In spring and autumn, icicles, accumulations of ice, and frozen snow form along the edges of roofs. During the day, melted water flows into drains, and at night it freezes. Gradually, this leads to the destruction of roof elements and facade decor. Sometimes blocks of ice fall down, which is dangerous for people and their property.
If you do not clear the roofs of icicles and snow, they become the causes of:
• gutter breaks due to the weight of ice; • increasing the load on the fastenings, their faster wear; • damage and scratches on pipes due to careless ice removal.
This is especially dangerous for complex roofs with a variety of internal corners, joints, and architectural elements. A reasonable way out of such situations is cable heating of gutters and roofs, which prevents the formation of ice.
The benefits of timely cleaning of roofs from icicles include:
• increased service life, more efficient operation of drainage systems; • the ability to avoid manual snow removal; • protection from icicles and ice blocks for people and property; • prevention of destruction of facades; • fully automated operation of heating equipment; • no additional costs during use.
Proper design of roof heating allows you to be an economical consumer of electricity. Heating gutters and drains with self-regulating cables, thermostats, and temperature sensors helps to effectively combat the undesirable consequences of harsh Russian winters. Typically, anti-icing systems are turned on only during thaws or snowfalls, when the ambient temperature is close to zero. Thanks to this, users save money on electricity bills.
Heating device for building roofs
The ability of a wire to heat up and give off heat is used in roof de-icing. Modern equipment helps protect cornices and gutters from annual winter problems: icicles, ice, and accumulations of snow masses.
Heating cables
Cable is the main element of roof anti-icing systems. When installed in a gutter system, it warms the roof runoff and prevents clogging. Installation of heating and the use of snow retention structures help prevent the melting of snow masses. The precipitation melts and then flows safely down the gutter.
For cable roof heating systems, 2 types of wires are used.
Constant power cables.
They have constant resistance along the entire length and a fixed length of sections.
Self-regulating cables.
In different temperature conditions, they change the level of heat generation, thanks to this they do not overheat, do not fail, and ensure the safety and reliability of systems. Heating cables can be easily cut into sections of arbitrary length up to several tens of meters; they are convenient to use. Designed with a flat cross-section for good surface contact and reduced heat dissipation into the environment.
Heating system elements
Any cable roof heating system includes heating sections and other components:
• control system, • fastening elements, • power supply system.
The control system consists of regulators, temperature and precipitation sensors. Thanks to it, you can use several algorithms for the operation of electric heating, taking into account its purpose, weather conditions, and the wishes of the owner or tenant of the building.
Fastening elements securely fix wires or sections without violating the tightness of the roof. The parts are resistant to temperature changes. Fastenings in the form of metal strips prevent the heating cable from moving. All elements are placed so that they are not noticeable and do not change the appearance of the coating.
The power supply system consists of equipment for supplying electricity to the heating sections: distribution boxes, power cables, plastic or metal pipes, boxes for laying signal wires.
Anti-icing roofing systems are universal - they are suitable for any type of structure. The equipment can be installed at ready-made facilities. For efficient operation, cables are laid in all places where ice most often forms, and in areas where melted snow melts.
The service life of electric roof heating systems is at least 10 years. The average operating time of installed equipment per season is about 1.5 months. Thanks to this, the cost of installing roof heating systems pays off in just 2–3 years. The annual allocation of funds from the budget for mechanical snow removal or preventive roof repairs requires larger investments than heating from ice.
What is a roof heating system
It is called differently: snow melting system, heating system or anti-ice. Such a device consists of a large number of sensors, wires, actuating and control devices, as well as heating elements. This complex prevents the formation of icing on the roof surface and prevents excess snow from accumulating.
It is not necessary to heat the entire surface of the roof, so for installing heaters, certain places are selected that are most susceptible to the accumulation of ice and snow, as well as places that can allow moisture to pass into the roofing pie. So the system must necessarily cover the edges of the slopes and the surface of the valley, as well as cover the entire length of the gutters.
Important! The roof heating system must be located below the snow guards. Firstly, this will prevent you from wasting too much electricity on heating areas of the roof that do not require it. Secondly, the melting of the snow cap on the roof increases the thermal conductivity of the roofing pie, which entails accelerated heat loss.
It is also convenient that the cables can be installed after construction at any free time, because the system is most often located on the surface of the roofing material.
roof heating Roof heating cable can be installed at any time Source kryshadoma.com
If the roof heating system of your house is done correctly and competently, then you can forget about snow falling from the roof. This device also lightens the load on the rafter system, which contributes to greater durability of the roofing pie. Additionally, you will receive good gutter protection. After all, there are often cases when it cracks due to the frozen water accumulated inside.
By the way, the anti-icing system saves home owners from regular manual cleaning of the roofing material.
See also: Catalog of companies that specialize in roof repair and design.
Principles of laying cables for heating drainpipes
The installation of roof electric heating is simple and does not take much time. Installation rules depend on the type of heating.
Endovy.
The cables are placed at least 2/3 of the length of the valleys in two threads. In places where the roof adjoins vertical walls, the wires are also laid in two threads.
Cornice.
The wiring is mounted along it in 2-3 threads if the width of the structure is less than 300 mm. When heating roof eaves, the calculation is 250–300 W/m². The wire is installed in the form of a snake. The laying step for soft roofs is 35–40 cm; on hard ones it should be a multiple of the pattern.
Drainage gutter.
At least two threads of wire are placed on it. The total rated heating power of the gutter per linear meter is 50 W or more.
Dropper.
Lay 1 or 2 threads of cable - this depends on the design of the drip line.
Drainage trays.
Calculation of heating of gutters depends on the size of the trays. At a rated power of 50 W/m with a tray width of 50–100 mm, two threads of cable are required, from 60 W/m with a tray width of 100–150 mm - at least two threads, from 75 W/m with a tray width of more than 150 mm - at least three threads.
Drainpipes with funnels.
The rated power depends on the pipe diameter. If it is up to 120 mm, it should be equal to 25–30 W/m, one thread of cable is required. To heat funnels with a diameter of more than 120 mm, two strands of wire with a power of 50–60 W/m are used.
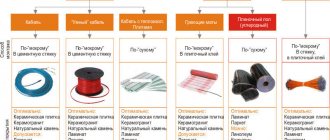
Types of heating cables
The main element of the anti-icing system is available in several variations.
Resistive heating cable
Although the definition of “resistive” for this type of cable is firmly established, it is not entirely correct. It would be more correct to call this cable option “unregulated”, since all heating cables are resistive in nature.
An unregulated cable has the simplest design. This is an elongated heating element made of a metal alloy with high electrical resistance (usually nichrome is used), enclosed in a shielding shell and insulation. Its advantages are the following:
- has low cost;
- during switching on it does not cause a significant jump in current (the so-called inrush current).
Resistive cable is easy to connect and inexpensive, but it uses electrical energy inefficiently
Flaws:
- Has constant heat output. Because of this, those areas of the roof that currently need less heat are subject to overheating, and even at the expense of the user (overconsumption of electricity). In addition, if there is insufficient heat dissipation, an unregulated cable may overheat and burn out. Particularly susceptible to overheating are the areas where two cable lines overlap.
- It is impossible to shorten the length of the cable in an already installed system, since this will reduce its electrical resistance and, accordingly, increase the current strength in the circuit.
- The linear power also depends on the length.
- If the heating core breaks, the entire cable becomes inoperable.
The unregulated resistive cable is available in two versions:
- single-core;
- two-wire.
In fact, a two-core cable also uses one core, only it is folded in half. This allowed us to win the following:
- There is no longer any need to close the circuit by pulling the other end to the connection point. Thus, the two-core cable is laid in one thread, and not in two, like a single-core cable, therefore, the danger of overlap when large masses of snow converges is eliminated. It should also be noted that a system with such a cable is simpler to design and install.
- The currents flowing in the cable cores, and essentially in the two halves of one core, have opposite directions, so the magnetic fields they generate cancel each other out. A single-core cable in close proximity to a person (for example, if the attic is residential) can cause harm to health with its electromagnetic field.
Zone resistive cable
The heating core is also made of nichrome, but the cable is designed slightly differently: it consists of two insulated current-carrying wires (phase and zero), and the heating wire is wound on them in the form of a spiral. In this case, the nichrome conductor is divided into segments, which at their ends are connected to the current-carrying conductors. Thus, a zone cable consists of many heating fragments connected to the electrical network in parallel. This provides the following benefits:
- The length of the cable can be reduced, since the current at the input decreases, and the linear power remains constant at any length.
- If the heating core breaks in any place, other areas remain operational.
When the length of a resistive cable decreases, its linear power remains unchanged
A zonal resistive cable, as you might guess, costs more than a regular cable.
Self-regulating cable
This cable, like the zonal one, has two conductive cores, but the heating wire is made of a completely different material: it is a special polymer with semiconductor properties, called a “matrix”. It is laid not around the current-carrying conductors, but between them. The peculiarity of the matrix is that its electrical resistance depends on temperature: the stronger the heating, the fewer current-carrying paths are active.
In the end, when heated to a certain temperature, the polymer generally turns into a dielectric, that is, it turns off, while areas with an acceptable temperature continue to function. The advantages of a self-regulating cable are obvious:
- Burnout in areas of overlap or due to insufficient heat removal is physically impossible.
- If the roof overheats in any place, the corresponding section of the cable automatically reduces the heat generation power, so that electricity is consumed very rationally. As practice has shown, on average, a system based on a self-regulating cable consumes 2 times less electricity than one equipped with an unregulated analogue.
- All current-carrying paths are connected in parallel, so the cable length can be reduced. A matrix break does not lead to cable failure.
- The service life is about 30 years. This is several times (!) more than that of an unregulated cable.
A self-regulating cable is more expensive than a regular cable, but it is much more reliable and economical to operate.
But there are also negative aspects:
- the cost of a self-regulating cable is 3 - 5 times higher than the cost of a non-regulated one (240 - 660 rubles / linear meter versus 90 - 150 rubles / linear meter);
- in a cold state, the matrix has a very low electrical resistance, so when turned on, a high inrush current occurs (more expensive protection devices have to be used).
Heating of roofs and roofs in residential buildings
To organize reliable protection from ice blocks or snow masses, you can use the FreezStop Roof kit. It is designed for high-quality heating of roof gutters: pipes, trays, small valleys, structures for ground drainage. The set of equipment promotes the formation of a channel for drainage of melt water, prevents clogging of the pipeline, and removes formed ice.
The system elements are installed in plastic or steel gutters, on roofs made of galvanized metal, metal tiles, metal profiles or soft tiles with a bitumen base. If the roof is made of zinc-titanium or copper, fasteners made of the same materials are used to heat the external drain.
Gutter heating kit
FreezStop Roof brand kits are included. include:
• self-regulating FreezStop cable, • KTU set for creating sealed heating sections, • perforated strip, • installation and use instructions, • packing box.
Each heating section consists of a cable of the required length, a power wire for connecting to the power supply, end and connecting couplings. Depending on the control method, total power, and the distance of the heating zone from the power source, intermediate connection boxes or control equipment may be required.
Cable design for heating a drainpipe
The FreezStop self-regulating cable is made of two parallel copper conductors. The gap located between them is filled with a matrix (semiconducting composition). It changes its resistance as the temperature of the object increases or decreases.
The system for heating gutters using a self-regulating cable has the following characteristics:
• supply voltage – 220–240 V, • maximum operating temperature – up to +65 °C, • minimum installation temperature – up to –30 °C, • linear power – 25 W/m, • operating temperature range – from –50 °C up to +50 °C, • flame resistant, • black outer shell.
To improve electrical safety and protect the semiconducting matrix, thermoplastic elastomer (TPE) insulation is provided. A tinned copper braid and a TPE sheath are placed on top of it. The shell has the following properties:
• resistance to ultraviolet radiation, precipitation; • high mechanical strength; • resistance to temperature changes.
These qualities ensure stability of operating parameters and reliability of the system throughout its entire service life - it is over 25 years.
Self-regulation principle
Heating occurs when current passes through the semiconducting matrix from one core to another. The change in matrix resistance depends on the temperature of the surface on which the cable roof heating system is mounted. The linear power of the wiring is affected by changes in temperature indicators: when they increase, the resistance of the matrix increases, and the power decreases, and vice versa. The manufacturer recommends using the cable in conjunction with thermostats.
To start operating self-regulating equipment, it is necessary to connect it to the electrical network when the first frost occurs and the temperature drops to +5 °C. The anti-icing system operates in automatic mode: voltage is supplied to the sections only during those periods when ice formation is most likely. If the ambient temperature is outside the range set on the regulator, the power supply is cut off.
There are several basic operating principles.
• If the air temperature is within the set range, but there is no snow or water in the trays, the cable reduces its power. • When precipitation occurs, the cable increases power to effectively melt snow or ice. • If you turn on the system late, if the trays are already filled with snow or ice, the efficiency of the equipment will decrease.
To automatically control and reduce energy consumption, various devices compatible with the FreezStop Roof kit are used.
• Temperature regulator TP 140
– wall-mounted operating temperature regulator.
• Electronic thermostat RT-330
– a device for heating control, installed in a cabinet with DIN-rail mounting.
• Repeater-relay “Roomstat” 190
– a device for connecting an additional load. It is ordered in addition to the kit when the total system power is over 3.5 kW.
Installation of a roof heating system
First you need to figure out which area of the roof requires heating. As already mentioned, these are valleys, overhangs and places where large amounts of snow and ice accumulate, as well as gutters. It is worth noting that the benefit from partial heating of areas that need it is significantly lower than from heating the roof in all problem areas. Once you have decided on the area that needs to be heated, you need to calculate the required amount of materials and purchase them.
So, after all materials have been selected and purchased, installation can begin. Below you will find information on how to correctly install the entire system.
It is recommended to entrust this procedure to professionals who have experience in organizing roof heating.
Experienced hands will not make mistakes when installing a roof cable heating system Source promalp-moskva.ru
The first step is to completely clean the entire surface of the roof, as well as the gutters, of debris or leaves. Next, the fastening tape is installed in the required places. The next stage is installation of the junction box. It is worth bringing and securing the “cold” end of the cable, previously threaded into the corrugated tube. After completing this procedure, you should lay out the cable inside the gutters, securing it with the tendrils of the fastening tape. Now you need to secure the wire inside the drainpipe. To do this, the cable is attached to the chain, for example, with plastic ties, and this entire system is threaded into the pipe. After this, it is worth securing the upper segment. The bottom edge can be secured using metal ties. Next, you need to lay the loops over the surface of the roof and secure them using the tape's tendrils. If the roof slopes are too steep, then it would be better to add plastic ties. Now you can install weather sensors. They should be located on the north side of the building next to the distribution box. The next step is to check the entire wiring system. The quality of the system can be determined by measuring the resistance in the circuit and comparing the readings obtained with the data specified in the product data sheet. All that remains is to secure the control panel inside the room. After installation is complete, you need to measure the system temperature to compare it with the data you entered.
Structure of a heating system on the roof Source liderbudowlany.pl
Where is the equipment installed?
Heating sections
connected through a separate power wire with a circuit breaker installed in the distribution board. The circuit must contain a residual current device (RCD) with a rated operating current of no more than 30 mA.
Wiring
for power cables and power supply wires, sections are made in plastic corrugated or smooth pipes. You can also use metal hoses in grooves or plastic boxes. For structures with a fire hazard in the attic, power wiring and installation wires are laid in steel pipes.
Thermostats
TP 140 is built into a wall indoors next to the heated zone. The RT-330 electronic regulator with DIN rail mounting is mounted in a distribution cabinet. To do this, you can use an already installed distribution cabinet or a new separate cabinet with a circuit breaker and RCD. All equipment should be placed in dry rooms where the air temperature does not fall below +5 °C.
Temperature sensors
installed outdoors. For this purpose, use a sealed plastic box with a degree of protection of IP44. The sensor box should not be left in direct sunlight. The wire is led through a corrugated tube in pre-prepared grooves to the installation site of the regulator or through a plastic box.
The maximum cable length for connecting the roof heating to the thermostat should not exceed 82 m. If it is necessary to use a wire longer than 82 m, a repeater relay should be installed together with the regulator.
Precautionary measures
To avoid a short circuit, do not connect current-carrying wires to each other. The heating cable or section must be protected from mechanical stress and tension. Otherwise, you may damage the shell or allow moisture to get inside. Do not use PVC insulating tape to seal the ends of the wire. The manufacturer prohibits even short-term inclusion of a heating section rolled into a coil into the electrical network.
It is important to ensure maximum safety when installing roof heating from snow:
• carry out all work at height only in dry, windless weather, during daylight hours; • wear shoes with non-slip soles; • use insurance: cables, belts; • do not step on wet or slippery roofs; • install ladders or scaffolding on a flat surface - they must be securely fastened.
Before installation begins, the roof and gutters must be cleared of branches, leaves, and debris. It is necessary to eliminate leaks in the system, check the tightness of the roof, and check the tilt of trays and gutters.
It is necessary to correctly determine the length of the heating sections. To do this, make a sketch of the heating zones on a sheet of paper, specifying the dimensions and drawing a preliminary layout. The locations where the junction box and regulator will be located should be indicated. This scheme for connecting gutters and drains helps to avoid possible mistakes.
To effectively heat roof gutters and maintain the functionality of the equipment throughout the entire period of use, preventive maintenance is performed before the first use and the beginning of each season. It is necessary to clean the drainage system, roof, temperature sensors from dust and accumulated debris. Typically, soft brushes dipped in water are used as tools.
Installation of roof heating and gutters
To create a reliable system, a heating section or several sections are made. They are installed in the areas selected for this, then power is supplied through a separate power wire that has its own circuit breaker.
In a hanging tray. A perforated strip is inserted into it, then bent along the profile of the tray. It is necessary to bend the number of strips specified in the project. A heating section is attached to them, which is then placed in a tray. Rivets are used to secure the strips. The connecting and end couplings are fixed in the upper part of the tray. For this purpose, strips or rivets are used.
In the gutter.
The installation procedure for roof heating will be the same as for a suspended tray.
In the drainpipe.
Below, at the pipe outlet, it is important to organize enhanced heating - create a loop from the heating section. For this purpose, remove the lower drain pipe, form a loop, and fasten it with a perforated strip. After this, you can install the pipe in its intended place, and secure the edge of the loop to its end.
Connecting the section to power supply
To connect the section to the power supply, the power wire is used as follows:
• current-carrying cores of the matrix – L (phase) and N (zero), • shielding braid – PE (protective grounding), • the section is connected directly to the temperature controller or circuit breaker through the power wire.
For the convenience of connecting several sections, you should use a junction box fixed in the heating zone. It is usually mounted on the wall under the roof. The heating sections are connected on one side of the box, and the power cable is supplied on the other.
If the box is installed in an area of possible precipitation, it and the cable entries are made sealed. The degree of protection must be at least IP 55. It is also important to ensure free access for servicing the equipment.
Heating of roofs with cables in private houses
As a rule, houses in the private sector have a pitched roof. The roofing material is metal tiles.
To heat a house on the roof:
• 1 or 2 strands of heating cable are laid in each recess of the metal tile or metal profile, • it is attached to the lower snow retention pipe, • it is placed on the upper element of tubular snow retention systems.
Wiring must be installed in all gutters, gutters and downpipes around the perimeter of the roof. It is possible to additionally install roof heating in a private house in problem areas such as a valley or other elements with a complex structure. If there is no drainpipe or gutter along the edge of the roof, one thread of wire is suspended under the roof - it “cuts” the icicles.
Roof heating and its functions
Now this innovation is just coming into widespread use. Many people neglect roof de-icing work because they are afraid of wasting energy and money on creating the system itself. However, it is worth considering that this approach can lead to accelerated failure of the roofing pie. This will entail unscheduled repairs, and, consequently, unnecessary financial costs. Let's figure out how roof heating protects the roof.
So, the use of this system allows you to get rid of systematic ice, which causes significant damage to the structure, violating its waterproofing. By the way, you shouldn’t hope that timely cleaning will solve the problem. It will not cope with all the moisture that accumulates on the roof and gutters. In addition, when heating the roof, you get rid of falling icicles and snow, thereby increasing safety.
There are other ways to combat icing. For example, installing a special attic ventilation system or treating the roof with anti-icing emulsions. However, all these methods are imperfect, require constant financial costs and take a lot of your time, and also lower the temperature inside the building. Therefore, the best option is proper roof heating.
Installation of an icing channel will help get rid of many problems Source eurohouse.ua
Heating of roofs from ice in multi-storey buildings
As a rule, office and business centers, schools, administrative buildings, and apartment buildings have a flat roof.
There are a number of principles for heating roofs and roofs of this shape.
• A flat area around the funnel with an area of 1 m² must be heated at a rate of at least 250 W/m². • If the architect provides a warm under-roof room, they organize heating of the drainage funnels, the upper and lower parts of the drainpipes. • In other cases, when heating funnels on the roof, the pipe is heated along its entire length.
Video description
You can familiarize yourself with the installation procedure for heating the roof, gutters and gutters by watching the video:
If the test shows the correct result, it means that the anti-icing system was installed correctly. In this case, you get good, reliable heating of the roof and gutters. Such a system will increase the service life of the roof, and will also eliminate the inconvenience associated with falling icicles and snow from the overhangs.
Heating of industrial buildings
At pumping stations, oil depots, and shipping terminals, complex systems of measuring and process pipelines, tanks, and buildings are installed that need to be heated in cold weather. At oil refineries, freezing of process units, treatment facilities, and transport routes must also not be allowed.
In winter, serious problems arise in the fields when transporting oil, water, gas, and various process fluids. If circulation stops, any compositions, especially highly viscous or waxy oils, freeze and clog the lines. Most often this leads to pipe ruptures. High viscosity is the cause of overloads of pumping units and excessive consumption of electrical energy.
At industrial enterprises it is necessary to install equipment that protects against freezing. Industrial roof heating is used to maintain specified temperatures in containers and pipelines. Using cables, you can protect any devices from damage, including those in hazardous areas. Thanks to this, you will maintain the impeccable quality of petroleum products and various technical fluids. At the same time, the operation of heating tapes will always be safe.
Self-regulating heating cables
Products of the SST PROFI brand, VL, VM, VR, VC, VX series, have a flat shape. The semiconducting matrix is made of materials that change resistance when temperatures change. It is fixed between two conductive wires.
The linear power of each point of the heating tape corresponds to the temperature conditions. This allows you to save energy by preventing overheating at the intersections of cables. The outside of the matrix is covered with a layer of elastomer insulation and braided tinned copper wire. They provide reliable grounding and mechanical strength.
Tapes are used in the following areas:
• food industry; • electric power industry, fuel industry; • ferrous and non-ferrous metallurgy; • chemical and petrochemical industry; • mechanical engineering and metalworking; • forestry, woodworking industry; • farms.
VM cables
with a power of 11 or 17 W/m protect against freezing and maintain the required temperature in small-diameter pipes, small-sized tanks, and process equipment with an operating temperature of no more than +65 °C.
VL cables
have a power of 23 or 27 W/m. They are designed for more intense electrical heating of roofs and gutters than VM. With their help, you can protect pipes with a diameter of up to 10 cm from freezing, compensate for heat loss during the transportation of technical fluids, and warm up industrial installations.
VR cables
suitable for industrial and architectural heating. They have a power of 11, 17, 27 or 31 W/m. Heating tapes help effectively combat icing of elements of industrial structures. The shell is made of elastomer, resistant to water and direct sunlight. The fluoropolymer shell reliably protects against corrosive chemical solutions and vapors. The operating temperature, as in the cases of VM and VL, does not exceed +65 °C.
VC cables
designed for use in harsh conditions. Heating tapes have a power of 17–60 W/m. They operate at temperatures up to +120 °C, without load they can withstand temperatures up to +190 °C. VC cables heat process equipment, pipelines with petroleum products, and prevent the hardening of paraffins. The black fluoropolymer jacket is required for protection in corrosive environments.
VX cables
technical characteristics resemble VC, but have a red shell. It is made from resistant fluoropolymer VX-F for use in chemically aggressive environments: organic solvents, acids, alkalis. Such tapes allow you to build simple and effective roof electric heating systems. They have a wide power range: 10, 30, 45, 60, 95 W/m. The wire does not overheat and does not burn out even if it crosses itself.
Other industrial system components
Thermostats compensate for heat loss and optimize heating power by maintaining the required temperature. The RTM-2000 model is classified as a universal multifunctional multiprogram regulator. It is designed to measure temperature indicators and control the process of maintaining specified parameters in anti-icing systems in open areas. With the help of this regulator, industrial buildings, pipelines, tanks are heated, and various types of roof heating using electric cables are organized.
The thermostat offers 5 heating control algorithms. To select the most suitable option, use the on-screen menu. The advantages of the equipment include:
• control of four independent channels, • high accuracy of measurements, • noise immunity of all channels, • temperature range from –100 °C to +600 °C, • extremely simple setup, • mounting on a DIN rail, • storage of all parameters in non-volatile memory.
Algori allows you to use this model for de-icing of roofs, gutters, trays, drips, drains in order to clean them from precipitation and prevent the formation of ice. Using this program, you can also remove ice from open areas.
A large number of settings help adapt the thermostat to the local climate in order to use the generated heat with high efficiency. Thanks to this, when heating the roofs of buildings, you can save up to 40% of electricity.
Temperature sensors
continuously measure the performance of a variety of non-aggressive media: air, cement screed. The devices are used in conjunction with regulators in heating systems for drains, open areas, pipelines, and tanks. For example, you can install model TST01. Devices of this brand have different design features. Depending on the type of sensing element, they can be digital or analog.
To avoid rupture of pipelines and damage to surfaces, it is important to properly organize the heating of the internal drainage in any building. This can be done using the technological solutions proposed in the article. Cables laid in gutters or pipes will heat up to certain temperatures, melt the snow, and prevent it from accumulating. The melted ice will flow down in the form of water.
Installation
Installation of heating gutters is easy to do with your own hands; the main thing is to calculate how much energy the system needs. In most cases, wires with a power of 35 W are sufficient, but it is advisable to contact specialists so that they can help calculate these parameters individually, depending on the material of the drain and the climate of a particular region.
Photo - pulling wires
The entire heating system consists of a control panel and wires. The panel includes a general circuit breaker, one circuit breaker for each phase, a thermostat, a contactor and an RCD. At the same time, the following wires will be required:
- Heating units that will be installed in gutters and around funnels;
- Signal signals that will connect the thermostat unit;
- Mounting boxes for providing branching;
- Parts for hermetically sealed cable connections, couplings, etc.
Photo - connecting the cable yourself
Step-by-step instructions on how to install heating on a drainage system:
- A heating cable is stretched across the entire area of the pipes. Experts recommend installing it in several threads, then maximum operating efficiency is guaranteed. The number of cables is calculated based on parameters of 200 W per square meter;
- Using the mounting boxes in which the wires need to be laid, it is necessary to branch the heating system along the roof, laying it also in funnels and on the eaves of the roof. For installation, you can use double-sided adhesive tapes, since self-tapping screws can damage the integrity of sewer lines. But in a funnel or on the lower section of a drain (for example, if the gutter is led into the drainage system), the wire can be installed with rivets;
- It is not the whole cable that is brought out to the drip, but only 10 centimeters, since in this place the drainage system is located at a right angle to the wall of the house. The most important thing is to ensure that the pipes are heated at the junction of horizontal gutters and vertical drains;
- Next, you need to check the length of the wires and the heating of all the necessary sections of the roof, and install installation boxes in which control switches for heating the gutters will be located;
- When the power cable is laid, the signal cable is laid. It needs to be connected to the thermostat;
- Upon completion of installation work, all communications are called, their grounding is checked and the thermostat is adjusted.
You can buy systems for heating gutters in any city (Nizhny Novgorod, Moscow, St. Petersburg, etc.). The price depends on the type of wires used and the functionality provided. The most popular models are produced by Devi and Ultra (for plastic).
Which roofs produce more snow and ice?
As a rule, the roof of a private house is a pitched structure consisting of two or more slopes located at an angle of 30-50 degrees to the base. The roof structure is specially designed in such a way that melt or rain water is drained away as efficiently as possible, and snow melts away better.
Experienced craftsmen note that the following types of roofing are more actively covered with ice and icicles:
- Warm type roofs . Experts note that a warm roof, in which the slopes are thermally insulated and the attic floor is heated, is more prone to icing in winter. This is explained by the fact that due to the high temperature of the lower surface of the roofing material, the snow cap on the slope begins to melt, and when it freezes it becomes an ice crust.
- Roofs with metal coatings . Metal-based roofing materials, for example, metal tiles or corrugated sheets, have a higher thermal conductivity coefficient, so due to temperature changes they are more likely to become covered with ice than roofs covered with tiles, slate or asphalt shingles. For the same reason, ice formation occurs inside metal gutters.
- Roofs with a low slope . From slopes with a slope of more than 45 degrees, snow masses easily slide off on their own, and on gentle slopes, snow accumulates, and an ice crust forms in places where it comes into contact with the roofing material.
Causes of roof icing
Important! If a roof has at least one risk factor for icing, a roof heating system is required. The use of this simple and inexpensive device will help to significantly simplify and secure the operation of the roof structure, as well as increase its service life.
Why install heating and what options are there?
There are three reasons to install a special heating system on the roof:
- Safety of people, animals and personal property that may fall into the area under icicles and ice blocks. Agree, it’s a shame not only to get a concussion from a rolling ice block, but also to damage your favorite car.
- Reducing the weight load on the roof and the entire building that ice can create.
- Preserving the integrity of the roof and drainage system, protection from destruction due to the formation of ice.
But let's understand some individual concepts.
Roofs on which both snow and ice melt at a temperature of -10°C are called “warm”. This is where they have problems with icing and cannot do without additional heating. If the ice on the roof melts at an even lower temperature, such a roof is called “hot”, and a conventional cable heating system may no longer be sufficient.
In order to get rid of ice on the roof, the following methods are used today:
- The rarest type of roof heating today is electric pulse systems. They require expensive equipment, which pays for itself only in a few years, due to fairly low electricity consumption. But gutters and drains cannot be protected from ice in this way.
- Heating the roof with a heating cable is the most modern and safe way to get rid of ice. This system is convenient for heating not only the edge of the roof, but also gutters and drains, even of the most complex design.
- The third method is to apply special emulsions to the roof that prevent icing. But emulsions are not cheap, and they need to be applied to the roof several times in one winter.
The most popular is electric heating of the roof and attached gutters, which will be discussed further.
The main thing is to avoid mistakes!
Now let's look at all the most annoying mistakes in installing a heating cable, which can easily lead to problems.
Mistake #1. Rough installation
If you fasten the cable carelessly, it can easily be broken in several places. Because of this, the entire heating system is eventually destroyed.
Mistake #2. Mobility
If the cable is movable due to the fact that it is attached only to the mounting tape, it will not last even two years. And all because it will constantly be subject to mechanical impact from snow and ice.
Mistake #3. Incorrect fasteners
Heating cables for roofs cannot be secured with tape, which is used for installing heated floors. The clamps used are completely unsuitable for fastening the cable, and easily unbend under the pressure of sliding snow. Why then are clamps used for floors? This is a temporary measure, and their function ends when the floors are filled with cement screed.
Special plastic cable fasteners are also not suitable for this purpose if they are mounted with a click. In a few years, such a fastening will crumble due to fragility due to ultraviolet rays. And even more so, you cannot attach white plastic ties - only black ones, and only from a good manufacturer. Conventional ties not for roofing are, of course, cheaper, and visually hold the cable no worse, but they will not last more than one winter.
Mistake #4. Excess of mounting holes
Any hole in the roof, even one that is well sealed with sealant, begins to leak over the years. Therefore, it is absolutely wrong to strive to secure the cable as tightly as possible.
Mistake #5. Incorrect cable insulation
If a heat-shrink tube is installed on the tip of the heating cable and crimped with pliers, then when the wire is heated, the tightness will be lost. Can you imagine the consequences?
Mistake #6. No cable
The heating cable, of course, can be lowered into the drainpipe without a cable, but thermal expansion and the weight of the ice will do their job - the system will break.
Happiness on your head, or where do the icicles on the cornice come from?
Are you interested in knowing why icicles form on the edge of the roof? And where do they even come from in winter, because for this the snow needs to melt?
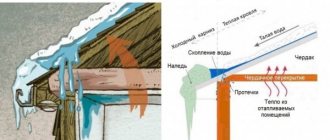
The thing is that snowflakes, falling on a relatively warm roof, melt and simply flow down. Gradually they overcome a surface that is warmer in temperature and end up on a completely cold cornice, which is located outside the building and no longer receives heat from it. This is where the water freezes, forming large icicles. And they are already causing us so many problems.
The formation of an “ice shell” on the roof indicates the presence of a serious temperature difference between the heated part of the roof and the unheated eaves. And there may be several reasons for this.
Reason #1. Incorrect thermal insulation
Note that they were put on the roof - most often due to improper insulation. So, if the heat loss of a house largely goes through the roof (due to the lack of normal thermal insulation), then this same heat slightly melts the snow on the roof. And that, as you already understand, creates the main problems.
And, if ice on the roof is a sign that the roofing pie was designed incorrectly, then literally in two or three years all this will come out sideways: rotting insulation, mold on the walls and the smell of dampness. That is why, ideally, a properly equipped roof does not need heating, because... ice does not form on it. Unless the weather is crazy.
Reason #2. Climate Features
According to the meteorologist, during the winter in Russia, on average, up to 70 temperature jumps over the 0°C mark are recorded! But such fluctuations are precisely what cause the most problems. So, the air quickly heats up and cools quickly, the snow begins to melt - and immediately turns into ice.
Severe frosts overnight give way to a thaw, and then unexpected sub-zero temperatures. Is this a familiar picture? Is this what the weather is like in that area? Thaws are especially problematic, when in one day the street temperature can easily be on both sides of the zero mark. As a result, the snow on the roof melts during the day and quickly freezes at night.
Reason #3. Complex roof structure
Popular roof turrets, internal corners, collars and horizontal platforms add their own complexity. All of them form additional snow cover, which causes even more problems. That’s why designers recommend for Russian latitudes to give preference to a simple roof shape with an angle of inclination of 30°, but in Europe let them fantasize, they don’t have that much snow.
Why heat the roof ↑
The main feature of the temperate climate zone (and adjacent to it) is seasonality. But the problem lies in the fact that during one winter period the weather changes many times, alternating thaws with frosts. As a result, the snow cover melts, after which all this “wet” mass accumulates on the eaves of the roofs, freezing in huge blocks. And this is just a global vision of the issue. Icing of cornices with drainage systems is also possible for two other reasons.
- Temperature changes over the course of one day. Most often, such processes are inevitable at the beginning and end of winter. When during the day the snow cover melts, moving towards the roof overhangs, and at night the entire mass freezes again. And this can be repeated over a long period, accompanied by the fall of new layers of snow.
- "Warm" roof. Today, installing a “warm” roofing pie is already commonplace, but most often a similar roof scheme is used when arranging a residential attic. This provokes the melting of the lower layer of snow with the subsequent flow of water to the overhangs, where it freezes.
Such processes are not only dangerous due to their collapses, which can injure people and damage, for example, a parked car under a house, but they also greatly increase the load on the roof eaves and drainage systems. Sooner or later this will cause deformation of the parts, with immediate destruction.
Options for solving the glaciation problem
There are several ways to resolve the issue:
- Constantly thoroughly cleaning the roof from the mass of snow (which is almost impossible).
- Design a roof structure with large slope angles. This will prevent large amounts of snow from accumulating on the surface. However, this option is not always possible, for example, the roof is already in use, it is impossible to create too steep slopes (the height of the structure increases and, as a result, the wind load on it increases).
- Install anti-icing systems along the edges of the eaves.
The last option is the most acceptable, since the installation of such devices is possible on already constructed roofs, and also without taking into account the angle of inclination of the slopes, and especially the type of structure with the flooring material.
What you should know about the systems, how to select the appropriate types along with components.
Why is this necessary ↑
Before determining the feasibility of installing anti-icing, you need to carefully consider the processes that occur when drainage elements are exposed to negative temperatures.
In winter, gutters are subject to increased loads. They undergo a serious test of strength under the influence of an avalanche-like descent of snow from the roof and accumulation of ice in the gutters. The latter are an inevitable consequence of the processes occurring at this time of year: water formed when the snow melts on the roof falls into the gutter. There it freezes layer by layer. It is also necessary to add the uneven loads that icicles exert on the gutters.
The only possible radical solution to the problem is an anti-icing system for gutters and roofs, that is, a device in the gutters, as well as in the pipes of heating electrical wires. It prevents melted snow from turning into ice, but, on the contrary, allows you to promptly remove melt water and other precipitation.
If the air temperature drops below zero, the water begins to crystallize. This negatively affects the condition of the drainage components and directly affects its performance.
- Reducing the maximum capacity of gutters and pipes. The formation of an ice crust prevents the passage of the required volume of liquid.
- Deformation and destruction of components. During the crystallization of water, its volume increases. This can damage the joints and disrupt the integrity of the highway.
- Formation of ice jams. Together with foreign debris, so-called ice plugs may appear in gutters and pipes. They prevent water from draining, causing it to fall on the walls of the building and the foundation.
Heat the roof or gutter?
How to select materials and install everything correctly, without overpaying for unnecessary things? Here everything will depend on the thermal insulation of your roof.
If everything is fine with it, warm air from inside the house simply will not be able to get out, the roof will not heat up, which means there will simply be nothing for icicles to form from.
In this case, ice will only appear at outside temperatures not lower than -5C.
Mistake #1
In this situation, there is no need to heat the roof itself, but it is enough to get by with heating only the drainage system.
Thermal insulation and energy efficiency, as they say, rule.
But if the roof’s thermal insulation is of poor quality, the snow begins to melt even at relatively low air temperatures (-10C).
In this situation, water will flow towards the bottom edge and gutters.
It will freeze there, turning into pieces of ice. Here you will already need to lay a cable for complex heating:
the roof itself
gutters
gutters
Our prices
The PRO-OBOGREV company has been installing roof heating systems for more than 10 years. The staff includes only professional employees who have all the necessary permits for electrical work. Our prices are as transparent and affordable as possible, and a wide range of products allows you to select components for installation taking into account all the customer’s wishes.
| Name of works | units change | price, rub. |
| Installation of heating cable in a drainpipe | m | 150 |
| Installation of heating cable in a trench | m | from 200 |
| Installation of heating cable on the roof | m | from 200 |
| Measurer's visit | PC |
View the full price list for roof heating
Components of the anti-ice system
Heating of the roof and gutters is arranged using a heating cable, the laying pattern of which depends on the type of roofing structure and gutter material. The main functional elements of the anti-ice system:
Distribution node
Designed for connecting cables (power and heating). May include the following elements:
- Power cable – for connecting the heater to the electrical network.
- Signal cable – for connecting temperature and humidity signal sensors with a thermostat.
- Connection couplings - to create a sealed electrical heating system.
- Mounting boxes.
Heating cable
The basis of the system is a soft heating cable, which consists of a conductive core placed in dielectric protection.
To connect the cable, special couplings and plugs are provided.
Weather station
It is a set of sensors for measuring humidity and temperature. More advanced models include sensors to measure the level of snowmelt and precipitation.
Sensors are installed on roof slopes and in the main elements of the drainage system - funnels, gutters, drains and pipes. They provide timely data collection for automatic heating control.
Logic controller
A control device that ensures the coordinated operation of the entire roof anti-icing system. A simple option is represented by a special thermostatic device designed for a minimum temperature range of +2 to -7 degrees.
A logical electronic controller is designed for automated control of the heating system. Such equipment is used to control the snow melting process, measure precipitation levels and ambient air temperature.
Based on the data received, the controller makes the necessary changes and selects the most efficient mode of operation of the heating system.
Automatic control panel
The equipment is provided to monitor the safe operation of all elements of the system. The following devices are used to organize the control panel:
- Input circuit breaker for 3 phases.
- Differential circuit breaker (RCD).
- 4-pole contactor.
- Signal lamp.
- Circuit protection for thermostat.
- 1-pole circuit breakers.
To fix the devices, special fasteners are used: roofing nails, rivets, screws, heat-shrinkable tubes and mounting tape.
Rules for operating systems
It is best to entrust the calculation of the required power level and determination of other parameters of the anti-icing system to specialists. If this is not possible, then you should take into account the operating rules and recommendations of experts, because the safety and efficient operation of the devices depends on this. The basic rules are as follows:
installation of the system is carried out only in dry, warm weather on a clean, dry surface; during the fastening process, it is important to avoid damage to the cable, and if this happens, then the heating element must be completely replaced; the roof is cleared of snow after the system is turned off and as carefully as possible - the cable and sensors must not be damaged; you need to install a circuit breaker to protect the circuit from short circuit; all sensors must be located in places accessible for maintenance; time relays and programmable switches will provide automatic control, since manual control is not always possible.
When operating the system, it is important to monitor the condition of the cable, promptly identify its damage and replace failed elements. If you need a durable and effective system, then it is best to purchase a high-quality cable that has a good outer layer of protection
Therefore, experts advise not to skimp on the quality of all components of the anti-icing system and to purchase a high-quality and safe option.
Video: connecting a self-regulating cable
The anti-icing system is convenient not only for roofs and gutters, but also for external staircase steps and other surfaces on which it is necessary to prevent the formation of ice.
At the same time, it is important to make sure that the electrical system is safe and carry out qualified installation in compliance with all the rules specified in our article
Installation features
Installation of a heating system for roof communications should be carried out taking into account the following rules and in the following sequence:
- It is necessary to take care of the presence of a temperature change controller, a power supply with a temperature sensor, and a precipitation control sensor;
- A wire of the required length is prepared according to measurements and diagrams. Ideally, install the cable before installing the top layer of the roof and finishing;
- The cable is tied into bundles using special clamps and then laid in trays and pipes. The cable at the edge of the roof is mounted in a zigzag, secured using special clamps;
- The heating cable is secured in gutters and pipes using mounting tape, in stripes across. If the heated drain or sewer pipe is longer than 6 m, the wire is first attached to a sheathed metal cable, and then the entire structure is lowered into the pipe;
- To heat drainpipes, lay 2 pieces of the required power at the same time. Installation is carried out from above and below.
- The place where the wire is attached must be inspected for sharp edges and unnecessary objects;
- Thermostat sensors are fixed;
- The control panel is installed;
- Commissioning work is being carried out.
Why is all this dangerous for the roof?
So why be afraid? Already the first water frozen on the cornice forms an ice dam, in front of which water continues to accumulate. According to invisible physical laws, the liquid now begins to move up the seams of roofing joints, just as water moves in communicating vessels (these are the ones used as construction hydraulic levels). And this, in turn, becomes the cause of leaks!
Moreover, ice manages to form not only on the roof, but also in gutters, and even in vertical drainpipes. And, if the melt water no longer has a way out due to the gutter clogged with ice, it begins to flow under the roofing. And there, moisture will always find a way out to the insulation and the internal space: holes on the waterproofing film after the stapler, small tears, damage, joints with roofing elements. The result is rotten rafters, damp insulation and the proliferation of fungus in the attic.
In addition, if you have ever encountered broken gutters, know that this is the work of ordinary rain and melted snow, when there is no protective anti-icing system.
Also, if there is no snow on the roof, because... it constantly thaws and slides down, then the roofing itself will eventually be subject to constant cycles of freezing and thawing. And this is a noticeable reduction in the life of the roofing. Moreover, the soft roof suffers the most, as it loses its stone chips and clogs the drains with them, the ceramic tiles burst, and water eventually flows under the rolled roofing. Even metal is torn by ice.
That is why heating of roofs is necessary for any building, and not just where icicles threaten to fall on the heads of city residents. Moreover, modern technical solutions are quite simple and accessible to everyone.