To connect electrical equipment to a power supply network up to 1000 volts, as well as to install internal networks in domestic and industrial premises, various modifications of the VVG cable are most often used (for example, version VVGng). This demand is explained by its operational and technical characteristics. We invite you to familiarize yourself in detail with this type of cable products, find out the possible design options, their features and main technical parameters. Let's start with the design features.
Typical design
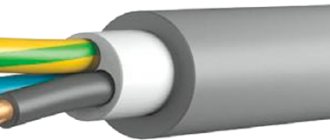
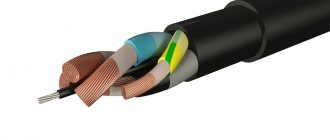
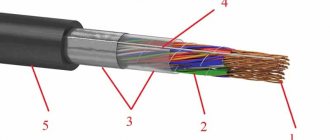
A cable of this type consists of copper or aluminum current-carrying conductors in the amount of 1-5 pieces (see B in Fig. 1). Depending on the design, they can be monolithic or multi-core.
VVG cable design
Each of the cores is covered with an insulating sheath (C) based on polyvinyl chloride (hereinafter referred to as PVC). A special dye has been added to its composition, which allows you to identify the wires in accordance with the color marking. The current-carrying parts of the cable are placed in a common PVC sheath (A).
This design is typical for all varieties, with the exception of the VVGP version and its modifications, which have a flat rather than round shape.
Cable VVG-P
Decoding VVG markings and common modifications
The marking allows you to determine the characteristics and properties of cable products; it is deciphered as follows:
- Indicates the material from which the current-carrying elements are made. For aluminum, the symbol “A” is accepted; if the conductors are made of copper, then there is no designation.
- The purpose of the cable is that it can be control (marked “K”) or power (marked “K”). The former are used in control circuits of electrical equipment, the latter for powering it, respectively, control cables are designed for a lower current load, in fact, this and the large number of cores distinguishes KVVG from VVG.
Electric cable KVVG produced by the Concord plant (Smolensk) - The insulation material for current-carrying elements, in our case it is the symbol “B”, which indicates the use of PVC materials.
- A symbol indicating what the outer (general) insulating covering is made of. The letter "B" indicates that PVC is used.
- The presence or absence of protection, in the first case “B” is indicated, this means that the cable is armored, in the second case “G”.
In the basic version, the number of current-carrying elements and their cross-section are further indicated (highlighted in red in Fig. 4); if there is a grounding conductor of a smaller cross-section, it is indicated separately, for example: “3x10.0 + 1x6.0”.
Labeling example
Next, the rated voltage is indicated (circled in green in the figure - 0.66 kV), followed by GOST and/or TU (marked in yellow).
Structure
The guaranteed VVG-png cable transmits and distributes electric current in devices of a permanent type. A special feature of the conductor element is increased fire protection. The wire has six cores, the maximum cross-section of which reaches 240 square millimeters. The permissible installation current is 70 amperes, which can be used for drawing up the circuit. The maximum weight is two tons per kilometer, and the minimum is one hundred and twelve kilograms. The price depends on what characteristics the product has, in particular the number of cores with a total volume.
You might be interested in this All about the KVVG cable
Their main feature is the reduction of smoke during a fire. The temperature during operation varies from −50 to +50 degrees. Operating time approximately 30 years. The cable is used in networks with alternating current up to a thousand volts at a frequency of 50 hertz. It is used in structures such as trays and boxes.
What does VVGng consist of?
Marking of various versions
Before the parameter indicating the number and cross-section of cores, the marking may contain designations indicating design options, the most common of which are the following:
- NG - indicates the presence of special additives in PVC insulation that prevent the spread of fire (sometimes an alternative marking is used - “fr”). This version differs from the basic type in that group installation is allowed during electrical installation.
- LS – the insulation contains additives that release smoke from the material. As a rule, this execution is done in conjunction with the previous one, in such cases the marking looks like ngls, lsfr or ngd.
Power fire-resistant and smokeless cable VVGngd produced by Sevkabel - LSx - this designation indicates the low toxicity of emissions during fire. Please note that for VVG it is unrealistic to achieve such a condition, since the material used is PVC, which in such a situation releases phosgene and other chlorine compounds.
- HF is another unrealistic designation for PVC insulation. It indicates the absence of halogens (corrosive substances) in the smoke released during a fire, which is an outright lie, since the insulation material is PVC plastic.
- HFLTx - no comments, everything is said in the two previous descriptions.
A brief explanation is necessary for the last three performances. According to the standards of GOST 53315, when designing social facilities, it is necessary to lay cables that have a low LTx level (toxicity during fire). Actually, this prompted the designers to invent an unrealistic design. Note that in the new GOST 53769 there is not even a mention of the LTx index.
Appointments
The VVGng power cable is needed to transmit and distribute electricity throughout a stationary installation that operates on alternating and direct voltage of one kilowatt. Can be used in places with temperate, cold and tropical climates. It is laid where there is no danger of mechanical damage. Installed on a special cable rack, in a fire hazardous room, in an explosive class and for laying group lighting networks where there are explosive zones of class B-Ia.
Note! The cable is needed to protect the vibration-prone unarmored appearance of the cable elements. Not capable of spreading fire. It is required that cable structures with premises function properly. It heats up to 80 degrees and works no more than 8 hours a day.
Wiring as the main area of application
Examples of common modifications and explanation of their markings
As mentioned above, in order to find out the purpose and properties of the cable, you need to decipher its markings. Here are some examples of common modifications:
- KVVGEng, based on the markings, we can say that this is a control cable (the first character is “K”). It has copper conductors (there is no “A” symbol), non-flammable PVC insulation type (“ng”), a screen (“E” symbol), non-flammable design. Should not be confused with VVGEng, which is not a control cable, but a power cable
- PGVVP interpretation: flat flexible wire with PVC insulation and sheath and copper conductors.
- KSVVng interpretation: control wire for alarm systems (symbol “C”) with PVC insulation and non-flammable sheath.
Advantages of VVG cables
The main task of power supply is considered to be maximum preservation of the quality of transmitted energy. To maintain these parameters, modern electrical conductive products must have characteristics such as low resistance and high quality insulating coating.
VVG copper cables cope with this task quite well and have some advantages:
- The non-combustibility of the shell allows wiring to be installed in rooms with a possible fire risk.
- Possessing high-strength insulation not only simplifies wiring installation, but also protects the electrical network from short circuits due to mechanical stress on the wires.
- The high dielectric properties of the insulating material made of PVC make it possible to produce powerful and reliable wires of small diameter.
- Moisture resistant. This property is necessary when using wiring in rooms with high humidity.
- Convenient color and digital marking of current-carrying conductors.
- Long period of use (service life of at least 30 years).
VVG power cable, protected by corrugated sleeves or cable boxes, is highly reliable in use.
List of main characteristics
Despite the wide range of cable products and the differences between their modifications, there are general parameters that describe the technical and operational characteristics. First of all, these include dimensions:
- The number of current-carrying parts and their cross-section (indicated in mm2). This is a rather important parameter, information about which is included in the marking, for example: 3x10, 4x1, 5x1, etc.
- Thickness of the overall insulating shell (mm).
- Core insulation thickness (mm).
- Ø of conductive elements without insulation (mm).
- Ø outer (mm).
Electrical characteristics include: throughput, specific, and inductive reactance.
During design and installation work, it will be useful to know such cable properties as bending radius (indicated in diameters) and weight (calculated kg/km).
As for performance characteristics, these include:
- Maximum permissible temperature (short-term and long-term).
- Operating temperature range.
- Permissible humidity, etc.
Below is a table with the main characteristics of various brands of copper three-core cables.
Table 1. Main parameters of VVGng three-core cables
| Number of TPGs and their cross-section (mm) | External insulation thickness (mm) | TPG insulation thickness (mm) | Ø TPG (mm) | Cable Ø (mm) | RTPG (Ohm/km) | Cable weight (kg/km) |
| 3x1.5 | 1,50 | 0,80 | 1,48 | 9,70 | 12,10 | 140,0 |
| 3x2.5 | 1,50 | 0,80 | 1,88 | 10,50 | 7,41 | 182,0 |
| 3x4.0 | 1,50 | 1,0 | 2,38 | 12,50 | 7,41 | 268,0 |
| 3x6.0 | 1,50 | 1,0 | 2,88 | 13,50 | 3,08 | 344,0 |
| 3x10.0 | 1,50 | 1,0 | 3,67 | 15,30 | 1,83 | 491,0 |
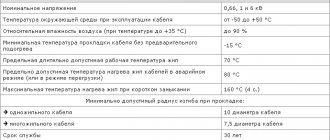
Technical characteristics of cable VVGng(A)
| Operating temperature range: | from -50 °С to +50 °С |
| Rated voltage: | 0.66/1/3 kV frequency 50 Hz |
| Peak test voltage: | 12-38 kV |
| Core flexibility class: | 1 or 2 |
| Construction length: | by customer order |
| Maximum operating temperature of the core during operation: | +70°С |
| Short circuit duration, no more: | 5 s |
| Test holding time: | 10 min |
| Insulation resistance at 20 °C: | not less than 4.8…12.0 MOhm km |
| Insulation resistance at 70 °C: | not less than 0.005 MOhm km |
| Relative air humidity at temperatures up to +35 0C: | up to 98% |
| Permissible core heating temperature: | 70°C |
| Maximum core heating temperature during overload: | 90°C |
| Maximum core heating temperature at short-circuit current: | 160°C |
| Installation temperature: | -15°C |
| Minimum bending radius for stranded: | 7.5 outer diameters |
| Warranty period: | 5 years |
Installation methods
Let's consider four options for laying VVGng:
- Open laying. A cable of this type can be laid openly, provided that the installation is carried out on a non-combustible surface. Installation on suspended structures that do not allow stretching or sagging is also permitted. With this installation method, the cable must be placed in a metal hose or pipe to provide additional protection.
An example of open installation (VVGng is laid in corrugation)
Please note that this requirement is mandatory if the surface is flammable, for example, wood.
- Laying in cable-supporting structures. Based on their operating conditions, group installation of VVGng is allowed, which means this method is quite acceptable. This method is widely used when organizing an electrical network in industrial premises.
Installation of VVGng in a cable tray - Organization of hidden wiring. This method is widely used in organizing electrical networks in residential and office premises. How to properly install hidden wiring, as well as learn all the nuances of this method, can be found on our website.
Installation of hidden wiring - Laying in the ground. According to the performance characteristics, VVGng is not suitable for this installation method. This is due to the fact that the cable may receive mechanical damage. To get around this limitation, you need to place it in a pipe or tunnel or organize another acceptable method of protection.
Pipes for laying cables in the ground
Areas of use
Due to its technical characteristics, the VVG cable is actively used when installing wiring outdoors, as well as in wet rooms, and the humidity level is allowed at 98%. It can be used in industrial premises, power plants, distribution and lighting devices, residential premises (as wiring).
In premises intended for living , it is recommended to lay VVGng or VVGng-ls grades; when installing under plaster, it will be more convenient to use a flat cable. In an open manner, the product is mounted on surfaces made of non-combustible materials (brick, concrete, plasterboard). On wooden walls, protection in the form of special channels and corrugated sleeves is required.
You might be interested in this: Planning and laying hidden wiring in a wooden house
A similar cable is used when installing wiring in tunnels, collectors, channels and similar places. It is not recommended to lay it in the ground without special protection, as it will be subject to mechanical and corrosive influences.
It is also considered advisable to use such wiring in rooms where there is a risk of fire or explosion (armored cable is installed in explosive areas).
How to choose a cable?
The type and characteristics are indicated in the design documentation. If there is none, you need to decide on the number of cores; their number depends on the power supply circuit of the connected equipment. Next, you should select the cross-section of the TPG taking into account the connected load. Detailed information about such calculations can be found on the pages of our website.
The question of choosing between single-core and stranded (multi-core) TPGs often arises. The latter have greater flexibility and are certainly better and more convenient for wiring. But the ends of such a wire must be tinned or crimped with special tips.
In single-core cables, crimping or tinning the ends is not necessary, but such conductors are more rigid, which can somewhat complicate installation; in addition, they are critical to repeated bending.
The question of the TPG material need not even be raised. It is necessary to purchase copper; its electrical and mechanical properties are significantly superior to aluminum.
Before deciding on a manufacturer, it is advisable to familiarize yourself with the ratings of manufacturers on thematic websites and forums, where the best of them are presented. We advise you to visit several resources, since no one has canceled the increase in ratings and black PR.
Each cable coil must be accompanied by a passport indicating the technical parameters, as well as other related documentation.
When purchasing a mandatory product, check for a certificate of conformity. If you purchase a VVGng cable, you must also check the fire certificate.
Is there an alternative?
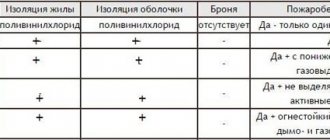
Often, NUM (NYM) cable is offered as a replacement for VVGng, as an analogue made using European technology. Its main difference is the presence of filler. Below is a table with the comparative characteristics of these cable products.
Comparison table of characteristics of NYP with VVG and VVGng
As can be seen from the table, NYM is inferior in terms of the boundaries of the operating range and in that it cannot be laid in a group. Note that the latter is easily corrected when choosing an NYP LS cable. On the other hand, this type of service life exceeds domestic cables by 10 years. As for the cost, it is also higher.
If the choice is made in the direction of NYM, then it should be taken into account that it is better to purchase imported products, since Russian manufacturers prefer to adhere to domestic specifications rather than the VDE standard. This approach affects quality; as a result, the products have practically no advantages over VVGng, although they are more expensive.