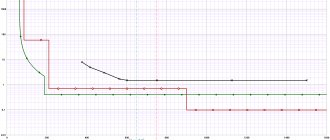
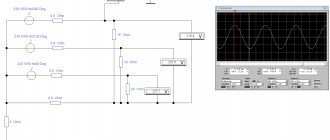
What is shown in the graph of the time current characteristic
On the graph you can see how the current flowing through the circuit breaker affects the dependence of its shutdown time. The multiple of the current flowing in the circuit to the rated current of the machine (I/In) is shown on the X-axis, and the response time, in seconds, is shown on the Y-axis.
It was said above that the machine includes an electromagnetic and thermal release. Therefore, the graph can be divided into two sections. The steep part of the graph shows protection against overload (operation of the thermal release), and the flatter part shows protection against short circuit (operation of the electromagnetic release).
As you can see in the graph, if you connect a load of 23 A to the C16 machine, it should turn off in 40 seconds. That is, if an overload of 45% occurs, the machine will turn off after 40 seconds.
The machine is able to respond instantly to large currents that can lead to damage to the insulation of electrical wiring due to the presence of an electromagnetic release.
When a current of 5×In (80 A) passes through the C16 circuit breaker, it should operate in 0.02 seconds (this is if the machine is hot). In a cold state, under such a load, it will turn off within 11 seconds. and 25 sec. (for machines up to 32 A and above 32 A, respectively).
If a current equal to 10×In flows through the machine, then it turns off in 0.03 seconds in a cold state or in less than 0.01 seconds in a hot state.
For example, if there is a short circuit in a circuit that is protected by a C16 circuit breaker and a current of 320 Amperes occurs, the circuit breaker shutdown time range will be from 0.008 to 0.015 seconds. This will remove power from the emergency circuit and protect the machine itself, which has short-circuited the electrical appliance and electrical wiring, from fire and complete destruction.
Machines with what characteristics are preferable to use at home?
In apartments, if possible, it is necessary to use category B machines, which are more sensitive. This machine will work from overload in the same way as a category C machine. But what about the case of a short circuit?
If the house is new, has a good condition of the electrical network, the substation is located nearby, and all connections are of high quality, then the current during a short circuit can reach such values that it should be enough to trigger even the input circuit breaker.
The current may be small in the event of a short circuit, if the house is old, and there are bad wires with huge line resistance going to it (especially in rural networks, where the phase-to-zero loop resistance is high) - in this case, a category C machine may not work at all. Therefore, the only way out of this situation is to install machines with type B characteristics.
Consequently, the time-current characteristic of type B is definitely more preferable, especially in dacha or rural areas or in old buildings.
In everyday life, it is quite advisable to install type C on the input machine, and type B on group line circuit breakers for sockets and lighting. In this way, selectivity will be maintained, and somewhere in the line, during a short circuit, the input machine will not turn off and “extinguish” the entire apartment.
Similar materials on the site:
setpoint
setting:
The temperature value at which the alarm is triggered (released).
The specified value of the controlled parameter at which the alarm device is triggered
The specified value of the controlled parameter at which the signaling device is triggered
See also related terms:
105. Setting of the device according to the influencing quantity
The set value of the operation or non-operation value to which the device is adjusted
106. Device time setting
The time delay value for which the device is adjusted
127. Electrical relay time delay setting
D. Einstellwert der Verzögerung
E.Setting value of a specified time
F. Valeur d'ajustement d'une temporisation
Specified time delay value at which the electrical relay must operate
64. Electrical unit (power plant) voltage setting
The value of the regulated voltage change of the electrical unit (power plant), by which it is changed manually
3.9 Leakage current setting
— the rated value of the leakage current at which the residual current device is triggered.
88. Setting for the characteristic value of the measuring electric relay
E. Einstellwert der Wirkungsgrösse
E. Setting value of the characteristic quantity
F. Valeur d'ajustement de la grandeur caractéristique
Specified value of a characteristic quantity at which the measuring electrical relay should operate
3.3 alarm setting:
The specified parameter value at which an alarm is activated to warn of a condition that needs to be corrected.
1.3.2.20 calibration temperature setpoint (calibration setpoint):
The temperature at which the calibrated gas flow rate is obtained when the thermostat is adjusted in the operating position and in the direction specified by the manufacturer.