Description of single-pole switches ABB S201 C
Modular single-pole switches ABB S201 C are designed to protect electrical circuits from overloads and short circuits in cable lines, electric motors, lighting systems, and socket lines. They have two different trip mechanisms: a delayed thermal trip mechanism for overload protection and an electromechanical trip mechanism for short circuit protection.
Circuit breaker device
The body material of the S201 C is made from the most advanced materials, consisting of the latest generation of thermoplastics, which do not contain halogen pollutants and are recyclable.
All circuit breakers are equipped with contact position indication (CPI). You can easily determine whether the circuit breaker is in the on position, which makes maintenance work easier and safer.
Features of ABB series
ABB series circuit breakers are reliable and durable. Their versatility lies in the fact that they are installed on a DIN rail and in one place you can assemble and install a group of machines for monitoring circuits for various purposes - lighting, heating devices, sockets for household appliances, etc. You can assemble an electrical panel for servicing apartments on one floor, an entrance, or a house. This simplifies the wiring of electrical wires and makes it convenient to maintain electrical equipment in the living space.
- ABB circuit breakers are manufactured in a fire-safe version; they instantly disconnect the load during overloads and short circuits.
- They have the ability to control additional accessories - signal and trip contacts.
- Allows the connection of single and multi-core conductors.
- ABB circuit breakers have a reserve of emergency operations from 4,500 to 10,000 times. Activation of the operating state after an accident is carried out by setting the lever to its original state.
Selecting a circuit breaker
The choice of switches is mainly carried out according to the load power and the cross-section of the connected wire, taking into account 2 parameters: overload current and short-circuit shutdown current.
Current overload occurs when devices and devices are connected to the network, the total power of which will lead to excessive heating of conductors and contact connections. Therefore, the machine that will be installed in a specific circuit must have a shutdown current greater than the so-called reserve or equal to the calculated one. It is determined by summing the power of the electrical devices intended for use, which is often indicated in the passport. Next, the resulting figure is divided by 220 and our overload current is obtained. One more important circumstance should also be taken into account: this current should not be greater than the current that can flow through the conductor.
The shutdown current during a short circuit is the value at which the circuit breaker turns off; it is also called cutoff. It is also calculated and then selected according to the type of protection. The type of protection contains the values of the shutdown current in relation to the probable short-circuit current, depending on the type of load in the electrical network. In everyday life and for small objects, devices are used with the symbol characteristics B, C, and at the input - D. Most often, in addition to the circuit breakers for each group line, the electrical circuit also includes an input circuit breaker, an RCD or a differential circuit. machine.
Automatic switches ABB s200
ABB S200 series circuit breakers are grouped into four types - S201, S201, S203, S204. Each of them comes in the five denominations mentioned above. The third digit in the name of the type means the number of poles of the machine.
S200 series circuit breakers have the following advantages over other types of circuit breakers:
- multi-pole, allowing you to control one-; two-; three-phase circuits with and without a neutral wire;
- the design of the terminals of the machines allows you to connect multi-core wires and wires of different sections to them;
- the horizontal or vertical position of the machine does not affect its performance;
- the modular principle of devices, which determines the versatility of application.
Marking of S201 C machines
The housing of the S201 C series circuit breakers contains all the necessary markings, such as:
- - manufacturer;
- — model;
- — rated current and type of response characteristic;
- — operating voltage of the network;
- — breaking capacity;
- — current limitation class;
- — schematic diagram of the switch operation.
ABB circuit breakers comply with IEC/EN 60898-1 and IEC/EN 60947-2 standards and carry all relevant certification marks for each market and segment for which they are designed. Certification marks are also printed on the circuit breaker body. For the inspection and acceptance procedure, certification marks are clearly visible on the body. All markings are made using laser printing technology, which is resistant to abrasion and solvents, which ensures a long service life and ease of product identification.
Problems with counterfeit ABB machines
Before we talk about the ABB machine and how to distinguish an original from a fake, we need to focus on the problems associated with counterfeits.
Original products undergo thorough testing and quality control before appearing on store shelves. This is a multi-step process. If the machine fails on one of them, it is rejected and sent for processing.
The fake machine, which imitates ABB, does not pass any such tests. The maximum is to check the functionality of the on and off button. After all, you need to create an imitation of performance.
A fake machine is dangerous because it is tested and also does not pass the tests. That is, it is unknown what can be expected from such a device.
Yes, some fakes that imitate the original have a good body and relatively good filling. But you still find yourself in Russian roulette conditions. Whether you're lucky or unlucky.
Will the device work for several years, or will it burn out during the first serious test in real conditions? And at the same time, it will lead to serious problems with the electrical wiring of the entire house and create difficulties for household appliances.
Are you happy with this option? Hardly. Therefore, you need to find out how to distinguish a fake ABB.
Application of single-pole circuit breakers S201 C
Modular circuit breakers S201 C, as a rule, have all possible designs according to the operating characteristics of circuit breakers, which indicates their wide application segment. They are usually used for surge protection by installing on a DIN rail in distribution boards, boxes located in residential buildings, offices, warehouses, and other industrial and commercial premises. S201 C is used to protect circuits with active and inductive loads and low pulse current (providing electricity to apartments, offices, industrial facilities).
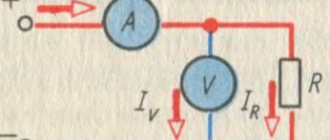
ABB automatic machines. Operating principle
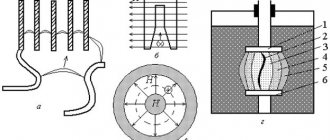
In normal operation, ABB circuit breakers pass through themselves a current not exceeding the rated current for an infinite time. But if an overload occurs in the lines on which ABB circuit breakers are installed (current - which does not significantly exceed the rated current), in which case the ABB circuit breakers are turned off by a thermal release . The bimetallic plate (5) of the thermal release heats up (overload) and activates the tripping mechanism of the ABB circuit breaker. Triggering of the thermal release when I rated is exceeded. from 1.13 to 1.45 will occur in a time exceeding 1 hour, over 1.45 from I nom. in less than 1 hour. That is, the thermal release will turn off the ABB circuit breaker when you connect several heaters and electric kettles to this cable.
If a short circuit occurs on the line and devices connected to it, i.e. a current several times higher than the rated current “appears”, in this case the ABB circuit breaker triggers an electromagnetic release , which turns off the ABB circuit breaker. A current several times higher than the rated current flows through the winding of the solenoid (9), inducing a magnetic flux that moves the coil core, opening the contacts of the ABB machine. Unlike a thermal release, an electromagnetic release operates in a fraction of seconds, almost instantly turning off ABB circuit breakers.
Characteristics of the electromagnetic release
According to the response characteristics of the electromagnetic release, ABB circuit breakers are divided into the following types (classes):
ABB automatic machines type B (3-5)*I nom - for residential and commercial premises, widely used in Europe. I recommend installing ABB circuit breakers with characteristic B on all cable lines in apartments and private houses, with the exception of those with large starting currents (pumps, motors, etc.).
ABB automatic machines type C (5-10)*I nom are the most common type in Russia. In older networks, where the lines are in poor condition and short-circuit currents may be small, ABB type C circuit breakers may not operate at all. It is correct to install “B” machine guns in new shields.
ABB automatic circuit breakers type D from (10-20)*I nom - used mainly in industry, in control circuits of motors, machine tools, low-voltage transformers and other devices where inrush currents are high.
ABB circuit breakers type K from (10-14)*I nom - used to protect electric motors, transformers and control circuits.
ABB automatic circuit breakers type Z (2-3)*I nom – protection of control circuits from short circuits and small continuous overloads.
The designation of the characteristics (type) of the electromagnetic release for ABB circuit breakers is applied to the housing.
Depending on the sensitivity (type of electromagnetic release), ABB circuit breakers are produced with different rated currents. Because machines with characteristic B are more sensitive than C and D, then ABB does not make them less than 6 A:
ABB type B circuit breakers (rated currents from 6 to 63 A)
ABB automatic machines type C and type D (rated currents from 0.5 to 63 A)
Connecting circuit breakers
Switches S201 C are equipped with terminals: 35 mm + 10 mm (for devices up to 2 2 63A), and 50 mm + 10 mm 2 2 (for devices 80, 100 A) for separate connection of busbar wiring and cables - cylindrical bidirectional terminals with protection from improper installation, resistant to impact, which are accessible even after installing a modular machine. In the absence of bus wiring, it is possible to connect two pairs of conductors of different cross-sections. S201 C have special clamping jaws for quick installation of the circuit breaker on a DIN rail located in distribution boards, boxes and cabinets. If the product is replaced, the same lock allows you to quickly dismantle it. For ease of cable installation, the switches are equipped with captive screw technology, and the degree of protection against finger contact in the connection area reduces the risk of electric shock and the possibility of a short circuit.
Connection diagram for circuit breakers S201 C:
How are circuit breakers installed?
Installation of circuit breakers is simple. Disconnect power from the panel or rack on which you will install the module. Secure the circuit breaker to the rail of the rack or panel, and secure the incoming and outgoing wires to the panel or rack to prevent accidental short circuits. Connect the power wires to the fixed contacts of the machine, and the load wires to the moving ones.
Checking the reliability and correctness of connections, the safety of operation of the electrical network with an installed machine is carried out as follows. Turn off all loads. Apply mains voltage and check for sparking and hissing sounds. If there are none, turn on the load and check the sparking again. The absence of sparking and noise indicates the correct and reliable installation of the circuit breaker.
The functionality of the switch is checked by creating a short-term artificial short circuit. Using the socket, short-circuit phase and neutral for a moment. The machine will turn off instantly. Otherwise, look for a fault in the switch itself or replace it.
Technical characteristics of switches S201 C
| General information | Standards | GOST R 50345-2010 (IEC 60898-1) GOST R 50030.2-2010 (IEC 60947-2) | |
| UL 1077 | |||
| Number of poles | 1P | ||
| Triggering characteristics | C | ||
| Rated current In | A | 0.5…63 A | |
| Rated frequency f | Hz | 50 / 60 Hz | |
| Rated insulation voltage Ui acc. IEC/EN 60664-1 | IN | 250 V AC current (phase-ground), 500 V a.c. current (phase-phase) | |
| Overvoltage category | III | ||
| Degree of pollution | 3 | ||
| Data acc. IEC/EN 60898-1 (except data according to IEC/EN 60898-2) | Nom. operating voltage Un | IN | 1P: 230/400 V AC current; 1P+N: 230 V AC current; |
| Max. power frequency voltage recovering after shutdown (Umax) | IN | 1P: 253 V AC current; 1P: 72 V DC current; | |
| Min. operating voltage | IN | 12 V AC current - 12 V DC current | |
| Rated short-circuit breaking capacity Icn | kA | 6 kA | |
| Energy limitation class (B, C up to 40 A) | 3 | ||
| Nom. impulse withstand voltage Uimp. (1.2/50 µs) | kV | 4 kV (test voltage 6.2 kV at sea level, 5 kV at 2000 m altitude) | |
| Insulation test voltage | kV | 2 kV (50 / 60 Hz, 1 min.) | |
| Trip calibration temperature | C | 30 C | |
| Electrical durability | operations | In < 32A: 20,000 operations (AC), In ≥ 32 A: 10,000 operations (AC); 1,000 operations (DC) (1 cycle 2 s - ON, 13 s - OFF, In ≤ 32A), (1 cycle 2 s - ON, 28 s - OFF, In > 32 A) | |
| Data acc. IEC/EN 60947-2 | Rated operating voltage Ue | IN | 1P: 230 V AC current; |
| Max. power frequency voltage recovering after shutdown (Umax) | IN | 1P: 253 V AC current; 1P: 72 V DC current; | |
| Min. operating voltage | IN | 12 V AC current - 12 V DC Current | |
| Rated ultimate short-circuit breaking capacity Icu | kA | 10 kA | |
| Rated operating short-circuit breaking capacity Ics | kA | 7.5 kA | |
| Nom. impulse withstand voltage Uimp. (1.2/50 µs) | kV | 4 kV (test voltage 6.2 kV at sea level, 5 kV at 2000 m altitude) | |
| Insulation test voltage | kV | 2kV (50 / 60 Hz, 1 min.) | |
| Trip calibration temperature | C | 55 C | |
| Electrical durability | operations | In < 32A: 20,000 operations (AC), In ≥ 32 A: 10,000 operations (AC); 1,000 operations (DC) (1 cycle 2 s - ON, 13 s - OFF, In ≤ 32A), (1 cycle 2 s - ON, 28 s - OFF, In > 32 A) | |
| Data acc. UL/CSA | Rated voltage | IN | 480Y / 277 V AC current; |
| 60 V DC current; | |||
| Rated breaking capacity acc. UL 1077 | kA | 6 kA AC current | |
| Short circuit current power acc. UL 489 | — | ||
| Application | Add. protection for common appl. Application codes: TC2, OL0, SC: U1 | ||
| Trip calibration temperature | C | 25 C | |
| Electrical durability | operations | 6000 ops (AC), 6000 ops. (DC), 1 cycle (1 s – ON, 9 s – OFF) | |
| Mechanical characteristics | Frame | Insulation class II, RAL 7035 | |
| Lever arm | Insulation class II, black, sealed | ||
| Contact position indication | Marking on the lever (I ON / 0 OFF), indication of the actual contact position (red ON / green OFF) | ||
| Degree of protection acc. EN 60529 | IP20*, IP40 for housing with cover | ||
| Mechanical wear resistance | operations | 20,000 operations | |
| Impact resistance according to IEC/EN 60068-2-27 | 25 g - 2 beats - 13 ms | ||
| Vibration resistance according to IEC/EN 60068-2-6 | 5 g - 20 cycles at 5...150...5 Hz with a load of 0.8 In | ||
| Resistance to tropical climates acc. to IEC/EN 60068-2-30 | rel. humidity | 28 cycle. at 55 C/90-96% and 25 C/95-100% | |
| Ambient temperature | C | -25 … +55 C | |
| Storage temperature | C | -40 … +70 C |
Time-current characteristics (VTC) of circuit breakers
To bookmarks
Introduction
As is known, automatic circuit breakers can have the following types of releases that provide protection of the electrical circuit from overcurrents: electromagnetic - protecting the network from short circuits, thermal - providing protection from overload currents and combined, which is a combination of electromagnetic and thermal releases (for more details, read the article “circuit breakers”).
Note: Modern circuit breakers designed to protect electrical networks up to 1000 Volts usually have combined releases.
Circuit breaker releases are actuators that ensure disconnection (disengagement) of an electrical circuit when a current higher than the permissible one occurs in it, and the greater this excess, the faster the disconnection should occur.
The dependence of the tripping time of a circuit breaker on the magnitude of the current passing through it is called the time-current characteristic or abbreviated as VTC .
Conditions and values of VTX
The performance characteristics of the machines are determined by the following values:
1) Instantaneous trip current - the minimum current value that causes automatic operation of the circuit breaker without a deliberate time delay. (GOST R 50345-2010, clause 3.5.17)
Note: operation without a deliberate time delay is ensured by the electromagnetic release of the machine.
The instantaneous tripping current is determined by the so-called “trip characteristic” or, as it is also called, the tripping characteristic.
According to GOST R 50345-2010, there are the following types of circuit breaker response characteristics:
Note: there are also other, non-standard types of characteristics, we talked about them in the article “circuit breakers“.
As can be seen from the table above, the instantaneous tripping current is indicated as a range of values, for example, characteristic “B” assumes that the machine will provide instantaneous tripping when a current flowing through it is 3 - 5 times greater than its rated current, i.e. If a circuit breaker with this characteristic has a current rating of 16 Amps, then it will provide instantaneous tripping at a current of 48 to 80 Amps.
The response characteristics of a circuit breaker can usually be determined by the markings on its body:
2) Conditional non-trip current - a set value of the current that the circuit breaker is capable of conducting without tripping for a given (conditional) time*. (GOST R 50345-2010, clause 3.5.15) According to clause 8.6.2.2 of GOST R 50345-2010, the conditional non-trip current is equal to 1.13 of the rated current of the machine. 3) The verbal trip current is a set current value that causes the circuit breaker to trip within a specified (conditional) time*. (GOST R 50345-2010, clause 3.5.16) According to clause 8.6.2.3 of GOST R 50345-2010, the conditional tripping current is equal to 1.45 of the rated current of the machine.
* The conditional time is 1 hour for switches with a rated current up to 63 A inclusive and 2 hours with a rated current over 63 A. (GOST R 50345-2010, clause 8.6.2.1)
The time-current characteristic of the circuit breaker is determined by the conditions and values given in Table 7 of GOST R 50345-2010 :
Note: The table is valid for machines installed in accordance with the test conditions given below and operating at a temperature of 30+5 °C
VTX charts
For convenience, manufacturers in the passports for circuit breakers indicate the time-current characteristics in the form of a graph where the X axis shows the multiple of the electrical circuit current to the rated current of the circuit breaker (I/In), and the Y axis shows the tripping time of the release.
For a detailed consideration, let’s take as an example the VTX graph for a circuit breaker with characteristic “B”
NOTE: All graphs below are provided as an example. Different manufacturers' performance characteristics may differ (see the machine's passport), but in any case they must comply with the requirements of GOST R 50345-2010 and, in particular, the values specified in Table 7 above.
As you can see, the VTX graph is represented by two curves: the first curve (red) is the characteristic of the machine in the so-called “hot” state, i.e. machine is in operation, the second (blue) is the characteristic of the machine in a “cold” state, i.e. machine through which electric current has just begun to flow.
At the same time, the blue curve has an additional dashed line, this line shows the characteristics of the machine (its thermal release) with a rated current of up to 32 Amperes, this difference in the characteristics of machines with ratings up to and above 32 Amperes is due to the fact that in machines with a higher rated current there is a bimetallic plate The thermal release has a larger cross-section and, accordingly, it needs more time to warm up.
In addition, each curve has two sections: the first - showing a smooth change in the response time depending on the current of the electrical circuit is a characteristic of the thermal release, the second - showing a sharp decrease in the response time (at a current of 3 In in the hot state and from 5 In in the cold state) , is a characteristic of the electromagnetic release of the circuit breaker.
As you can see, the VTX graph shows the main values of the characteristics of the machine according to GOST R 50345-2010 at 1.13 In (Conventional non-trip current) the machine will not operate for 1-2 hours, and at a current of 1.45 In (Conventional trip current) the machine will turn off chain in less than 50 seconds (from a hot state).
As mentioned above, the instantaneous tripping current is determined by the operation characteristic of the machine; for circuit breakers with characteristic “B” it ranges from 3In to 5In, while according to the above GOST (Table 7) at 3In the machine should not operate in less than 0.1 second from a cold state, but must turn off in less than 0.1 seconds from a cold state with a current in the circuit of 5In and as we can see from the graph above, this condition is met.
Also, using the time-current characteristic, you can determine the operation time of the machine at any other current values, for example: a machine with characteristic “B” and a rated current of 16 Amperes is installed in the circuit; when operating in this circuit, an overload occurred and the current increased to 32 amperes, we determine The triggering time of the machine is as follows:
- We divide the current flowing in the circuit by the rated current of the machine
32A/16A=2
Having determined that the current in the circuit is twice the nominal value of the machine, i.e. is 2In, we plot this value along the X-axis of the graph and lift the conditional line up from it and see where it intersects with the curves of the graph:
As we can see from the graph, at a current of 32 Amps, a machine with a rated current of 16 Amps will open the circuit in less than 10 seconds from a hot state and in less than 5 minutes from a cold state.
Here are examples of the performance characteristics of circuit breakers with all standard response characteristics (B, C, D):
NOTE: Time-current characteristics in accordance with GOST R 50345-2010 are indicated for automatic machines operating at a temperature of +30+5 °C mounted in accordance with certain conditions:
Test conditions. Correction factors.
According to GOST R 50345-2010 During testing, switches are installed separately, vertically, in the open air in a place protected from excessive external heating or cooling.
circuit breakers are tested at any air temperature, and the results are corrected at a temperature of +30 °C based on correction factors provided by the manufacturer.
In this case, in any case, the deviation of the test current from that specified in Table 7 should not exceed 1.2% per 1 °C change in calibration temperature.
The manufacturer shall prepare data on the change in trip characteristic for calibration temperatures other than the reference value.
Thus, in order to accurately determine the shutdown time of circuit breakers operated under conditions different from the test conditions, it is necessary to use correction factors that must be provided by the manufacturer of these breakers.
Here is an example of such correction factors (usually there are only 2):
- Temperature coefficient (K t )
The temperature coefficient takes into account the difference between the ambient temperature at which the circuit breaker was tested and the actual ambient temperature at which it is operated:
As can be seen from the graph, the lower the ambient temperature, the higher this coefficient. This is explained simply - the lower the ambient temperature, the greater the current must flow through the circuit breaker in order to heat the release to the temperature required for its operation.
- Coefficient taking into account the number of machines installed nearby (Kn)
As mentioned above, when testing circuit breakers, they are installed separately, but in practice they are installed in electrical panels in a row with other circuit breakers, which accordingly worsens their cooling due to deterioration in the circulation of air and heat from the circuit breakers installed nearby:
Accordingly, as can be seen from the graph, the more machines installed nearby, the lower this coefficient.
Knowing the correction factors, you can adjust the rated current of the machine depending on its operating conditions.
For example: there is a circuit breaker with a rated current of 16 Amps installed in a panel with 5 other circuit breakers at an ambient temperature of +10°C.
- Using the graphs above we will find the correction factors:
- K t =1.05
- Kn=0.8
- Knowing the correction factors, we will adjust the rated current of the machine:
In/= In* K t * Kn=16*1.05*0.8=13.44 Ampere
Accordingly, when operating a circuit breaker under the above conditions, to determine its operation time, it is necessary to take a current of not 16 Amperes, but 13.44 Amperes.
Was this article useful to you? Or maybe you still have questions ? Write in the comments!
Didn’t find an article on the website on a topic that interests you regarding electrical engineering? Write to us here. We will definitely answer you.
↑ Up
10
https://elektroshkola.ru/apparaty-zashhity/vremya-tokovye-xarakteristiki-vtx-avtomaticheskix-vyklyuchatelej/
S201 C installation specifications, dimensions, compatibility
| Installation | Terminals | double cylindrical terminals | ||
| Conductor cross-section (top/bottom) | solid/stranded | mm2 | 35 mm2 / 35 mm2 | |
| flexible | mm2 | 25 mm2 / 25 mm2 | ||
| AWG | 18 - 4 AWG \ 14 - 4 AWG | |||
| Tire cross section (top/bottom) | mm2 | 10 mm2 / 10 mm2 | ||
| AWG | 18 - 8 AWG | 14 - 8 AWG | |||
| Terminal tightening torque | Nm | 2.8 Nm | ||
| inch-lb | 18 in-lb | |||
| Screwdriver | Pozidrive screwdriver No. 2 | |||
| Installation | On 35 mm DIN rail according to EN 60715 via quick fixing system | |||
| Mounting position | any | |||
| Power connection | top and bottom (for S200M UC, polarity must be taken into account) | |||
| Dimensions and weight | Installation dimensions acc. to DIN EN 43880 | Installation size 1 | ||
| Dimensions (H x D x W) | mm | 85- 88 x 69 x 17.5 mm | ||
| Weight | G | OK. 115-125 g | ||
| Compatibility with accessories | Auxiliary contact | Yes | ||
| Signal contact | Yes | |||
| Remote release | Yes | |||
| Undervoltage release | Yes | |||
| Motor drive | Yes | |||
Rated current table S201 C
| Number of poles | Rated current | Number of modules | Series | Manufacturer's code |
| In A | [17.5 mm] | |||
| 1P | 0,5 | 1 | S201 C0.5 | 2CDS251001R0984 |
| 1P | 1 | 1 | S201 C1 | 2CDS251001R0014 |
| 1P | 1,6 | 1 | S201 C1.6 | 2CDS251001R0974 |
| 1P | 2 | 1 | S201 C2 | 2CDS251001R0024 |
| 1P | 3 | 1 | S201 C3 | 2CDS251001R0034 |
| 1P | 4 | 1 | S201 C4 | 2CDS251001R0044 |
| 1P | 6 | 1 | S201 C6 | 2CDS251001R0064 |
| 1P | 8 | 1 | S201 C8 | 2CDS251001R0084 |
| 1P | 10 | 1 | S201 C10 | 2CDS251001R0104 |
| 1P | 13 | 1 | S201 C13 | 2CDS251001R0134 |
| 1P | 16 | 1 | S201 C16 | 2CDS251001R0164 |
| 1P | 20 | 1 | S201 C20 | 2CDS251001R0204 |
| 1P | 25 | 1 | S201 C25 | 2CDS251001R0254 |
| 1P | 32 | 1 | S201 C32 | 2CDS251001R0324 |
| 1P | 40 | 1 | S201 C40 | 2CDS251001R0404 |
| 1P | 50 | 1 | S201 C50 | 2CDS251001R0504 |
| 1P | 63 | 1 | S201 C63 | 2CDS251001R0634 |
| 1P | 80 | 1 | S201 C80 | 2CDS251001R0804 |
| 1P | 100 | 1 | S201 C100 | 2CDS251001R0824 |
Let's move on to counting the number of devices
The required quantity primarily depends on the area of your home, living rooms and electrical equipment used. After all, for a boiler and a washing machine, it is recommended to install separate automatic switches and, according to the regulations, for each individual outlet, but this is too expensive and takes up a lot of space in the panel. Therefore, we will consider a universal option that will protect reliably and at the same time remain affordable.
So:
- 1 input machine in addition to the one located near the meter (available in every house, this is a requirement of Oblenergo).
- One switch for each group of consumers (for lighting and sockets). For a two-room apartment this is 8 pieces.
- For individual consumers according to need and desire. We have one per boiler.
In total there were 10 circuit breakers.
Rated current is the main indicator
Indicates how much current the machine can pass through itself without tripping. ABB has models designed for rated currents from 0.5A to 160 A. (for a residential building, 6A is enough for lighting groups, and 10-16A for sockets).
For our calculation:
we will need 1 piece (16A) for each room, plus 1 piece (10A) for the socket group for the bedroom (after all, we don’t plan to turn on anything there, more powerful than a telephone charger and a vacuum cleaner) and one (16A) for all sockets. We take a 25 A input circuit breaker; for a boiler, 16 A is enough.
Total: 4 pcs for 6A, 4 pcs for 16A, 1 pc. for 25 A and one for 10 A.
Calculate the required power and add 20-30%. A machine installed with a large margin may operate later than necessary and fail to fulfill its functional duties.
In addition to the rating, it is important to choose the right number of poles
Select polarity depending on the number of phases
. For single-phase networks, everything is simple - here choose among single-pole ones if you will install only on the phase wire and two-pole ones if you need to protect the neutral as well.
As for three-phase networks, it is advisable to install a four-pole circuit breaker at the input (before the lines are laid out) - on each line and neutral, in order to protect yourself in cases where, during a break, the phase wire falls to the neutral wire. After wiring, you will need single-phase AVs, because most likely you have either one line for the whole house, or (which is better) the phases are divided into each room. Then you will need single-pole or double-pole options.
For an apartment where there are no three-phase networks and the same consumers, we choose two- and single-pole circuit breakers.
The next step is the characteristic of the release
For ABB, these are devices with characteristics B and C. These letters indicate the delay before operation. That is, switches with characteristic B will operate instantly, and with characteristic C they will have a short delay before turning off.
It’s easy to explain the need for a delay: there are electrical appliances, such as pumps, that, at the moment of switching on, create inrush currents that are several times higher than the rated ones. To ensure that the circuit breaker does not go into emergency mode every time the pump starts, buy a circuit breaker with characteristic C.
It is unlikely that there will be a powerful pump in the apartment, so for our calculation we select B characteristic.
All you have to do is choose a series
For household use, ABB has two series:
- Compact Home - marked SH - are designed specifically for use in residential buildings. They do not have anything superfluous (there is no possibility to connect additional devices such as comb buses, but they are not needed in everyday life). Easy to install.
- System pro M compact - the same quality as the previous series, but with many different additions. The S subseries is suitable for domestic use - it is designed for rated currents up to 63A.
For the apartment in our example, we choose devices from the Compact Home series.
Advantages
has been selling a wide range of different types of circuit breakers for more than 10 years, and during this time has accumulated vast experience and established contacts when choosing a supplier of these products.
At the same time, our specialists regularly study and analyze the quality of circuit breakers, their exact compliance with classes and characteristics. Having purchased ABB S201 C switches in, you can be sure that you have purchased truly reliable, high-quality products that meet all GOST requirements. If necessary, you can always obtain a quality certificate and test report for the batch of circuit breakers you are interested in. Return to list
Signs of counterfeit ABB machines
A person without experience in this matter will not be able to recognize counterfeit ABB machines. Especially in situations where the analogue is made quite well.
But electricians and sellers of electrical goods do not make such mistakes. They understand perfectly well where ABB is a fake and where the original product is.
If, when buying a machine, you have doubts about the authenticity, but the seller assures you otherwise, then the issue is his honesty. He can tell the truth. Or he may try to sell counterfeit products, since part of the proceeds will go into his pocket.
There are several recommendations on how to distinguish a fake ABB machine from the original.
You can do this by:
- quality of plastic;
- barcode;
- switch position;
- labeling;
- weight;
- spark arrester;
- approval of Rostest;
- RFID tag;
- packaging.
Now in more detail about the ABB machine and how to distinguish a fake by these signs.
If you have figured out how to distinguish a counterfeit battery, or understand the principles of counterfeiting Honda generators, then you can handle automatic machines without any problems. You just need to know what to look for and where to look.
Plastic quality
This is not the most obvious sign by which counterfeit ABB machines are identified. But he can also help you.
In counterfeit devices, the body has a smoother surface. And if you press with your fingers, you will feel the effect of a spring. This is due to the fact that the Chinese use cheap raw materials. They try to do it as budget as possible. Hence the thin plastic.
The original should be a little rough. The body is not shiny, but rather matte.
Hold the device in your hand. You should not have the feeling that the plastic is cheap and thin.
Barcode
It is applied to the back of the device body. Both the original and the fakes have it.
But if real machines use the laser printing method, then in copies the barcode is usually applied using regular paint.
This fact is quite easy to verify. Try picking at the code with your fingernail. If this is an original product, then such manipulations will not harm and will not spoil the inscription. The paint on copies wears off and scratches easily.
Switch position
The original ABB machines have their own peculiarity. It lies in the fact that products are always sold with switches in the ON position. That is ON.
At the same time, illegal manufacturers often do not pay attention to this nuance. As a result, counterfeits are sold in the OFF position.
The situation here is not the most obvious. After all, it will not be difficult for the seller to switch the position on the fake to ON. But at the same time, if you see a machine in the OFF position, then this is 100% fake. Under no circumstances should you take such a device.
Weight characteristics
Another way to distinguish counterfeit ABB machines from the original. To do this you need to compare two devices.
Counterfeits will be easier in 99% of cases. At least a few grams, but definitely lighter, with equal characteristics.
The reason is simple. Chinese underground production saves on materials, as well as internal components. The plastic is cheap and thin. The electronics inside are as budget as possible. Hence the lower weight.
Marking
Place the machine in a vertical position, with the front side facing you. In this case, the manufacturer's marking must be applied to the upper part.
Comparison with the original is not so difficult. Just find a photo on the official website. And compare what the markings look like there and there.
And one moment. The text, like the logo, is always different on fake devices. These may be details, but they are key. So try to look carefully at all the elements. If you see the difference, then the conclusion is obvious. They are trying to sell you a counterfeit product.
Spark arrestor
This is one of the key reasons why buying counterfeit machines is strictly not recommended. This is due to the lack of a spark arrestor in the copies.
But the spark arrester is the most important element of the machine. It directly affects reliability and fire safety.
But since the presence or absence of a damper greatly affects the cost of assembly. Therefore, for the Chinese, who are accustomed to saving on everything, it is more profitable to assemble machines without a spark absorber.
The only problem is that to check this fact you will have to disassemble the device. But no one in the store will allow you to tinker with the new machine. There is only one solution. Refuse to purchase if you have doubts about other parameters, or buy, disassemble and then make a decision.
Approval from Rostest
Quite an effective way to identify a fake machine.
Genuine ABB devices have a quality certificate. Therefore, the devices always contain the corresponding Rostest markings. It is applied to the body.
In some cases, instead of the Rostest sign, the sign of the Customs Union is applied. The corresponding innovation appeared in 2012. If there are no marks on the case, it is 100% fake.
Please note that the likelihood of buying a machine that was assembled more than 8 years ago is extremely low. But getting into counterfeit products is much easier.
RFID tag
Always applied to the side of the body. This is exactly how the original product works.
Although the mere fact of having a label is not a 100% guarantee of quality. Similar marks are sometimes found on counterfeit devices.
If there is no sticker, then you can rest assured. This store is trying to sell you counterfeit goods.
Package
Since packaging from vending machines is the least obvious sign of a fake, they decided to leave it for last.
Some copies are packaged in perfectly crafted boxes. And the originals may even be slightly dented and deformed.
It is almost impossible to distinguish an original box from a fake one by appearance. But there is one caveat. Almost all copies come to the Russian market from China. But local underground specialists are not so good with spelling.
So in the Russian text there are errors every now and then. The original doesn't allow itself to do this.
Even if you find one error, this is already a good reason to doubt the authenticity. It's not worth the risk.