rated thermal power" in other dictionaries: rated thermal power
—
The value of
total
power
,
power
per unit length or unit surface area of the electric heater at
rated
values of voltage, temperature and length, expressed in W/m or W/m2.”>
Skip to content
The rated power of the boiler is the main thermal characteristic of the boiler and is expressed in different measurement systems used in the Russian Federation, in kW (mW) or Mcal (Gcal) with their following ratio - 1 Gcal = 1.163 MW.
Installed capacity of the power plant
Due to the insufficient reliability and severe deterioration of electrical networks in remote villages, dacha communities and other populated areas, accidents often occur on the lines, resulting in power outages. But this causes a lot of inconvenience: refrigerators defrost, heaters and air conditioners do not work. You can protect yourself from such troubles with the help of autonomous sources of electricity, powered by a gasoline or diesel engine and called power plants (generators).
When purchasing a power plant, consumers have to take into account many parameters, such as the rated, maximum or installed power of the power plant, non-stop operation interval, voltage, number of phases and much more.
Power plants capacity
The capacity of a power plant is the rate at which electricity is transmitted or converted.
In principle, in order to select a power plant for domestic use, it is not at all necessary to delve deeply into the physical meaning of this concept. It is enough to know a few nuances related to its units of measurement and calculations of the required value. So, both the rated and maximum and installed power of a power plant are measured in kilowatts or kilovolt-amperes. These values differ only for three-phase units (by a factor = 0.8). For single-phase devices, the values expressed in kW coincide with those measured in kVA.
Rated and maximum power
Rated power is the value indicating the power of a power plant during normal operation.
The maximum power of a power plant is the value at maximum load. In this mode, the power plant can be operated only for a very limited period of time.
The concept that consumers rarely encounter is the installed capacity of a power plant. They talk about it only if it is planned to use several units to provide electricity. The sum of their rated capacities will be the installed capacity of the power plant.
The use of two or three electric generators can be economically justified in several cases. For example, you already have several units, but they are not enough to provide electricity to all the necessary equipment (household appliances, electric or garden tools, welding machine). In this case, some devices are connected to one generator, and some to another.
Another case when several nodes can carry out parallel network backup is to provide electricity to responsible consumers. In this case, two generators can be used: the main and backup.
Having understood these three concepts, you can begin to calculate the power of the power plant that you will need. To do this, you need to sum up the power of all electrical appliances that you are going to use at the same time: light bulbs, refrigerator, electric stove, TV, etc. The resulting value will approximately indicate the rated power of the power plant that will suit you.
Mode - rated load - Great Encyclopedia of Oil and Gas, article, page 1
Mode - rated load
Page 1
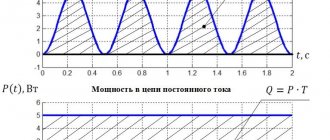
The rated load mode for a district heating turbine is the mode at which the power specified in the delivery specifications is achieved, i.e. the greatest power that a turbine unit can develop for a long time at the generator terminals at nominal values of thermal extraction of all main parameters (fresh steam, intermediate superheat, in extractions and in the condenser) and when using unregulated steam extractions for constant auxiliary needs of the power unit and with fully open control valves. [1]
In rated load mode (Fig. 22 6), the phase currents are equal to the rated current. [3]
The parallel excitation motor operates in rated load mode. [4]
Thus, the most economical mode is the rated load mode. This is true for all domestic power units. [6]
Determine the voltage on the field winding in rated load mode, if the inductive leakage resistance of the armature winding is Xa 0 31 Ohm, the resistance of the field winding is Rf 0 678 Ohm, the main inductive resistance of the armature winding, calculated without taking into account saturation, Xa 4 6 Ohm. [7]
The vibration characteristics of the pump are measured in rated load mode. The valve sets the pressure at the pump outlet corresponding to its rated capacity. Vibration is measured at three radial points located in the area of the upper bearing of the pump and oriented at an angle of 120, and one axial point located on the valve flange. [9]
When moving from idle mode to rated load mode, the power factor increases from the cos value. With further increase in load, coscpj decreases slightly. [10]
When transitioning from idle mode to rated load mode, the power factor increases from the value sozf. With a further increase in load, sozf1 decreases slightly. [12]
Let us assume that the synchronous generator was operating at rated load, and then the load was completely dropped, but the rotation speed and field current remained unchanged. To determine this value, we will do the following (Fig. 16.14): in the same coordinate axes we will construct the characteristics of no-load and short circuit. [13]
Features of electric drill engines are high slip in the rated load mode and a significant starting torque, reaching (1 2 - il 7) MH. The choice of such a characteristic is due to the desire to provide the maximum possible starting torque, accompanied by a small multiplicity of the starting current. [14]
The change in generator voltage is characterized by an increase in voltage during the transition from rated load mode to no-load mode, related to the rated voltage (Fig. [15]
Pages: 1 2 3 4
www.ngpedia.ru
Nominal load is... What is Nominal load?
Nominal load – technological load specified in the machine passport as the maximum for the intended normal operating conditions.
[Terminological dictionary of construction in 12 languages (VNIIIS Gosstroy USSR)]
Term heading: General terms, equipment
Encyclopedia headings: Abrasive equipment, Abrasives, Highways, Automotive equipment, Motor transport, Acoustic materials, Acoustic properties, Arches, Reinforcement, Reinforcement equipment, Architecture, Asbestos, Aspiration, Asphalt, Beams, Uncategorized, Concrete, Concrete and reinforced concrete, Blocks, Window blocks and doors, Logs, Beams, Cables, Ventilation, Weighing equipment, Vibration protection, Vibration technology, Types of reinforcement, Types of concrete, Types of vibration, Types of fumes, Types of tests, Types of stones, Types of bricks, Types of masonry, Types of control, Types of corrosion, Types of loads on materials, Types of floors, Types of glass, Types of cement, Water-pressure equipment, Water supply, water, Binders, Sealants, Waterproofing equipment, Waterproofing materials, Gypsum, Mining equipment, Rocks, Combustibility of materials, Gravel, Lifting mechanisms, Primers, fiberboard, Woodworking equipment, Woodworking, DEFECTS, Ceramics defects, Paint defects, Glass defects, Concrete structure defects, Defects, woodworking, Material deformations, Additives, Concrete additives, Cement additives, Dispensers, Wood, chipboard, Railway transport, Factories, Factories, production, workshops, Putties, Concrete fillers, Concrete protection, Wood protection, Corrosion protection, Sound-absorbing material, Ash, Lime, Wooden products, Glass products, Tools, Geodesy tools, Concrete testing, Testing equipment, Cement quality, Quality, control, Ceramics, Ceramics and refractories, Adhesives, Clinker, Wells, Columns, Compressor equipment, Conveyors, Precast concrete structures, Metal structures, Other structures, Corrosion of materials, Crane equipment, Paints, Varnishes, Lightweight concrete, Lightweight concrete fillers, Stairs, Trays, Mastics, Mills, Minerals, Installation equipment, Bridges, Spraying, Firing equipment, Wallpaper, Equipment, Equipment for the production of concrete, Equipment for the production of binders, Equipment for the production of ceramics, Equipment for the production of glass, Equipment for the production of cement, General, General terms, General terms, concrete, General terms, woodworking, General terms, equipment, General, factories, General, aggregates, General, quality, General, corrosion, General, paints, General, glass, Fire protection of materials, Refractories, Formwork, Lighting, Finishing materials, Test deviations, Waste, Production waste, Panels, Parquet, Lintels, Sand, Pigments, Lumber, Feeders, Plasticizers for concrete, Plasticizing additives, Plates, Coatings, Polymer equipment, Polymers, Flooring, Floors, Pressing equipment, Devices, Devices, Purlins, Design, Production, Anti-frost additives, Fire-fighting equipment, Others, Others, concrete, Others, putties, Others, paints, Others, equipment, Types of wood, Destruction of materials, Mortar, Crossbars, Piles, Piling equipment, Welding , Welding equipment, Properties, Properties of concrete, Properties of binders, Properties of rock, Properties of stones, Properties of materials, Properties of cement, Seismic, Warehouses, Hardware, Dry mixtures, Resins, Glass, Construction chemicals, Building materials, Superplasticizers, Drying equipment , Drying, Drying, woodworking, Raw materials, Theory and calculation of structures, Thermal equipment, Thermal properties of materials, Thermal insulation materials, Thermal insulation properties of materials, Thermal and damp treatment of concrete, Safety precautions, Technologies, Concreting technologies, Ceramic technologies, Pipes, Plywood, Trusses, Fiber , Foundations, Fittings, Cement, Workshops, Slags, Grinding equipment, Putties, Veneer, Plastering equipment, Noise, Crushed stone, Economy, Enamels, Emulsions, Power equipment
Source: Encyclopedia of terms, definitions and explanations of building materials
Encyclopedia of terms, definitions and explanations of building materials. — Kaliningrad. Edited by V.P. Lozhkin. 2015-2016.
construction_materials.academic.ru
What is it and how to calculate the load
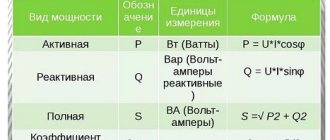
Electric current load is a quantity characterizing its properties. Shows how much energy is consumed by electrical appliances. The current power is measured using a special device - a wattmeter.
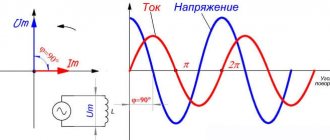
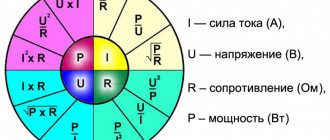
If you connect a meter in series, you can check the current strength. When connecting in parallel, the voltage is determined. The amount of circuit consumption is calculated using the formulas: P = I x U or P = U2/ R = I2 x R.
The electrical load is equal to the voltage across the consumer multiplied by the amount of current flowing through it.
P = U x I
The formula indicates which measurements determine this parameter. If the load is active, it is measured in Watts, the reactive unit of electrical power is VA.
Reactive unit of electrical power - VA Source infourok.ru
Taking into account the type of load
Household electrical appliances are characterized by two types of load:
- Active;
- Reactive.
The active (ohmic) load is consumed by devices that convert the received energy into heat. This is an electric stove, iron, hair dryer, air heaters, etc. The reactive load is consumed by other electrical appliances, which convert only a small portion of the energy into heat. The bulk of the energy consumed is used for another purpose. Examples of such appliances include a refrigerator, vacuum cleaner, TV, computer, etc.
If you need help choosing the generator power for your home, industrial workshop or any other facility, contact our specialists for qualified advice.
Power
The battery produces power from a low start
Mobile device users are convinced that powerful batteries are those that last a long time on a single charge. If the battery is weak, then the device will not only have to be charged frequently, it may not even turn on, or it may first turn on and then suddenly turn off when the load increases. How does this all fit in with the container? It turns out that powerful batteries are capacious batteries. What's the difference then?
Power consumption
- The rated power
is calculated under the condition that the battery will produce the same current = 1C with the same voltage for an hour. For example: the battery for Apple iPhone 5S (C1.02.1010) has a capacity of 1690mAh and a nominal voltage of 3.8V. Let's multiply one by the other and get 6.4W. - The maximum power
is calculated based on current = 2C. For the previous example, maximum power = 12.8W. When operating at maximum power, batteries are safe, but wear out very quickly. - The maximum safe power
will correspond to a current of 3C. In our example = 19.2W. The battery may explode after 1 minute of such load.
In general, what is the greatest power a battery can produce? In laboratory conditions, we obtained peak currents of lithium batteries of several tens of Amperes. Peak loads only last a few miles/micro seconds, which is not enough to heat up and explode the battery.
Attention:
Autonomous operation
If there is no choice, the device is already in your hands, then the only thing you can do is set up an energy-saving mode or stupidly save battery power. Battery life isn't just about the time between charges - it's about precious life cycles. When the battery life runs out, you will go for a new battery. or a new phone.
Fast charge
Sudden outages
FAQ:
High power batteries - myth or reality?
- Yes, reality, but within reasonable limits.
- It is not possible to significantly increase the capacity without increasing the size.
Are CRAFTMANN batteries more powerful than the original ones?
- Unfortunately, not all. It is too presumptuous to make such a statement.
- Only LingLife series batteries are more powerful than the original ones and are completely interchangeable.
- The +2 Energy series batteries have double the capacity, but also double the thickness.
Is it dangerous to use more powerful batteries?
- No, it's not dangerous. Powerful batteries will simply last longer.
- The actual current consumed is determined by the mobile device. Familiarize yourself with and always follow battery safety guidelines
- Familiarize yourself with and always follow battery safety guidelines.
Design power (definition)
One of the main stages in the design of power supply systems for a facility is the correct determination of the expected (calculated) electrical loads of both individual electric power supply units and load nodes at all levels of the power supply system.
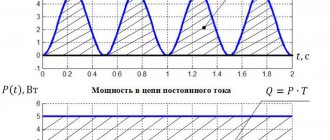
Load design values are loads corresponding to such a constant current load (
), which is equivalent to the actual time-varying load for the greatest thermal impact (without exceeding permissible values) on the element of the power supply system.
There are various methods for determining design electrical loads, which in turn are divided into main ones; and auxiliary.
The calculated electrical loads include the calculated values of active power (
), reactive power (
), full power (
) and current (
).