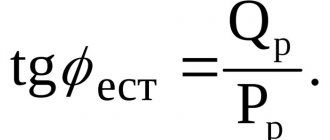In physics, a lot of attention is paid to the energy and power of devices, substances or bodies. In electrical engineering, these concepts play no less important role than in other branches of physics, because they determine how quickly the installation will perform its work and what load the power lines will bear. Based on this information, transformers for substations, generators for power plants and the cross-section of conductors of transmission lines are selected. In this article we will tell you how to find the power of an electrical appliance or installation, knowing the current, voltage and resistance.
Ohm's Law Calculator:
The online calculator team has provided a simple and effective tool known as Ohm's Law Calculator through which you can easily find out the value of Voltage (V), Current (I), Power (P) and Resistance (R). relative to the simple Ohm's law formula.
However, you need to know two of these values in order to calculate the remaining two values.
Therefore, remember that you will receive results regarding the standard units you choose!
How does our power calculation work?
There is no need to resort to specific mathematical calculations to determine the values of voltage (V), current (I), power (P) and resistance (R). Our resistance calculator will do everything for you in a couple of seconds. Our (Ohm's Law calculator) is not only easy to use, but also works efficiently! Let's take a look!
- In the Ohm's Law calculator above, you can find four fields: voltage (V), current (I), resistance (R) and power (P), respectively.
- You simply need to enter any two of these values in relation to their SI units.
- Once you have selected two values and their SI units, you simply need to click the calculate button to get the remaining two values.
As mentioned above, you will receive your results in relation to the SI units you chose before calculating!
Ohm's law equation:
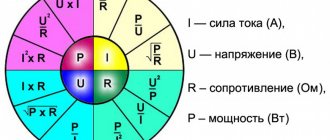
According to Ohm's law, the amount of current (I) passing through a metal conductor in a circuit is directly proportional to the voltage (V) applied to it, for the corresponding temperature. Georg Simon Ohm expressed his discovery in the form of a simple equation of Ohm's law, which describes the relationship between voltage, current calculation from power and resistance:
V = IR
In this Ohm's Law equation, voltage (V) equals current (I) times resistance (R). So, using this Ohm's law equation can be divided into two options, solving for current (I) and resistance (R) respectively:
I = E/R and R = E/I
Calculation options
Ohm's law connects these three parameters, which we need to calculate electrical power. Let's look at three possible calculation options:
- The current and voltage are known.
- The current and resistance are known.
- The resistance and voltage are known.
Power is equal to the product of voltage and current. Accordingly, if we know these two quantities, we simply need to multiply them. For example, the current in a circuit is 10 amperes and the voltage is 200 volts. Accordingly, the power is 2 thousand watts.
If we know the resistance and current , then the formula will be slightly different. First let's find the voltage. To do this, you need to multiply the current and resistance. After this, the result must be multiplied by the current. Accordingly, in this case, the voltage is equal to the product of resistance and current squared. For example, the resistance is 50 ohms and the current is 10 amperes. We need to multiply 50 by 10, and then again by 10. We get a result equal to 5 thousand watts.
How to calculate current?
Our power calculation also works as a current calculator as it deals with a simple current formula. Once the voltage (V) and resistance calculation are given, you should use the formula to calculate current from power. You can calculate the current using this formula!
Current formula:
[Current (I) = Voltage (V) ÷ Resistance (R)] I (A) = V (V) ÷ R (Ohm)
For example:
Find the current flowing through a 3 ohm resistor when a potential difference of 30 V is applied across it.
Solution: Current (I) = V ÷ R; I = 30 V ÷ 3 Ohm; I = 10 A
Current to power conversion calculator
In the middle of the last century, most homes had a fairly limited number of electrical appliances - a radio, a television, an electric heater and a few incandescent lamps. Today the situation has changed radically - the number of all kinds of electrical appliances and gadgets that we use every day is constantly growing, and, accordingly, energy consumption is growing. Against this background, residents of houses and apartments increasingly began to abandon traditional single-phase inputs, preferring three-phase input.
a three-phase network really have undeniable advantages that force us to abandon the traditional solution?
There is no clear answer to this question. Many people think that thanks to a three-phase network, they can easily increase energy consumption. However, not all so simple. As a rule, technical regulations for connection for single-phase networks provide a rated power of up to kW; for three-phase networks a power of 15 kW is provided. Thus, the difference in power in the three-phase input is insignificant or does not exist at all.
Another advantage of three-phase networks is considered by many to be the possibility of using input wiring of a smaller cross-section. Accordingly, the rating of the circuit breaker will also be lower.
However, the above advantages can hardly be considered significant. Moreover, the smaller cross-section of the cable and the lower rating of the machine will more than make up for a very large distribution board of a three-phase network. The impressive dimensions of the shield are associated with the size of the meter, which in the three-phase version is obviously larger than the single-phase one. In addition, three or even four circuit breakers are installed here, as well as three-phase RCDs, which have significant dimensions.
If we talk about the real advantages of a three-phase network, it is the ability to connect powerful three-phase energy consumers, such as electric boilers, asynchronous motors, powerful electric heaters, and other devices. Connecting powerful consumers does not lead to phase imbalance, which is typical for a single-phase network.
In general, the topic of phase imbalance is quite serious. As you know, all main power lines are three-phase. It is almost impossible to ensure a uniform load on all three phases, as a result of which the voltage on the phases is never the same. Three-phase input does not solve this problem, since many consumers are connected to this network. To partially solve the problem, you should distribute the load across the phases as evenly as possible.
In single-phase networks, phase misalignment leads to the supply of reduced voltage to consumers. For owners of three-phase networks, this problem is not relevant, since they have the ability to connect the most important and powerful single-phase electrical appliances.
The voltage of three-phase electrical networks is 380 V, which is significantly higher than the traditional voltage of 220 V. This imposes additional responsibility on consumers, who are advised to pay increased attention to compliance with electrical safety rules. Compliance with fire safety standards is no less important, since three-phase input is more dangerous in the event of a short circuit. As follows from the above, three-phase input has both advantages and disadvantages.
First, let's list the advantages.
• Possibility of redistributing the load between phases to avoid phase imbalance.
• Possibility of connecting three-phase electrical appliances to the network. Perhaps this is the most attractive advantage of three-phase networks.
• If you have permission from the electricity sales authorities, it is possible to increase the maximum permitted power consumption. Unfortunately, three-phase electrical networks are not without serious disadvantages, including:
• Significant dimensions of the distribution board. For owners of cottages and large estates, this drawback is not relevant, however, in small apartments and houses, the presence of an oversized panel is not entirely appropriate.
• The need to equip the network with modular surge suppressors. By the way, it is recommended to install this protection element in single-phase networks, but in three-phase input this is a mandatory measure.
To summarize the topic, it can be noted that the installation of a three-phase input is advisable for houses with an area exceeding 100 square meters. meters. “Three-phase” is also relevant for premises in which it is planned to connect many single-phase consumers - the ability to redistribute the load will help to avoid phase imbalance. Well, and finally, three-phase input is the only condition that allows you to operate electrical equipment designed for 380 volts.
It is not recommended for other consumers to switch to a three-phase network, since this will not add anything to them except unnecessary problems and red tape.
Risks are insured!
ORTEA equipment is insured for three million rubles.
Read more »
ORTEA – quality guarantee!
ORTEA stabilizers are provided with two years of full warranty and three years of free post-warranty service at official service centers.
Read more »
Stabilizers Site map
Single-phase Atlas Vega Antares Gemini
Three-phase Orion Orion Plus Aquarius Sirius Odyssey
How to choose How to choose a stabilizer? How to determine power?
Services Warranty Delivery Installation Payment and returns
About the company News Articles Presentations Documents Privacy Policy
Contacts Italy Russia Kazakhstan Belarus
Moscow, Sevastopolsky Avenue, 56/40 © 2022 ORTEA LLC
+7 (495) 518-51-11
Request a call
| Moscow, Sevastopolsky Avenue, 56/40 © 2022 ORTEA LLC |
how to find resistance?
power calculation is also called resistance calculator because it helps to calculate the resistance calculation. Once the voltage (V) and current (I) are given, you can determine the resistance using a simple formula for resistance.
Resistance formula:
[Resistance (R) = Voltage (V) ÷ Current (I)] R (Ohms) = V (volts) ÷ I (amps)
For example:
Find the value of an unknown resistor that drops 5 V when a current of 20 mA flows through it.
Solution: Resistance (R) = Voltage (V) ÷ Current (I) in amperes; R = 5 V ÷ 20 mA; R = 250 Ohm
How to find out the current strength, knowing the power and voltage.
To answer the question of how to determine current, you need to divide the electrical voltage by the total number of watts. In this case, you can do all the necessary calculations yourself, or you can resort to a special online calculator.
Calculation of power indicator by amperes and watts.
You can find out the electricity consumption by the current strength of the resistor by multiplying the former by the resistance, expressed in Ohms. The result is a value expressed in volts multiplied by ohms. It turns out ampere.
Note! If there is no resistance, you need to divide the watt indicator by the current energy, that is, you should divide the watts by amperes and you will get the value of electricity in volts. You can understand the power reading through the amount of electricity with electrical voltage by multiplying the corresponding readings from the device.
Calculation of electricity through electrical power and voltage
how to find current strength?
The above mentioned Ohm's Law calculator is reliable for this! Once the current and resistance calculation are known, you can easily find out the voltage using a simple voltage formula:
Voltage formula:
[Voltage (V) = Current (I) x Resistance (R)] V (volts) = I (amps) x R (ohms)
For example:
Find the voltage applied across a 15 kΩ resistor when a current of 10 mA flows through it.
Solution: voltage (volts) = current (amps) x resistance (ohms); V = 10 mA x 15 kOhm; V = 150 V
For AC
However, for an AC electrical circuit, it is necessary to take into account the apparent, active and reactive, as well as power factor (cosF). We discussed all these concepts in more detail in this article: .
We only note that in order to find the total power in a single-phase network by current and voltage, you need to multiply them:
S=UI
The result will be obtained in volt-amperes; to determine the active power (watts), you need to multiply S by the coefficient cosФ. It can be found in the technical documentation for the device.
P=UIcosФ
To determine reactive power (reactive volt-amperes), sinФ is used instead of cosФ.
Q=UIsinФ
Or express from this expression:
And from here calculate the required value.
Finding the power in a three-phase network is also easy; to determine S (total), use the calculation formula for current and phase voltage:
S=3UфIф
And knowing Ulinear:
S=1.73*UлIл
1.73 or root of 3 - this value is used for calculations of three-phase circuits.
Then, by analogy, to find P active:
P=3UфIф*cosФ=1.73*UлIл*cosФ
You can determine reactive power:
Q=3UфIф*sinФ=1.73*UлIл*sinФ
This is where the theoretical information ends and we move on to practice.
how to find power?
The above calculator will help you find power using a simple power formula. If the voltage and current calculation for power are specified, then the power value can be easily calculated.
Strength formula:
Power (P) = Voltage (V) * Current (I)
For example:
If applying a voltage drop of 15 across a resistor causes a current of 10 mA to flow through it, then how to estimate the power dissipated across it.
Solution: P = V * I; P = 15 V * 10 mA; P = 0.15 W
Well, it's time to learn about the limitations of Ohm's law.
Relationship between work and power
The power of an electric current is estimated by the amount of work that is performed during a given time. From the physics course we know that DC power is expressed by a simple formula:
P = U × I
Direct current is an electric current that does not change its direction. If we return to the analogy above, then the water pressure is precisely direct current. Alternating current in a closed circuit changes its polarity at a certain frequency, and this leads to a voltage lag. For AC circuits, it is necessary to take into account the voltage shift, which in vector algebra is the cosine of the angle fi between the current and voltage vectors:
P = U × I × cosfi
If the vectors are co-directional (the angle between the vectors is 0 degrees), then the cosine of 0 turns into one. Obviously, in the work formula we can replace the product U × I with power and get a simple formula:
A = P × t or P = A / t,
from which it follows that power is the amount of work done per unit of time.
Our calculator is suitable for calculating the power of direct or alternating current: the formula includes the final power value, so the nature of the current is not important to us. To use the tool, it is enough to fill two out of three cells, after which the unknown will be calculated automatically. In school problems, you will need to calculate power as the product of current and voltage, and in everyday questions, power is always indicated on the electrical panel.
Limitations of Ohm's Law:
- Keep in mind that Ohm's Law cannot be applied to one-way networks - these networks contain one-way elements including diodes, transistors, etc., which means that these elements do not have the same voltage-to-current ratio for both directions of current.
- Optimistic studies show that Ohm's law does not apply to non-linear elements - these are elements in which the current is not directly proportional to the applied voltage, which means that the resistance value of these elements changes for different voltage values and calculate the current by power. Examples of nonlinear elements: thyristor, electric arc, etc.
Final words of the online calculator:
Our Power Calculator is a simple tool that uses the simple formula of Ohm's Law to determine Voltage (V), Resistance (R). Current (I) and power (P).
Other Languages: Ohms Law Calculator, Ohms Lov Lommeregner, Ohmsches Gesetz Rechner, Ohmin Laki Laskuri, Strømkalkulator, Kalkulator Ampere Watt, Ohm Hesaplama, Prawo Ohma Kalkulator, Calculadora Lei De Ohms, حساب قانون أوم, Calculateur Loi D'ohm, Calculadora Ley De Ohm, Calcolatore Ohm, オームの法則計算, Ohmův Zákon Kalkulačka, 옴의 법칙 계산자