. They have the lowest sensitivity, which is why their main area of application is electrical panels located on the approach to the building. In other words, these shields provide a kind of safety net for apartment devices: if for some reason the latter do not operate after a critical situation is detected, the general network is turned off by these devices.
There are also special machines for networks with loads above 1000 volts. Such circuit breakers are complex equipment that is manufactured to order for the required voltage class. In most cases, they are mounted at transformer substations. They must be reliable, safe, easy to use, quickly respond to emergencies and be relatively silent during operation.
Comments:
Evgen
And I thought that the three-pole one is connected as phase-zero-ground, but it turns out to be like this... Live and learn! Can it be used in a panel for a single-phase network, if three circuits need to be disconnected at once?
Vasiliy
Evgen, why is it needed then? Power all three phases through a single-pole switch and they will turn off at the same time without any problems! And you'll save space on the rack.
Denis
Why can't you use a three-pole switch in a single-phase network? Disconnect phase, neutral and ground at the same time? If you place it, for example, at the input to the panel. It seems to me that this is more correct.
Alex
Denis, why do you need to disconnect the ground at the input? A three-pole switch is only
in a three-phase network, but using it in a single-phase network is possible, but impractical. Just as impractical as disconnecting the ground in the example you gave
Vladimir
Sometimes it’s useful to turn off the zero - when there is a phase imbalance, in villages all the time. But you need to tear up the ground ONLY if there is a split trans, and AFTER it.
Virtual Private Servers
One of the most prominent, in the literal sense of the word, characteristics of a circuit breaker is the characteristic that determines the number of poles of the circuit breaker.
Max
and if you need to disconnect two phases and three-pole zero will work
Leave a comment Cancel reply
Related Posts
What is the difference between RCDs and differential circuit breakers and what to choose for the panel equipment
How to connect pass-through switches in your home, tips.
How to quickly and easily connect a Viko switch
Installing a socket or switch in a plasterboard wall, brief instructions
How to choose a circuit breaker
It is believed that the most reliable version of a circuit breaker is a device that can withstand the maximum load and provide the room with the most effective protection. If you follow this logic, you can use air machines in any network, and thus save yourself from most problems, but in practice the situation is somewhat different. Depending on the parameters of a particular circuit, the type of switch that is best installed in it will also depend. If you choose the wrong circuit breaker, it can ultimately turn out extremely negatively.
How do air circuit breakers work?
Above we looked at devices that are used in everyday life and in production. But it is worth considering the operating principle of automatic air switches - this is a completely different category of devices. They are classified according to the type of air movement:
- Transverse.
- Longitudinal.
Air breakers can have a large number of contact breaks, it all depends on what voltage they are designed for. To facilitate arc extinguishing, a resistor is connected to the contacts as a shunt.
The arc chamber is a set of partitions that break the arc into small components. That is why the arc cannot flare up and it goes out quickly enough. High voltage circuit breakers operating with compressed air differ in that they either have a separator or not. If the design has a separator, then the power contacts are connected to the pistons. The result is a single mechanism. The separator is connected in series with the arc extinguisher contacts.
The separator and arc extinguisher contacts are the first pole of the machine. When a shutdown signal is given, a mechanical pneumatic valve is activated. It opens and the air begins to act on the arc extinguisher contacts. The contacts open, and the arc is extinguished using compressed air. After this, the separator is also turned off. It is worth noting that it is necessary to clearly regulate the air supply so that it is sufficient to extinguish the arc.
Types of circuit breakers - what types of circuit breakers there are
Circuit breakers are devices whose task is to protect an electrical line from exposure to powerful current that can cause overheating of the cable with further melting of the insulating layer and fire. An increase in current strength can be caused by too much load, which occurs when the total power of the devices exceeds the value that the cable can withstand in its cross-section - in this case, the machine does not turn off immediately, but after the wire heats up to a certain level. During a short circuit, the current increases many times over within a fraction of a second, and the device immediately reacts to it, instantly stopping the supply of electricity to the circuit. In this material we will tell you what types of circuit breakers are and their characteristics.
Device selection
To select a high-quality protective device, you need to focus on the conductor cross-section. To do this, you will need to calculate the power and current of the equipment and power line. Based on the displayed data, you can select a machine. As a rule, you can take all the information from special diagrams.
Criteria for choosing electrical equipment
A two-pole circuit breaker is a device designed to protect an electrical circuit. It has its own functional purpose, advantages and disadvantages. It also has its own technical characteristics.
You might be interested in Homemade power supply for a screwdriver
Automatic safety switches: classification and differences
In addition to residual current devices, which are not used individually, there are 3 types of network circuit breakers. They work with loads of different sizes and differ in their design. These include:
- Modular AV. These devices are installed in household networks in which negligible currents flow. Typically have 1 or 2 poles and a width that is a multiple of 1.75 cm.
- Molded switches. They are designed to operate in industrial networks with currents up to 1 kA. They are made in a cast case, which is why they got their name.
- Air electric machines. These devices can have 3 or 4 poles and can handle currents up to 6.3 kA. Used in electrical circuits with high power installations.
There is another type of circuit breaker for protecting the electrical network - differential. We do not consider them separately, since such devices are ordinary circuit breakers that include an RCD.
Types of releases
Releases are the main operating components of the automatic circuit breaker. Their task is to break the circuit when the permissible current value is exceeded, thereby stopping the supply of electricity to it. There are two main types of these devices, differing from each other in the principle of tripping:
Electromagnetic type releases ensure almost instantaneous operation of the circuit breaker and de-energization of a section of the circuit when a short circuit overcurrent occurs in it.
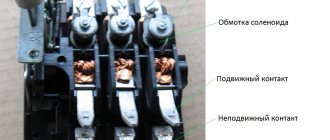
They are a coil (solenoid) with a core that is drawn inward under the influence of a large current and causes the tripping element to operate.
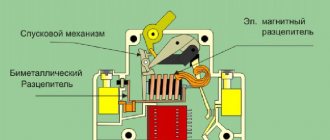
The main part of the thermal release is a bimetallic plate. When a current exceeding the rated value of the protective device passes through the circuit breaker, the plate begins to heat up and, bending to the side, touches the disconnecting element, which trips and de-energizes the circuit. The time it takes for the thermal release to operate depends on the magnitude of the overload current passing through the plate.
Some modern devices are equipped as an addition with minimum (zero) releases. They perform the function of turning off the AV when the voltage drops below the limit value corresponding to the technical data of the device. There are also remote releases, with the help of which you can not only turn off, but also turn on the AV, without even going to the distribution board.
The presence of these options significantly increases the cost of the device.
Types of releases
The following types of releases are most often found in household circuit breakers: thermal, electronic and electromagnetic. They quickly recognize a critical situation (the appearance of overcurrents, overloads and voltage surges) and open the circuit breaker contacts, preventing damage to electrical equipment and protecting the wiring. In addition to these types, there are also zero-voltage, minimum-voltage, independent, semiconductor, and mechanical releases.
Overcurrent is an increase in current strength in the electrical network that exceeds the rated current of the machine. These are overload and short circuit currents.
Overload current - overcurrent in a functional network.
Short circuit current is an overcurrent resulting from the short circuit of two network components with extremely low resistance between these elements.
Thermal release
The thermal release opens the contacts of the circuit breaker when the rated current is slightly exceeded and is characterized by an increased response time. In case of short-term excesses of the current load, it does not operate; this is convenient in networks where short-term excesses of the rated current of the machine are frequent.
The thermal release is a bimetallic strip, one end of which is located next to the release trigger. If the current increases, the plate begins to bend and approach the trigger mechanism, touches the bar, and it, in turn, opens the contacts of the circuit breaker. The operating principle is based on the physical properties of metal, which expands when heated, which is why such a release is called thermal.
The advantages of a thermal release include the absence of surfaces rubbing against each other, resistance to vibration, low cost due to its simple design
But you also need to pay attention to the disadvantages - the operation of the thermal release is highly dependent on the ambient temperature, they should be placed in places with a stable temperature regime away from heat sources, otherwise numerous false alarms are possible
Electronic release
The electronic release includes measuring devices (current sensors), a control unit and an actuating electromagnet. Electronic releases are designed to issue a command to automatically turn off the machine with a given program when an overcurrent or short circuit occurs in the electrical circuit. When the current through the circuit breaker is exceeded, the electronic release unit begins counting the response time in accordance with the time-current characteristic. If during the actuation time the current decreases to a value below the threshold, then automatic operation will not occur.
The advantages of electronic releases include: a wide range of settings, strict adherence of the device to a given program, and the presence of indicators. The main disadvantage is the rather high cost, as well as the sensitivity of the release to the effects of electromagnetic radiation.
Electromagnetic release
The electromagnetic release (cut-off) operates instantly, preventing the slightest possibility of damage to the components of the electrical circuit. This is a solenoid with a movable core that acts on the tripping mechanism. As current flows through the solenoid winding, if the current load is exceeded, the core is retracted under the influence of the electromagnetic field.
The electromagnetic release is triggered when the short circuit current is exceeded. It has sufficient strength, is resistant to vibration, but creates a magnetic field.
Number of poles
As already mentioned, the circuit breaker has poles - from one to four.
Selecting a device for a circuit based on their number is not at all difficult; you just need to know where different types of AVs are used:
- Single-pole circuits are installed to protect lines that include sockets and lighting fixtures. They are mounted on the phase wire without touching the neutral wire.
- The two-terminal network must be included in the circuit to which household appliances with sufficiently high power are connected (boilers, washing machines, electric stoves).
- Three-terminal networks are installed in semi-industrial networks, to which devices such as well pumps or auto repair shop equipment can be connected.
- Four-pole AVs allow you to protect electrical wiring with four cables from short circuits and overloads.
The use of machines of different polarities is shown in the following video:
Features of the selection of machines
Some people think that the most reliable circuit breaker is the one that can handle the most current, and therefore can provide the most protection to the circuit. Based on this logic, you can connect an air-type machine to any network, and all problems will be solved. However, this is not at all true.
To protect circuits with different parameters, it is necessary to install devices with the appropriate capabilities.
Errors in the selection of AB are fraught with unpleasant consequences. If you connect a high-power protective device to a regular household circuit, it will not de-energize the circuit, even when the current significantly exceeds what the cable can withstand. The insulating layer will heat up and then begin to melt, but no shutdown will occur. The fact is that the current strength destructive to the cable will not exceed the AB rating, and the device will “consider” that there was no emergency. Only when the melted insulation causes a short circuit will the machine turn off, but by then a fire may already have started.
We present a table that shows the ratings of machines for various electrical networks.
If the device is designed for less power than what the line can withstand and which the connected devices have, the circuit will not be able to operate normally. When you turn on the equipment, the AV will constantly knock out, and ultimately, under the influence of high currents, it will fail due to “stuck” contacts.
Visually about the types of circuit breakers in the video:
Breaking capacity of circuit breakers
The circuit breaker must instantly disconnect the electrical network in the event of a short circuit (short circuit). This indicator refers to a characteristic such as breaking capacity. Short circuit currents can instantly reach thousands of amperes. The disconnecting device must not only withstand such currents, but also quickly disconnect the line. Such a characteristic does not belong to the category of complex.
The breaking capacity indicator indicates how much short-circuit current it can turn off and still maintain its functionality. Short circuit currents depend on various factors, but in any case, short circuit currents are determined experimentally. As for the electrical wiring of a house or apartment, short circuit currents are not particularly powerful, since the electrical network is located at a considerable distance from the transformer substation.
Although there are houses that are located next to transformer substations. In such houses, short circuit currents are much higher. In such cases, you should choose circuit breakers with a short-circuit current of about 10,000 A; in other cases, it is sufficient to install circuit breakers with a short-circuit current of no more than 6,500 A. In rural areas, circuit breakers with a short-circuit current of about 4,500 A are sufficient, since here there are usually old power lines and large There are no short circuit currents. The greater the breaking capacity of the machine, the more expensive it is. Therefore, when choosing electrical equipment, such factors should be taken into account. Why pay more?
Often, owners do not pay attention to these indicators and install circuit breakers with low breaking capacity in residential premises. Of course, such a machine is capable of protecting against short-circuit currents, but there is no guarantee that it will remain in working condition after this. There is also a possibility that such a machine simply will not have time to work, since the contacts may melt before it works. Then the consequences can be very dire.
Electric machines. Types and work. Characteristics
From the very beginning of the emergence of electricity, engineers began to think about the safety of electrical networks and devices from current overloads. As a result, many different devices have been designed that are distinguished by reliable and high-quality protection. One of the latest developments is electric automatic machines.
This device is called automatic because it is equipped with a function to turn off the power in automatic mode in the event of short circuits or overloads. Conventional fuses must be replaced with new ones after tripping, and the circuit breakers can be turned on again after eliminating the causes of the accident.
Such a protective device is necessary in any electrical network circuit. A circuit breaker will protect a building or premises from various emergency situations:
- Fires.
- Electric shocks to a person.
- Electrical wiring faults.
Types and design features
It is necessary to know information about the existing types of circuit breakers in order to correctly select the appropriate device during purchase. There is a classification of electric machines according to several parameters.
Breaking capacity
This property determines the short circuit current at which the machine will open the circuit, thereby turning off the network and devices that were connected to the network. Based on this property, machines are divided into:
- 4500 ampere circuit breakers are used to prevent faults in the power lines of older residential buildings.
- At 6000 amperes, they are used to prevent accidents during short circuits in the network of houses in new buildings.
- At 10,000 amperes, used in industry to protect electrical installations. A current of this magnitude can occur in the immediate vicinity of a substation.
The circuit breaker trips when a short circuit occurs, accompanied by the occurrence of a certain amount of current.
The machine protects electrical wiring from damage to insulation by high current.
Number of poles
This property tells us about the largest number of wires that can be connected to the machine to provide protection. In the event of an accident, the voltage at these poles is switched off.
Features of machines with one pole
Such electrical circuit breakers are the simplest in design and serve to protect individual sections of the network. Two wires can be connected to such a circuit breaker: input and output.
The purpose of such devices is to protect electrical wiring from overloads and short circuits of wires. The neutral wire is connected to the neutral bus, bypassing the machine. Grounding is connected separately.
Electrical machines with one pole are not input, since when it is disconnected, the phase is broken, and the neutral wire still remains connected to the power supply. This does not provide 100% protection.
Properties of machines with two poles
In cases where an emergency requires complete disconnection from the electrical network, circuit breakers with two poles are used. They are used as introductory ones. In emergency situations or in the event of a short circuit, all electrical wiring is switched off at the same time. This makes it possible to carry out repair and maintenance work, as well as work on connecting equipment, since complete safety is guaranteed.
Operating principle
Externally, the device has a heat-resistant plastic case with a handle responsible for starting and ending work. It has a latch at the back and screw terminals at the bottom.
The main thing in the circuit breaker is the structural unit, namely the main contact system, arc extinguishing system, drive with release and auxiliary contact. The contact system can be one-, two- or three-stage. The arc extinguishing system includes chambers with arc extinguishing grilles or narrow slots.
Regardless of the design, there is a maximum operating current that does not break the machine, since due to excess voltage the contacts burn or weld.
You might be interested in The simplest asynchronous current generator
A circuit breaker is made with the addition of a manual or motor drive. It can be stationary or mobile. The drive is needed to switch the system on and off automatically. The system also contains a direct-acting relay. This is an electronic trip unit that includes levers, latches, rockers and trip springs.
Design
The device works very simply. The mains voltage goes to the top terminal, which is connected to a fixed contact. Energy flows from it to the moving contact. He already transfers it to the copper conductor and the thermal release. Finally, current is supplied to the bottom terminal. In the event of an accident, for example, an overload or a short circuit, the protected electrical circuit is switched off due to the fact that the electromagnetic release begins to operate.
Note! It is important to note that an electromagnetic release is an element with a solenoid that has a movable steel core that is held in place by a spring. When the current voltage exceeds, an electric field appears in the coil. The core gets inside the coil and overcomes the spring resistance. As a result, the release is triggered. Without an accident, the electric field strength is not enough to cause decoupling.
Operating principle