During the operation of electrical networks, the main attention is paid to the safety of wiring, connected household appliances and equipment. The main dangers are short circuit currents and overloads. The appearance of overcurrents leads to destruction of insulation, ignition of wiring and fire. To avoid such situations, it is necessary to select the correct circuit breakers. There are certain criteria, parameters and technical characteristics in accordance with which the use of switches and fuses is planned. If necessary, at the design stage, calculations of protective equipment used in complex electrical network circuits are performed.
Basic functions of circuit breakers
The main task of all circuit breakers is to reliably protect the wires and insulating layer from overheating and subsequent melting. Based on this, the input device is also selected. When the conductor heats up to a critical temperature, the voltage is automatically turned off.
Similar situations arise when connecting loads whose power significantly exceeds the capabilities of the network. Exactly the same shutdowns occur in the event of short circuit currents.
Disconnecting protective devices are selected primarily based on the number of wires that need to be de-energized. The choice of circuit breaker based on power is of great importance. The shutdown process itself must be timely, preventing the destruction of insulation and the occurrence of a fire. The main criteria for choosing a specific machine, which is determined by the state standard, are its rating, the time-current characteristic associated with the electromagnetic release and the breaking capacity, depending on the cut-off current.
When solving the problem of how to choose a circuit breaker for your home, all its parameters are of great importance for ensuring the workflow. They are selected in accordance with the load connected to a given network and the location of the wiring relative to the supply substation. The correct choice of device largely depends on knowledge of the design features and operating principle of the machine.
Current cut-off (for AV with two-stage VTX)
The current cutoff of the switch is adjusted from the starting current of the electric motor, which consists of a periodic component, almost unchanged throughout the entire starting time, and an aperiodic component, attenuating over several periods. Failure to operate the cut-off when starting the engine is ensured by selecting the current cut-off according to the expression:
where kn.start = kз·ka·kр – reliability factor for detuning the cut-off from the starting current of the electric motor;
1.05 – coefficient taking into account that in normal mode it can be 5% higher than the rated voltage of the electric motor;
kз – safety factor;
ka – coefficient taking into account the presence of an aperiodic component in the starting current of the electric motor;
kр – coefficient that takes into account the possible spread of the cut-off current relative to the setting.
Instantaneous current cut-off (for AV with three-stage VTX)
For switches with a three-stage protective characteristic, the instantaneous cutoff of the switch is adjusted from the peak value of the starting current of the electric motor:
In addition, the current cut-off must reliably protect the electric motor from the minimum short-circuit current in case of damage at the end of the cable line: where (1)
k.RI – minimum single-phase current at the end of the cable, calculated taking into account the current-limiting effect of the arc at the point of damage.
General structure and principle of operation
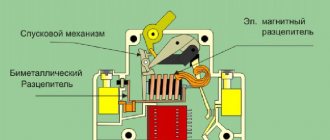
All circuit breakers differ only in minor details, but in general each of them consists of the following mandatory elements:
- Poles in a set number from 1 to 4, subject to switching on and off. In essence, they are power contacts that make and break the wire circuit.
- Arc extinguishing system. Performed in different versions. In one case, these are special chambers in which the arc is divided into parts due to narrow slots. Or the arc is extinguished through the grille. The machine, designed to operate in powerful circuits, can be used with a combined option.
- Drive of the release mechanism.
- Trip release. It is made on a bimetallic, electronic, electromagnetic basis or on a microprocessor basis. If an abnormal current condition occurs, this element performs an instant automatic shutdown. The design of the release includes levers, latches and trip springs that speed up operation.
- Block contacts in the amount of one or several pairs. They are also called auxiliary contacts located in control or signaling circuits.
Online power calculators
If you use an online calculator for calculating machines by power, several factors must be taken into account:
- type;
- equipment power;
- minimum and maximum indicators;
- general voltage level.
According to the instructions, the calculation initially begins with the selection of equipment:
- household units;
- propulsion devices;
- remote installations.
The power used is indicated in kilowatts; it is necessary to enter the maximum permissible values. Fortunately, the product document provides all the necessary information. If several connection points are used, the total power is calculated. So, the following devices can be connected in the apartment:
- fridge;
- TV;
- microwave;
- heater;
- computer.
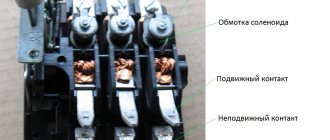
Operation of the electromagnetic release
It is necessary to separately consider the action of the electromagnetic release, on which the performance of the main functions of the machine depends. Its characteristics are determined by the state standard.
The main part is the solenoid coil. It is equipped with a moving part that activates the mechanism for breaking the wire circuit. Flowing through the power contacts, the current also captures the solenoid. If the procedure for calculating the current is observed within the nominal limits, then in normal operating mode the machine does not turn off. The magnetic forces are not sufficient to move the latch by the trip armature, so the protective device remains switched on.
When a short circuit occurs, the threshold current value is exceeded. As a result, a rapid increase in the magnetic flux begins, causing movement of the moving part of the coil. In this case, the machine turns off instantly.
There are machines that operate with direct current. They protect electric motors and are equipped with several releases at once. Due to this, shutdown is significantly faster, even if one of the tripping systems has failed.
Calculation of machine indicator by cable cross-section
Having chosen an online calculator, the visitor is asked to determine the values:
- type of gasket;
- grounding;
- cable section;
- aluminum, copper.
Since the materials are different, the cross-sectional indicator is interpreted differently. Each substance has its own overheating threshold. Resistance to insulation failure is taken into account. During overloads and short circuits, the temperature increases. The online calculator recalculates taking into account the permissible current of the electrical network.
Classification of circuit breakers
Automatic switches, depending on the modification, can be used in single- and three-phase electrical networks. In the first option, devices with 1 or 2 poles are used. Single-pole models are intended only for connection via a phase cable. They are installed in apartments and private houses with normal operating conditions on a common bus. This type of protection is used for groups of sockets and lighting lines located in different rooms. Regardless of the number of poles, which machine is installed, it will work.
Phase and neutral wires are connected to automatic machines with two poles. This breaks both circuits, thereby providing a higher level of protection. In this case, the circuit is turned off not partially, but completely, which is especially important when voltage enters the neutral wire. It is recommended to install two-pole devices on a common comb of dedicated lines with connected powerful equipment or in the presence of difficult operating conditions.
Two- and three-pole circuit breakers are connected to three-phase networks. Three phases of the wire are supplied to devices with three poles at once, so in emergency situations the circuit provides for their simultaneous disconnection. As a rule, they are used on inputs or on lines with connected three-phase consumers. Instead of them, automatic machines with four poles can be installed, which also disconnect zero along with the phases. On individual lines of a three-phase network, two-pole switches are used with simultaneous disconnection of the phase and neutral wires.
How to choose the right machine
Until recently, porcelain fuses with fusible elements were widely used. They were well suited for the same type of load in Soviet apartments. Nowadays, the number of household appliances has become much larger, as a result of which the likelihood of a fire with old fuses has increased. To prevent this, you need to carefully select a machine with the right characteristics. Excessive power reserves should be avoided. The final choice is made after completing a few simple steps.
Determination of the number of poles
When determining this switch parameter, you should follow a simple rule. If you plan to secure sections of the circuit with devices that have low power consumption (for example, lighting devices), then it is better to leave your choice on a single-pole circuit breaker (usually class B or C). If you plan to connect a complex household device with significant power consumption (washing machine, refrigerator), then you should install a two-pole circuit breaker (class C, D). If you are equipping a small production workshop or garage with multiphase motor systems, then you should choose a three-pole option (class D).
Power consumption calculation
As a rule, by the time it is planned to connect the machine, the wiring to the room has already been installed. Based on the cross-section of the conductors and the type of metal (copper or aluminum), the maximum power can be determined. For example, for a copper core of 2.5 mm2 this value is 4–4.5 kW. But the wiring is often supplied with a large margin. Yes, and the calculation should be done before all installation work begins.
In this case, you will need a value about how much total power will be used by all devices. It is always possible to turn them on simultaneously. So, in an ordinary kitchen, the following appliances are often used:
- refrigerator – 500 W;
- electric kettle – 1700 W;
- microwave oven – 1800 W
The total load is 4 kW and a 25 A circuit breaker is enough for it. But there are always consumers who turn on sporadically and can create factors that contribute to the circuit breaker tripping. Such devices can be a combine or a mixer. Therefore, you should take a machine with a reserve of 500–1200 W.
Rated current calculation
Since power in single-phase networks is equal to the product of voltage and current, the current can easily be determined as the quotient of power and voltage. For the above example, this value is easy to calculate, knowing that the network voltage is 220 V. The current consumed is 18.8 A. Taking into account the reserve of 500–1200 V, it will be 20.4–23.6 A.
In order to ensure that the work does not stop even with such short-term excess loads, the rated current for the machine can be taken equal to 25 A. The nominal value corresponds to approximately the same value, based on a copper cable with a cross-section of 2.5 mm2, which is sufficient with a margin for such a load . A circuit breaker with a rated current of 25 A will work before it starts to heat up.
Determination of time current characteristic
This parameter is determined using a special table that lists the starting currents and their flow time. For example, for a household refrigerator, the starting current multiplicity is 5. With a power of 500 W, the operating current is 2.2 A. The starting current value will be 2.2 * 7 = 15.4 A. Periodicity data is also taken from a special table.
Table No. 1. Starting currents and pulse durations for household appliances
| device | inrush current multiple | starting current pulse duration, s |
| incandescent lamps | 5–13 | 0,05–0,3 |
| fluorescent lamps | 1,05–1,1 | 0,1–0,5 |
| computers, televisions | 5–10 | 0,25–0,5 |
| household appliances, office equipment | until 3 | 0,25–0,5 |
| refrigerators, air conditioners, pumps | 3–7 | 1–3 |
For the selected device, this characteristic does not exceed 3 s. The choice becomes obvious: for such a consumer it is necessary to take a type B circuit breaker. It is permissible to select a circuit breaker based on load power. You can skip the last step and opt for a class B switch. For domestic needs, the characteristics of class B and C electrical switches are most often sufficient.
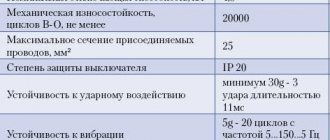
Main selection criteria, table
In order not to use complex formulas in calculations, there is a universal table:
The table presents the main parameters and technical characteristics of circuit breakers that must be taken into account when making calculations and selection of protection. Some of them should be considered in more detail.
Overload sensitivity
One of the criteria used to select the correct circuit breaker is the magnetic trip unit. The response speed and the degree of sensitivity to overloads depend on it. An optimally selected element provides the necessary delay that occurs when triggered. It is needed to eliminate false alarms that often occur when starting electric motors.
The machine is triggered when the current value exceeds the set mark. The choice of denomination plays a big role. At the same time, many short-term overloads regularly occur in the network, mainly due to inrush currents. At such moments, the device should not operate, for which a certain delay is set. A special formula is used for calculation.
Often, an increase in current occurs not due to overload, but due to short circuit current. During the delay, the contacts can easily melt. At this moment, the operation of the electromagnetic release begins. When the current reaches a selected value that exceeds normal overloads, it is automatically triggered. This parameter is also known as cut-off current, since in this case the line is completely cut off from the power supply. The trip current can have different values and is indicated by alphabetic symbols. They are located in front of the digital rating designation and are used to select the circuit breaker.
Devices with certain characteristics in accordance with GOST, have a wide selection of settings and are designed for various operating conditions:
- A - used with wiring connected to a highly sensitive load on a common bus. In case of overload, the machine is instantly triggered.
- B - conventional devices used for apartments in networks with groups of sockets and switches operating at standard loads. When the current increases by 3-5 times the calculated value, the machine operates with a slight delay. Several machines are connected into a common comb.
- C – protects electrical wiring in networks with high inrush currents. The device ignores minor voltage surges, and operates when the current increases by 5-10 times the nominal value. Machines of this type are most widespread.
- D – used for loads arising from high inrush currents. It is installed as an input machine that controls the entire electrical network. Shutdown occurs when the current jumps 10-50 times higher than the nominal value.
Selecting a machine by rating and load
An equally important criterion by which a circuit breaker is selected is the rating of the protective device. The fact is that under the influence of the flowing current the conductor heats up. With an increase in current load at a constant cross-section, heat generation will also increase. Thus, the main task of the machine is to turn off the power before the current exceeds permissible limits. In this regard, the rating of the switch must be lower than the permissible current of the electrical wiring.
Overload protection
The overload protection trip current is determined from the conditions for the protection to return after the end of the start or self-start of the electric motor:
where kn is the reliability coefficient, taking into account a certain current reserve, setting inaccuracies and the spread of protection operation (1.0 - for modern Schneider Electric AVs, 1.15 - for AE20, A3700; 1.25 - for A3100, AP-50; 1.2, 1.35 – for VA51);
kв – protection return coefficient.
Protection is considered effective if:
For circuit breakers with thermal and electromagnetic (combined) releases, condition (6.5) is ensured automatically when selecting the rated current of the release according to condition (6.2). The best protection against overload is provided if it is possible to select a switch that has In.rast = Idn. In this case, keeping in mind that for thermobimetallic thermal relays kv = 1, the overload protection operating current will be:
Standards for installing a circuit breaker
When a circuit breaker is installed in a residential or non-residential premises, regulatory services check compliance with the standards:
- GOST 503 45.
- GOST 689 28.
- GOST 500 30.
- Fire safety standard dated July 22, 2008.
The following standards apply in Europe:
- EC 6947;
- EC 6947.2.
Main points in the standards:
- throughput;
- current-carrying circuit parameters;
- duration of overload;
- number of outages;
- current limit;
- Rated voltage;
- thermal resistance;
- exposure to current;
- shutdown time.
The standards specify the parameters of acceptable switches. Their physical properties and dimensions are taken into account. For the purpose of safe operation, the permissible distance from the equipment is specified. To do this, the standards take into account the type of devices and conditions.
Selective equipment
If a switch uses a time delay, it is called selective. The devices can have one or several stages. They are set regardless of the voltage level. The switches are able to function without additional power.
Some call the devices modular or compact. According to the schemes, 2 flow paths are provided. There are main and additional contacts. The coil in the center is used with a bimetallic strip.