The need to arrange passage nodes
The main purpose of the roof passage elements is to remove contaminated and exhaust air. The design of such elements is carried out in accordance with GOST 15150, where the distances from the passage unit to the edge of the slab, as well as the diameters of the holes that are located in the floor slabs, are precisely determined. It is possible to equip passage units not only for roof ventilation, but also for chimney systems in those buildings that are equipped with fireplace or stove heating. This method of installation is sometimes called roof penetration.
Based on the type of roof structure and the ventilation intended for it, the air duct passage through the roof can have the following forms:
- square;
- round;
- oval;
- rectangular, etc.
In appearance, the nodes resemble holes made in the ceilings. Metal pipes are passed into these holes, which are mounted on the roof or on reinforced concrete glasses. The thickness of the material used should not be less than 1 millimeter. Manufacturers produce ventilation units of various sizes, this applies to both their length and thickness. The type of ventilation system that serves as the connection point for the pipe can be either natural or forced.
Before you finally make a decision in favor of one type or another, you should focus on factors that can influence your choice, such as:
- humidity indicators;
- gas pollution coefficient;
- the lowest and highest air temperature inside the structure;
- dust factor, etc.
The roof passage element is mounted using special reinforced concrete systems by fixing them to anchor bolts, which, in turn, are installed in the glasses during their construction.
The entire installation process depends on the following criteria:
- angle of inclination of the roof slope;
- interval from penetration to roof ridge;
- roofing thickness;
- the area that the space under the roof has.
If the base of the floor is reinforced concrete, then at the location of the ventilation fungus on the roof it is necessary to use special slabs equipped with ready-made holes. If the diameter of this hole does not coincide with the integrity of the slab, then in the area where the roof penetration is installed, places made of concrete in the form of a monolith are installed.
In this case, the passage through the roof with a light metal frame will be the same, but the glasses must be made of metal. A large building, which carries the functions of residential, industrial or civil purposes, requires calculation of the location of roof passages at the design stage.
Installation of ventilation, detailed in the video:
Advantages of using heating
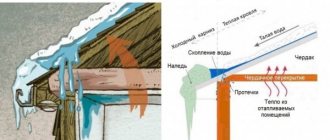
After temperature changes and various unwanted precipitation, the appearance of icicles and hummocks on the roofs of buildings is observed. Eventually:
- the weight of frozen water damages the roof;
- falling icicles can become a serious threat to life;
- icing of the drainage system causes their destruction and roof leakage.
Installing a cable that has a heating purpose, intended for the roof, allows you to remove ice without damaging the structure. However, there is absolutely no need to constantly and regularly spend money on the services of professionals for high-quality cleaning of the roof from snow cover.
Is it possible to lay a cable on the roof of a building according to the PUE?
Laying electrical wiring on the roofs of residential and public buildings, on the roofs of entertainment and entertainment enterprises, in accordance with the PUE, is not allowed (clause 2.1.75). The exception is when it comes to power supply inputs to buildings and branches to them. The rules use the “except” wording, from which it follows that the roof can still serve as a cable installation site when it comes to power input. However, paragraph 2.1.75. does not confirm this.
It is recommended (clause 2.1.79) that the entrance cable into the building be passed through the wall in a pipe (for more details, see the article: https://samelectrik.ru/kak-provesti-kabel-cherez-stenu.html). As a less desirable option, the roof of the house is used as the power input point. The cable must be in a steel pipe. The rule clause regulates the vertical distances between the roof and the wires. The minimum value of this distance prescribed by the PUE should be 2.5 meters. These conditions exclude the option in which a cable or wire is laid directly on the roof, that is, the roof cannot be used to lay a power line.
Important point! The effect of this chapter of the rules applies to wires or cables related to power or lighting networks with a voltage of up to 1000 Volts of direct or alternating current. This also refers to secondary circuits. If you are wondering whether it is possible to lay a heating conductor on the roof, the answer is yes, because... This is not prohibited by current rules. We talked in more detail about heating the roof and gutters in the corresponding article.
How the roof heating system works
In our country, winters are sometimes severe and the formation of ice is not uncommon. Snow accumulates on the roof, and when the temperature rises, it begins to melt, and at night it freezes again, causing dangerous icicles to appear on the roof. And all this leads to its destruction.
There is only one way out of this situation; it is simply to ensure the unhindered flow of water into the sewer. There are special devices that allow ice to melt on the roof.
But this system alone is not enough, because melt water will go into gutters and pipes and then freeze. Then there is a risk that the heavy ice that forms will tear off the fastenings that hold the pipes, and the whole thing will then fall down.
The main principle of this system is the implementation of heating in places:
- on roof ledges;
- in gutters;
- in all elements of drainpipes;
- on all roof connections.
GOST R 50571.5.52 requirements for external electrical wiring
Standard GOST R 50571.5.52-2011. “Low-voltage electrical installations. Part 5-52. Selection and installation of electrical equipment. Electrical wiring”, with a few exceptions, establishes requirements for electrical wiring without dividing them into internal and external.
We can highlight the most important requirements, which also apply to external electrical installations.
In accordance with 521.6 GOST R 50571.5.52:
– electrical wiring systems in pipes must comply with IEC 61386 (GOST R IEC 61386.1-2014 Pipe systems for laying cables. Part 1. General requirements is in force in Russia);
– electrical wiring systems in cable or special cable boxes - IEC 61084 (GOST R IEC 61084-1-2007 Cable and special cable boxes systems for electrical installations. Part 1. General requirements);
– electrical wiring systems on cable trays and cable ladders - IEC 61537 (GOST R 52868-2007 Cable tray systems and cable ladder systems for laying cables. General technical requirements and test methods).
Chapter 522 GOST R 50571.5.52 “Installation of electrical wiring under external influences” contains important requirements regarding the protection of electrical wiring from moisture, tensile forces on vertical sections of the route from its own weight, displacement of building structures and other mechanical influences.
Requirements for roof heating systems
When designing anti-icing systems, the following requirements must be taken into account:
- Heating cables must be certified to fire safety standards. For anti-icing systems, heating elements are selected for external installation. They have a sealed shell and a reinforcing braid.
- The system must be equipped with RCDs or automatic circuit breakers to protect against leakage currents and short circuits.
- The system must have a sensor and an adjustable switch on and off depending on the temperature of the air and the surface of the coating.
- Heating elements are installed along the entire water removal path, including collection trays and drainpipes.
- All electrical elements of the roof heating system must have a dust and moisture protection level of at least IP66.
Heating elements are placed on flat areas, at the joints of roof slopes of complex configurations. In most cases, it is sufficient to install heating cables along eaves, in downpipes and inside gutters.
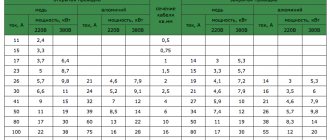
The total power is selected according to the table
| Location of heating cables | The total power of the heating cable on the roof above an unheated attic. W/m2, W/m | Total power of the heating cable on the roof above the warm room W/m2, W/m | Specific power of the heating cable W per linear meter |
| Along the cornice and valley | 180-300 | 300-400 | 15–50 |
| Plastic trays | 30-40 | 40-50 | 15–50 |
| Metal gutters | 30-40 | 50-70 | 15–50 |
| Drainpipes | 40-50 | 50-70 | 15–50 |
The table shows approximate values for the temperate climate zone. When designing anti-icing, it is necessary to take into account the average annual precipitation level and daily temperature difference.
Requirements of the GOST R 50571.5.51 standard
GOST R 50571.5.51-2013/IEC 60364-5-51:2005 “Low-voltage electrical installations. Part 5-51. Selection and installation of electrical equipment. General requirements".
At a minimum, this standard must take into account the following requirements:
512.2.1 Electrical equipment shall be selected and installed in accordance with the requirements of Table 51A, which specifies the required characteristics of electrical equipment appropriate to the external influences to which it may be subjected.
512.2.2 If the electrical equipment by its design does not meet the requirements that satisfy external influences at the installation site, then it can be used with the installation of appropriate additional protection when installing the electrical equipment. Such protection must not have a harmful effect on the functioning of the electrical equipment.
Cable laying methods
- On trays. This installation technology ensures an aesthetic appearance of the network, protection from aggressive environments and humidity. The choice of tray is carried out taking into account the weight and cross-section of communications.
- In the trench. The channel is being prepared for laying the network in the ground. Next, backfilling is done from below and backfilling is done from above. Installation of 6 wires is allowed in the trench.
- In the pipes. They protect networks from damage. The technology is used for organizing cable routes in places with unfavorable conditions (on aggressive soils, uneven surfaces, etc.).
- On overpasses. The structures are used for installation of communications in permafrost and aggressive environments.
- In special channels. They are made of brick or reinforced concrete and reliably protect wiring from mechanical damage.
- In sewer structures. This method provides protection against mechanical influences, soil shifts, electromechanical corrosion, and temperature fluctuations.
We carry out installation work in Moscow and the Moscow region:
Special cases of laying electrical cables on the roof
Installation of an open electrical power cable on the roof with a cross-section of less than 16 mm² is unacceptable. Among the installation methods in clause 2.3 of the Rules, there is also no mention of installing wiring in excess of this norm. The above rule is valid for power lines with voltages up to 1,000 W.
At the same time, a low-voltage heating cable is quite acceptable and even necessary to use where ice forms. This will allow you not to damage the roof eaves, and most importantly, protect yourself from the involuntary melting of a large amount of snow. The load gradually increases, the snow block and icicles create a danger especially for people.
Recently, the possibilities of laying communication cables are limited by the capacity of internal channels. This results in an extensive web of wires from different providers on the roofs of multi-storey buildings. Their installation also has its own specifics.
Note: There are specifics to laying power cables in pitched roofs. This problem has one more aspect: the roof, like the roof, can be of different types, including pitched ones, made of flammable materials, such as wood. There is a difference between the concepts of roofing and roofing as a whole, since in the latter case the attic space of pitched roofs may also be implied.
After the electrical cable is introduced into the facility, it inevitably passes through the roof attic; it is reasonable to assume that the above rules also regulate the conditions for further installation.
This is a hotel specificity and we will not consider it here.
Let's just say that according to the rules, the cable must be in a protected fireproof sheath (metal hose) secured to metal clamps, and pass through the roof attic exclusively in the open.
Installation of heating cable
Pitched roof designs vary, but one thing is certain: they all have a cornice. That is, there is a section of roofing along the lower part of the roof, and the cable in the form of a snake is laid along it. The width of the wire coil is set arbitrarily, but more often at 50 cm, in increments of 10 to 30 cm. The rest of it passes through the roof drainage system.
The heating wire is laid along the roof eaves
In order not to damage the surface of the roofing material, the heating cable is attached to it with special SLT-C clips. They, in turn, are mounted on self-tapping screws with a press washer. Where there are valleys, metal cables are used, since drilling a flat metal sheet can make an unsealed hole.
Most often, cables are laid on the roof in all its structures, including in drainage funnels and gutters. This is especially true for flat roofs. The electric wire runs along the inside of the parapet and is snaked into the drain for internal water drainage. As a rule, at a distance of at least 400 mm from it.
The laying of the communication cable allows it to be mounted on a rigid base, for example, a high roof wall for ventilation shaft outlets.
Selecting a cable for roof heating
For heating purposes, a self-regulating and, less often, resistive type of cable is usually laid. Self-regulating is able to independently adjust the temperature of the heat it generates. By the way, for comparison, the amount of energy released by a resistive cable is in the range of 5–30 W, and a self-regulating one is capable of delivering from 6 to 100 W per meter of roof area.
Self-regulating cable structure
Benefits of using a heating system
As a result of sudden temperature changes, precipitation provokes the formation of ice icicles and even large hummocks on the roofs of houses. As a result:
- falling icicles threaten the life and health of bystanders;
- the weight of frozen water damages the roof;
- Icing of gutters leads to their premature destruction and can also cause roof leaks.
Installing a heating cable on the roof makes it possible to successfully deal with ice, preventing damage to the roofing material and supporting structures. At the same time, there is no need to regularly spend significant amounts of money on paying for the services of industrial climbers to clear the roof of snow and icicles.
Marking of the roof passage unit
The modern construction market is ready to provide 11 types of ventilation passage units with different sizes. However, in some cases their manufacture requires a non-standard approach.
In the marking of passage units, the main designations are the letters “UP”, as well as numbers from 1 to 10, meaning that the units do not have an element that collects condensate, as well as a valve.
A series of numbers from 2 to 10 indicates that the passage has a valve in its design that operates using manual control, but does not have a condensate ring. The designations “UPZ-UPZ-21” indicate that the passage unit is equipped with all elements: manual control, valve, condensate ring.
Installation of SIP on wooden walls and siding
What to do if your wall is not brick or concrete, but is made of siding or other fire-hazardous material?
Here are the results of SIP burnout right inside the support clamps. Imagine this will be on your wall.
You can hide it in a metal sleeve, and then attach it all to the wall using clips with long self-tapping screws. To make it more beautiful, you can choose a metal hose with double insulation.
This option is widespread, but has both advantages and disadvantages.
Pros:
- the whole structure looks more aesthetically pleasing
- This option is applicable when you don’t want the SIP to protrude from the walls by as much as 6cm
- provides additional mechanical protection
Flaws:
- extra costs for a metal hose and fastenings to it
- No matter how hard you try, you will not be able to ensure sufficient tightness of the structure. Here is a real review from one of the users from forumhouse.ru
- By placing a SIP wire in a corrugation or pipe, you worsen its cooling conditions
At hot ambient temperatures and rated load, such a wire is no longer capable of passing the maximum possible current through itself without consequences. Which can lead to damage to the insulation.
Moreover, this will happen inside the corrugation and you won’t even see it. This applies primarily to main SIPs of large cross-sections.
Branch bushings into houses with a cross-section of 16 mm2 usually have a large reserve of rated current. For SIP 2*16 Inom=75A.
This is almost 2 times more than the input machine installed in most ASUs and metering cabinets (32-40A). To overheat such a SIP with a household load, you need to try very hard.
It is also important to remember that a simple SIP cannot be installed inside the house. To do this, it must be marked Ng-non-flammable
More information about such brands and their characteristics can be found in the article “Brands of SIP wires - differences, characteristics.”
Options for installing roof penetrations
Today, manufacturers produce passage units of various types:
- equipped with a valve;
- without valves;
- equipped with insulation;
- without insulation;
- equipped with technology that controls the opening and closing of valves.
Units that have manual control in their design are usually used where there is no need to regularly use multiple ventilation modes. The manual control unit includes:
- tailor's cloth;
- counterweight;
- cable;
- management sector.
A special mechanism helps control the valve, which regulates the position of the valve through two main commands - “open” and “closed”. To create penetrations for the roof, manufacturers use a black sheet of metal, the thickness of which does not exceed 2 millimeters, as well as a sheet of stainless steel, having a thickness of 0.5 to 0.8 millimeters.
The production of the passage unit can also be carried out on the basis of galvanized steel along with insulation, which is most often represented by a layer of mineral wool 50 millimeters thick. This option involves installing umbrellas or deflectors treated with zinc in the system. When installed on a fan assembly, its internal structure can be made of perforated steel and equipped with electrically conductive plastic tubes. With this installation method, the passage unit will also perform a soundproofing function.
Types of electrical cable
When choosing an electrical cable for a heating system, you should consider
:
- specifications;
- the ability to change the installation length (a cable with a fixed length of segments is more difficult to install);
- specifics of use (manufacturer's recommendations regarding installation location).
Domestic and foreign manufacturers offer various types of electrical cables
:
- resistive;
- armored;
- zonal;
- self-regulating.
Resistive heating cable for roofing is characterized by a fixed length of sections, which can be 10 - 200 meters. The released power is from 5 to 30 W/m. The advantages of the product include its affordable price. The downside is the same heat transfer along the entire length, while different sections of the roof require different amounts of heat. As a result, in some areas the system will run idle, while in others its power will not be enough for the necessary heating of the structure.
Armored electrical cable is a fairly new invention. Unlike resistive, it has a heating temperature of up to 150 °C and has increased mechanical strength. It is used for installation on existing roofs, since this type of heating cable is laid on a concrete base. During the process, you can adjust the length of the segment within 1-2 meters.
Zone cable is primarily intended for installation in drainpipes and gutters. Like resistive, zonal is characterized by a fixed heat transfer power (up to 200 W/m). In this case, the installation of heating cables on the roof can be done with free adjustment in length during the installation process.
Self-regulating is characterized by the ability to adapt to environmental conditions. Heat transfer varies between 6-100 W/m and completely depends on the amount of ice in the installation area. To install a roof heating system, a self-regulating thread can be laid in pieces of any length - only the maximum length is limited, which ranges from 6 to 150 meters, depending on the brand.
The self-regulating cable pays for its high cost during the operation of the system, which has less need for distribution lines and provides significant energy savings.
Anti-icing system for roofing
The roof heating system includes a number of devices and components, including
:
- heating cable with fasteners for the appropriate type of roof;
- roof funnel with electric heating;
- snow retention elements that prevent cable damage;
- communication lines (power and information wires, etc.);
- sensors, thermostats, automatic system controls.
The use of residual current equipment is mandatory! If the wire insulation is broken, such a device instantly de-energizes the heating lines.
Tips for use
The system will work long and efficiently if it is used correctly. Some procedures need to be followed:
- in the fall, after the leaves have completely fallen, it is necessary to clean the drainage trays with soft brushes so as not to damage the cable
- Recommended operating range of the system is from -15°С to +5°С
- prophylaxis should be performed every 3 months. During the inspection, the strength of the fastenings is checked and the insulation is restored.
- in the most difficult places, where pieces of ice or icicles may fall, the cable is protected with barriers
Fulfillment of these simple requirements will ensure high-quality and long service of both the heating element and the entire system as a whole.