Description
VVG cables are used to supply power to electrical equipment and lighting both inside buildings and on external cable structures and electrical appliances. Technical characteristics allow it to be used even at sites with relative humidity up to 98% (mines, etc.), as well as for high-altitude air installation. Thanks to this versatility, this conductor is the most popular material for laying networks.
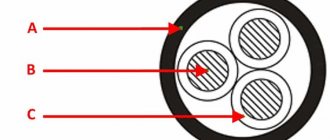
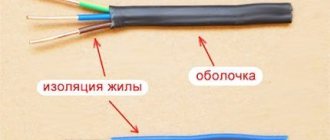
The VVG cable is a wire made of one or more current-carrying cores, each of which has its own insulating layer. These wires are twisted together and laid inside a common insulating sheath. It is made of PVC with low fire hazard, which is very important when installing electrical networks at oil, gas and chemical enterprises. The production of all brands of VVG cable is regulated by the state standard GOST 16442-80.
Technical characteristics of VVG cable
The features of using different types of VVG cable were discussed above, and now we will talk about the technical parameters of conductors of this brand.
- Can be laid at temperatures down to -15°C. At lower temperatures, it is necessary to heat the cable, which is not easy to organize (the sheath becomes too rigid and is very difficult to bend).
- Operating temperature range - from -50°C to +50°C. At the same time, when installing outdoors on the street, additional protection from ultraviolet radiation is required.
- Bending is possible with restrictions: VVG with single-core conductors; minimum bending radius is 10 radii;
- with stranded ones - 7.5 radii (due to greater flexibility). There are flat options (two and three wires)
- for a short circuit in which the conductors remain operational depends on the manufacturer and can range from +160°C to +250°C.
It must be said that the technical characteristics of the VVG cable depend not only on the specific type, but also on the manufacturer. Therefore, before purchasing, look at the cable passport (you can ask the seller). The above are parameters common to all brands of VVG cable.
It is not surprising that these conductors are very popular - with good technical indicators, they cost relatively little, and can be used almost everywhere - both in enterprises and offices, and in houses and apartments.
Section and number of cores
The cross-section of the VVG cable cores of any brand can be from 1.5 mm² to 240 mm². Conductors with conductors up to 35 mm² are usually on sale; other, larger sizes must be ordered.
As already mentioned, there are VVG cables with 2, 3, 4 and 5 cores. The number of cores is written immediately after the abbreviation: VVG 2 x 3.5; VVGng 4 x 4, etc. The first number is the number of cores, the second is the cross-section of the conductor.
Approximate range of VVG cables
There may be VVG cables with “neutral” and “grounding” conductors. Moreover, there are options in which the protective wires are of the same cross-section, and others with a smaller diameter (to save copper and lower cost). Most often, the “ground” conductor is made smaller; in some cases, the “neutral” is also made a little smaller. If the protective conductor has a smaller diameter, it is designated as +1. For example, VVGng 4 x 4.0+1 (read as 4 wires with a cross-section of 4 mm² and 1 step less than 2.5 mm²). These VVG cable options are also standardized, their parameters are given in the table below.
Parameters of VVG cables with cores of different diameters
Continuous current
When selecting a cable cross-section, a more correct method is based on the maximum current. In this regard, such a characteristic as long-term permissible current is standardized. It depends on the number and cross-section of the cores, as well as on the method of laying - open or closed.
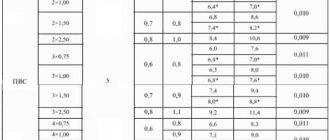
| Core cross-section | Continuously permissible current | ||
| with two main cores | with three main cores | with four main cores | |
| 1.5 mm² | 24 A | 21 A | 19 A |
| 2.5 mm² | 33 A | 28 A | 26 A |
| 4 mm² | 44 A | 37 A | 34 A |
| 6 mm | 56 A | 49 A | 45 A |
| 10 mm | 76 A | 66 A | 61 A |
| 16 mm | 101 A | 87 A | 81 A |
| 25 mm | 134 A | 115 A | 107 A |
| 35 mm | 208 A | 177 A | 165 A |
Two modifications of VVG cables are produced - with a rated voltage of 0.66 kW and 1 kW.
Kinds
The VVGng cable is produced in various insulating materials, each of which directly affects the features of use and technical characteristics:
- VVG is a standard wire with PVC insulation, non-flammable.
- VVGng - differs from the previous one in that the outer insulating sheath of this wire is made of a material with the addition of halogen elements that prevent combustion (ng - non-flammable).
- VVGng ls - for the production of cables of this type, halogen-free polyvinyl chloride is used, which prevents the spread of smoke. ls stands for Low Smoke.
- Cable VVGng -frls – designed for use in conditions of high risk of fire. The abbreviation frls stands for Fire Resistance Low Smoke and means that when a fire occurs, the wire emits a minimal amount of gas and smoke, and also does not spread fire when laid in groups.
- VVGng hf is a cable with polyvinyl chloride outer insulation made of material that does not propagate flames (when laid in groups) and does not emit hazardous gases when ignited.
- VVGng-frhf is a non-flammable PVC cable that does not spread fire when laid in groups and does not emit harmful gases and smoke when ignited.
Halogen-free polyvinyl chloride, used for the production of VVGng ls and VVGng-frls wires, is a fire-resistant material. It has the same insulating properties as standard PVC, but is low on fire, has virtually no fire propagation and produces minimal smoke.
In addition to the main cable types listed, the following variations are found:
- The AVVGng cable is an analogue of VVGng with one difference - the conductors in it are made not of copper, but of aluminum.
- AVVGng ls. In this cable, the conductors are made of aluminum, and the external insulation is made of plastic compound of the “low smoke” class (reduced gas and smoke emission).
- VVGngd - the letter “d” means that the cable design uses double insulation.
- AKVVGng ls or AKVVGng-sltx is an aluminum control cable with insulation made of non-flammable polyvinyl chloride, which does not spread smoke and fire. The letter “K” in the abbreviation of the wire brand means that it is a control wire.
- PVVGng – standard VVGng cable with reinforced core insulation (thermocrosslinked polyethylene). Wires of this brand are intended for installation inside industrial and industrial premises.
Usually the manufacturer puts appropriate markings on the wire indicating its type. The decoding of the abbreviation VVG is simple and means “vinyl-vinyl-naked.” This means that VVG is a wire with double polyvinyl chloride insulation over the core wire. The letters “ng” indicate that the insulating material is flame retardant if the cable is laid in a group.
Deciphering the cable markings requires knowledge of some additional symbols:
- The metal from which the conductors are made: by default - copper; if the marking contains “A” - aluminum.
- Material of the insulating sheath of current-carrying conductors: “P” - polymer; “B” - PVC, “Pv” - polyethylene.
- Cable armor: by default – without armor, “B” – there is armor.
- Material and design of the outer insulating shell: “P” - polymer; “V” - PVC, “Shv” - design with a protective hose, “Shp” - with a polyethylene protective hose.
Explanation of the abbreviation NYM
The Latin abbreviation NYM stands for the following:
- N – standard type cable (German gradation);
- Y – the insulating sheath of the cores is made of polyvinyl chloride (PVC);
- M – with outer shell.
As usual, the absence of the letter “A” in the first place indicates that the cable cores are made of copper. In addition to the three standard letters in the designation, J or O can be added through a hyphen - with or without a yellow-green conductor (ground conductor).
After the alphabetic symbols there are necessarily digital symbols, indicating the number of cores and the cross-section of each of them. For example, the product NYM-O 4×4.5 - 0.66 can be deciphered as follows:
- standard cable with polyvinyl chloride core insulation and outer sheath;
- consists of four cores with a cross-sectional area of 4.5 square meters. mm each;
- used at voltages up to 0.66 kV (660 V).
Color coding
Such a cable must be produced with standardized color markings. The absence of this indicates that the product is not certified and is a counterfeit. The standards for the color of conductors are prescribed in the rules for electrical installations (PUE).
The set of colors varies depending on the exact number of cores located inside the outer sheath:
- there are no regulations for single-core cables;
- two conductors without a grounding cable - black and blue conductors;
- three cores without a grounding cable - black, brown and gray;
- four cores without a grounding cable - black, brown, gray and blue;
- three cores with a grounding cable - black, blue and yellow-green;
- four cores with a grounding cable - black, brown, gray and yellow-green;
- five cores with a grounding cable - black, brown, grey, blue and yellow-green.
Depending on the color marking, specialists can easily determine the main purpose of the cable. The blue wire is usually used to connect the neutral wire in single-phase networks. In three-phase, the blue core acts as a neutral. The yellow-green conductor in all cases serves as a grounding conductor.
Important! In accordance with GOST, the NYM cable should not contain conductors with white or white-blue insulation. If there is one, the conclusion is simple - it is a fake. Further use of such products, if possible, is at your own peril and risk.
Application
Today, VVGng cable is the best option in terms of quality and price. This wire is universal not only in terms of design capabilities, but also for fire safety. It is used for installing networks under the following conditions:
- at height, in the absence of probability of breakage or damage during further operation;
- in tunnels, shafts and half-shafts, canals, niches, collectors, industrial facilities, partially flooded buildings;
- over cable bridges and overpasses;
- in buildings with a high fire hazard;
- at facilities with the following explosion hazard classes V-11, V-11a, V-1b, V-1d.
The technical characteristics of each type of VVG cable are defined in GOST 16442-80, but sometimes they may differ from the standard ones. As a rule, the operating voltage is no more than 0.6 V, but the wire can be used with larger parameters if this is expressly stated in the certificate. The cable service life is at least 20 years, but it is required to check the integrity of the insulating sheath at intervals of 5 years. When used under optimal conditions, the wire can last up to 30 years.
Despite the fact that the VVGng cable is universal, it is still more often used in conditions of increased danger, both electrical and fire.
What is a power cable?
Even from school, we must remember that the electric current used to power all electrical appliances and equipment without exception is the ordered movement of charged particles (electrons). This phenomenon happens everywhere, but to use it on the current scale it is necessary to create certain conditions. First of all, this concerns the choice of shape, design, weight of the conductive medium, which will not only economically transfer power to consumers, but also safely.
The generally accepted cable form factor today is a multi-core conductor enclosed in protective insulation with a linear or concentric arrangement of conductors. Cable products are classified according to various criteria, but one of the most important is its functional purpose. If we are talking about the need to transmit electric current of industrial frequency and voltage, then use power cables, for example, VVG-KhL, VVG-Png, VVGng-HF, etc. In a narrower sense, this means interconnecting the input distribution device (IDU) , main switchboard) and the end consumer (industrial equipment, household appliances, lighting fixtures, etc.). The nature of the connection organization depends on the required operating conditions, cable weight, etc.
VVGng LS
VVGng ls is an electrically conductive cable, the outer insulating sheath of which is made of polyvinyl chloride with a low fire hazard coefficient. It is designed for laying AC electrical networks with voltage up to 1 kV and frequency 50 Hz.
The VVGng ls cable is used in facilities with a high fire hazard. As a rule, these are industrial and production buildings, nuclear power plants of classes 2, 3 and 4, as well as public institutions. Electrical installation rules do not recommend installation of VVGng ls in trenches and ground.
According to TU 16.K71-310-2001, this cable can have up to 5 cores and the following design:
- One or more power strands, each of which consists of one or many copper wires. Shape – sector or round.
- The insulating shell and filler are made of low-flammability plastic compound, which has a low coefficient of gas and smoke emission (low smoke – ls in the marking). If the outer shell is also used to fill gaps, no filler is installed.
- A twist of conductor cables insulated from each other.
- A two-core VVGng ls cable must have an equal cross-sectional area of both cores. If the cable includes from 3 to 5 cores, one of them may have a smaller cross-sectional area if it is “zero” or ground.
- The insulation of the conductor wires is also made of low-flammable PVC. Sheath colors are used to distinguish the wires from each other: zero is blue, ground is a yellow-green wire.
Technical characteristics of VVGng ls:
- operating temperature range: -50˚C – +50˚C;
- design voltage – 660 V and 1000 V;
- relative humidity in the room (+35˚С) – up to 98%;
- current frequency – 50 Hz;
- cable laying temperature without heating: not lower than -15˚C;
- the smallest permissible bend radius during installation: 7.5 outer diameters for a multi-core cable and 10 for a single-core cable.
- maximum temperature of current-carrying conductors during operation: up to +70˚C; in emergency mode – up to 90˚C; with a short circuit - up to 160˚C;
- maximum temperature of prolonged exposure to VVGng cable ls: +400˚C;
- service life – up to 30 years.
VVGNG cable for an apartment, which one to choose?
When choosing which cable is better: flat or round VVGNG, as well as LS or NYM, you must first determine for which room the wiring is being done. For rooms with high humidity, NYM is better. When choosing a nym or vvgng ls cable, which is better for wooden houses or apartments with plastic combustible sheathing, you should give preference to VVGNG over LS or NYM.
Apartment cable VVG or VVGNG, as well as LS, NYM and other types of products are in the company’s catalog, and you can order them with delivery in the required quantity.
VVGng-HF
VVGng HF is a power cable used for conducting and installing AC power networks with voltages of 660V and 1000V. First of all, the VVGng HF cable is recommended for organizing power supply for lighting and electrical equipment at large industrial and public facilities: power plants, factories, petrochemical industry facilities, stadiums, concert halls, train stations, airports, educational and medical institutions, shops and other buildings with increased requirements to fire safety.
Characteristics of VVGng HF cable:
- rated voltage: up to 1 kV;
- operational ambient temperature range: -30˚C – +50˚C;
- cable laying temperature (without heating): not lower than -15˚C;
- relative humidity in the room (at +35˚С) – up to 98%;
- maximum heating of cores during operation: up to 70˚С (up to 90˚C in PVVGng);
- maximum heating of cable cores during overload: up to 90˚C (up to 130˚C in PVVGng);
- maximum permissible temperature for prolonged exposure – 400˚C;
- the smallest permissible bend radius of the wire during installation: 10 diameters for single-core cables and 7.5 for multi-core cables;
- service life – 30 years.
What is the difference between NYM and VVGng
The NYM cable will be useful only for single installations. If you are planning a group session, then it is better to make a choice in favor of VVG. Structurally, both products consist of several copper cores with polyvinyl chloride insulation and the same outer shell. However, only VVGng (the prefix “ng” indicates the non-flammability of the cable) is able to stop the flame and prevent its spread during group installation of several conductors.
We list the main technical and operational characteristics of NYM and VVGng and compare them in the table below:
Characteristics Permissible voltage Current frequency Number of cores Cross-sectional area of one core Service life Filling of empty space Does not support the spread of fire Possibility of operation in difficult conditions
| NYM | VVGng |
| 660 V | 660 V |
| 50 Hz | 50 Hz |
| 2-5 pcs. | 1-5 pcs. |
| 1.5-35 sq. mm | 1.5-240 sq. mm |
| 40 years | 30 years |
| Present | Absent |
| Single gasket only | Any gasket, including group gasket |
| Moisture protection, not UV resistant | Can be used in any situation |
Design features
A description of the design of an electrical cable brand VVG NG ls is given by GOST 22483. It includes a single-, double- or multi-wire conductor made of copper. A polyvinyl chloride composition characterized by a low fire hazard coefficient is used as an insulating material.
VVGNG technical power cables are produced both round and flat. There can be a maximum of 5 current-carrying cores in a wire. They come in round and sector shapes. The cores are insulated with polyvinyl chloride in a distinctive color. So, for example, the core responsible for zero has a blue coating, and the grounding is covered with a PVC composition of a greenish-yellow color.
The conductors are class 1-2, twisted, the wire is filled with extruded PVC plastic, which has low smoke and gas emissions. In two- and three-core models, cores of the same cross-section are used; in four- and five-core wires, one core has a smaller size.
The thickness of the plastic compound must be at least 0.3 mm; the sector cores do not need to be filled with an inner sheath of plastic compound; it is enough to overlap them with polyethylene terephthalate film or thermally bonded fabric. The outer covering is made of PVC composition.
Conductor
Round, segment or sector shape - these are the main design forms of current conductors in a cable. The range of core sections is standard; the conductors themselves are made of aluminum or copper.
Interesting. Electrolytic copper is used, grades MO or MI. Aluminum is taken grades AO or A01.
Phase insulation
Each phase conductor in the cable is covered with individual (phase) insulation. Also P.L. Schilling in the mid-19th century used gutta-percha insulation for wires used to detonate mines at sea.
Modern phase insulation must meet the following requirements:
- flexibility;
- mechanical strength;
- electrical strength.
The choice between flexibility and thinning is always problematic. Electric strength is the main indicator for insulation. It can be made of cross-linked polyethylene, polyvinyl chloride, rubber or oil-impregnated paper.
Important! Reducing the thickness increases flexibility, reduces weight, and improves heat dissipation, which means the cable can withstand high operating current. Reducing the insulation thickness leads to the likelihood of breakdown, therefore, the electrical strength decreases.
Outer shell
This is a protective layer covering the entire complex structure of the SC. The outer shell can be made of PVC (polyvinyl chloride plastic). For example, VVGP ng, if you pay attention to its marking, has a PVC shell.
Additional items
These include components that increase the internal insulation, strength and protection of the cores. Additional elements may be as follows:
- shielding braid;
- waist insulation;
- lining (pillow) under the armor;
- protective outer layer of metal strips (armor);
- internal filler of spaces between conductors.
Number and cross-section of cores
The SC can include from 1 to 5 current-carrying wires. The nominal cross-section of conductors ranges from 1.5 to 1000 mm2. In SCs they have the same cross-section, but in four-core cables one of the conductors may have a smaller cross-section. Usually this is a neutral conductor.
Marking
Correct decoding of the markings will allow you to determine the characteristics and properties of VVGng:
- B – core insulation made of polyvinyl chloride plastic;
- B – polyvinyl chloride plastic is used as a material for the outer shell;
- G – “naked”, i.e. there is no protective cover or armor;
- ng – the cable does not support or spread combustion after the source of ignition has been eliminated.
After the letter markings, numbers are indicated that inform about the number of cores and their cross-section, as well as the rated voltage class.
The cable can be manufactured in a flat design. To identify it, the letter “P” is additionally indicated in the designation.