Due to the improvement in the technical equipment of attackers, hacking or entering any premises today is only a matter of time, which in such situations is not on the side of the owner. To prevent unauthorized intervention, security alarms are now widely used as an effective means of preventing theft or reducing the extent of its consequences. How the alarm system works and what principles to follow when choosing it we will look at in this article.
Compound
A security alarm is a component of a complex of security systems designed to provide notification in the event of a violation of private property. The effectiveness of the system directly depends on the ability to assess penetration factors and transmit information about it. In accordance with clause 4.1. GOST R 52435-2015 the alarm system includes:
- Notification modules;
- Reception and control unit;
- Alert modules;
- Alarm control devices.
Rice. 1. Composition of a security alarm
Notification module
The notification module is a system of sensors that respond to changes in the parameter they measure (sound, movement, temperature, pressure, circuit integrity, etc.).
Rice. 2. Sensors for security alarms
Based on the principle of operation and purpose, there are a huge number of different categories of sensors, but the most commonly used sensors in security alarm systems are:
- Openings - a magnetic key/lock, one half of which is installed on the frame, and the second on the doors or window. When the latter are opened, the magnetic key moves away from the lock and opens the way for the signal to flow.
- Movements - perceive information about the state of the entire volume of premises and give a signal if there is any movement in space.
- Glass breakers – can be mounted both directly on glass and nearby. Most of these models respond to high- and low-frequency sound vibrations and vibration.
- Thermal - react to temperature fluctuations in space, since the temperature of the human body differs significantly from the environment.
If a sufficient level of the measured value occurs, the sensor converts it into an electrical signal, which is then transmitted via communication lines.
Reception and control unit
The receiving and control unit is used to take readings coming from sensor circuits. It collects and processes the received information and, if the signal data matches, it launches an alarm and notification algorithm. Typically, this unit contains an electronic controller programmed to operate on a number of incoming and outgoing communication lines.
Alert modules
Alert modules are designed to report intrusion or perimeter violation. To do this, they can transmit data to law enforcement agencies, security companies, display it or use other methods of influence. By type they are divided into the following types:
- Sound sirens are dynamic or piezoelectric sirens. Designed to scare intruders, cause panic and force them to leave the territory.
- Light - similar to the previous ones, but they have light effects. Depending on the method of influence, they can blink or simply turn on the light, simulating the movement of guards around the territory.
- Combined - combine sound and light methods of influence, are considered more effective due to increasing psychological stress in offenders.
- Telephone – transmit information via communication lines in the form of a recording to security organizations or an authorized department.
- Mobile – notify the owner and other structures about the incident via SMS notification.
- Telecontrol – provides data about an incident to a remote control or mnemonic panel.
In practice, not one, but several options are installed at once, which is why several data transmission channels are output from the receiving and control unit at once. In some security alarm models, logic can be set by priority or depending on influencing factors.
Control device
Security alarm control devices allow you to set an operating mode, activate or disable sensors, open doors or give a green light in certain situations.
For this purpose the following can be used:
- Keyboard with display – installed at checkpoints, indoors. Allows you to operate the security alarm by entering codes and commands.
Rice. 3. Keyboard with display
- A portable remote control or key fob allows you to change the configuration of work processes or interact with the security alarm in the friend or foe mode.
- The key is an original version of access through the system into the premises, into the territory of the facility. Cards, key tablets and other devices are used as keys.
Rice. 4. Using a tablet key
Principles and methods for constructing combined fire alarm systems
Security and fire alarm systems are a set of jointly operating technical means for detecting signs of unauthorized entry of a person (intruder) into a protected object and (or) a fire on them, transmitting, collecting, processing and presenting information in a given form to the user. In accordance with the international classification according to IEC 839-4-1-88, the fire and security alarm system refers to alarm systems designed to detect several types of danger. The corresponding Russian standard GOST R 50 775-95 defines such a system as combined].
The elements of the system are technical means of security and fire alarm systems. A generalized diagram characterizing the composition of the alarm system is shown in Fig. 1. For a specific system, the composition of technical means is determined by the method of organizing security, as well as the needs of the user. Depending on the type of security, it can be organized as autonomous or centralized . Autonomous security is characterized by the presence of one protection object, which is one or a complex of premises located within one or several buildings, united by a common territory. In this case, the required elements of the system are the detector, siren and their power source. Centralized security is organized for a large number of objects spatially distributed over a large area. In this case, it is additionally necessary to have a notification transmission subsystem. In practice, the connection between the detector, siren and the notification transmission system at the facility is always carried out through a fire alarm control panel.
In order to increase the reliability of the information received, when organizing the security of an object, multi-faceted alarm systems are used. Each of the boundaries is a set of jointly operating technical detection means (detectors), interconnected by an electrical circuit (loop), which allows issuing an independent separate notification about the penetration or attempted penetration of an intruder into a protected area (or several zones that make up the boundary). At the same time, detectors based on different operating principles must be included in each alarm line. In the case of autonomous security, a multi-line security alarm system can be organized using a multi-loop device that has a separate indication of the activation of detectors included in the alarm zone and making up the line or its dedicated part.
“controlled area” is also found in the technical literature . Usually this is a part of a protected facility, controlled by one security alarm loop (for security alarm systems), one fire alarm loop (for fire alarm systems), one security and fire alarm loop, or a combination of security and fire alarm loops (for security and fire alarm systems) . In a broader sense, this is a controlled object (or part of an object), for which its state can be unambiguously displayed using indication, warning, or transmitted to the monitoring station, and separate control is also provided (arming, disarming manually or automatically , facility equipment management, etc.).
Fig.1. Generalized diagram of the alarm system
1 - detector; 2, 8 — light and (or) sound annunciator; 3 — control installation (security and fire control panel); 4, 10 — power supply; 5 - device controlled by the control unit; 6 — programmable input device (cipher device); 7 — signal interface (notification transmission system); 9 — control installation (central monitoring console)
Generalized diagram of the alarm system
Features of designing security alarm systems for private security facilities
Features of the design and operation of an alarm system are: 1. In an alarm system, the operational reliability, sensitivity and noise immunity of each of its functional parts must not be inferior to each other in order to ensure an overall high level of security of the facility. At the same time, the purpose of creating an integrated alarm system is to increase reliability and (or) reduce the costs of its implementation. 2. When processing and displaying alarm and service diagnostic information in the fire alarm system, priority should be given to information that meets the requirements for ensuring the safety of people, as well as the fire safety of the facility. 3. When operating an alarm system, a response to alarm signals must be organized by the relevant services (facility personnel), taking into account the possible complex manifestation of threats. The design of security alarm systems and complexes and engineering and technical measures to strengthen the security of various security facilities on the territory of the Russian Federation are subject to the building standards “Security Alarm Systems and Complexes”. “Engineering and technical strength. technical means of security. Requirements and design standards for protecting objects from criminal attacks RD 78.36.003-2002. This document was introduced on January 1, 2001 to replace RD78.143-92 and RD78.147-93. These standards do not apply to facilities of federal executive authorities and organizations that have departmental or industry standards and requirements for their protection, agreed upon with the Main Directorate of Military Administration of the Ministry of Internal Affairs of Russia, as well as to facilities equipped in accordance with orders. norms and requirements of the Ministry of Internal Affairs of Russia. It is recommended to carry out design tasks in accordance with the guidance document “Automatic fire extinguishing, fire, security and fire alarm systems. The procedure for developing a design assignment" RD 25.952-90. The designed technical security means should be used in accordance with industry and departmental regulatory documents and lists of objects to be equipped with security means, approved by ministries and departments in the prescribed manner or by the project customer. The use of technical security means for equipping facilities must be comprehensive and take into account the type and tactics of security, the nature and significance of material assets, as well as the possibility of their movement during working hours and changing the configuration of the loading of protected premises. The composition of technical means of protecting objects should be determined depending on their membership in groups and subgroups of objects RD 78.36.003-2002. The effectiveness of the use of technical means in protecting objects of various forms of ownership depends on many factors that must be taken into account when organizing security. The main ones are: - costs of equipping the facility with technical security equipment and their operation; - reliability of the equipment used (failure rate and - the amount of possible damage from theft from a protected facility; - structural characteristics of buildings and premises of the facility; - social factors (crime prevention).
The assessment of the reliability of security of objects should be carried out according to the methodology set out in the “Recommendations for checking the reliability of security of state objects when putting into operation security alarm installations”, approved by the Scientific Research Center “Security” of the All-Russian Research Institute of Poultry of Internal Affairs of the USSR on March 27, 1991. At the same time, a technical and economic assessment should be developed justification for the option of equipping the facility with technical signaling means. The task of the feasibility study is to select a rational option, which is determined by the structure of the security alarm system. It is necessary to take into account the total costs of equipping the facility with fire alarm systems and their operation throughout the year, as well as the amount of possible damage from theft from the facility. Calculations carried out to determine rational options for equipping objects have shown that ensuring the required level of security reliability of an object is achieved by the number of security lines; minimizing the total costs of equipment for the object is achieved by varying the types of detectors and control panels in each security line. Techniques for feasibility studies of equipment options for specific facilities are described in detail in the following technical guidance materials; “Methodology for calculating the probabilistic characteristics of detecting object security alarm systems” VNIIPO Ministry of Internal Affairs of the USSR, M., 1990; “Feasibility study for the choice of options for equipping national economic facilities with security and fire alarm systems” VNIIPO Ministry of Internal Affairs of the USSR, M.. 1990.
Detectors in the fire and security alarm system
A detector in a fire alarm system is a device that generates a notification when a fire or intrusion occurs. Depending on the method of actuation, it can be automatic or manual (non-automatic). The functions of the automatic detector include detecting factors associated with a fire, as well as attempts at penetration or physical impact exceeding the normal level, and generating an alarm notification. The detector is a structurally complete device that performs independent functions in the alarm system. The closest in meaning to the word “detector” is “detector” (from the Latin detector - opener, detector). The security and fire alarm system can use both independent security and fire detectors, and security and fire detectors that combine the functions of a security and fire detector (for example, an ultrasonic detector “Echo-A”). One of the main components of the detector is the sensitive element, which performs the functions of an information converter and responds to external physical influence. If the sensitive element is isolated and placed in a separate structurally complete part of the detector, it is called a sensor. The classification of security and fire detectors in accordance with regulatory documents, as well as established practice, is based on the following main features: - type of detection zone; - operating principle; — the nature of the protected object; - method of operation; - method of power supply.
The type of detection zone characterizes the shape and size of the area controlled by the detector in relation to the entire protected space. In accordance with this, point (1), linear (2), surface (3) and volumetric (4) detectors are distinguished. The characteristic size of the detection zone (range) is an additional classification feature. One of the main features for classifying detectors is their operating principle . It characterizes the physical nature of the applied method of obtaining and converting information that underlies the operation of the detector. In other words, these are physical phenomena or effects used to construct a detector or its main component - a sensitive element (Fig. 2). Based on the nature of the protected object and the associated resistance to environmental climatic factors, detectors are divided into technical means intended for use inside buildings or outside (in open areas and perimeters of objects). Moreover, depending on the range of operating temperatures inside buildings, they are classified as detectors for heated or unheated indoor spaces. Based on the method of operation, a distinction is made between passive and active detectors. Active security and fire detectors emit energy from an electromagnetic, acoustic or other field, and the surrounding space is monitored by changing the parameters of the received signal. Passive detectors do not emit anything during operation, but only receive and analyze signals generated in the controlled area associated with the detected threat. According to the method of power supply, detectors are divided into those powered from a separate power source (autonomous or external), as well as from a two-wire alarm loop of the control panel. Currently used detectors use both of these methods, while the external source can be either a separate network power supply unit (type MBP-12 or the like) or one built into the control panel.
Fig.2. Operating principles of security and fire detectors
Operating principles of security and fire detectors
The established abbreviated designation of detectors is assigned by the parent organization for standardization in the field of security and fire alarms - the Scientific Research Center "Security" of the Main Military District of the Ministry of Internal Affairs of Russia, located in the city of Balashikha, Moscow region. The designation has the following structural formula:
where X1 is the abbreviated designation of the purpose: IO - security detector, IOP - security and fire detector; X2 - characteristic of the type of detection zone (the corresponding number is indicated in parentheses when determining the type of zone); X3 - principle of operation (the two-digit number corresponds to that shown in Fig. 2); X4 - serial number of development of a detector of this type (determined by the parent organization); X5 - serial number of the design; X6 - letter designation of modernization (Russian letter in alphabetical order, starting with A).
For example: IO 329-3 – surface sound security detector. In order to facilitate the understanding of a specific type, detectors, as a rule, have a name indicated in the technical documentation, which is an abbreviation or, more often, a conventional name. For example: SMK-3, “Harp”, “Falcon-2”. Let's consider generalized functional diagrams that differ for active and passive detectors (Fig. 3).
a)
1.1 ... 1.N – sensitive elements; 2 – signal processing block; 3 – display block; 4 – notification generation block; 5 – power supply; 5′ – supply voltage control.
b)
1 – receiving converter; 2 – radiating converter; 3 – signal processing block; 4 – generator 5 – display unit; 6 – notification generation block; 7 – power supply; 7′ – supply voltage control.
Rice. 3. Generalized functional diagrams of passive (a) and active (b) detectors
During operation, the passive detector (Fig. 3a) receives signals using a sensitive element (sensor) 1 and converts them into electrical signals entering the processing unit 2. In this unit, the signals are amplified and analyzed according to the characteristics identified. When a signal is identified as corresponding to a detected danger, a control signal is generated at the output of the processing unit and transmitted to the notification generation unit, which generates an “Alarm” notification in the communication line. The notification generation unit also controls the operation of the built-in light indicators (indicator) 3, which display the status of the detector. Power supply 4 provides power to the detector units. The dotted line indicates the option of powering the detector from the alarm loop, while control of the supply voltage (line 5/) is usually absent. For detectors with several detection zones, for example the “Window” series, several sensitive elements (sensors) 1.1 – 1.N can be connected to the signal processing unit. For an active detector (Fig. 3b), it is additionally necessary to have a generator 4 and a radiating converter 2. The parameters of the interface between the detectors are defined in regulatory documents and reflected in the technical documentation.
Reception and control devices
Reception and control devices refer to technical means of monitoring and recording information. They are designed for continuous collection of information from detectors included in the loop, analysis of the alarm situation at the facility, generation and transmission of notifications about the condition of the facility to the central monitoring console, as well as control of local light and sound alarms and indicators. In addition, the devices provide arming and disarming of an object according to accepted tactics, as well as, in some cases, power supply to detectors. Thus, devices are the main elements that form an alarm system (complex) at the facility. It should be noted that in centralized security and fire alarm systems, the terminal device of the notification transmission system can be used as a control panel. In accordance with the current regulatory documents, as well as the draft new standard for security and fire alarm control panels, it is possible to determine the classification of the control panel according to the following characteristics: - by type of organization of the alarm system at the facility; - according to the method of monitoring detectors; — according to the formed structure of AL wire lines; - by type of communication channel with detectors; - by information capacity; - in terms of information content.
Based on the type of alarm system organization at the facility, devices can be divided into: autonomous - designed to provide autonomous, separate alarm systems, in which notifications about the state of the controlled object are issued only to sound and light alarms installed on the protected object or in close proximity to it; local – designed to provide autonomous (local) alarms at the facility, in which status notifications, as well as control of the controlled loop (zones) are carried out using their own information display and control means (indicator panels, remote controls), which are part of the control panel; centralized – intended for centralized signaling and operation together or as part of an alarm monitoring system, in which notifications from the control panel are transmitted to the monitoring station of the alarm monitoring system through the use of various communication channels (telephone lines, radio channels, leased lines, etc.). Based on the method of monitoring detectors, control panels are divided into: addressless – devices in which the monitored detector is not identified (devices that have only addressless alarm loops or addressless communication channels); addressable – devices in which the address (identification number) of the monitored detector is determined (devices with addressable alarm loops, addressable alarm lines or addressable communication channels); combined – devices that have addressless alarm loops and addressable communication lines (channels). Based on the formed structure of AL wire lines, control panels are distinguished with: - radial structure; — ring structure; — tree structure; - combined structure.
Based on the type of communication channel with detectors, control panels can be divided into: - wired , using physical communication lines (alarm loop, address lines, electrical or radio broadcast network, optical fiber, etc.); - wireless using acoustic, optical, radio or other communication channels with detectors.
In general, information content includes notifications: - characterizing the state of the loop (address, zone) per one loop (address, zone), as well as the state and operating mode of the device; -displayed by internal light and sound indicators, indicator panels, device consoles, as well as external light and sound annunciators; — SPI transmitted to the monitoring station (for centralized alarm control panels). In terms of resistance to environmental climatic factors, devices belong to technical equipment intended for use inside buildings, and depending on the range of operating temperatures, they can be divided into devices for heated and unheated premises. According to the type of power supply and the organization of its redundancy: there are devices powered from an alternating current network, from an autonomous power source, without power supply redundancy, with redundancy from a direct current source, switched to a central monitoring panel. Based on the type of communication channels used, devices can be divided into wired and wireless (daisy chain). Modern wireless devices mainly use a radio channel to communicate with detectors.
The established abbreviated designation for control and control devices has the following structural formula:
where X1 is an abbreviated designation of the name of a technical device, characterizing its functional purpose in relation to the flow of information and the scope of application of the technical device: PKPO - security alarm control panel; PKPOP - fire and security control panel; X2 - type of communication channel used: 01 - via special wire lines of a radial structure; 02 - via special wire lines of a chain structure; 03 - via special wire lines of a tree structure; 04 - via dedicated lines of the telephone network; 05 - via telephone network lines switched during the security period; 06 - on busy lines of the telephone network; 07 - through the channels of compression equipment used in the telephone network; 08 - via low-voltage electrical network; 09 - via radio broadcast network; 10 - via radio channel; 11 - via optical channel; 12-28 - reserve; 29 - via other communication channels. X3 - used method of information transmission: 1 - digital; 2 - temporary; 3 - frequency; 4 - multi-wire; 5-8 - reserve; 9 - other methods of transmitting information. X4 - basic (without increasing) number of controlled directions. X5 - the maximum number of controlled directions achieved by extension using a block or modular design (in the absence of extension, X5 is not given). X6 is the serial number of the development of this type of technical tool. X7 is the serial number of the design modification. X8 is a Russian capital letter characterizing the modernization of a technical device (the first modernization is the letter A, subsequent ones are in alphabetical order). Example of an entry: PKPOP 014 - 4 - 3B - security and fire alarm control panel, using special wire lines of a radial structure, multi-wire method of information transmission, four controlled directions, registration number -3, second (B) modification. When using communication channels of several types or several methods of information transmission, instead of X2 or X3, the corresponding digital designations are given in a row. For example: 1004 (via radio channel and dedicated line of the telephone network). For ease of perception, most devices are assigned a name indicated in the technical documentation, which is a conventional name or its abbreviation. For example: UOTS-1-1A (security television alarm device), "Accord", "Rubin-8P", "Signal-20". The number in the name usually indicates the serial number of the development and (or) the number of connected alarm systems, and the letter is a distinctive sign of modification or modernization. A generalized functional diagram of an addressless control panel with low information capacity is shown in Fig. 4. The loop with detectors installed in it is connected to a control unit, which supplies it with power and analyzes several parameters. These parameters include, first of all, the amplitude values of the controlled electrical signals, as well as their time characteristics, which make it possible to isolate the signal when the detector is triggered or when the normal state of the loop is disrupted (its break or short circuit) and to distinguish it from a possible interference signal. At the output of the control unit, a signal normalized in magnitude is generated when the monitored parameters exceed the established threshold values.
Rice. 4. Generalized functional diagram of a control panel with low information capacity
It enters the processing unit, which carries out logical analysis and generation of output signals that control the unit for switching on the sirens, as well as the unit for generating notifications. The processing unit determines the tactics for arming/disarming an object, the mode for turning on light and sound alarms, and the characteristics of generated notifications.
Using indicators located on the device, on a remote display or control panel, in general, light and sound signaling is provided: - loop conditions; — operating mode of the device; — availability of main power supply; — presence and malfunction of backup power (discharge or malfunction of the battery). The siren activation unit directly controls external sound and light sirens. according to the accepted tactics. For stand-alone control panels, it is possible to combine light and sound alarms in one housing. The notification generation unit ensures communication between the device and a central monitoring console or other device, transmitting notifications about the normal or alarm state of the object in accordance with the established interface. It is necessary in the functional diagram to have a power supply that provides power to the device units. In general, the device may have additional output circuits to control engineering systems or devices for actively counteracting detected hazards. Control panels for local security must be able to connect a printer, computer or other device to ensure logging of events, or have a built-in non-volatile memory for storing event data with the ability to subsequently view events. Information about events must contain data on time, type of event and address (loop number, address, zone). Centralized security devices may have the ability to connect remote elements for monitoring the state of the control panel (attendance control circuit): a light indicator and a control sensor (electric contact or other type). In normal condition, the indicator light should be off. When the control panel operates in conjunction with a notification transmission system, when the control sensor is triggered, a corresponding notification can be transmitted to the control panel (for example, “Arrival of order”). The main parameters of the joints: “device - alarm loop”, “device - sirens”, “device - central monitoring console line”, “device - power source” are defined in regulatory documents, including current State standards.
Literature
1. GOST R 50 776-95 (IEC 839-1-4-88) Alarm systems. Part 1. General requirements. Section 4: Design, Installation and Maintenance Guidelines. 2. Kiryukhina T.G., Chlenov A.N. Technical safety equipment. Part 1. Security and fire alarm systems. Video monitoring systems. Access control and management systems M.: NOU "Takir", 2002 - 216 p. 3. Chlenov A.N., Kiryukhina T.G. Reception and control devices of security and fire alarm systems M.: Scientific Research Center "Security", 2003. - 112 p. 4. Antonenko A.A. Technical operation of security and safety equipment at the NOU “Takir” facility, M.: MAKTSENTR. Publishing house", 2002 – 48 p.
Principle of operation
Let's simulate a situation when some movement occurs in a protected space. The motion sensor will detect movement in the coverage area and send a signal via communication lines to the receiving and control unit. Here the received data will be processed and sent via loops to the executive body. The warning module will begin to turn on the lighting in the area and start a siren or strobe light.
Fig.5. The principle of operation of the security alarm
If the security alarm is connected to the security post or is displayed on the police console to the duty officer, then the data will be sent via the mobile channel to the authorized structures. In addition, information can be transmitted to the owner’s mobile phone through an SMS alert system or through a specialized mobile application.
The security alarm can be turned off using a separate button or by entering a special command code to stop. The system is triggered in a similar way by any other type of notification module.
Targeted security systems for objects
The classic security alarm system is analog (threshold) , the sensor generates a signal using dry contacts, and the system checks for the presence or absence of a short circuit (or a certain resistance value) on the loop. The system performs its functions perfectly when each security alarm loop is associated with a relatively small room, which is uniquely identified by the loop number.
If several rooms are “assembled” in a loop, for example, one floor, then identification will be difficult, or it will be necessary to divide the loop into several, lay additional cable lines and allocate additional contact groups on the control panels.
To avoid increasing the capacity of security alarm cable lines (loops), addressable systems have been developed.
An addressable security alarm system allows you to determine the location of unauthorized entry into an object with an accuracy of the location of the detector. This is ensured by the fact that each of the system’s detectors has a unique address registered in the system. This system is intended for use at medium and large facilities.
The main advantages of address systems:
- Accuracy of determining the location and method of penetration (the address of the sensor indicates the principle of its operation);
- Protection against substitution of the detector by an employee of the facility with the appropriate clearance;
- Impossibility of intentional shunting of relay output contacts;
- Fewer cable routes;
- Simple visualization of the location of the intruder detection on the plans of protected premises. On analog systems this is also possible, but with more labor;
The main disadvantages of addressable systems are the higher cost of equipment and the lack of a unified information exchange protocol between different manufacturers; for example, an analog detector with dry contacts will fit any analog (non-addressable) system, and an addressable sensor from one manufacturer will not fit a control panel from another manufacturer.
Analogue addressable systems combine the capabilities of the first and second. They can work with both types of detectors and are optimal for use in medium and small objects. Fire alarm monitoring systems constantly analyze telemetric information coming from detectors: air temperature, presence of smoke, etc.
Types
Security alarms are developed and implemented according to certain templates of technical specifications. The implementation of solutions to certain problems is carried out through systems of a certain type. Depending on the criterion, several types are distinguished; thus, according to the method of influence, there are two types:
- Active - have a direct impact on robbers by attracting security, alerting law enforcement agencies, and other methods of influence.
Rice. 6. Active type of security alarm
- Passive - create a number of effects designed to scare away intruders. This includes light, sound and other impacts that occur within protected objects.
Depending on the type of communication lines through which information about an incident is transmitted, there are two large categories - wired and wireless models.
Wired systems are divided into:
- Analog - transmit information through a loop over a wire to a specific notification point. They are a cheap, but uninformative system.
- Addressable - has an assigned address for each object, the information is processed by a microprocessor and transmits a signal about a specific sensor to the operator.
Wireless security alarms can also be divided into several groups, depending on the transmission channels:
- By radio signal - uses radio transmission devices to send an alarm signal, can be done with or without feedback;
- Via mobile channels – uses modems with classic or specialized SIM cards;
Rice. 7. Mobile transmission
- Via Wi-Fi signal – uses Internet resources to send alarm protocols.
Sensors
A reliable security alarm system also uses motion detectors, which are triggered as soon as an object is within the detection zone of the sensor. These devices come in different types, but for private security alarm systems, passive infrared motion detectors are used. They are cheaper than radio wave microwave sensors and more reliable than ultrasonic ones. Each sensor has a clearly defined detection zone.
Most infrared motion sensors have a zone length of 10-12 meters and a capture angle of 900.
Typically, such devices are installed according to the principle of one room, one sensor, but there are exceptions. If a room has several windows located on one wall, then an infrared “curtain” detector is installed, which forms a narrow vertical but extended horizontal zone that blocks all windows along the wall.
Sound (acoustic) sensors respond to the sound of breaking glass. They form an additional security line. As a result of installing three types of sensors, the room will be completely blocked and entry into it through the window and door is almost impossible. Vibration sensors respond to attempts to undermine or destroy (break) a wall and are used extremely rarely in household security alarms.
Sirens
In addition to sensors, any security alarm system must have a warning device. Most often, a low-current siren is used, combined in one housing with an LED indicator. Such a device, in case of violation, emits a sharp signal with a sound pressure from 90 to 115 dB, which will simply scare away the intruder. In addition, the sound of the siren along with the red flashes of the LED indicator will attract the attention of neighbors.
Power alarm
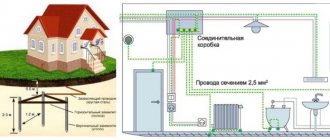
For reliable and uninterrupted operation of the security alarm system, care should be taken to ensure proper power supply.
Power outages require the use of power supplies with built-in batteries in security systems. Such devices allow the alarm to function normally for several hours. To perform installation work you will need a wire, cable duct and fasteners. The security alarm is wired using KSPV 4 X 0.5 wire. Two of the four wires are used to supply power to the sensors, and two more form a signal loop. To connect the network, use a ShVVP wire or similar. Installation of sensors and laying of the cable channel is carried out using dowels and self-tapping screws.
PKP - the heart of the security alarm system
The basis of the security alarm system is the control panel - PKP . For a simple security system, it is enough to use a device with one or two loops. Such a device is inexpensive, but has well-developed functionality and is perfect for a small apartment alarm system.
Common devices with one loop:
- Quartz
- Astra 712/1
- VERS-PK 1
The cost of the devices does not exceed 1900 rubles. The case of each device has a place for installing a battery. Arming and disarming is carried out using Touch Memory electronic keys, which are included in the delivery package.
Video on how to make an alarm from your phone:
Security alarm features
Before choosing a specific model, it is important to determine the main characteristics of the protected object. Namely, you must inspect the premises or territory to identify the most likely points of entry, points of storage of valuables, documents, etc. Determine where the control unit will be installed, the distance to the sensors and source elements, and whether communication will be established with the dispatch console.
For a private home.
In a private home, it is important to install both wired and wireless security alarm systems. It is important to note that control is established both inside the house and outside: at the entrance, near the gate, along the perimeter of the fence, etc. Along with classic security modules, the “smart home” option is gaining popularity today, which also provides the ability to control the open/closed position of windows and doors, program the reaction of sensors to movement in rooms, and much more. It also allows video surveillance of both individual rooms and the surrounding area.
For an apartment.
Depending on the size of the apartment, the area of the rooms and the number of windows, you can install a passive system that responds immediately throughout the entire home or an active system that transmits burglary data to the control panel. It is desirable that the security alarm monitors all rooms without exception; the coverage also includes loggias, balconies, storage rooms and other components through which penetration is possible. For small areas, you can use autonomous alarms that work only inside the apartment.
For the dacha.
The main difficulty of a summer cottage is its remoteness from the owner and, possibly, from a populated area, which significantly complicates the process of going to the site and actively responding. Therefore, a passive security alarm system that outputs data via a GSM channel to the owner’s phone is relevant for a dacha. It is also important to trigger light and sound alarms to scare away intruders.
For the office.
Rice. 8. Organization of an alarm system in the office
If the premises for an office are rented, then using a wired security alarm system is not practical; it is much more profitable to install devices that operate via wi-fi or a radio signal. In office settings, a video surveillance system is a good help, which, in addition to security functions, will help monitor the work of employees. Depending on the assigned tasks, the security alarm can have both active and passive versions. For example, in small buildings with departmental security or a watchman, a sounding siren will be enough to attract their attention.
Main types of security alarm sensors and installation locations
Motion (volume) sensor is a passive receiver of IR radiation.
Activation (opening of the internal relay contacts) of the IR sensor is initiated when a moving object with a temperature exceeding the ambient temperature (person) enters the coverage area. Standard viewing angles are 70-110˚, so a rational installation location is in the corner of the room, while ensuring effective coverage of the room volume. Installation height 2.2 – 2.4 meters from the floor.
To avoid false alarms, the installation location should be remote from heating appliances and radiators. It is not advisable to install it opposite window openings that are not covered with thick blinds.
Sunlight often triggers a false alarm, both by illuminating the photodetector and by heating it.
Reed switch is a passive magnetic contact sensor.
Consists of two parts: a magnet and a reed switch. Triggering is initiated by separating the magnet and the contact. Installed on doors and windows. A magnet is on the opening panel at a distance of 5-20 cm from the outer edge of the panel on top or (rarely) on the side.
The sealed contact group (with wires or connection terminals) on the box opposite the magnet when closing is at a distance of 0-5 mm from each other. For reliable operation, less than 5 mm is better. The contact opens when doors and windows are opened. The placement of unintended magnets near the reed switch is excluded to prevent the contact from “sticking”.
Security sensors include the following devices: glass break, microwave, microwave, combined and laser (see Types of motion sensors and their application). Temperature, humidity, level and fire sensors are connected to the alarm loop. In autonomous do-it-yourself alarms, they are used as desired.
Nuances of installation and assembly
Modern security alarm units can be easily installed by yourself, but some rules and nuances should be taken into account:
- If you install motion sensors, then you should take into account that in accordance with paragraphs 2.2.7 - 2.2.9 of GOST 26342-84, these devices have a gradation based on the volume of the room and the speed of movement of a person. Which you should consider when setting up protection.
- When choosing a wireless alarm, keep in mind that the coverage distance of the sensors depends on their technical parameters.
- When installing equipment outdoors, take into account the temperature conditions of your region, otherwise the security alarm may stop working at extremely low temperatures.
- If power surges occur, be sure to install a battery for uninterrupted operation.
- The fewer sensors you install, the less security alarm coverage and functionality you will have.
- Do not skimp on components; your safety and the safety of your property depend on their quality.
Installation and placement
During installation, the security system is conventionally divided into parts, on which their location depends. Control, signaling and power supply devices are placed separately from the sensors in poorly accessible places. Often, a single distribution cabinet is used for this, inside which the controls and batteries (if used in the design) are located. The opposite situation also happens, when the control panel is located in places where access is more convenient.
The sensors themselves are distributed according to their operating principles:
- laser and induction guarding the perimeter in the path of the alleged intruder;
- vibration, magnetic and linear in places of access to the room - windows and doors;
- motion sensors are installed so that their coverage area extends to as large an area as possible, into which an intruder is sure to fall.
Disguised wiring is laid between the sensors and the rest of the system. It is possible to use a radio circuit instead. Unfortunately, the latter is not reliable and is susceptible to interference from other electrical equipment.
What to choose?
On the modern security alarm market there is a fairly large range of products from a variety of manufacturers. Therefore, next we will consider the most reliable and proven companies that operate on the market:
- Jablotron is a world-class manufacturer producing the latest security alarm equipment;
- Visonic Ltd is an Israeli manufacturer of security alarms that has held a leading position in the market for about half a century;
- SATEL is a Polish concern whose products are characterized by affordable prices and acceptable quality;
- Sapsan is a domestic manufacturer of security alarms; the devices are reasonably priced and well adapted to our conditions;
- Ajax is a relatively new company that has already proven itself to be the best in the market.
List of used literature
When writing this article, the following textbooks were actively used:
- O. M. Lepeshkin, V. V. Kopytov, A. P. Zhuk “Integrated security means and technical means of fire alarm systems” 2009
- Vorona V.A., Tikhonov V.A. "Technical security and fire alarm systems" 2018
- G.M. Punegov “Secrets of installing security systems” 2017
- Biryukova O.V. "Electronic alarm systems" 2015
- Gruba I.I. “Security alarm systems. Technical means of detection" 2012
Let's take care of the alarm
Do you need a project?
A fire alarm project is needed, and not so much for formal reasons. Only a security guard with extensive experience will be able to accurately indicate the location of devices, their types and connection diagram. Otherwise, the flame may rage beyond repair, and the attacker, immediately spotting the “homemade” (they are well versed in alarms), will only grunt and, having “bombed the hut,” will sit at ease in the owner’s favorite chair, drinking the owner’s cognac, smoking the owner’s cigar, gently stroking the bag on her knees, tightly stuffed with the owner's goods and looking ironically at the sensors in full combat readiness.
However, security companies, generally rightly believing that the main thing is real security, not paperwork, often make concessions to potential subscribers: they agree to do a cheaper project, a sketch, or limit themselves to an even cheaper consultation: where to install which sensors, where to place the alarm control panel, what cable and how to connect everything.
Then, after checking the work, they put him under guard, and based on the documents, they pass him by retroactively. The owner is no worse off for this: once the contract is signed and the apartment is already under control, the security guards bear all the responsibility. The components of a modern fire alarm system are completely reliable; fire alarm maintenance comes down to periodic checks of its operability and readiness, which, together with the security company on duty, can be carried out by the owner himself, so, as a rule, there are no problems with service.