What is and how to do zeroing
WITH
With the advent of electricity in everyday life, the question of its safe use arose.
Let's see how to solve this important problem, let's figure out: what grounding is, how grounding works, how to make grounding
in a private house with your own hands.
And besides, is it possible to use grounding instead of grounding?
1.
What, how and where it comes from.
2.
Grounding in the apartment.
3.
Residual current device.
4.
Zeroing.
5.
Let's consider a couple of situations.
6.
In conclusion, about zeroing.
What, how and where does it come from?
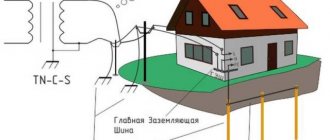
It is known that electricity is produced by power plants. From them, an electric current with a voltage of tens and hundreds of thousands of volts travels through three phase wires to the consumer.
The voltage is so high because, according to the laws of physics, the higher the voltage, the lower the losses during transmission over long distances.
Then step-down transformer substations convert the high voltage into a much lower (but still dangerous) one, and it will come through wires or underground cables into our home.
The current must come to the electrical appliance, do useful work and leave. In the case of alternating voltage used in everyday life, the phase (supply) and neutral wires are used for this. Where the electric current comes from is clear; but where does the electricity go? To the ground! A little simplified, but by and large it is true. Right into the ground.
The substation transformer has a ground connected to a separate line wire. This is the same “zero” in our sockets. Those who are especially curious can verify this by examining a regular transformer substation with overhead lines. 3 wires came in, 4 came out. At the input there are three phases of high voltage, at the output there are three phases of low voltage and a neutral wire.
Now let's move on to the main thing - human protection.
Grounding in an apartment
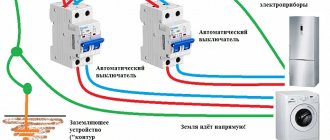
The most reliable way to protect against electric shock at home is to ground electrical appliances. After all, many of our home assistants have metal (read: conductive) cases, and as a result of a break or damage to the insulation, the phase wire may touch the body of the device. And then touching him becomes deadly...
To avoid trouble, the body of the device is connected to the ground. Now, when a phase hits the housing, a short circuit occurs and the protection is triggered, cutting off the current supply.
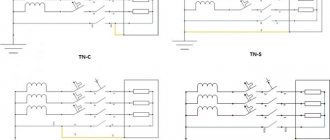
In modern apartments, electrical wiring is carried out according to a three-wire circuit:
•
phase;
•
zero;
•
Earth.
Grounding of electrical appliances occurs through the third contact of the plug and socket. The situation is more complicated in houses where the wiring is installed in a two-wire circuit and there is no ground wire in the sockets. In this case, the grounding wire will have to be drawn directly from the device body.
Where can I get “land” in an apartment in a multi-story building? The answer is simple: in the electrical panel installed on each floor.
Before performing a grounding installation (it is better, of course, to do this with the participation or supervision of a professional electrician), carefully examine the electrical panel. After all, if there is no reliable grounding at the switchboard, connecting the apartment’s grounding wire to it is not only in vain, but also dangerous!
Let's explain with an example. The neighbor has a short circuit. The current will travel the following path: the neighbor’s phase – the neighbor’s “zero” – the floor electrical panel – your ground wire – the body of your device!
Electricity from zero and ground electrode
This method is suitable for residents of private houses if they have a ground loop. Did you know that there is often a potential difference of 10-20 Volts between the ground electrode and the neutral wire? This means they are free to use. You can increase them using a transformer.
The energy consumed in this way will not be taken into account by the meter. This voltage can be determined either with a voltmeter or by connecting a low-voltage light bulb, such as those installed in car lights or dashboards, between these two wires.
Zero made from grounding
Electricians with experience in their work often encounter this issue in practice.
Any electrician, before performing electrical installation work, be it connecting an outlet or switch at home, installing a chandelier, sensors, or disconnecting a distribution box, begins by determining where the phase and zero are in the electrical wiring.
In my articles, I often focus on the fact that when connecting a switch, it is the phase that should be supplied to the break. So one of the readers asked me a question: how to determine this? Where is which wire? Of course, this question is very simple, but as it turns out, it’s not for everyone.
Therefore, today we will practically analyze how to determine where the phase and zero are and which tools can/should be used and which cannot.
The importance of determining where the phase and zero are located is not only a technological necessity, but also necessary for the safe performance of work.
For example, before performing any work on live parts of an electrical installation, it is necessary to check the absence of voltage. Checking the absence of voltage is carried out with respect to the phase-phase and phase-zero wires.