A standard question in the industry is how to deal with static electricity in production. Such a charge, accumulating on work surfaces, can lead to damage to expensive equipment, failure of entire production lines, injury or, in serious cases, even death of an employee. The nature of the phenomenon practically eliminates spontaneous dissipation: a charge is formed on the surface of the dielectric, in close contact (mechanical friction) with the conductor, between two dielectric shells.
The danger of static electricity in production is associated with the possibility of charge accumulation also under strong mechanical influence (impact, crushing, rupture) of the dielectric. Another dangerous type of static is atmospheric accumulation, which manifests itself as lightning. Potential removal is an important issue for industry: it will carry out the necessary measurements and take measures to neutralize the danger. We have our own mobile laboratory containing all the necessary instruments for measuring the danger of static electricity. After completion of the work, LABSIZ will generate a technical report suitable for submission to any supervisory authorities. It is possible for electricians to visit sites in Moscow and populated areas of the Moscow region.
Static Relief Devices
Our range includes the following devices:
- Devices that eliminate static voltage from film materials (high-voltage transformer with a special rail).
- Equipment for removing high electrostatic voltage that occurs in electroplating shops, electronic and medical equipment assembly departments, etc. (air ionizer guns).
- Fans that provide ionized air to industrial premises are devices that are optimally suited for removing static voltage in broadly focused areas. They are used in thermoplastic machines, in packaging printing devices, in assembly shops for medical and electronic equipment.
- Devices for measuring static voltage readings.
You can buy all the equipment we offer for antistatic production in production with delivery both in Moscow and in the regions of Russia. You can always get detailed information on prices, as well as advice on the use of static voltage removal devices from our consultants by calling the phone number listed on the website.
offers a wide range of devices for neutralizing static electricity produced by ELTEX (Germany).
During the production process associated with the processing of roll materials such as paper, foil, or film, a voltage of the order of tens, sometimes hundreds of kilovolts arises. Static electricity can completely stop a production process or cause irreparable damage to equipment. In addition, static electricity can cause serious fires.
Removing static electricity is a top priority in any industry involving the production and processing of roll materials.
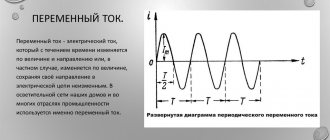
Static electricity: how an electrical discharge is formed and why it is dangerous - briefly
The word “static” implies a stationary state of matter. In relation to electricity, it is used to describe phenomena occurring in the surface layer or inside dielectrics associated with the formation, conservation and relaxation of charges.
How does a static charge arise in dielectrics, liquids and gases?
An ordinary neutral atom of a substance has a nucleus with a positive charge balanced by the number of electrons orbiting around it. If the balance of the atom is disturbed, then charges with different signs are formed:
- positive - when there are not enough electrons;
- negative - with an excess of electrons.
Particles of the same charge always repel, and those with opposite signs always attract.
Electrification in dielectrics is created due to the action of friction forces of dissimilar substances, which redistribute electrons. Inside gases and liquids, charge carriers are additionally ions:
- anions with a negative charge (-);
- cations - positive (+).
During electrification, dielectrics accumulate charges in such a way that the potential difference between neighboring substances can reach tens and even hundreds of kilovolts.
What is the danger of static electricity: 6 real-life examples
Static discharge occurs when the insulation layer between two charged substances breaks down. In most household cases, its current strength is quite low and does not cause much harm to a person.
In everyday life, we often use plastic combs when styling our hair, plastic bags, and polystyrene foam. These substances accumulate a negative charge, and its effect on the body is practically not felt.
The most powerful and insidious shock of static electricity is lightning.
The thunderstorm period covers the beginning of spring and all summer. It is associated with the movement of thunderclouds containing enormous moisture evaporation. Electrification occurs in the process of moving air masses under the influence of wind over very long distances.
Lightning has enormous destructive power. It is capable of splitting tall trees along the trunk, burning building structures, and damaging power lines.
Residential buildings can only be saved by a lightning protection system, which includes three components: a lightning rod, a lightning rod, and a building grounding system.
The second danger of lightning is the induction of dangerous electrostatic potentials on insulated metal parts, which operates according to the law of electrostatic induction.
They can cause serious harm to human health and damage electronic and electrical equipment. To prevent them, a potential equalization system for multi-storey buildings is used.
How does a car catch fire due to static discharge?
There are still cases at gas stations where, when pouring fuel into a car tank, sparks from synthetic or woolen clothing provoke the start of a fire.
Video bloggers often post similar situations on YouTube.
Why is static electricity dangerous during loading and unloading operations?
Just take 20 seconds to watch a short video from the owner of “Vidosika”, which clearly proves that the risks and dangers of losing health in this matter are very enormous, and jokes are not appropriate.
Why the car is electrocuted: 2 factors
Unpleasant sensations of static discharge accompany drivers when exiting a passenger car. This is explained by two reasons that you need to know:
- When a car moves, as a result of the friction of its body against the air, a fairly high electrical potential accumulates in the latter.
- The car owner's clothes made of synthetics or wool become electrified from contact and friction with the interior trim: seat and steering wheel covers, floor mats, upholstery...
To remove the accumulated static charge from the body, special grounding conductors are used - antistatic, made of conductive rubber. They are attached to the back, ensuring contact with the ground.
This principle is used to operate grounding circuits on gas stations transporting flammable liquids. Otherwise, they always accumulate a high potential that can cause a fuel fire.
A sequence of three simple steps allows the driver to painlessly remove the charge accumulated on the body from clothing while exiting the car:
- connecting potentials that arise on the body and the car - open the door and grab any metal part of the car with your hand;
- creating contact for painless flow of static discharge through the resistance of the shoe - lower your foot to the ground;
- get out of the car and let go of your hand.
How static electricity can damage electronic devices
Experienced radio amateurs know that semiconductor junctions of microcircuits and field-effect transistors are easily penetrated by the potential accumulated on the human body.
Simply touching the body of a semiconductor with your hand can trigger its breakdown.
Therefore, they are stored wrapped in foil or inside shielded metal cases.
There are special rules explaining how to solder field-effect transistors:
- all contact pads (source, drain and gate) are bridged with a thin jumper;
- workplace on the board, tools: tweezers, soldering iron are connected with a flexible wire to equalize potentials;
- the operator puts on a conductive bracelet on his free hand, connected to the ground circuit through a current-limiting resistor of 1 megaohm and combines it with the assembled chain through his own body;
- soldering is performed with a low-voltage soldering iron and the circuit is disassembled.
Features of grounding an acrylic bathtub
The bathroom is a wet room and requires the installation of an additional potential equalization system.
A modern acrylic bathtub has many operational advantages, but it accumulates a static charge well in its area. And he can cause big trouble.
To discharge it, it is necessary to connect a PE conductor through a potential equalization box.
The owner of the video “Electronics Manufacturing Technologies” shows where static electricity comes from and how it should be dealt with at home and in the workplace
How to remove static?
A static neutralizer, skillfully installed at the right points on the production line, .
is a supplier of antistatic equipment and accessories that neutralize static electricity from polymer materials, paper, fabric, foil and protect production workers from the harmful effects of electrostatics.
Our catalog includes a wide range of passive and active static electricity neutralizers from leading European manufacturers:
- antistatic strips
- electrodes
- ionizers
- Power supplies
- transformers
Antistatic agents from Eltex allow you to completely get rid of problems with static electricity . Modern static electricity neutralizers make it possible to ensure complete safety at work and prevent emergencies.
About antistatic equipment
Static neutralization equipment can vary in design and size depending on the industry for which it is intended.
For weighing in laboratory conditions, special antistatic bowls and frames are used. They are used instead of standard ones and provide passive removal of static charge. This device is great for weighing small samples.
Many high-precision scales can be equipped with a built-in ionizer, which will also remove static charge from the samples and utensils being weighed.
Another means of passively removing static is antistatic strips. They are used in industrial environments and, like other passive static eliminators, are not connected to the electrical network.
Active antistatic equipment is connected to a high voltage source, thereby creating a flow of negative or positive ions that neutralize the charge on the surface. For higher efficiency, equipment is used that creates an ionized stream of compressed air.
There are both industrial antistatic equipment and compact benchtop instruments that are suitable for use in laboratories. Portable devices allow you to work with small samples of materials and laboratory glassware.
What is electrostatics?
There are two types of electricity - current, which flows through conductors and is used as a power source for the machines and mechanisms that support the modern world, and static, which is usually found on non-conducting materials and which does not flow as current.
Electrostatics is the study of static electricity. For many reasons, electrostatics was a neglected field of science, since statics was not as useful as "regular" electricity. This is changing because in the industrial world, statics are a problem in many industries. But it can also be productively used in modern industrial methods and processes.
Causes of static electricity in production
Five main causes of static:
- The joining or separation of two materials, usually between a roll and a film or by rubbing the materials against each other.
- Rapid heating, usually in ovens for curing or drying.
- Cutting processes - sheet cutters, trimming or cutting with cylindrical knives (slitters).
- Irradiation with certain waves of the ultraviolet spectrum.
- Induced induction is when one charged object creates a charge on another object.
How to get rid of static electricity?
If the object is conductive, simply ground it and any static charge generated on it will flow harmlessly to the ground. If the object is non-conductive such as plastic, paper, cloth, glass, wood etc then this becomes more difficult as the charge will not flow down the ground but will remain in place. That's why it's called static.
Increasing the ambient humidity will reduce the generation of static on materials that absorb moisture (cotton, textiles, paper), but this is not very effective on other materials that do not absorb moisture.
How to choose a static removal device?
There are many factors to consider when choosing a static eliminator.
Distance to material: Some devices are designed for short range, others for long range. As a general rule, we recommend choosing a short-range ionizer if your technology allows it. Short-range ionizers are cheaper and solve problems effectively.
Modern Developments: There has been a revolution in the performance of static removal equipment. It began around 2004 with the launch of the Ionstorm long-range ionizer system by Fraser. Since then, progress has been very rapid. Modern DC static removal devices are many times better than older equipment with separate high voltage transformers. Older equipment may still be suitable for many applications, but it is unwise to select a device based solely on cost. Modern DC ionizers are typically 10% more expensive, but they provide up to 100% more power and have many other benefits.
Use of static electricity
Static electricity in industry is generally considered a problem to be avoided. But it can be productively used in many modern processes, such as:
- Manipulation of cells in biological technologies, for example, using electrostatic tweezers.
- Removing dust and contaminants from industrial furnaces.
- Temporary adhesion.
Temporary adhesion is a rapidly growing application area for static electricity. It is a clean, controlled and safe process that requires no consumables and is also relatively cheap. To learn how to use static electricity for temporary adhesion, contact Fraser Anti-Static or your local representative.
Why is a charge formed?
Harmful and dangerous potential for equipment and employees of an enterprise can arise in industry in any case, since the process is not associated with a violation of technology, and therefore requires regular prevention.
Static electricity can be generated:
- On belt drives due to continuous friction of dielectric surfaces, which contributes to good charge accumulation.
- When moving hydrocarbons through pipes.
- When moving through pipes, almost all discharged gas compounds.
- During the drawing, processing and cutting of paper, which may occur in paper mills or printing shops.
- In the oil industry. It is also important to protect against static electricity when filling or emptying tanks intended for the temporary storage of hydrocarbon compounds.
- If weaving and spinning equipment is operating, then the dielectric threads, which are constantly in motion, come into contact with the metal base.
- When preparing a composition for making rubber glue in a mixer.
- When a large number of organic dust particles accumulate in the workshop.
Also, the danger of static electric current charge accumulation is associated with the employee’s use of a special uniform made of silk, nylon and other materials capable of accumulating charge.
Statics can also form in other processes. This is why it is important to make sure there is no danger. Experts will help with this.
Removing static in conversion
Converting is a complex industry involving many processes for which static electricity is a major problem. This includes roll and sheet cutting, coating, die cutting and many others. Problems caused by static can include product malfunction, dust attraction, operator shocks, and even fires.
With production speeds exceeding 1000 m/min, static control becomes a critical part of many processes.
Fraser has become a supplier of antistatic devices to many of the industry's global manufacturers and suppliers because we offer a modern, cost-effective solution to emerging problems.
Can neutralization occur spontaneously?
The main danger of static electricity cannot be eliminated spontaneously. The discharge process proceeds extremely slowly, so you cannot be one hundred percent sure that the currently available electric charge will be quite insignificant. Natural removal of potential can occur due to discharge into the ground or uniform distribution over all areas. The same options can be used for artificial processes that will ensure safety for electrical installations and for people. The same methods can eliminate the fire hazard caused by static electricity, which is expressed in the possibility of fire due to sparks or due to a sharp increase in temperature after a short circuit.
If you do not remove the potential, then a gradually accumulating charge, which can reach more than 10 thousand volts, leads to:
- The worker may receive an electric shock if he touches a charged surface. Electric current passes through the entire human body, affecting the heart, nervous system and other internal organs.
- Removing static electricity at an enterprise is also necessary to prevent damage to material, finished goods or breakdowns in wiring, short circuits, fires and explosions.
All of the above consequences will have a negative impact on production. We will have to stop production lines, replace expensive equipment and chain components, and pay compensation to the victims. provides protection against static electricity in production and helps protect the health and lives of workers.
Static removal in plastics production and processing
Static electricity can be a serious problem in the plastics industry due to the non-conductive nature of the materials used in its processes.
Injection molding or extrusion generates high levels of static charge that remains on the product, causing production, quality and electrical safety problems.
There are usually fairly cost-effective solutions to most static problems with plastics. The best way to find out about them is to contact Fraser or its representatives.
Application of antistatic equipment
Antistatic equipment is widely used in weighing small masses with high precision of more than 0.1 mg. The equipment is used in research, medical, pharmaceutical laboratories, industry and production.
Static removal devices are widely used in electronic component manufacturing. Static electricity can lead to failure of microcircuits, so you need to take care of antistatic agents.
In laboratory conditions, antistatic equipment is used to remove static charges from laboratory glassware, polymer films, paper, weighing samples, as well as any products made of plastic, glass, fabric and other materials.
For weighing, special antistatic bowls are used, which passively neutralize the electrical charge. Their use is very convenient when working with small samples.
In some industries, antistatic equipment is used to remove static electricity from the workplace and work surface.
Solving static problems in cleanrooms
Static control in cleanrooms is a very important topic as more and more industries require the use of controlled atmospheres. Clean rooms are not only used in electronics, medicine and high technology as before, but they are becoming commonplace in many areas of plastic processing - injection molding, extrusion, converting, assembly. In all of these technologies, static can cause serious problems. Fraser Anti-Static has developed a range of anti-static devices that have been tested and certified for use in cleanrooms. In this article you will find examples of the most common problems that our equipment in emergency situations eliminates.
Static removal equipment
- Models
- Video
Antistatic device Sartorius Stat-Pen YSTP01 Stat-Pen YSTP01 is a desktop device that neutralizes static charges near the location of the neutralizing probe connected to the power supply via a flexible cable. Technical characteristics: — The probe has a handle for convenient placement in the hand; — Preferred distance from the probe to the object: 30-50 mm; — Processing time, approximately: from 2 to 10 seconds. — Power supply 240 V; — Neutralization: up to ± 30 V; — Power consumption: 0.1 W; — Dimensions: 120x120x55mm, packaging dimensions: 290x180x110 mm; — Gross weight 1 kg. U-shaped ionizer YIB02-230V Manufacturer: HAUG company. The YIB02-230V ionizer consists of a U-shaped frame with an electrode connected to a voltage source using a high-voltage cable. Technical characteristics - Distance from frame to sample: minimum: 10 mm; optimal: 20-30 mm; maximum: 80mm. — Power supply 230 V; — Voltage at the electrode: from 7 to 8 kV; — Current strength at the electrode: up to 5 mA; — Energy consumption: no more than 60 W; — Frame dimensions: 240x140mm, — Cable length: 200 cm; — Weight, about: 4.7 kg; — Dimensions of the power supply: 170x110x100, weight: 3.5 kg; — Packaging dimensions: 420x260x330mm; — Gross weight: 5.5 kg.
The tabletop device produces positive and negative ions and transfers them to a statically charged object through an air flow. Technical characteristics: — Changing/regulating the air flow speed is carried out using an adjusting screw. — The device neutralizes a working area of 600 mm x 600 mm. Items that need to be neutralized must be in this area before being placed in the scale display case. — Power supply from 240 V or 115 V using the supplied adapter; — Neutralization: up to ± 20 V; — Power consumption: 2 W; — Maximum air flow: 125 l/min; — Package size: 320x230x130mm; – Weight: about 0.6 kg / gross weight: 1 kg. Antistatic Bowls Antistatic bowls are used in place of standard 0.1 or 0.01 mg scales for weighing small samples and filters that are susceptible to electrostatic charge buildup. Due to a special manufacturing technology, they contribute to the passive removal of static charge from the filter surface. Modifications for various series of scales: YWP01MS - antistatic weighing bowl, diameter 130 mm, for scales of the Cubis series with readout resolution of 0.1 or 0.01 mg; YFW01SQP - special cup with a diameter of 130 mm; for scales of the Secura/Quintix series with readout resolution of 0.01 mg; YWP01ME – antistatic cup for ME series scales, models with readability 0.01 mg and 0.1 mg.
Influence of static charge on weighing results
Automotive Static Removal
The increasing use of plastics means that static is becoming an increasing problem in the automotive industry. Ensuring vehicle bodies and parts are clean and free of static charges that attract dust before painting is critical to maintaining paint quality and controlling costs. If dust has gotten into your car's paint, it can cost thousands of dollars to fix. If a bumper or fender is rejected, the cost can be hundreds of dollars in costs.
Where to Install the Static Removal Device
As a general rule, an antistatic ionizer should be installed directly in front of the area where static is causing problems. If you place it too far in front of the site, the charge may be renewed by passing through shafts or other static-generating processes.
How far from the material? It depends on the type of device - there are long- and short-range antistatic ionizers. Whichever one you use, the lifetime of the ionized air produced by the device is limited and the correct clue is usually: "The closer, the better." The minimum distance is specified by the device manufacturer.
The material must be in free space. This is a very important rule that is often ignored. When the material touches another object, such as a shaft or conveyor, the static charge combines with that object and cannot be properly measured and neutralized. If you place an ionizer to neutralize the film where it moves over the roller, it will not be effective. This is the most common mistake when installing antistatic equipment.
- The emitters must be directed towards the material.
- The ionizer is at a distance of more than 50 mm from the shafts or parts of the machine.
- Material in the air.
- The distance to the material is the minimum for the selected device. The closer, the better. Selected empirically.
- The distance between the axes of the emitter needles, if two ionizers are installed opposite, the displacement between them is more than 50 mm.
- The cable bending diameter is at least 70 mm.
- The installation area is dry and free of oil.
Static neutralizers
Consumables and spare parts for flexo printing and printing / Spare parts / Static neutralizers
Electrostatic charge neutralizer
An antistatic bar or static neutralizer (separates air molecules into positive and negative ions) acts on any statically charged material that passes through the area of action of the bar - attracts the opposite charge to itself, neutralizing it.
The use of strips and emitters in the following cases:
- Plastic products;
- Packaging production (elimination of dust before lamination, during the manufacture of bags);
- Printing on various materials (prevents labels from sticking);
- Cutting and rewinding of materials;
- Textile industry;
Anti-static strip advantages:
- For roll and sheet materials;
- Does not require human intervention;
- Compact arrangement on the equipment;
- The system neutralizes static electricity. The high concentration of positive and negative ions allows you to quickly neutralize static electricity on any material surface at a distance of up to 2 - 5 cm. Bonato
The neutralizer reduces static adhesion on paper, film, plastic, which can cause adhesion of dust and foreign materials, deteriorate the presentation of the package, cause rupture or jamming in the machine.
| Frame | Anodized aluminum PVC profile. Epoxy filler and hardened stainless steel pins |
| Length | 200-XX The length of the active part is manufactured (80 mm – 6000 mm); Total length = active length + 50 mm. 201-ХХ The length of the active part is manufactured (130 mm - 6000 mm); connector on both sides (170-6000 mm). Total length = active length + 90 mm, active length + 120 mm. |
| Cable | Flexible shielded cable up to 30 kV. The minimum bending radius is 40 mm. The standard cable size is 2 meters, but it can be made to any size. |
| Working temperature | 0 - 60ºC |
| Humidity maximum | 70% RH |
| Safety | The amount of current in the contact is limited to 50 µA for operational safety |
| The best performance is between 20 and 50 mm from the processing material |
There is also a neutralizer on sale with an air blower to neutralize static electricity at a distance, which is very convenient for installation when it is not possible to place the bar close to the material or canvas. Planks with an air blower are suitable for high-speed machines. There are a large number of models of different lengths available. Check with the manager which one is right for you!
Antistatic. Package
Antistatic strips
Antistatic
Planks
Set
power unit
Replacing the antistatic ionizer
How will you know if your antistatic ionizer is working? The easiest way is to use an electrician's indicator, the glow or sound of which will indicate that the ionizer is producing an electric field.
If an electric field is produced, the next thing to make sure is that the ionizer is clean. A dirty device is ineffective because it allows energy to flow away through the dust instead of producing ionization.
If there is no electric field in the ionizer, the problem may be a malfunction of the ionizer itself or the high-voltage power supply. Most high-voltage power supplies are current limited and turn off if a fault is detected in the ionizer. If you are using several ionizers, disconnect them from the power supply one at a time and see if the high voltage is restored. This way you will find which ionizer is faulty. If the high voltage is not restored with all devices turned off, then the problem is in the power supply itself. It may be a fuse that is easy to replace. Or is it a transformer problem, in which case you will need to contact the manufacturer for further advice.
Where does the positive charge in our body come from?
Let us explain it in a language that is accessible and understandable to everyone, even those who are not experienced in physics. Material objects accumulate any charge through friction. Each atom that makes up any material body (including the human one) has electrons rotating around its nucleus. Let's give a simple example.
When we take off our clothes over our heads and throw the blouse on the sofa, a large number of electrons, through friction, seem to be erased from their orbits and transferred to the blouse that we took off. It is well known that electrons are negatively charged particles, and therefore our blouse becomes negatively charged, since in its tissues there is now an excess of electrons from our body, while we ourselves become positively charged, since there is now a shortage of negatively charged particles in the tissues.
If we then decide to touch a metal object or another person, we will feel an electric shock. A microscopic lightning discharge will appear between the fingertips of the hand and the object, during which a discharge will occur in the literal sense of the word. Our body, through this discharge, will absorb the missing amount of electrons from this object, and the energy in it will again become balanced. Plus and minus will be balanced again.