To protect people in everyday life when they come into contact with an electrical device, the body of which has experienced a breakdown of electric current, there are 2 main options that differ from each other in terms of operation and conditions of use - this is connecting the ground or zero. Grounding is the transfer of current to the electrical panel with subsequent shutdown of the machine, and grounding is the removal of current to a grounding circuit in the ground without stopping the current supply. Let's look at what both protection schemes are, what their fundamental differences are, as well as how, when and in what way you can make zeroing in a private house.
A protected socket has 3 contacts - phase, neutral and neutral or grounding Source sense-life.com
Grounding
The transfer of electric current from the body of electrical equipment to a special circuit physically immersed in the ground is called protective grounding. A pair of conductors is supplied to each household appliance from the electrical panel - phase and neutral. Phase breakdown on a metal body (boiler, washing machine, radiator, etc.) poses a potential threat to the health and life of household members.
To prevent this, the device body is connected with a special insulated conductor to a ground loop. Due to this, during a phase breakdown, the electric current will simply go into the ground - along the path of least resistance. Therefore, even in the worst-case scenario, even if a person receives an electric shock from contact with faulty electrical equipment, it is completely safe for health.
There are 3 main options for how to perform grounding, the arrangement of which is carried out separately, without the use of grounding circuits:
- Professional . It is used to ensure uninterrupted operation of industrial installations in normal or emergency mode.
For reliable grounding in the courtyard of the house, a special circuit is made in the ground Source vodatyt.ru
- Household . Used to protect people at home during phase breakdown on the surface of electrical equipment.
- Spontaneous . Designed to protect devices from powerful current discharges that occur when struck by lightning.
In addition, protective grounding circuits are classified according to their origin into 2 types:
- Artificial . This is a specially made structure connected by conductors to electrical appliances. Angles, fittings, rolled pipes, and wires are used as components. They are distinguished by the maximum degree of reliability and fully perform their functions.
- Natural . It is a household structure that can act as a grounding loop. These can be steel well casing pipes, water supply, sewerage or reinforced concrete parts of the structure. The main feature is that to ensure operability, special conditions must be met - the structure should not be aluminum or coated, moreover, flammable compounds should not pass through it.
Natural grounding on a steel pipe in a private house Source otoplenie-gid.ru
Important! Unlike grounding, the grounding system provides a continuous and more reliable drainage of electric current from the surface of a household electrical appliance directly into the ground. At the same time, the grounding circuit stops the supply of current only at the moment of its breakdown on the housing, by turning off this branch of the network by the monitoring equipment.
See also: Catalog of companies that specialize in electrical work of any complexity
What systems exist
When developing power supply systems, the grounding problem is solved through the use of special circuits. With their help, grounding is installed not only at the substation, but also on the consumer side (taking into account the different set of wires connected to the load).
Among the well-known systems that provide grounding in an apartment , the following options are of particular interest:
- TN-C.
- TN-S.
- TN-CS.
Let's look at each of them in more detail.
TN-C is the most common, but also the most vulnerable system in terms of security. As can be seen from the diagram below, a separate PE conductor is not provided for in it, since it is combined with the working zero in the PEN bus. re -grounding in the apartment .
Important! You can distinguish the TN-C system from others by the type of liner on the floor panel.
It has four incoming conductors (3 phases and PEN). Only two wires enter the room: one of them is phase, and the second is the same PEN. To ensure at least some safety in such schemes, a grounding is installed in the apartment (in the hope that the overcurrent circuit breaker included in the line will trip). To do this, the grounding terminals of the sockets are connected with a jumper to zero (PEN).
The fundamental difference between the TN-S system and the previous scheme is that the PE and N conductors are separated, starting from the substation, and are not connected anywhere along the entire length of the laying line. In order to make sure that this scheme is used, just look into the ASU. At its input there should be five separate conductors: three of them are phase conductors, one working zero and one protective conductor. A cable with three wires is laid from it to the apartment panel: phase, neutral and PE.
The TN-CS system refers to intermediate options that combine the advantages of TN-S and the comparative low cost of TN-C. In this case, the neutral conductor on the segment from the substation to the facility combines the capabilities of N and PE. In the building's ASU, they are artificially split (on a piece of copper strip), after which they arrive at the apartment panel already completely separated. The set of busbars in this cable is the same as in TN-S.
Additional information: The TN-CS system is a modernized version of the outdated TN-C.
An artificially created split, which subsequently provides grounding in the apartment , makes sense only if there is a secondary circuit mounted at the entrance to the building (in the diagram it is indicated as additional). In its absence, it is no different from the option when zeroing is installed in the apartment.
Zeroing
When creating a protective grounding circuit, electrically conductive parts of equipment with which a person can constantly or accidentally come into contact are connected to the neutral conductor in the electrical panel. The principle of installation on the device itself is similar to the grounding circuit - only in this case, the contact on the body connected to the “ground” is connected to the “zero”. In both cases, protection is carried out using a separate conductor.
The operating principle of nulling protection is quite simple and boils down to the following algorithm:
- At the moment of phase breakdown on the housing or other conductive parts of the electrical device, the electric current is instantly transmitted by “zero” protection to the controlling module.
- A short circuit occurs at the point of contact between the “zero” of the electrical appliance and the phase.
Schematic difference between grounding and grounding Source tinkoffjournal.ru
- An electrical panel, fuse or other control equipment instantly cuts off the current supply in this part of the electrical circuit.
- As a result, the electrical appliance is de-energized, and the person is safe.
However, the main feature of such grounding is that the current generated during a protective short circuit and sent to the machine must be sufficient to trigger the equipment. Otherwise, the protection will be ineffective and people will be in danger. Moreover, the phase will begin to be distributed to other parts or electrical appliances also connected to the “zero” protection.
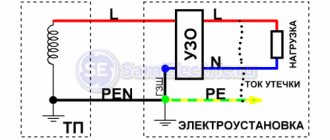
Residual current device
To increase safety during operation of electric devices also use the so-called residual current device, abbreviated as RCD. Together with grounding, RCDs provide a 100% guarantee of protecting people from electric shock.
Let's look at the principle of operation of an RCD, for which we imagine electrical wiring as a plumbing system. Water flows through pipes, just as current flows through wires. And if suddenly a hole appears in the pipe, the water begins to leave, and its amount at the exit of the section will be less than at the entrance. The RCD controls such a leak, but not of water, but of electricity.
If the device body is energized, but there is no leakage, the RCD does not respond. But as soon as a person touches the body, a path for current leakage appears, a “hole” - the RCD opens the circuit in a fraction of a second.
The difference between grounding and grounding
There are the following number of main differences between the two protection methods under consideration:
- Protection of the “ground” type diverts the current into the ground, and of the “zero” type into the electrical panel.
- The grounding conductor, by removing electric current from the device body, reduces the voltage to a value that is safe for humans. The neutralizing conductor leads current to the machine, which de-energizes a certain area without affecting the characteristics of electricity.
Grounding is more reliable and easier to manufacture at home than grounding Source electric-doma.ru
What, how and where does it come from?
It is known that electricity is produced by power plants. From them, an electric current with a voltage of tens and hundreds of thousands of volts travels through three phase wires to the consumer.
The voltage is so high because, according to the laws of physics, the higher the voltage, the lower the losses during transmission over long distances.
Then step-down transformer substations convert the high voltage into a much lower (but still dangerous) one, and it will come through wires or underground cables into our home.
The current must come to the electrical appliance, do useful work and leave. In the case of alternating voltage used in everyday life, the phase (supply) and neutral wires are used for this. Where the electric current comes from is clear; but where does the electricity go? To the ground! A little simplified, but by and large it is true. Right into the ground.
The substation transformer has a ground connected to a separate line wire. This is the very “zero” in our → sockets. Those who are especially curious can verify this by examining a regular transformer substation with overhead lines. 3 wires came in, 4 came out. At the input there are three phases of high voltage, at the output there are three phases of low voltage and a neutral wire.
Now let's move on to the main thing - human protection.
Features of arranging grounding in the house
When arranging protection for electrical appliances across “zero”, a number of rules must be followed. First of all, it is necessary to correctly install the electrical circuit:
- One neutral conductor is supplied to the automatic distribution panel from the pole.
- It is further divided into two directions, each of which goes to its own bus.
- One of the cores becomes the working “zero” or neutral, the other becomes the neutral wire, the one that will provide protection.
- From the machine, the neutral is distributed to all electrical appliances for their normal operation.
- The neutral conductor is connected to the electrical panel housing. In this case, a conductor with a characteristic yellow-green sheath is used for connection, which typically indicates its protective function.
- The yellow-green core is connected to a similar one in the electrical wiring of the house and is then distributed to all sockets. Through them, the housings of all electrical appliances requiring protection will be connected to a common neutralizing system.
- After leaving the automatic protective equipment in the home, the standard neutral wire and the grounding wire are no longer in contact.
Start of installation work: choosing a suitable location
The degree of safety of using the grounding system largely depends on the choice of a suitable location. Therefore, this stage should be approached with all responsibility and attention. In case of problems with the wiring and operation of the system, no one should be at the installation site. It is precisely because of the mortal danger that they most often choose a place away from the house, near the fence. The distance to the foundation must be at least one meter.
Helpful advice! It is recommended to fence off the area with the grounding system with a low fence or border to mark the dangerous place.
If you are not tempted by the prospect of having a fenced area behind the house for grounding, the system can be hidden with the help of a garden sculpture or large decorative stones. This way, the risk of entering the danger zone will be minimized, and the appearance of the garden will not be affected.
Briefly about the main thing
Grounding is the removal of voltage from the housing of electrical equipment to the ground through a grounding loop. There are professional, household and spontaneous versions. It can be artificial, specially created, or natural, when suitable metal structures are used as current transmitters.
Grounding differs from grounding in that the electric current during a breakdown on the housing is diverted not into the ground, but into the distribution panel. This artificially causes shortening, as a result of which the machine is triggered and the equipment is de-energized. The main differences between them boil down to the following features:
- Grounding drains the current into the ground, and grounding into the shield.
- Grounding reduces the voltage on the case, grounding completely de-energizes the circuit.
- Making a grounding circuit is accessible to any more or less literate person; protection through “zero” can only be arranged by a professional.
- Protection through grounding is more suitable for industrial facilities, grounding - for residential ones.
Grounding in the house is suitable as a temporary measure until a full-fledged grounding loop is created in the yard. It is necessary to equip protection across the “zero” with careful selection of suitable conductors and compliance with electrical installation rules.
How to make grounding in an apartment?
In old-style houses, the third wire is usually absent, that is, only phase and neutral are available. Reconstruction of such power supply systems is quite expensive and labor-intensive and is therefore rarely carried out. And the desire of individual residents to update the electrical wiring in their apartments and connect the grounding wire is not easy to implement. To do this, you need to stretch the wire from the basement to the apartment with the involvement of specialists from electrical installation companies. You cannot carry out such work on your own. For owners of apartments on the ground floor, this solution is, in principle, suitable, but for others it is practically impossible.
The apartment's protective grounding cable can be connected to the panel in several cases. If it has a grounding bus or if all panels on all floors of the house are connected to each other using a metal bus leading to a common grounding circuit for the entire house. This is the so-called re-grounding, when the entire building as a whole and an individual apartment in particular are grounded.