What is the difference between an automatic protective switch and an input circuit breaker? From a technical point of view, nothing. This is a device designed to automatically shut down electrical networks in case of overload and short circuit. The only difference is in the purpose and connection diagram. If a conventional (group) machine operates within one or several lines, then the input device is responsible for connecting (disconnecting) the entire facility, be it an industrial enterprise or an apartment (private house).
Externally, the input circuit breaker looks like a regular switch.
It can be 1, 2, 3 or even 4 pole, depending on your facility's power supply.
Design and principle of operation
The compact case contains the switching mechanism: two contacts, movable and fixed. When the cocking handle is moved to the working position, the contacts close and are mechanically fixed in the on state.
The circuit through which electric current flows includes two protective devices in series. One is triggered when the set threshold for temperature and current is exceeded (bimetallic plate), the second opens the contacts in the event of a short circuit, or rather, when the current value is significantly exceeded (electromagnetic release).
If the current gradually exceeds the permissible value (indicated on the marking of the machine), the plate heats up and mechanically opens the contacts. When a short circuit occurs, the current increases like an avalanche and activates the electromagnetic release. For multi-pole circuit breakers, it is enough to exceed the parameters on at least one line. The entire package of contacts will be disabled.
In all cases of protection activation, after the danger disappears, the circuit breaker does not return to its original state. A person is required to turn it on.
Types
The machine is selected taking into account the electrical network diagram and its needs. There are single-pole, two-pole, three-pole and four-pole devices.
Single pole
A single-pole switch is used in single-phase electrical networks. Different models have different characteristics, which determine the shutdown speed. The composition includes two release mechanisms - electromagnetic and thermal.
One is triggered when there is a short circuit, the second when the load is exceeded for a certain time. It is connected through the upper terminal, the outgoing wire is connected to the lower one. The principle of operation is the same as that of diverter machines, but the current rating is higher.
Bipolar
Used in single-phase input. The design consists of a block with two poles, which are equipped with levers and a common lock between the shutdown mechanisms. That is, the main difference from a single-pole network is that if there is a problem on any of the lines coming from it, both will be disconnected. Two-terminal networks are used in typical modern apartments.
You cannot replace one double-pole switch with two single-pole circuit breakers! This is prohibited by the PUE.
Three-pole
For three-phase networks, three-terminal and four-terminal networks are used. Such electrical networks are found in homes where food is cooked on electric stoves. To connect a three-pole circuit breaker, each terminal is connected in phase. In devices with four poles, a neutral wire is additionally used.
When installing it yourself, the ground (not the neutral) should never pass through the machine.
How to choose a machine based on current strength
We already know that all the electrical current to power the object will flow through this switch. According to Ohm's law, it is clear that the load must be summed up based on all consumers in the house (apartment). Calculating this value is quite simple.
Tip: It is not necessary to calculate energy consumption by summing up the power of all electrical appliances.
Of course, you can turn on the boiler, electric oven, air conditioner and iron at the same time. But such a “celebration of life” will require powerful electrical wiring. And the technical conditions for such input power will cost significantly more. For energy supply organizations, tariffs for coordinating connections grow linearly depending on the number of kilowatts.
For a typical apartment, we can assume the simultaneous operation of a refrigerator, TV, computer, and air conditioner. In addition to them, it is permissible to turn on one of the powerful appliances: a boiler, an oven or an iron. That is, the total power of electrical appliances will not exceed 3 kW. We don’t take lighting into account; today, every home has energy-saving lamps.
This is interesting: if you go back 20–30 years ago, when each chandelier had only incandescent lamps, a two-room apartment with full lighting could spend 500–700 W on light alone.
Usually, for a power reserve (force majeure circumstances are possible), 20–30% is added to the calculations. If you forget to turn off the boiler and start using the iron while the air conditioner is running, you won’t have to run to the electrical panel to restore the power supply. It turns out: 4 kW divided by 220 V (according to Ohm’s law), current consumption 18 A. The nearest circuit breaker is rated 20 A.
For reference: most manufacturers of electrical products produce circuit breakers with the following operating current ratings:
2 A, 4 A, 6 A, 10 A, 16 A, 20 A, 25 A, 32 A, 40 A, 50 A, 63 A...
The marking is in the product passport, and always on the body.
When selecting a device more accurately, especially when used in conjunction with a non-standard load (motors or other loads with significant starting currents), it is necessary to make a choice not only by the rated current, but also by the time-current characteristic.
For example, the input circuit breaker shown below in the picture has a rated current of 16A and a characteristic of type “C” (type “C” is well suited for the usual standard load - our apartments).
We will tell you more about the time-current characteristic below.
We are not interested in higher currents, this exceeds the power of 15 kW. No one will approve such a connection to your apartment. Typically, residential input is limited to automatic machines with an operating window of about 32 A.
For a private home, the figures may be higher. The calculation takes into account the increased living space, the presence of outbuildings with power supply, a garage, a workshop, and powerful power tools. An input circuit breaker for supplying power to a private house usually has an operating current of 50 A or 63 A.
What other parameters are important when choosing
Number of poles
For ease of understanding, we will put three-phase switches out of brackets. We choose between 1 and 2 pole designs. From the point of view of the Electrical Installation Rules (PUE), there is no difference. But the same rules imply high-quality organization of grounding or grounding. And if a problem arises with the appearance of a phase at zero (unfortunately, this is real in old housing stock), then it would be better to completely disconnect your apartment from the power lines. Therefore, if you can choose which input circuit breaker to install, take a two-pole one.
Important: this connection is suitable for the TN-S grounding system. If you have a TN-C circuit in your house, you can install a single-pole circuit breaker.
Time - current characteristic
There are different types of time-current characteristics curves, they are designated by Latin letters: A, B, C, D... Starting from A onwards, the sensitivity of the device gradually becomes rougher. For example, type “B” means operation of the electromagnetic release at 3–4 times the current, type “C” at 5–7 times, “D” at 10 times. The thermal release will operate in the same way for different types of time-current characteristics.
More accurate data should always be obtained from the manufacturer’s documentation for each specific product, for example, for BA47-29 incoming automatic machines the response characteristics are as follows:
An example of graphs for BA47-29 with characteristics (types) B, C, D are shown below in the picture, dependencies for other types can be found on the official websites class=”aligncenter” width=”1152″ height=”556″[/img]Selection of one type or another is determined by the type of load being connected, or more precisely by its ability to consume current intermittently. For example, motors have a starting current several times higher than the rated current, and depending on their types, type “C” or “D” devices can be used. Type “B” is recommended for loads that do not have significant inrush currents.
Also, the use of types with reduced sensitivity of operation makes sense to increase the probability of operation of lower groups of circuit breakers.
Rated current
The main characteristic on which the device is mainly selected. However, as we saw in the previous section, it is also necessary to take into account the time-current characteristic, since the actual operation current depends simultaneously on both the rated current and the type of characteristic. In the previous tables, the rated current is indicated as In. Theoretically, in the absence of inrush currents, a load consuming a current equal to the rated one should not lead to operation (shutdown) of the device.
Mounting method
Today, there is no alternative. These are switches that are mounted on a DIN rail. No direct screwing to the wall or panel body. DIN mounting only. However, with the use of special accessories, other types of fastening are possible.
The device can be in a separate housing, or installed in a common panel - it doesn’t matter. The main thing is to provide free access for the owner. An important point: sealing the input machine. There are many ways to restrict access to contacts (to prevent unauthorized connections). You can install plugs on the holes to tighten the screws on the contacts.
Or simply put seals on the covers covering the contact groups.
The main thing is that after sealing you can easily turn on and off the power supply.
Number of poles
Depending on the number of poles, the machines are:
- Single-pole (1p, 1p). This is the most common type. It stands in a circuit and protects one wire, one phase. This is shown at the beginning of the article.
- Bipolar (2p, 2p). In this case, these are two single-pole circuit breakers, with a combined switch (handle). As soon as the current through one of the machines exceeds the permissible value, both will turn off. These are mainly used to completely disconnect a single-phase load when both the zero and the phase break. It is the two-pole circuit breakers that are used at the entrance to our apartments.
- Three-pole (3p, 3p). Used to break and protect three-phase circuits. Just as in the case of two-pole ones, these are actually three single-pole circuit breakers, with a common on/off handle.
- Four-pole (4p, 4p). They are rare, they are installed mainly at the input of three-phase switchgears (switchgears) to break not only the phases (L1, L2, L3), but also the working zero (N). Attention! Under no circumstances should the protective grounding (PE) wire be broken!
What does energy sales think about this?
Let's say you have organized exemplary electrical wiring in the house, calculated each consumer to the nearest ampere, and want to get a certain current load at the input. And when you contacted power engineers, you were refused. You should know that the energy sales company is not interested in which input machine you choose. They have limits on the electrical supply line, or the nearest transformer substation. And no one has the right to exceed these standards: otherwise it will not be possible to connect the next people who want to, or the entire line will operate in constant overload mode.
Therefore, before planning the energy supply scheme for your home, visit the organization that will supply you with electricity.
Time-current characteristics
Obviously, the machine does not always turn off instantly, and sometimes it needs to “think and make a decision”, or give the load a chance to return to normal.
The time-current characteristic shows after what time and at what current the machine will turn off. These characteristics are also called tripping curves or current-time characteristics. Which is more precise, since it depends on the current after what time the machine turns off.
Tripping curves or current-time characteristics
Let me explain these graphs. As I said above, the circuit breaker has two types of protection - thermal (against overcurrent) and electromagnetic (against short circuit). In the graph, the operation of thermal protection is a section that smoothly descends. Electromagnetic – the curve abruptly breaks down.
The thermal one works slowly (for example, if the current is twice the nominal value, the machine will go out in about a minute), and the electromagnetic one works instantly. For graph B, this instant “begins” when the current exceeds the nominal value by 3-5 times, for category C - 6-10 times, for D (not shown, since it is not used in everyday life) - 10-20 times.
How it works - you can imagine what will happen if the current exceeds the nominal value by 5 times, and the protection is with the “C” characteristic, as in all houses. The machine will only go off after 1.5-9 seconds, depending on your luck. In 9 seconds the insulation will melt and the wiring will need to be changed. In this case, therefore, short circuit is better than overload.
You want to change the parameters of the input switch (if it is knocked out)
One of the reasons is that your input circuit breaker is constantly knocked out at the same time as the internal circuit breaker in the distribution panel. And this didn’t happen before. Why is this happening? There are switches on the home panel with a similar maximum current value. For example, you had a 25 A ceramic fuse in your entrance (an old house). After repairs, it was replaced with a modern 20 A circuit breaker. And the distribution switches in the apartment have the same rating. It would seem easier to replace the machine at the entrance, and everything will fall into place. However, this is fraught with a fine from the energy supply company.
We will have to redo the home panel and install group circuit breakers with a lower value.
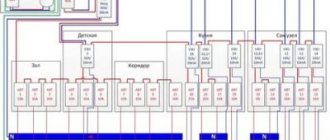
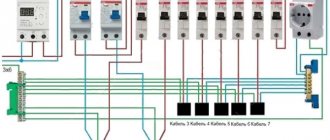
Switching circuit of the introductory machine
In addition to the main task (ensuring electrical safety), the input switch is designed to disconnect the consumer from the power supply for work. For example, metering device maintenance. Therefore, in most cases the machine is installed in front of the electric meter.
This is the area of responsibility of electricians; the owner of the apartment (household) has no right to interfere. For apartment buildings - this is an entrance shield, for a private house - a pillar, fence, or outer wall of the household. This scheme is used in 90% of residential properties. Between the sealed input machine and the metering device (which also has seals), there is no access for unauthorized connection. This is done to prevent illegal extraction of electricity. Many homeowners install a duplicate input circuit breaker for ease of maintenance and repair of the distribution panel. It is connected between the energy meter and group circuit breakers, and is mounted inside the panel of the apartment (household).
How to choose the right automatic backup machine?
The optimal solution is that the protection current should be less than at the input device and greater than at the group switches. For example, a 32 A circuit breaker is installed at the input, and group circuit breakers are installed at 20 A. This means that the backup must operate at a load current of 25 A. If such a ratio cannot be achieved, the current cutoff of the backup must correspond to the input circuit breaker. In this case, it simply acts as a disconnecting device (for carrying out work). And in an emergency, it will operate simultaneously with the input device.
Performance
Its service life largely depends on how quickly the switch turns on and closes its contacts. However, is it possible to determine at home how well your device corresponds to this parameter without disassembling the case itself and without resorting to specialized laboratory tests?
Of course you can. Everything is done very simply. Take a regular battery-powered indicator screwdriver. Exactly with the battery.
It is usually used for testing and determining the integrity of the circuit. Although knowledgeable people use this useful device in many other ways. Read about which ones in a separate article.
Use the tip of a screwdriver to touch the upper contact, pressing the metal patch on the handle from above, and with the finger of your other hand, touch the lower contact of the switch.
After which, you slowly begin to turn on the machine, cocking the tongue.
The contact should appear (the LED in the screwdriver will light up) only at the very last moment, when the device has already clicked.
If the same manipulation is done with another switch, the light comes on when the power lever reaches the middle of the stroke.
It turns out that the device is not yet cocked, but the contacts are already closed. This is what this sometimes leads to under heavy load (view of the contacts from inside the machine):
This ultimately affects the rapid wear and burnout of contacts. While the quick-start mechanism increases the service life of the product by almost 30%.